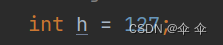目录
一、string.h
二、string.cpp
三、Test.cpp
对string的各种接口进行一个简易版的模拟实现,在模拟实现完之后对string的底层实现有了进一步的理解,了解大佬的编程写法思路。也算是对string有了一个小总结。
一、string.h
接口的声明。放在.h文件中
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;
namespace bit
{
class string
{
public:
typedef char* iterator;//迭代器本质上就是指针
typedef const char* const_iterator;
iterator begin() const
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _str + _size;
}
string(const char* s = "");
string(const string& s);
string& operator=(string s);
~string();
void push_back(char c);
string& operator+=(char c);
string& operator+=(const string& s);
string& operator+=(const char* str);
void append(const char* str);
void clear();
void swap(string& s);
const char* c_str()const;
//capacity
size_t size();
size_t capacity();
void resize(size_t n, char c = '\0');
void reserve(size_t n);
bool empty()const;
bool operator<(const string& s);
bool operator<=(const string& s);
bool operator>(const string& s);
bool operator>=(const string& s);
bool operator==(const string& s);
;
bool operator!=(const string& s);
char& operator[](size_t i);
const char& operator[](size_t i) const;
//返回字符第一次在字符串出现的位置
size_t find(char c, size_t pos = 0) const;
;
//在pos位置插入字符c
string& insert(size_t pos, char c);
//在pos位置插入字符串
string& insert(size_t pos, const char* str);
//返回子串在字符串中出现的位置
size_t find(const char* str, size_t pos = 0);
string substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);
// 删除pos位置上的元素,并返回该元素的下一个位置
string& erase(size_t pos, size_t len = npos);
private:
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
char* _str;
//静态变量可以赋值处理的前提是有const修饰,这个可以看作是编译器的特殊处理,只能适用于整形家族
static const size_t npos = -1;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s);
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s);
}
二、string.cpp
接口的各种实现。进行声明定义分离时,要注意格式上的变化,指定类域,声明和定义中,只有声明中可以给缺省值,定义中不能给。string的构造函数有传统写法和现代写法,现代写法更简洁,但和传统写法本质上没有太大的区别
#include "string.h"
namespace bit
{
//string()
// :_str(nullptr)//不能给空,析构时会对空指针解引用,从而报错
// ,_size(0)
// ,_capacity(0)
//{}
//string()
// :_size(0)
// ,_capacity(_size)
// ,_str(new char[_capacity + 1])//这样必须给定成员变量声明顺序。
//{}
string::string(const char* s)
{
_size = strlen(s);
_capacity = _size;
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, s);
}
//传统写法
/* string(const string& s)
{
_str = new char[s._capacity + 1];
_size = s._size;
_capacity = s._capacity;
strcpy(_str, s._str);
}*/
//现代写法
string::string(const string& s)
{
string tmp(s._str);
swap(tmp);
}
//传统写法
//string& operator=(const string& s)
//{
// if (*this != s)
// {
// char* tmp = new char[s._capacity + 1];
// delete[] _str;
// strcpy(tmp, s._str);
// _str = tmp;
// _size = s._size;
// _capacity = s._capacity;
// return *this;
// }
// return *this;
//
//}
//现代写法
/*string& operator=(const string s)
{
string tmp(s._str);
swap(tmp);
return *this;
}*/
string& string::operator=(string s)
{
swap(s);
return *this;
}
string::~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
}
//modify
void string::push_back(char c)
{
if (_size == _capacity)//初始化容量以及判断容量是否满了
{
size_t newcapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2;
/* if (_str != "")
{
char* tmp = new char[newcapacity + 1];
memcpy(tmp, _str, _size);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = newcapacity;
}*/
reserve(newcapacity);
