参考资料:
(1)单例模式—— 代码随想录
(2)我给面试官讲解了单例模式后,他对我竖起了大拇指!
(3)C++ 单例模式详解
(4)单例模式之C++实现,智能指针,线程安全版本
(5)深入探索单例设计模式:以百度 Apollo 为例
1 单例模式
单例模式:创建型设计模式
核心思想:保证一个类只有一个实例,并提供一个全局访问点来访问这个实例
- 一个实例:在整个应用程序中,只存在该类的一个实例对象,而不是创建多个相同类型的对象
- 全局访问点:为了让其他类能够获取到这个唯一实例,该类提供了一个全局访问点(通常是一个静态方法),通过这个方法就能获得实例
单例模式的类型:
- 懒汉式:在真正需要使用对象时才去创建该单例类对象
- 饿汉式:在类加载时已经创建好该单例对象,等待被程序使用
2 使用单例模式的需求
- 全局控制:保证只有一个实例,严格的控制客户怎样访问它以及何时访问它,简单的说就是对唯一实例的受控访问
- 节省资源:避免多次创建了相同的对象,从而节省了系统资源,而且多个模块还可以通过单例实例共享数据
- 懒加载:只有在需要时才进行实例化
3 实现单例模式的步骤
- 私有的构造函数:防止外部代码直接创建类的实例
- 提供一个公有的静态方法:通过公有的静态方法来获取类的实例
- 在类中定义一个私有静态指针,指向本类的变量的静态变量指针:保存该类的唯一实例
4 懒汉式创建单例对象
懒汉式创建对象的方法是在程序使用对象前,先判断该对象是否已经实例化(判空),若已实例化直接返回该类对象。,否则则先执行实例化操作。
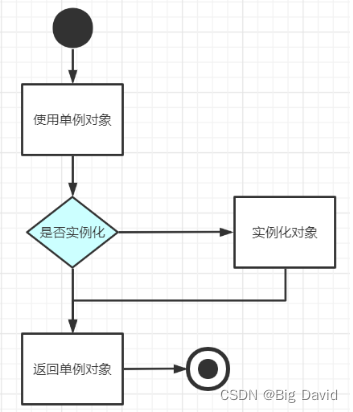
适用于单线程场景的懒汉式单例
class Singleton {
public:
static Singleton* getInstance() {
if (instance_ = NULL) {
instance_ = new Singleton();
}
return instance_;
}
private:
Singleton() = default;
static Singleton* instance_;
};
// 初始化静态成员变量
Singleton* Singleton::instance_ = NULL;
懒汉式单例模式存在内存泄漏的问题:
- 使用智能指针
class Singleton {
public:
static shared_ptr<Singleton> getInstance() {
if (instance_ == NULL) {
lock_guard<mutex> lock(mutex_);
if (instance_ == NULL) {
instance_ = shared_ptr<Singleton>(new Singleton());
}
}
return instance_;
}
private:
Singleton() = default;
static shared_ptr<Singleton> instance_;
static mutex mutex_;
};
shared_ptr<Singleton> Singleton::instance_ = NULL;
mutex Singleton::mutex_;
- 使用静态的嵌套类对象
class Singleton {
public:
static Singleton* getInstance() {
if (instance_ = NULL) {
instance_ = new Singleton();
}
return instance_;
}
private:
Singleton() = default;
static Singleton* instance_;
class Deletor {
public:
~Deletor() {
if (Singleton::instance_ != NULL)
delete Singleton::instance_;
}
};
static Deletor deletor;
};
// 初始化静态成员变量
Singleton* Singleton::instance_ = NULL;
Meyers 单例:静态局部变量的懒汉单例(C++11线程安全)
C++11规定了local static在多线程条件下的初始化行为,要求编译器保证了内部静态变量的线程安全性。《Effective C++》使用函数内的 local static 对象,这样,只有当第一次访问getInstance()方法时才创建实例。
如果多个线程同时尝试初始化相同的静态局部变量,初始化动作只会发生一次,这个内部特性通常也是通过双检锁模式实现的。
class Singleton {
public:
static Singleton& getInstance() {
static Singleton instance_;
return instance_;
}
private:
Singleton() {};
~Singleton() {};
Singleton(const Singleton&);
Singleton& operator=(const Singleton&);
};
多线程安全的懒汉式单例:双检锁 + 原子变量实现
(1) 使用双检锁确保性能:针对单检锁方法中存在的性能问题,有一种所谓的双检锁模式(Double-Checked Locking Pattern,DCLP)优化方案,即在 GetInstance 中执行锁操作前,在最外层额外地进行一次实例指针的检查操作(“双检”的体现),这样可以保证实例指针完成内存分配后,单纯的实例访问操作不会再附带锁操作带来的性能开销
class LazySingleton
{
private:
static LazySingleton *pinstance_;
static std::mutex mutex_;
private:
LazySingleton() {}
LazySingleton(const LazySingleton &) = delete;
LazySingleton &operator=(const LazySingleton &) = delete;
public:
~LazySingleton() {}
public:
static LazySingleton *GetInstance();
};
LazySingleton *LazySingleton::pinstance_{nullptr};
