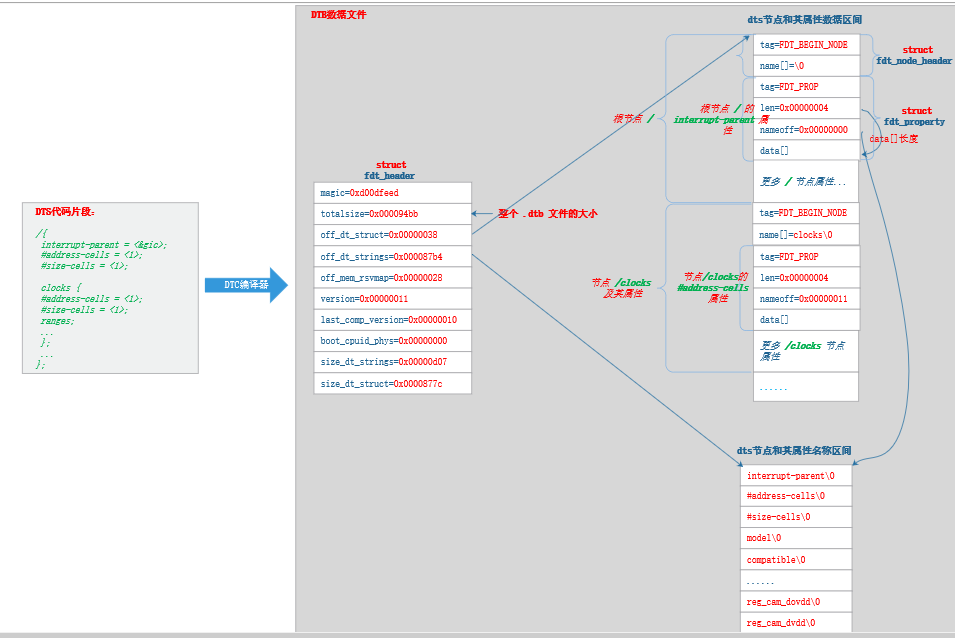
1. GIoU 计算
关于 GIoU 的实现,可直接参看原文给出的网站:
https://giou.stanford.edu/
G I o U = ∣ A ∩ B ∣ ∣ A ∪ B ∣ − ∣ C ∖ ( A ∪ B ) ∣ ∣ C ∣ = I o U − ∣ C ∖ ( A ∪ B ) ∣ ∣ C ∣ GIoU = \frac { |A \ \cap \ B | } { |A \ \cup \ B | } - \frac { | C \setminus (A \ \cup \ B) | } { | C | } = IoU - \frac { | C \setminus (A \ \cup \ B) | } { | C | } GIoU=∣A ∪ B∣∣A ∩ B∣−∣C∣∣C∖(A ∪ B)∣=IoU−∣C∣∣C∖(A ∪ B)∣
而 L o s s G I o U Loss_{GIoU} LossGIoU 则:
L o s s G I o U = 1 − G I o U Loss_{GIoU} = 1 - GIoU LossGIoU=1−GIoU
而 A A A 和 B B B 分别是预测框和 GT 框. C 是包含 A 和 B 的最小凸包矩形.
2. IoU 计算
先来看下 IoU 的计算方式,摘自 PaddleDetection :
def bbox_overlap(self, box1, box2, eps=1e-10):
"""calculate the iou of box1 and box2
Args:
box1 (Tensor): box1 with the shape (..., 4)
box2 (Tensor): box1 with the shape (..., 4)
eps (float): epsilon to avoid divide by zero
Return:
iou (Tensor): iou of box1 and box2
overlap (Tensor): overlap of box1 and box2
union (Tensor): union of box1 and box2
"""
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box1
x1g, y1g, x2g, y2g = box2
xkis1 = paddle.maximum(x1, x1g)
ykis1 = paddle.maximum(y1, y1g)
xkis2 = paddle.minimum(x2, x2g)
ykis2 = paddle.minimum(y2, y2g)
w_inter = (xkis2 - xkis1).clip(0)
h_inter = (ykis2 - ykis1).clip(0)
overlap = w_inter * h_inter
area1 = (x2 - x1) * (y2 - y1)
area2 = (x2g - x1g) * (y2g - y1g)
union = area1 + area2 - overlap + eps
iou = overlap / union
return iou, overlap, union
以上的 box1 和 box2 都是 xyxy 的列表,也就是 box* = [x1, y1, x2, y2], 而 x1 等列表元素为:
x1.shape 为 [..., 1]
可以简单考虑以下4种情况:

xkis1 = paddle.maximum(x1, x1g)
ykis1 = paddle.maximum(y1, y1g)
xkis2 = paddle.minimum(x2, x2g)
ykis2 = paddle.minimum(y2, y2g)
左上,左下,右下三种情况都会取得交集 box 正确的结果,[xkis1, ykis1, xkis2, ykis2] 是交集的左上角和右下角
而右上的图,得到的交集,左上角要比右下角大了,是错误的,所以下一步用来修正这个问题
w_inter = (xkis2 - xkis1).clip(0)
h_inter = (ykis2 - ykis1).clip(0)
overlap = w_inter * h_inter
如果,存在类似右上图的那种没有交集的情况,则 clip 为0,于是交集 overlap 为0
交集计算完毕,并集就好计算了,二者的面积之和减去交集,就是并集:
area1 = (x2- x1) * (y2 - y1)
area2 = (x2g - x1g) * (y2g - y1g)
union = area1 + area2 - overlap + eps
eps 防止潜在的除零错误,之后计算 IoU,并返回
iou = overlap / union
return iou, overlap, union
通过该函数,获取到 IoU, 交集 和 并集
3. GIoU loss
来看看 PaddleDetection GIoU Loss 部分
class GIoULoss(object):
"""
Generalized Intersection over Union, see https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.09630
Args:
loss_weight (float): giou loss weight, default as 1
eps (float): epsilon to avoid divide by zero, default as 1e-10
reduction (string): Options are "none", "mean" and "sum". default as none
"""
def __init__(self, loss_weight=1., eps=1e-10, reduction='none'):
self.loss_weight = loss_weight
self.eps = eps
assert reduction in ('none', 'mean', 'sum')
self.reduction = reduction
def bbox_overlap(self, box1, box2, eps=1e-10):
"""calculate the iou of box1 and box2
Args:
box1 (Tensor): box1 with the shape (..., 4)
box2 (Tensor): box1 with the shape (..., 4)