}
_str[_size] = c;
_size++;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
string& string::operator+=(char c)
{
push_back(c);
return *this;
}
string& string::operator+=(const string& s)
{
if (_size + s._size > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + s._size);
}
strcpy(_str + _size, s._str);
_size += s._size;
return *this;
}
string& string::operator+=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}
void string::append(const char* str)
{
if (_size + strlen(str) > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + strlen(str));
}
strcpy(_str + _size, str);
_size += strlen(str);
}
void string::clear()
{
_str[0] = '\0';
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
}
void string::swap(string& s)
{
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(this->_size, s._size);
std::swap(this->_capacity, s._capacity);
}
const char* string::c_str()const
{
return _str;
}
//capacity
size_t string::size()
{
return _size;
}
size_t string::capacity()
{
return _capacity;
}
void string::resize(size_t n, char c)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
reserve(n);
for (int i = _capacity; i < n; i++)
push_back(c);
}
else if (n > _size && n < _capacity)
{
for (int i = _size; i < n; i++)
push_back(c);
}
else if (n < _size)
{
_str[n] = '\0';
}
}
void string::reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n + 1];
strcpy(tmp, _str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
//_size = strlen(tmp);
_capacity = n;
}
}
bool string::empty()const
{
return _str == "";
}
bool string::operator<(const string& s)
{
return strcmp(_str, s._str) < 0;
}
bool string::operator<=(const string& s)
