目录
前言
一、索引语法
1.SQL语法
2.案例演示
二、SQL性能分析
三、慢查询日志
1.开启日志
2.测试样例
四、profile详情
1.开启profile
2.profile测试SQL语句
五、explain详情
1.语法结构
2.执行顺序示例(id)
3.执行性能示例(type)
前言
本期就要来去讲解SQL索引的相关语法,已经我们之前所用的SQL语句对其进行性能分析和执行效率来去判断如何来选择合适的SQL语句。下面看正文。(上一期链接:MySQL进阶-----索引的结构与分类-CSDN博客)
一、索引语法
1.SQL语法
CREATE [ UNIQUE | FULLTEXT ] INDEX index_name ON table_name (
index_col_name,... ) ;2. 查看索引
SHOW INDEX FROM table_name ;3. 删除索引
DROP INDEX index_name ON table_name ;2.案例演示
create table tb_user(
id int primary key auto_increment comment '主键',
name varchar(50) not null comment '用户名',
phone varchar(11) not null comment '手机号',
email varchar(100) comment '邮箱',
profession varchar(11) comment '专业',
age tinyint unsigned comment '年龄',
gender char(1) comment '性别 , 1: 男, 2: 女',
status char(1) comment '状态',
createtime datetime comment '创建时间'
) comment '系统用户表';
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('吕布', '17799990000', 'lvbu666@163.com', '软件工程', 23, '1',
'6', '2001-02-02 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('曹操', '17799990001', 'caocao666@qq.com', '通讯工程', 33,
'1', '0', '2001-03-05 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('赵云', '17799990002', '17799990@139.com', '英语', 34, '1',
'2', '2002-03-02 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('孙悟空', '17799990003', '17799990@sina.com', '工程造价', 54,
'1', '0', '2001-07-02 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('花木兰', '17799990004', '19980729@sina.com', '软件工程', 23,
'2', '1', '2001-04-22 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('大乔', '17799990005', 'daqiao666@sina.com', '舞蹈', 22, '2',
'0', '2001-02-07 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('露娜', '17799990006', 'luna_love@sina.com', '应用数学', 24,
'2', '0', '2001-02-08 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('程咬金', '17799990007', 'chengyaojin@163.com', '化工', 38,
'1', '5', '2001-05-23 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('项羽', '17799990008', 'xiaoyu666@qq.com', '金属材料', 43,
'1', '0', '2001-09-18 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('白起', '17799990009', 'baiqi666@sina.com', '机械工程及其自动
化', 27, '1', '2', '2001-08-16 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('韩信', '17799990010', 'hanxin520@163.com', '无机非金属材料工
程', 27, '1', '0', '2001-06-12 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('荆轲', '17799990011', 'jingke123@163.com', '会计', 29, '1',
'0', '2001-05-11 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('兰陵王', '17799990012', 'lanlinwang666@126.com', '工程造价',
44, '1', '1', '2001-04-09 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('狂铁', '17799990013', 'kuangtie@sina.com', '应用数学', 43,
'1', '2', '2001-04-10 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('貂蝉', '17799990014', '84958948374@qq.com', '软件工程', 40,
'2', '3', '2001-02-12 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('妲己', '17799990015', '2783238293@qq.com', '软件工程', 31,
'2', '0', '2001-01-30 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('芈月', '17799990016', 'xiaomin2001@sina.com', '工业经济', 35,
'2', '0', '2000-05-03 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('嬴政', '17799990017', '8839434342@qq.com', '化工', 38, '1',
'1', '2001-08-08 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('狄仁杰', '17799990018', 'jujiamlm8166@163.com', '国际贸易',
30, '1', '0', '2007-03-12 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('安琪拉', '17799990019', 'jdodm1h@126.com', '城市规划', 51,
'2', '0', '2001-08-15 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('典韦', '17799990020', 'ycaunanjian@163.com', '城市规划', 52,
'1', '2', '2000-04-12 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('廉颇', '17799990021', 'lianpo321@126.com', '土木工程', 19,
'1', '3', '2002-07-18 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('后羿', '17799990022', 'altycj2000@139.com', '城市园林', 20,
'1', '0', '2002-03-10 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO tb_user (name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status,
createtime) VALUES ('姜子牙', '17799990023', '37483844@qq.com', '工程造价', 29,
'1', '4', '2003-05-26 00:00:00');
这里我们先去查看这个表的索引:
show index from tb_user;
这里可以看到索引的名字,以及索引的类型是B+tree

A. name 字段为姓名字段,该字段的值可能会重复,为该字段创建索引。create index index_name on tb_user(name);再次查看:
B. phone 手机号字段的值,是非空,且唯一的,为该字段创建唯一索引。create unique index index_phone on tb_user(phone);
C. 为 profession 、 age 、 status 创建联合索引。create index pro_age_sta on tb_user(profession,age,status);
二、SQL性能分析
-- session 是查看当前会话 ;
-- global 是查询全局数据 ;
SHOW GLOBAL STATUS LIKE 'Com_______';
Com_delete: 删除次数
Com_insert: 插入次数
Com_select: 查询次数
Com_update: 更新次数
我们可以在当前数据库再执行几次查询操作,然后再次查看执行频次,看看 Com_select 参数会不会变化。
通过上述指令,我们可以查看到当前数据库到底是以查询为主,还是以增删改为主,从而为数据库优化提供参考依据。 如果是以增删改为主,我们可以考虑不对其进行索引的优化。 如果是以查询为主,那么就要考虑对数据库的索引进行优化了。
三、慢查询日志
1.开启日志
show variables like 'slow_query_log';

如果要开启慢查询日志,需要在MySQL的配置文件(/etc/my.cnf)中配置如下信息:
# 开启MySQL慢日志查询开关
slow_query_log=1
# 设置慢日志的时间为2秒,SQL语句执行时间超过2秒,就会视为慢查询,记录慢查询日志
long_query_time=2这里我们先通过vi /etc/my.cnf 指令进入到mysql里面进行对配置文件的编辑

systemctl restart mysqld 然后,再次查看开关情况,慢查询日志就已经打开了。
2.测试样例
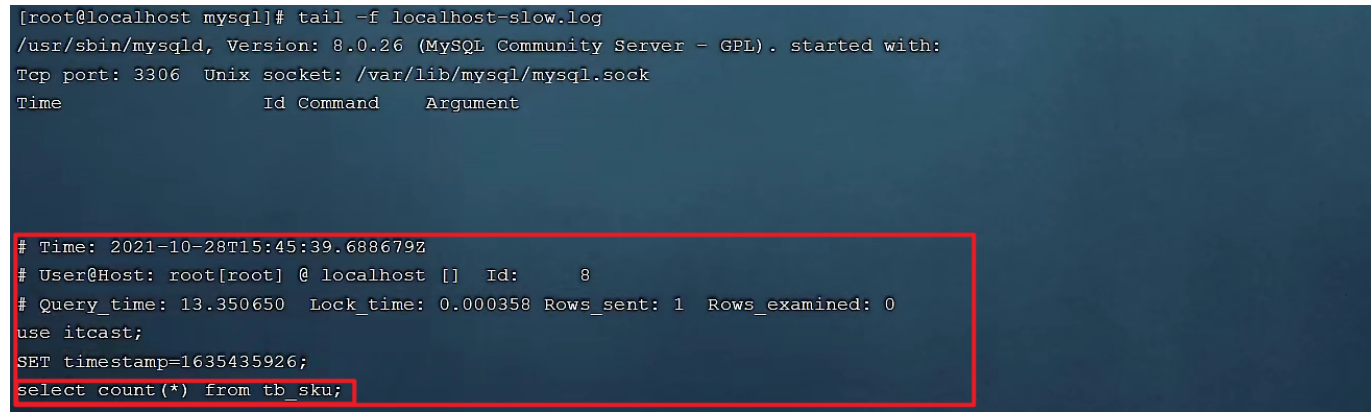
A. 执行如下 SQL 语句 :select * from tb_user; -- 这条SQL执行效率比较高, 执行耗时 0.00sec select count(*) from tb_sku; -- 由于tb_sku表中, 预先存入了1000w的记录, count一次,耗时 13.35sec
B. 检查慢查询日志 :最终我们发现,在慢查询日志中,只会记录执行时间超多我们预设时间( 2s )的 SQL ,执行较快的 SQL是不会记录的。
这样,通过慢查询日志,就可以定位出执行效率比较低的 SQL ,从而有针对性的进行优化。
四、profile详情
1.开启profile
SELECT @@have_profiling ;
select @@profiling;
如果显示0就表示未开启,那就要去开启:
SET profiling = 1;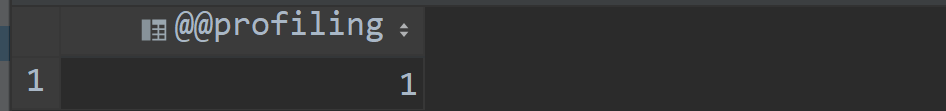
2.profile测试SQL语句
select * from tb_user;
select * from tb_user where id = 1;
select * from tb_user where name = '白起';-- 查看每一条SQL的耗时基本情况
show profiles;
-- 查看指定query_id的SQL语句各个阶段的耗时情况
show profile for query query_id;
-- 查看指定query_id的SQL语句CPU的使用情况
show profile cpu for query query_id;

五、explain详情
1.语法结构
语法:
-- 直接在select语句之前加上关键字 explain / desc
EXPLAIN SELECT 字段列表 FROM 表名 WHERE 条件 ;
Explain 执行计划中各个字段的含义:
| 字段 | 含义 |