std::mutex LazySingleton::mutex_;
LazySingleton *LazySingleton::GetInstance()
{
if (nullptr == pinstance_)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
if (nullptr == pinstance_)
{
pinstance_ = new LazySingleton;
}
}
return pinstance_;
}
双检锁方法初衷虽好,但却破坏了多线程场景下的安全性,这是由动态内存分配时 new 底层操作的非原子性导致的,执行 pinstance_ = new LazySingleton; 语句时,底层其实对应了三个步骤:
- 向系统申请分配内存,大小为 sizeof(LazySingleton)
- 调用 LazySingleton 的默认构造函数在申请的内存上构造出实例
- 返回申请内存的指针给 pinstance_
根本问题在于上面的这三个步骤无法确保执行顺序。例如,出于优化的原因,处理器很可能调整步骤 3 和步骤 2 的执行顺序(按照 1、3、2 的顺序执行)。
假设,现在某个线程执行到了 pinstance_ = new LazySingleton; 语句,底层操作完成了内存申请(步骤 1)和实例指针赋值(步骤 3),但尚未完成申请内存的构造(步骤 2),意即,现在 pinstance_ 指向的是一片脏内存。此时,另一个线程恰好执行到双检锁的最外层检查,该线程发现 pinstance_ 非空(发生了脏读),检查为 false,因而直接取走了尚未完成构造的实例指针(return pinstance_;),从而可能诱发程序未定义行为(undefined behavior)。
(2) 使用原子变量确保多线程安全性
可以通过封装一个单例指针类型的 std::atomic 原子对象,将单例指针的读写操作转化为对原子对象的操作,以此来确保双检锁实现的懒汉式单例的多线程安全性。
std::atomic 是 C++11 定义于 <atomic> 中的新特性,每个 std::atomic 模板的实例化和全特化定义一个原子类型,若一个线程写入原子对象,同时另一线程从它读取,则行为良好定义。另外,对原子对象的访问可以建立线程间同步,并按 std::memory_order 枚举类型中的枚举常量对非原子内存访问定序:
typedef enum memory_order {
memory_order_relaxed,
memory_order_consume,
memory_order_acquire,
memory_order_release,
memory_order_acq_rel,
memory_order_seq_cst
} memory_order;
下面给出经典的基于双检锁 + 原子变量的懒汉式单例实现:
class LazySingleton
{
private:
static std::atomic<LazySingleton *> ainstance_;
static std::mutex mutex_;
private:
LazySingleton() {}
LazySingleton(const LazySingleton &) = delete;
LazySingleton &operator=(const LazySingleton &) = delete;
public:
~LazySingleton() {}
public:
static LazySingleton *GetInstance();
};
std::atomic<LazySingleton *> LazySingleton::ainstance_;
std::mutex LazySingleton::mutex_;
LazySingleton *LazySingleton::GetInstance()
{
LazySingleton *tmp = ainstance_.load(std::memory_order_acquire);
if (nullptr == tmp)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
tmp = ainstance_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
if (nullptr == tmp)
{
tmp = new LazySingleton;
ainstance_.store(tmp, std::memory_order_release);
}
}
return tmp;
}
load:原子性地加载并返回原子变量的当前值,类似读操作。唯一形参类型为std::memory_order,默认值为 memory_order_seq_cststore:根据第一实参原子性地替换原子变量的当前值,类似写操作。第二形参类型为std::memory_order,默认值为memory_order_seq_cst
上面这种原子变量的使用方式称为 Acquire-Release Semantic 内存模型,如果保持 load 和 store 的 std::memory_order 参数缺省,则成为 Sequential Consistency 内存模型,性能会稍有损失。
5 饿汉式创建单例对象
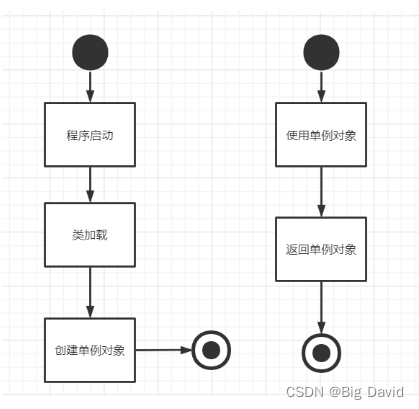
在main函数之前初始化,所以没有线程安全的问题。但是潜在问题在于no-local static对象(函数外的static对象)在不同编译单元中的初始化顺序是未定义的。就是说说,static Singleton instance_;和static Singleton& getInstance()二者的初始化顺序不确定,如果在初始化完成之前调用 getInstance() 方法会返回一个未定义的实例。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Singleton {
public:
static Singleton* getInstance() {
return instance_;
}
private:
Singleton() {cout << "a" << endl;};
~Singleton() {};
Singleton(const Singleton&);
Singleton& operator=(const Singleton&);
private:
static Singleton* instance_;
};
// initialize defaultly
Singleton* Singleton::instance_ = new Singleton();
int main()
{
cout << "we get the instance" << endl;
Singleton* a1 = Singleton::getInstance();
cout << "we destroy the instance" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
a
we get the instance
we destroy the instance
6 百度 Apollo 中的懒汉式单例:once_flag & call_once 实现
一个普通的 SensorManager 类经宏定义 DECLARE_SINGLETON(SensorManager) 修饰成为单例类:
class SensorManager {
// ...
//
// other code
//
// ...
DECLARE_SINGLETON(SensorManager)
};
DECLARE_SINGLETON(classname) 定义在 apollo/cyber/common/macros.h中:
#ifndef CYBER_COMMON_MACROS_H_
#define CYBER_COMMON_MACROS_H_
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <mutex>
#include <type_traits>
#include <utility>
#include "cyber/base/macros.h"
DEFINE_TYPE_TRAIT(HasShutdown, Shutdown)
template <typename T>
typename std::enable_if<HasShutdown<T>::value>::type CallShutdown(T *instance) {
instance->Shutdown();
}
template <typename T>
typename std::enable_if<!HasShutdown<T>::value>::type CallShutdown(
T *instance) {
(void)instance;
}
// There must be many copy-paste versions of these macros which are same
// things, undefine them to avoid conflict.
#undef UNUSED
#undef DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN
#define UNUSED(param) (void)param
#define DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(classname)
classname(const classname &) = delete;
classname &operator=(const classname &) = delete;
#define DECLARE_SINGLETON(classname)
public:
static classname *Instance(bool create_if_needed = true) {
// 提供对唯一实例的全局访问点
static classname *instance = nullptr;
if (!instance && create_if_needed) {
static std::once_flag flag;
std::call_once(flag,
[&] { instance = new (std::nothrow) classname(); });
}
return instance;
}
static void CleanUp() {
auto instance = Instance(false);
if (instance != nullptr) {
CallShutdown(instance);
}
}
private:
classname();
DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(classname)
#endif // CYBER_COMMON_MACROS_H_
DECLARE_SINGLETON(classname) 在预处理阶段会被替换为:
(1)静态方法 Instance
(2)私有的泛化默认构造函数和嵌套的宏定义 DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN
(3) 静态方法 CleanUp
7.1 泛化的单例
DECLARE_SINGLETON(classname)如何将任意一个类修饰为单例类的:
(1)提供对唯一实例的全局访问点
static classname *instance = nullptr;
实例访问点的全局性通过静态方法 Instance 实现。
(2)多线程安全
实现方式的多线程安全性由 std::once_flag 和 std::call_once 保证,两者都是 C++11 定义于<mutex>中的新特性,配合使用可以确保多线程场景下可调用对象的唯一执行。
std::once_flag 是 std::call_once 的辅助结构体,在 GNU 中的实现如下:
struct once_flag
{
private:
typedef __gthread_once_t __native_type;
__native_type _M_once = __GTHREAD_ONCE_INIT;
public:
/// Constructor
constexpr once_flag() noexcept = default;
/// Deleted copy constructor
once_flag(const once_flag&) = delete;
/// Deleted assignment operator
once_flag& operator=(const once_flag&) = delete;
template<typename _Callable, typename... _Args>
friend void
call_once(once_flag& __once, _Callable&& __f, _Args&&... __args);
};
call_once 被声明为 once_flag 的友元函数,为的是 call_once 可以修改 once_flag 中的 _M_once 成员(可调用对象的调用状态)。
std::call_once 是一个可变参数模板函数
可变参数经完美转发传入可调用对象,具体到 Apollo 中,可调用对象指的是为实例指针分配动态内存的 lambda 表达式:
[&] { instance = new (std::nothrow) classname(); }
std::call_once通过间接调用 pthread_once 函数来确保传入的可调用对象即使在多线程场景下也只能被执行一次
(3) 防止私自创建实例
#define DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(classname)
classname(const classname &) = delete;
classname &operator=(const classname &) = delete;
分析CleanUp静态方法,该方法允许用户调用时执行一些自定义的清理工作:
static void CleanUp() {
auto instance = Instance(false);
if (instance != nullptr) {
CallShutdown(instance);
}
}
CallShutdown 模板函数包含两个经类型萃取(type traits)进行重载的实现
template <typename T>
typename std::enable_if<HasShutdown<T>::value>::type CallShutdown(T *instance) {
instance->Shutdown();
}
template <typename T>
typename std::enable_if<!HasShutdown<T>::value>::type CallShutdown(
T *instance) {
(void)instance;
}
DEFINE_TYPE_TRAIT(HasShutdown, Shutdown)
#define DEFINE_TYPE_TRAIT(name, func) \
template <typename T> \
struct name { \
template <typename Class> \
static constexpr bool Test(decltype(&Class::func)*) { \
return true; \
} \
template <typename> \
static constexpr bool Test(...) { \
return false; \
} \
\
static constexpr bool value = Test<T>(nullptr); \
}; \
\
template <typename T> \
constexpr bool name<T>::value;
DEFINE_TYPE_TRAIT(HasShutdown, Shutdown)的具体含义是:创建类型萃取模板类 HasShutdown,HasShutdown可检查模板类型参数 T 中是否包含Shutdown方法。若是,则执行下面语句版本的CallShutdown会被CleanUp调用:
instance->Shutdown();
否则,执行下面语句版本的 CallShutdown 会被 CleanUp 调用:
(void)instance;
7.2 封装与验证
singleton.h
#ifndef SINGLETON_SINGLETON_H
#define SINGLETON_SINGLETON_H
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <mutex>
#include <type_traits>
#include <utility>
#define DEFINE_TYPE_TRAIT(name, func) \
template <typename T> \
struct name { \
template <typename Class> \
static constexpr bool Test(decltype(&Class::func)*) { \
return true; \
} \
template <typename> \
static constexpr bool Test(...) { \
return false; \
} \
\
static constexpr bool value = Test<T>(nullptr); \
}; \
\
template <typename T> \
constexpr bool name<T>::value;
DEFINE_TYPE_TRAIT(HasShutdown, Shutdown)
template <typename T>
typename std::enable_if<HasShutdown<T>::value>::type CallShutdown(T *instance) {
instance->Shutdown();
}
template <typename T>
typename std::enable_if<!HasShutdown<T>::value>::type CallShutdown(
T *instance) {
(void)instance;
}
// There must be many copy-paste versions of these macros which are same
// things, undefine them to avoid conflict.
#undef UNUSED
#undef DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN
#define UNUSED(param) (void)param
#define DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(classname) \
classname(const classname &) = delete; \
classname &operator=(const classname &) = delete;
#define DECLARE_SINGLETON(classname) \
public: \
static classname *Instance(bool create_if_needed = true) { \
static classname *instance = nullptr; \
if (!instance && create_if_needed) { \
static std::once_flag flag; \
std::call_once(flag, \
[&] { instance = new (std::nothrow) classname(); }); \
} \
return instance; \
} \
\
static void CleanUp() { \
auto instance = Instance(false); \
if (instance != nullptr) { \
CallShutdown(instance); \
} \
} \
\
private: \
classname(); \
DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(classname)
#endif //SINGLETON_SINGLETON_H
singleton_a.h
#ifndef SINGLETON_SINGLETON_A_H
#define SINGLETON_SINGLETON_A_H
#include <iostream>
#include "singleton.h"
class SingletonA
{
private:
~SingletonA() = default;
private:
static int num;
public:
static void GetNum()
{
std::cout << "\n number of instances of SingletonA: " << num << std::endl;
}
DECLARE_SINGLETON(SingletonA)
};
int SingletonA::num = 0;
SingletonA::SingletonA()
{
++num;
}
#endif //SINGLETON_SINGLETON_A_H
singleton_b.h
#ifndef SINGLETON_SINGLETON_B_H
#define SINGLETON_SINGLETON_B_H
#include <iostream>
#include "singleton.h"
class SingletonB
{
private:
~SingletonB() = default;
private:
static int num;
public:
// `Shutdown` method should be declared as `public` for type traits
void Shutdown();
static void GetNum()
{
std::cout << "\n number of instances of SingletonB: " << num << std::endl;
}
DECLARE_SINGLETON(SingletonB)
};
int SingletonB::num = 0;
SingletonB::SingletonB()
{
++num;
}
void SingletonB::Shutdown()
{
auto instance = Instance(false);
if (instance != nullptr)
{
delete instance;
num = 0;
}
std::cout << "\n SingletonB::Shutdown method was called." << std::endl;
}
#endif //SINGLETON_SINGLETON_B_H
main.cpp
#include <thread>
#include "singleton_b.h"
#include "singleton_a.h"
template <typename T>
void ThreadFunc()
{
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1000));
T *p = T::Instance();
}
int main()
{
std::thread tA1(ThreadFunc<SingletonA>);
std::thread tA2(ThreadFunc<SingletonA>);
std::thread tB1(ThreadFunc<SingletonB>);
std::thread tB2(ThreadFunc<SingletonB>);
tA1.join();
tA2.join();
tB1.join();
tB2.join();
SingletonA::GetNum();
SingletonB::GetNum();
SingletonA::CleanUp();
SingletonB::CleanUp();
SingletonA::GetNum();
SingletonB::GetNum();
return 0;
}
CMakeList.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.25)
project(singleton)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
add_executable(singleton main.cpp singleton.h singleton_a.h singleton_b.h)
运行结果:
number of instances of SingletonA: 1
number of instances of SingletonB: 1
SingletonB::Shutdown method was called.
number of instances of SingletonA: 1
number of instances of SingletonB: 0
- 在调用 CleanUp 方法前,虽然 SingletonA 和 SingletonB 各自被两个线程调用 Instance 方法,但默认构造均只发生了一次(实例数量均为 1),说明满足多线程安全性;
- 分别调用 SingletonA 和 SingletonB 的 CleanUp 方法后,SingletonB 的实例数量清零,因为其 Shutdown 方法被间接调用;SingletonA 实例数量仍为 1,因为其 CleanUp 方法什么也没做。
7 单例模式总结
- 懒汉式:在需要用到对象时才实例化对象,正确的实现方式是:Double Check + Lock,解决了并发安全和性能低下问题
- 饿汉式:在类加载时已经创建好该单例对象,在获取单例对象时直接返回对象即可,不会存在并发安全和性能问题。
如果在开发中如果对内存要求非常高,那么使用懒汉式写法,可以在特定时候才创建该对象;
如果对内存要求不高使用饿汉式写法,因为简单不易出错,且没有任何并发安全和性能问题
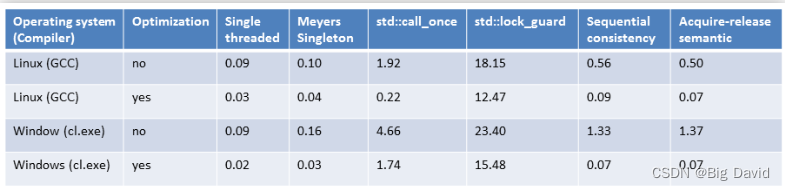
Meyers 单例不仅形式优雅,效率在多线程场景下也是最优的
class Singleton {
public:
static Singleton& getInstance() {
static Singleton instance_;
return instance_;
}
private:
Singleton() {};
~Singleton() {};
Singleton(const Singleton&);
Singleton& operator=(const Singleton&);
};
至此,单例模式懒汉式和饿汉式讲解到此结束,不正之处望读者指正。





![[PCL] PCLVisualizer可视化的应用](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/9c3e7de035434a47a250bbc51f357d9d.png)