{
return !(*this > s);
}
bool string::operator>(const string& s)
{
return strcmp(_str, s._str) > 0;
}
bool string::operator>=(const string& s)
{
return !(*this < s);
}
bool string::operator==(const string& s)
{
return strcmp(_str, s._str) == 0;
}
bool string::operator!=(const string& s)
{
return !(strcmp(_str, s._str) == 0);
}
char& string::operator[](size_t i)
{
return _str[i];
}
const char& string::operator[](size_t i) const
{
return _str[i];
}
//返回字符第一次在字符串出现的位置
size_t string::find(char c, size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos <= _size);
for (int i = pos; i < _size; i++)
{
if (_str[i] == c)
return i;
}
return npos;
}
//在pos位置插入字符c
string& string::insert(size_t pos, char c)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
if (_size == _capacity)
{
size_t newcapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2;
reserve(newcapacity);
}
if (pos == _size)
push_back(c);
else
{
size_t len = _size - pos;
while (len)
{
_str[pos + len] = _str[pos + len - 1];
len--;
}
_str[pos] = c;
}
_size++;
_str[_size] = '\0';
return *this;
}
//在pos位置插入字符串
string& string::insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (len + _size >= _capacity)
{
reserve(len + _size);
}
if (pos == _size)
{
append(str);
}
else
{
size_t ilen = _size - pos;
while (ilen)
{
_str[pos + ilen + len] = _str[pos + ilen];
ilen--;
}
for (int i = pos, j = 0; i < pos + len; i++, j++)
{
_str[i] = str[j];
}
}
_size += len;
_str[_size] = '\0';
return *this;
}
//返回子串在字符串中出现的位置
size_t string::find(const char* str, size_t pos)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (pos + len > _size)
return npos;
else
{
size_t fpos = find(str[0], pos);
for (int i = fpos, j = 0; i < fpos + len; i++, j++)
{
if (str[j] != _str[i])
return npos;
}
return fpos;
}
}
string string::substr(size_t pos, size_t len)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
string tmp;
size_t end = pos + len;
//if (len == npos || len >= _size - pos)
//{
// tmp.reserve(_size - pos);
// strcpy(tmp._str, _str + pos);
// return tmp;
//}
//else
//{
// memcpy(tmp._str, _str + pos, len);
// tmp[len] = '\0';
// return tmp;
//}
if (len == npos || len >= _size - pos)
{
end = _size;
}
tmp.reserve(end - pos);
for (int i = pos; i < end; i++)
{
tmp += _str[i];
}
return tmp;
}
// 删除pos位置上的元素,并返回该元素的下一个位置
string& string::erase(size_t pos, size_t len)
{
assert(pos < _size);
if (len == npos || len > _size)
{
_str[pos] = '\0';
}
else
{
/*size_t length = len + pos;
while (pos < length)
{
_str[pos] = _str[pos + len];
pos++;
}
_str[_size - len] = '\0';*/
strcpy(_str + pos, _str + pos + len);
_size -= len;
}
return *this;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s)
{
for (auto e : s)
{
out << e;
}
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s)
{
s.clear();
char buff[128];
char ch = in.get();
int i = 0;
while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n')
{
buff[i] = ch;
i++;
if (i == 127)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
i = 0;
}
ch = in.get();
}
if (i > 0)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
}
return in;
}
}
三、Test.cpp
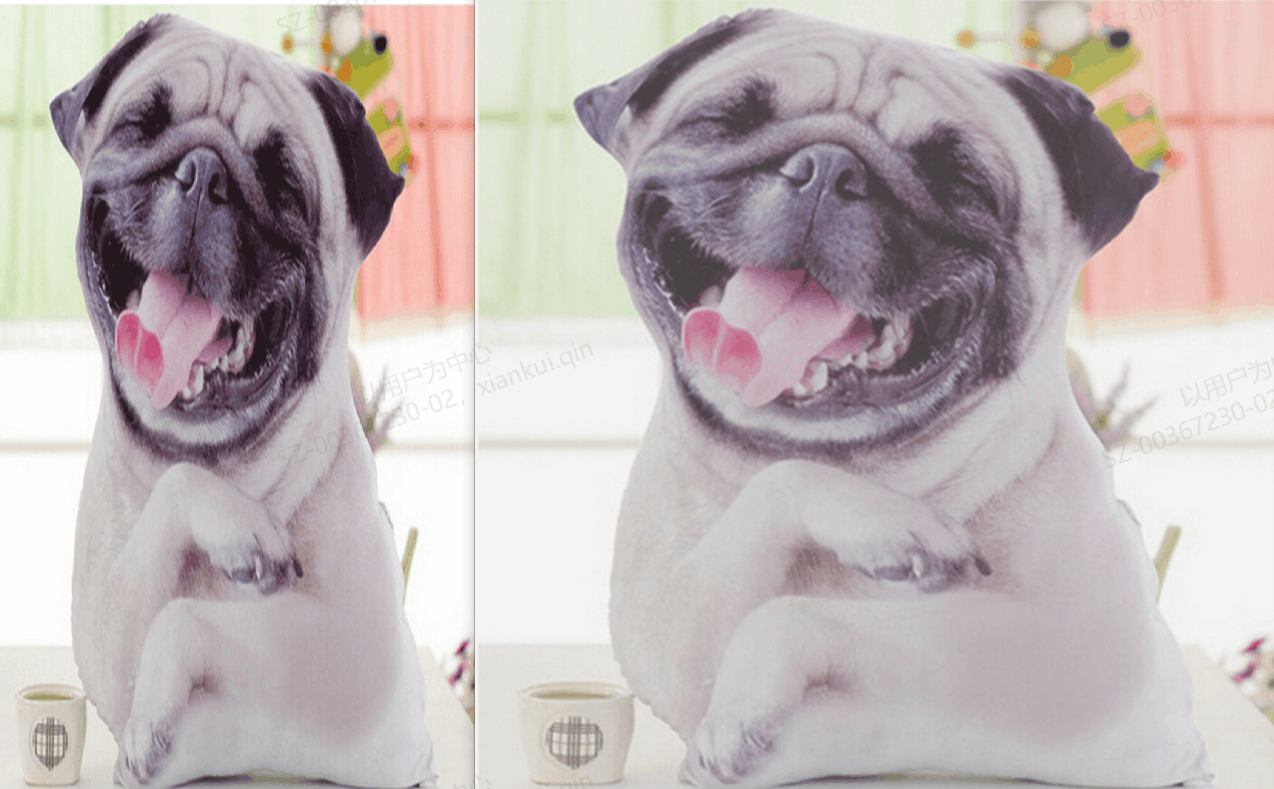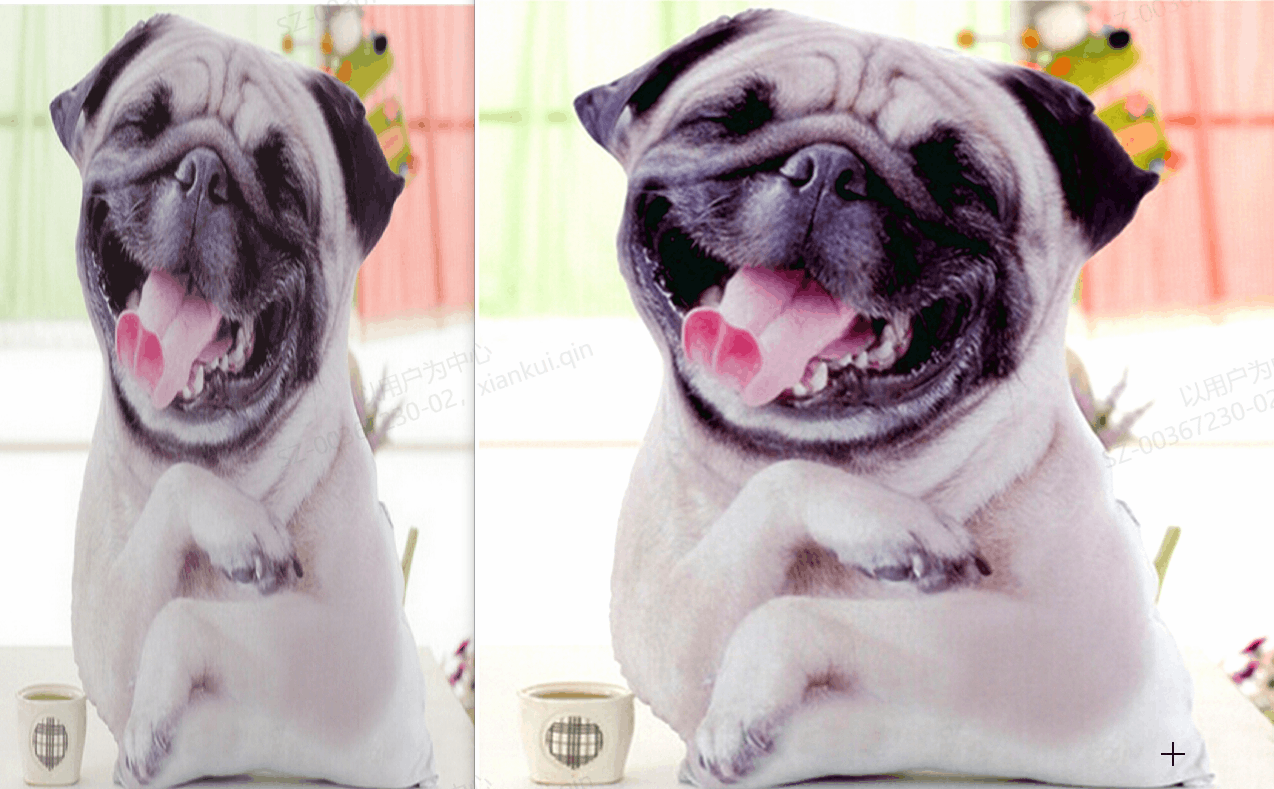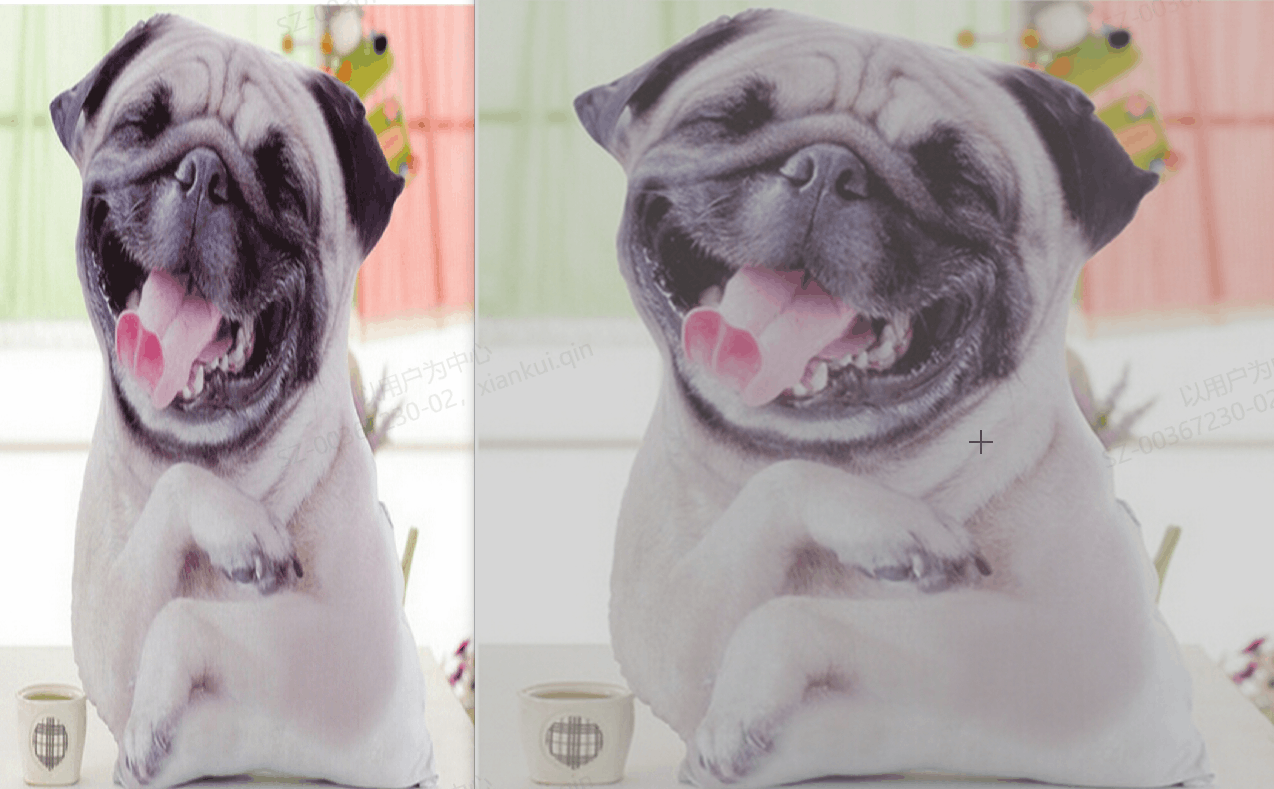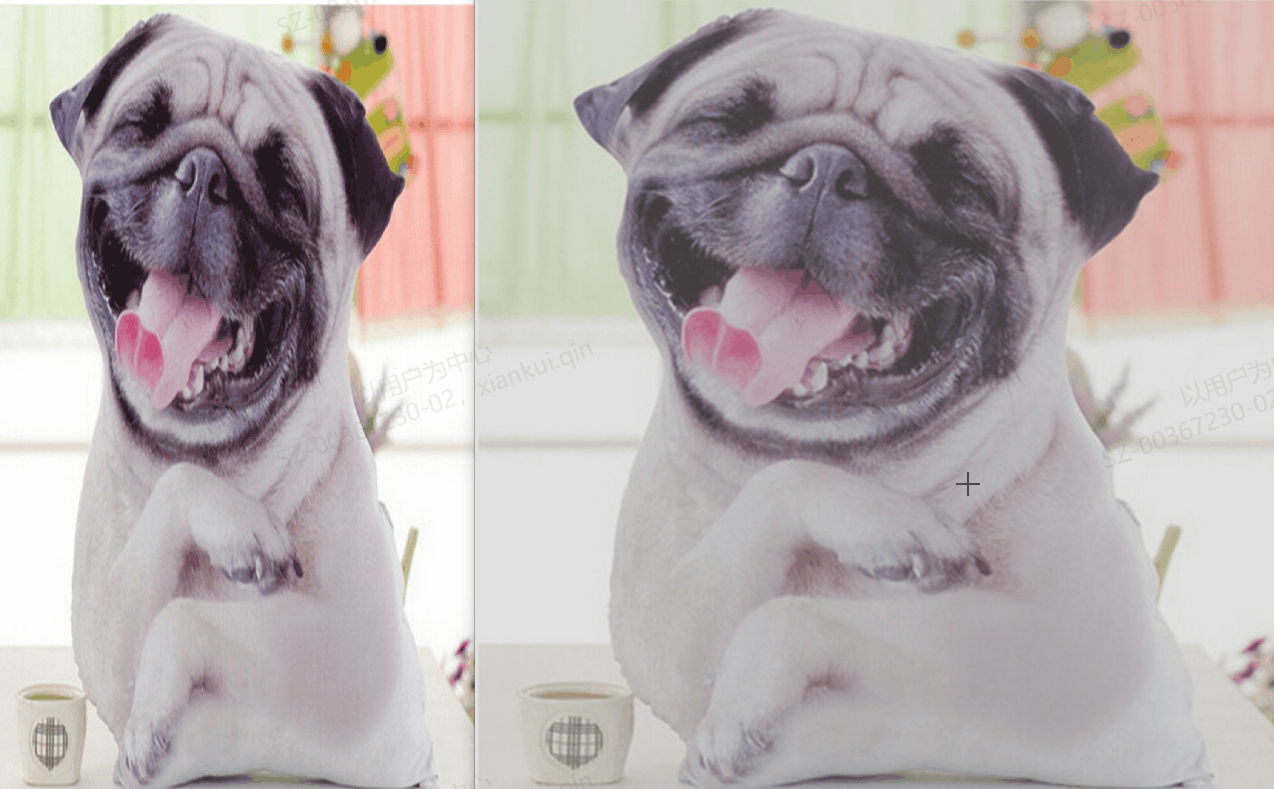
测试版本,对接口进行测试,写了三个测试版本,但并没有调用全部接口,进行一番演示,大致还行,可能还有错误,也是水平有限。
#include "string.h"
namespace bit
{
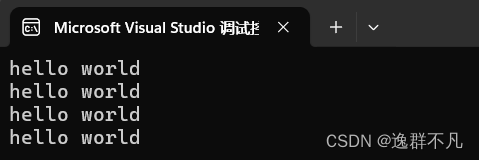
void stringtest1()
{
string s("hello world");
string::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it;
it++;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e;
}
cout << endl;
string s1(s);
string s2 = s1;
for (auto e : s1)
{
cout << e;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : s2)
{
cout << e;
}
cout << endl;
}
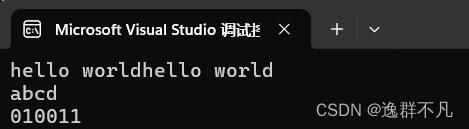
void stringtest2()
{
string s("hello world");
s += "hello world";
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e;
}
cout << endl;
string s1;
s1.push_back('a');
s1.push_back('b');
s1.push_back('c');
s1.push_back('d');
for (auto e : s1)
{
cout << e;
}
cout << endl;
cout << (s < s1);
cout << (s > s1);
cout << (s == s1);
cout << (s <= s1);
cout << (s >= s1);
cout << true;
};
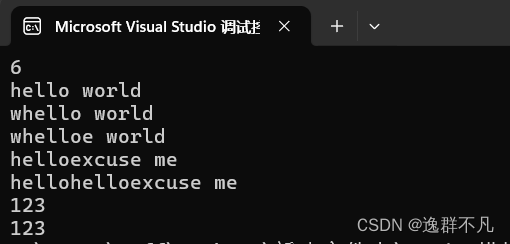
void stringtest3()
{
string s("hello world");
string s1 = "excuse me";
/*s.swap(s1);
cout << s.c_str() << " " << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
s.reserve(100);
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
s.resize(5);
cout << s.capacity() << " " << s.c_str() << endl;;*/
//cout << s[0];
size_t pos = s.find("world");
cout << pos << endl;
cout << s.substr().c_str() << endl;
s.insert(0, 'w');
cout << s.c_str() << endl;
s.insert(6, 'e');
cout << s.c_str() << endl;
s1.insert(0, "hello");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.insert(5, "hello");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cin >> s1;
cout << s1;
}
}
int main()
{
bit::stringtest1();
bit::stringtest2();
bit::stringtest3();
return 0;
}三个测试函数的输出结果 :