eps (float): epsilon to avoid divide by zero
Return:
iou (Tensor): iou of box1 and box2
overlap (Tensor): overlap of box1 and box2
union (Tensor): union of box1 and box2
"""
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box1
x1g, y1g, x2g, y2g = box2
xkis1 = paddle.maximum(x1, x1g)
ykis1 = paddle.maximum(y1, y1g)
xkis2 = paddle.minimum(x2, x2g)
ykis2 = paddle.minimum(y2, y2g)
w_inter = (xkis2 - xkis1).clip(0)
h_inter = (ykis2 - ykis1).clip(0)
overlap = w_inter * h_inter
area1 = (x2 - x1) * (y2 - y1)
area2 = (x2g - x1g) * (y2g - y1g)
union = area1 + area2 - overlap + eps
iou = overlap / union
return iou, overlap, union
def __call__(self, pbox, gbox, iou_weight=1., loc_reweight=None):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = paddle.split(pbox, num_or_sections=4, axis=-1)
x1g, y1g, x2g, y2g = paddle.split(gbox, num_or_sections=4, axis=-1)
box1 = [x1, y1, x2, y2]
box2 = [x1g, y1g, x2g, y2g]
iou, overlap, union = self.bbox_overlap(box1, box2, self.eps)
xc1 = paddle.minimum(x1, x1g)
yc1 = paddle.minimum(y1, y1g)
xc2 = paddle.maximum(x2, x2g)
yc2 = paddle.maximum(y2, y2g)
area_c = (xc2 - xc1) * (yc2 - yc1) + self.eps
miou = iou - ((area_c - union) / area_c)
if loc_reweight is not None:
loc_reweight = paddle.reshape(loc_reweight, shape=(-1, 1))
loc_thresh = 0.9
giou = 1 - (1 - loc_thresh
) * miou - loc_thresh * miou * loc_reweight
else:
giou = 1 - miou
if self.reduction == 'none':
loss = giou
elif self.reduction == 'sum':
loss = paddle.sum(giou * iou_weight)
else:
loss = paddle.mean(giou * iou_weight)
return loss * self.loss_weight
bbox_overlap 部分,刚刚已经看过,接下来看看 __call__ 部分
接下来,将 bbox 的4维坐标向量分离,传入 self.bbox_overlap 中计算 IoU, 交集 和 并集
x1, y1, x2, y2 = paddle.split(pbox, num_or_sections=4, axis=-1)
x1g, y1g, x2g, y2g = paddle.split(gbox, num_or_sections=4, axis=-1)
box1 = [x1, y1, x2, y2]
box2 = [x1g, y1g, x2g, y2g]
iou, overlap, union = self.bbox_overlap(box1, box2, self.eps)
接下来计算包含预测框和GT框的最小矩形,也就是公式中的 C C C
xc1 = paddle.minimum(x1, x1g)
yc1 = paddle.minimum(y1, y1g)
xc2 = paddle.maximum(x2, x2g)
yc2 = paddle.maximum(y2, y2g)
接下来计算 C C C 框的面积,以及计算 GIoU 即可
area_c = (xc2 - xc1) * (yc2 - yc1) + self.eps
miou = iou - ((area_c - union) / area_c)
最后计算 loss 以及 reduce 操作
giou = 1 - miou
if self.reduction == 'none':
loss = giou
elif self.reduction == 'sum':
loss = paddle.sum(giou * iou_weight)
else:
loss = paddle.mean(giou * iou_weight)
最后乘以 loss 的权重
return loss * self.loss_weight
最后可能有个 squeeze 的操作,比如我的操作最后返回的 shape 是 [200, 21, 1]
也就是预测框有200个,GT框有21个,比如以下代码中最后的 squeeze 操作
# Compute the giou cost betwen boxes
cost_giou = self.giou_loss(
bbox_cxcywh_to_xyxy(out_bbox.unsqueeze(1)),
bbox_cxcywh_to_xyxy(tgt_bbox.unsqueeze(0))).squeeze(-1)
债说一下这里,此处用于给loss做 reweight 操作,我暂时没用到
if loc_reweight is not None:
loc_reweight = paddle.reshape(loc_reweight, shape=(-1, 1))
loc_thresh = 0.9
giou = 1 - (1 - loc_thresh
) * miou - loc_thresh * miou * loc_reweight