之前想用boost1.69版本,但是boost与numcpp编译过程死活找不到boost1.69,踩坑无数,只能采用1.79版本。
https://www.cnblogs.com/tang-zhou-zhou/p/16067695.html
在 Windows 下通过 CMake 使用 Boost 库_cmake boost-CSDN博客
在VS2019中配置Boost C++、NumCpp、Eigen 和opencv4.3.0库环境_visual studio c++配置numcpp-CSDN博客
vs2017+win10配置Boost与NumCpp,以及boost与PLC 1.8.1冲突的解决方法_手动添加 numcpp 标头,您还需要手动包含boost标头-CSDN博客
boost下载地址:link
直接二进制地址: Boost C++ Libraries - Browse /boost-binaries/1.79.0 at SourceForge.net
官方地址为:https://www.boost.org/users/download/
1 编译boost

.\b2.exe --link=static --toolset=msvc-14.1 --address-model=64 --architecture=x64 variant=release测试程序:
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<boost/version.hpp> //包含boost头文件
#include<boost/config.hpp>
int main() {
using namespace std;
cout << BOOST_VERSION << endl;
cout << BOOST_LIB_VERSION << endl;
cout << BOOST_PLATFORM << endl;
cout << BOOST_COMPILER << endl;
cout << BOOST_STDLIB << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
注意的是Boost_DIR所在路径BoostConfig.cmake link



生成vs2017工程 
编译过程遇见error MSB3073: 命令“setlocal”错误
参考link解决
项目属性页——配置属性——生成事件——生成后事件——在生成中使用“是”修改为“否”
大功告成


