Linux命令200例:mount将文件系统挂载到指定目录下(常用) https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21891743/article/details/132220283
Linux磁盘卸载 https://blog.csdn.net/Mcy7ycM/article/details/124347504
能否通俗易懂,深入浅出地解释一下linux中的挂载的概念? https://www.zhihu.com/question/266907637
什么是挂载,Linux挂载如何实现详解 https://www.cnblogs.com/cangqinglang/p/12170828.html
--------------------------------------------------------------
关联参考:
mount --bind :目录挂载 (**) https://blog.csdn.net/ken2232/article/details/136937678
--------------------------------------------------------------
区别:
1. 完整的文件路径不一样
mount 法的路径为挂载点的目录路径,简单;真实完整路径,直接在挂载点目录下。
链接法的文件路径为源目录实际路径。访问操作简单,类似于 win 的目录快捷方式,文件路径为From dir 原来的路径。
编程场景:有时使用 mount 法更简洁吧?
特别是对哪些自动挂载的设备,文件名中有一长串的Hash值,这会造成在源码中使用绝对路径时,不仅麻烦,而且也不清晰。
有时,在源码内、或 IDE 已经包含了指定的绝对路径,这时使用目录挂载。
使用目录挂载的方法,还可以将工作数据,放到非系统分区的其他分区中,防止 OS崩溃时发生数据灾难。
以及其他方法等等。
永久化,需要修改 fstab:
2. 目录的图表样式不一样。
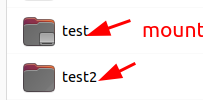
问题:ubuntu 22.04 目录卸载之后,目录图标不能恢复 ?
3. 硬链接:只适用于文件。
小结:
对于文件路径有特别要求的场景,使用 mount。
$ mount --help
Usage:
mount [-lhV]
mount -a [options]
mount [options] [--source] <source> | [--target] <directory>
mount [options] <source> <directory>
mount <operation> <mountpoint> [<target>]
$ umount --help
Usage:
umount [-hV]
umount -a [options]
umount [options] <source> | <directory>.
注:
<source> : From this dir
<directory> : To this dir, 挂载点
============================
摘录:linux mount一个目录到另外一个目录
https://www.cnblogs.com/sunsky303/p/11016924.html
从linux内核2.4.0以后mount支持mount --bind 一个目录到另外一个目录
比如:
[root@localhost wind]# mkdir test1 test2 dir3
mount --bind test1 test2
把test1挂载到test2,如果test2目录有内容将被遮住(dir2目录的内容一样存在。就好像窗帘把窗户遮住一样。窗户始终存在,只是被遮住而已,等umount了,原来dir2目录的内容就显示出来了)
要取消挂载使用umount即可
mount test1
或
mount test2