| id | select查询的序列号,表示查询中执行select子句或者是操作表的顺序 (id相同,执行顺序从上到下;id不同,值越大,越先执行)。 |
| select_type | 表示 SELECT 的类型,常见的取值有 SIMPLE(简单表,即不使用表连接或者子查询)、PRIMARY(主查询,即外层的查询)、 UNION(UNION 中的第二个或者后面的查询语句)、 SUBQUERY(SELECT/WHERE之后包含了子查询)等 |
| type | 表示连接类型,性能由好到差的连接类型为NULL、system、const、 eq_ref、ref、range、 index、all 。 |
| possible_key | 显示可能应用在这张表上的索引,一个或多个。 |
| key | 实际使用的索引,如果为NULL,则没有使用索引。 |
| key_len | 表示索引中使用的字节数, 该值为索引字段最大可能长度,并非实际使用长度,在不损失精确性的前提下, 长度越短越好 。 |
| rows | MySQL认为必须要执行查询的行数,在innodb引擎的表中,是一个估计值,可能并不总是准确的。 |
| filtered | 表示返回结果的行数占需读取行数的百分比, filtered 的值越大越好。 |
2.执行顺序示例(id)
数据准备:
# 创建学生信息表
create table students
(
id int auto_increment
primary key,
name varchar(10) null,
num varchar(20) null,
constraint students_num_uindex
unique (num)
);
#创建中间连接表
create table stu_cour
(
stu_id int null,
cour_id int null,
constraint stu_cour_courses_id_fk
foreign key (cour_id) references courses (id),
constraint stu_cour_students_id_fk
foreign key (stu_id) references students (id)
);
# 创建课程表
create table courses
(
id int not null
primary key,
c_name varchar(10) null
);
# 数据插入
insert into students values (1,'韩信','123451'),
(2,'李白','123452'),
(3,'公孙离','123453'),
(4,'司马懿','123454');
insert into courses values (1,'mysql'),
(2,'java'),
(3,'python');
insert into stu_cour values (1,2),
(1,3),
(2,1),
(2,3),
(3,3); 关系如图所示:
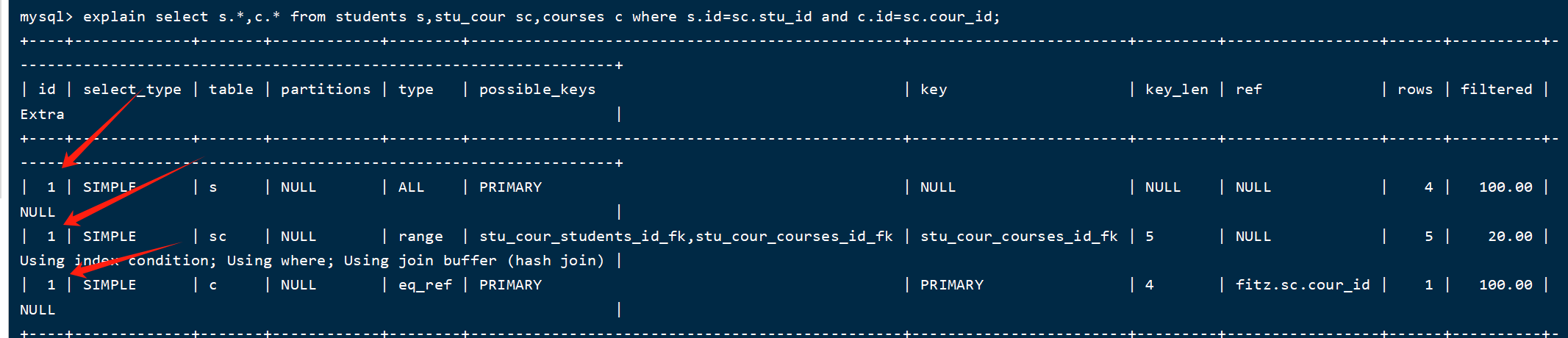
explain语句结果中select查询的序列号,表示查询中执行select子句或者是操作表的顺序(id相同,执行顺序从上到下;id不同,值越大,越先执行)。
(1)id相同案例:
explain select s.*,c.* from students s,stu_cour sc,courses c where s.id=sc.stu_id and c.id=sc.cour_id;
(2)id不同时案例:
explain select * from students where id=
(select stu_id from stu_cour where cour_id=
(select id from courses where c_name='mysql'));
3.执行性能示例(type)
(1)如果查询全部的话那就是全部扫描,结果为all
explain select * from tb_user;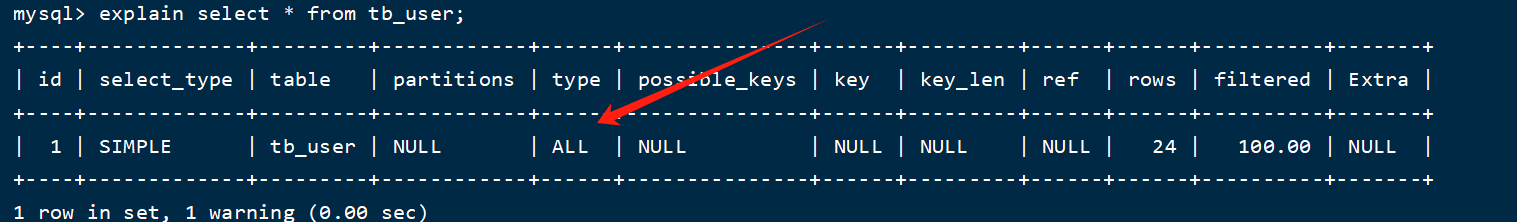
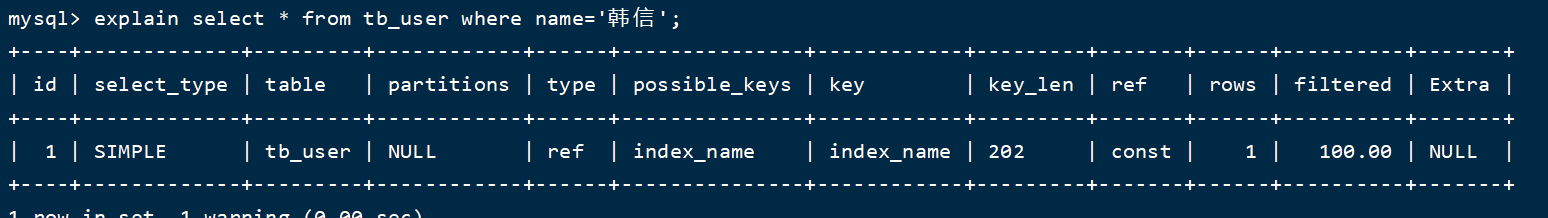
(2)如果查询指定条件的话,但没有建立索引,结果如下:
explain select * from tb_user where name='韩信';
(3)如果查询有建立索引的条件的话,结果如下:
explain select * from tb_user where id=2;

以上就是本期的全部内容,我们下次见!
分享一张壁纸: