本笔记主要用compile, fit, evalutate和predict来简化整体代码,使用这些高层API可以减少很多重复代码。具体内容请自行百度,本笔记基于FashionMnist的训练笔记,原始笔记如下:
Tensorflow2.0笔记 - FashionMnist数据集训练-CSDN博客文章浏览阅读347次。本笔记使用FashionMnist数据集,搭建一个5层的神经网络进行训练,并统计测试集的精度。本笔记中FashionMnist数据集是直接下载到本地加载的方式,不涉及用梯子。关于FashionMnist的介绍,请自行百度。https://blog.csdn.net/vivo01/article/details/136921592?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
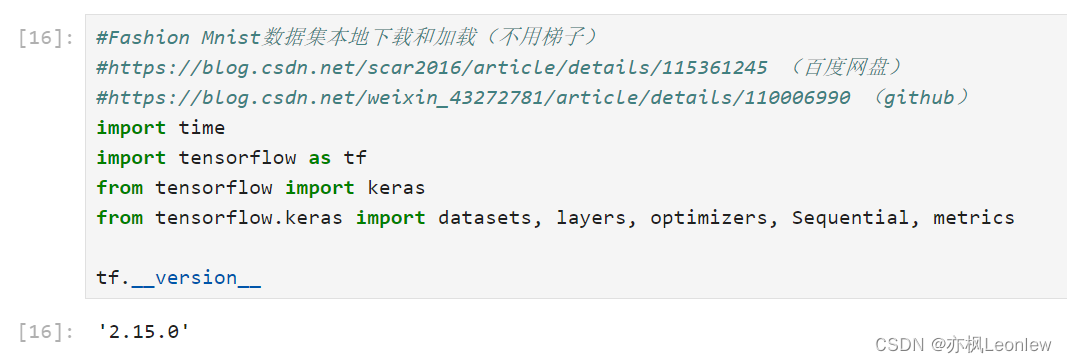
#Fashion Mnist数据集本地下载和加载(不用梯子)
#https://blog.csdn.net/scar2016/article/details/115361245 (百度网盘)
#https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43272781/article/details/110006990 (github)
import time
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import datasets, layers, optimizers, Sequential, metrics
tf.__version__
#加载fashion mnist数据集
def load_mnist(path, kind='train'):
import os
import gzip
import numpy as np
"""Load MNIST data from `path`"""
labels_path = os.path.join(path,
'%s-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz'
% kind)
images_path = os.path.join(path,
'%s-images-idx3-ubyte.gz'
% kind)
with gzip.open(labels_path, 'rb') as lbpath:
labels = np.frombuffer(lbpath.read(), dtype=np.uint8,
offset=8)
with gzip.open(images_path, 'rb') as imgpath:
images = np.frombuffer(imgpath.read(), dtype=np.uint8,
offset=16).reshape(len(labels), 784)
return images, labels
#预处理数据
def preprocess(x, y):
x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32)
x = tf.convert_to_tensor(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.int32)
y = tf.convert_to_tensor(y, dtype=tf.int32)
return x, y
#训练数据
train_data, train_labels = load_mnist("./datasets")
print(train_data.shape, train_labels.shape)
#测试数据
test_data, test_labels = load_mnist("./datasets", "t10k")
print(test_data.shape, test_labels.shape)
batch_size = 128
train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((train_data, train_labels))
train_db = train_db.map(preprocess).shuffle(10000).batch(batch_size)
test_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((test_data, test_labels))
test_db = test_db.map(preprocess).batch(batch_size)
train_db_iter = iter(train_db)
sample = next(train_db_iter)
print('Batch:', sample[0].shape, sample[1].shape)
test_db_iter = iter(test_db)
sample = next(test_db_iter)
print(sample[0].shape)
print(sample[1].shape)
#定义网络模型
model = Sequential([
#Layer 1: [b, 784] => [b, 256]
layers.Dense(256, activation=tf.nn.relu),
#Layer 2: [b, 256] => [b, 128]
layers.Dense(128, activation=tf.nn.relu),
#Layer 3: [b, 128] => [b, 64]
layers.Dense(64, activation=tf.nn.relu),
#Layer 4: [b, 64] => [b, 32]
layers.Dense(32, activation=tf.nn.relu),
#Layer 5: [b, 32] => [b, 10], 输出类别结果
layers.Dense(10)
])
print("\n=====Building Model=========\n")
model.build(input_shape=(None, 28*28))
model.summary()
total_epoches = 10
learn_rate = 0.01
#编译网络,使用compile(),传入优化器,损失函数和metrics度量
#https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_48169169/article/details/120793534
print("\n=====Compiling Model=========\n")
model.compile(optimizer=optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=learn_rate),
loss = tf.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['Accuracy'])
#使用fit()进行训练
print("\n=====Fitting Model=========\n")
model.fit(train_db, epochs=total_epoches, validation_data=test_db, validation_freq=2)
time.sleep(1)
#使用evaluate()进行模型验证,这里使用了test_db,实际中可以使用另外的数据集
print("\n=====Evaluating Model=========\n")
model.evaluate(test_db)
#使用predict()做数据预测
sample = next(iter(test_db))
#获得数据和标签
real_data = sample[0]
real_label = sample[1]
pred = model.predict(real_data)
pred = tf.argmax(pred, axis=1)
print("Predicted Labels:", pred.numpy())
print("Actual Labels:", real_label.numpy())运行结果: