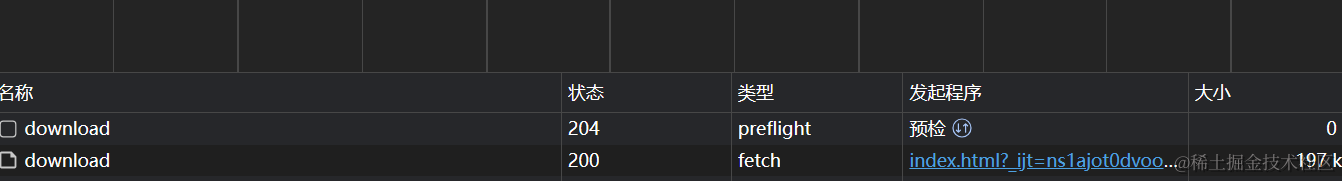
后端把文件以流的形式发送给前端,前端将流转成一个一个的blob文件,将这些 blob 转成url,将url放到a标签上,用于点击,下载文件,处理大型文件和动态生成的文件。
index.js
import express from 'express'
import cors from 'cors'
import fs from 'fs'
import path from 'path'
const app = express()
app.use(cors())
app.use(express.json())
app.post('/download', (req, res) => {
const fileName = req.body.fileName
const filePath = path.join(process.cwd(), 'static', fileName)
const content = fs.readFileSync(filePath) // 不加 utf8 配置返回就是一个 buffer 流
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/octet-stream') // octet-stream 二进制流
// Content-Disposition 直接预览而不是下载 默认inline 内联模式
// 改为 attachment 将文件当做一个附件进行下载
res.setHeader('Content-Disposition', 'attachment;filename=' + fileName)
res.send(content)
})
app.listen(3000,()=> {
console.log('server is running on port 3000')
})
index.html
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn">download</button>
<script>
const btn = document.querySelector('#btn')
btn.addEventListener('click', function () {
fetch('http://localhost:3000/download',{
method: 'post',
body: JSON.stringify({
fileName: 'cat1.png'
}),
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
}).then(res=>res.arrayBuffer()).then(res=> {
// 转成 blob
const blob = new Blob([res], {type: 'image/png'})
// 转成 url
const url = URL.createObjectURL(blob)
// 创建 a 标签挂载 url 模拟点击
const a = document.createElement('a')
a.href = url
a.download = 'cat1.png'
a.click()
})
});
</script>
</body>
</html>








![[C++初阶] 爱上C++ : 与C++的第一次约会](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/e6b7de6df3ca49cba01fe2d41bd77a72.png)