之后就是配置numcpp和boost,numcpp是hpp的库,配置简单

测试代码:
#include <NumCpp.hpp>
#include "boost/filesystem.hpp"
using namespace nc;
int main()
{
// Containers
nc::NdArray<int> a0 = { {1, 2}, {3, 4} };
nc::NdArray<int> a1 = { {1, 2}, {3, 4}, {5, 6} };
a1.reshape(2, 3);
auto a2 = a1.astype<double>();
// Initializers
auto a3 = nc::linspace<int>(1, 10, 5);
auto a4 = nc::arange<int>(3, 7);
auto a5 = nc::eye<int>(4);
auto a6 = nc::zeros<int>(3, 4);
auto a7 = nc::NdArray<int>(3, 4) = 0;
auto a8 = nc::ones<int>(3, 4);
auto a9 = nc::NdArray<int>(3, 4) = 1;
auto a10 = nc::nans(3, 4);
auto a11 = nc::NdArray<double>(3, 4) = nc::constants::nan;
auto a12 = nc::empty<int>(3, 4);
auto a13 = nc::NdArray<int>(3, 4);
// Slicing/Broadcasting
//auto a14 = nc::random<int>::randInt({ 10, 10 }, 0, 100);
auto a14 = nc::random::randInt({ 10, 10 }, 0, 100);
auto value = a14(2, 3);//randInt
auto slice = a14({ 2, 5 }, { 2, 5 });
auto rowSlice = a14(a14.rSlice(), 7);
auto values = a14[a14 > 50];
a14.putMask(a14 > 50, 666);
// Random
nc::random::seed(666);
auto a15 = nc::random::randN<double>({ 3, 4 });
auto a16 = nc::random::randInt<int>({ 3, 4 }, 0, 10);
auto a17 = nc::random::rand<double>({ 3, 4 });
auto a18 = nc::random::choice<double>(a17, 3);
// Concatenation
auto a = nc::random::randInt<int>({ 3, 4 }, 0, 10);
auto b = nc::random::randInt<int>({ 3, 4 }, 0, 10);
auto c = nc::random::randInt<int>({ 3, 4 }, 0, 10);
auto a19 = nc::stack({ a, b, c }, nc::Axis::ROW);
auto a20 = nc::vstack({ a, b, c });
auto a21 = nc::hstack({ a, b, c });
auto a22 = nc::append(a, b, nc::Axis::COL);
// Diagonal, Traingular, and Flip
auto d = nc::random::randInt<int>({ 5, 5 }, 0, 10);
auto a23 = nc::diagonal(d);
auto a24 = nc::triu(a);
auto a25 = nc::tril(a);
auto a26 = nc::flip(d, nc::Axis::ROW);
auto a27 = nc::flipud(d);
auto a28 = nc::fliplr(d);
// iteration
for (auto it = a.begin(); it < a.end(); ++it)
{
std::cout << *it << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
for (auto& arrayValue : a)
{
std::cout << arrayValue << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
// Logical
auto a29 = nc::where(a > 5, a, b);
auto a30 = nc::any(a);
auto a31 = nc::all(a);
auto a32 = nc::logical_and(a, b);
auto a33 = nc::logical_or(a, b);
auto a34 = nc::isclose(a, b);
auto a35 = nc::allclose(a, b);
// Comparisons
auto a36 = nc::equal(a, b);
auto a37 = a == b;
auto a38 = nc::not_equal(a, b);
auto a39 = a != b;
auto a40 = nc::nonzero(a);
// Minimum, Maximum, Sorting
auto value1 = nc::min(a);
auto value2 = nc::max(a);
auto value3 = nc::argmin(a);
auto value4 = nc::argmax(a);
auto a41 = nc::sort(a, nc::Axis::ROW);
auto a42 = nc::argsort(a, nc::Axis::COL);
auto a43 = nc::unique(a);
auto a44 = nc::setdiff1d(a, b);
auto a45 = nc::diff(a);
// Reducers
auto value5 = nc::sum<int>(a);
auto a46 = nc::sum<int>(a, nc::Axis::ROW);
auto value6 = nc::prod<int>(a);
auto a47 = nc::prod<int>(a, nc::Axis::ROW);
auto value7 = nc::mean(a);
auto a48 = nc::mean(a, nc::Axis::ROW);
auto value8 = nc::count_nonzero(a);
auto a49 = nc::count_nonzero(a, nc::Axis::ROW);
// I/O
a.print();
std::cout << a << std::endl;
auto tempDir = boost::filesystem::temp_directory_path();
auto tempTxt = (tempDir / "temp.txt").string();
a.tofile(tempTxt);
auto a50 = nc::fromfile<int>(tempTxt);
auto tempBin = (tempDir / "temp.bin").string();
nc::dump(a, tempBin);
auto a51 = nc::load<int>(tempBin);
// Mathematical Functions
// Basic Functions
auto a52 = nc::abs(a);
auto a53 = nc::sign(a);
auto a54 = nc::remainder(a, b);
auto a55 = nc::clip(a, 3, 8);
auto xp = nc::linspace<double>(0.0, 2.0 * nc::constants::pi, 100);
auto fp = nc::sin(xp);
auto x = nc::linspace<double>(0.0, 2.0 * nc::constants::pi, 1000);
auto f = nc::interp(x, xp, fp);
// Exponential Functions
auto a56 = nc::exp(a);
auto a57 = nc::expm1(a);
auto a58 = nc::log(a);
auto a59 = nc::log1p(a);
// Power Functions
auto a60 = nc::power<int>(a, 4);
auto a61 = nc::sqrt(a);
auto a62 = nc::square(a);
auto a63 = nc::cbrt(a);
// Trigonometric Functions
auto a64 = nc::sin(a);
auto a65 = nc::cos(a);
auto a66 = nc::tan(a);
// Hyperbolic Functions
auto a67 = nc::sinh(a);
auto a68 = nc::cosh(a);
auto a69 = nc::tanh(a);
// Classification Functions
auto a70 = nc::isnan(a.astype<double>());
//nc::isinf(a);
// Linear Algebra
auto a71 = nc::norm<int>(a);
auto a72 = nc::dot<int>(a, b.transpose());
auto a73 = nc::random::randInt<int>({ 3, 3 }, 0, 10);
auto a74 = nc::random::randInt<int>({ 4, 3 }, 0, 10);
auto a75 = nc::random::randInt<int>({ 1, 4 }, 0, 10);
auto value9 = nc::linalg::det(a73);
auto a76 = nc::linalg::inv(a73);
auto a77 = nc::linalg::lstsq(a74, a75);
auto a78 = nc::linalg::matrix_power<int>(a73, 3);
auto a79 = nc::linalg::multi_dot<int>({ a, b.transpose(), c });
nc::NdArray<double> u;
nc::NdArray<double> s;
nc::NdArray<double> vt;
nc::linalg::svd(a.astype<double>(), u, s, vt);
}遇见问题参考link 注释改行解决

最后有人说NumCpp 中看不中用
#include <NumCpp.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
int main(int, char **) {
auto a = nc::random::randInt<int>({ 1000, 1000 }, 0, 10);
nc::NdArray<double> u, s, vt;
// 计时开始
auto t0 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
nc::linalg::svd(a.astype<double>(), u, s, vt);
// 计时结束
auto t1 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto duration = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds> (t1 - t0);
std::cout << duration.count() << std::endl;
return 0;
} 实际测试性能能确实拉跨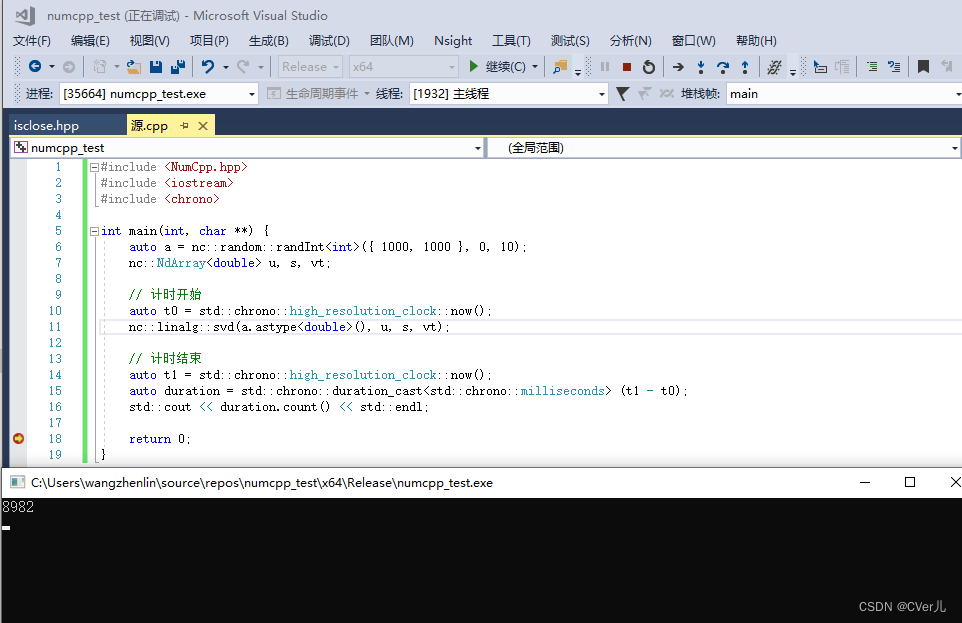
argmax测试:
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include "NumCpp.hpp"
int main() {
// 设置数组大小
constexpr uint32_t arraySize = 1000000;
nc::NdArray<double> largeArray = nc::linspace<double>(0, 100, arraySize);
// 定义测试次数
constexpr int numTests = 1000;
// 执行性能测试
std::chrono::duration<double> totalDuration(0);
for (int i = 0; i < numTests; ++i) {
auto start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto maxIndex = nc::argmax(largeArray);
auto end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
totalDuration += end - start;
}
// 输出平均执行时间
double averageTime = totalDuration.count() / numTests;
std::cout << "Average time for argmax function: " << averageTime << " seconds." << std::endl;
return 0;
}