F - Many Lamps
题目大意:

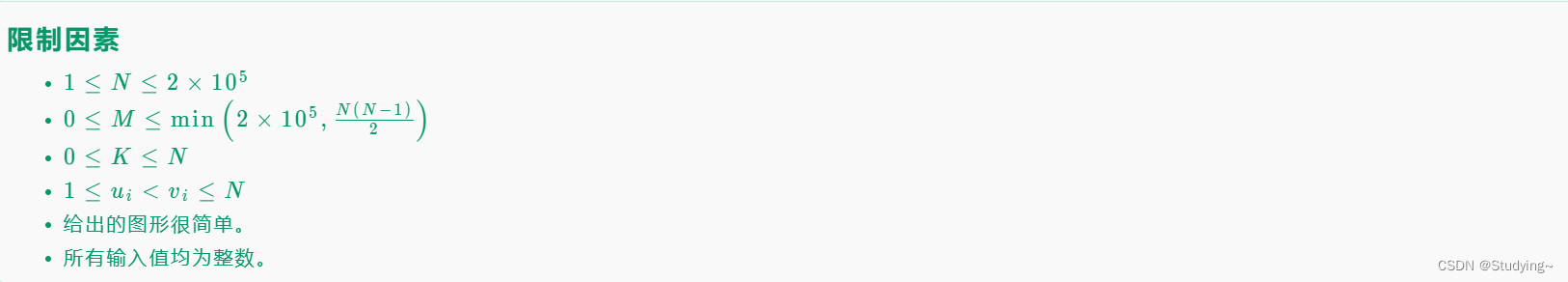
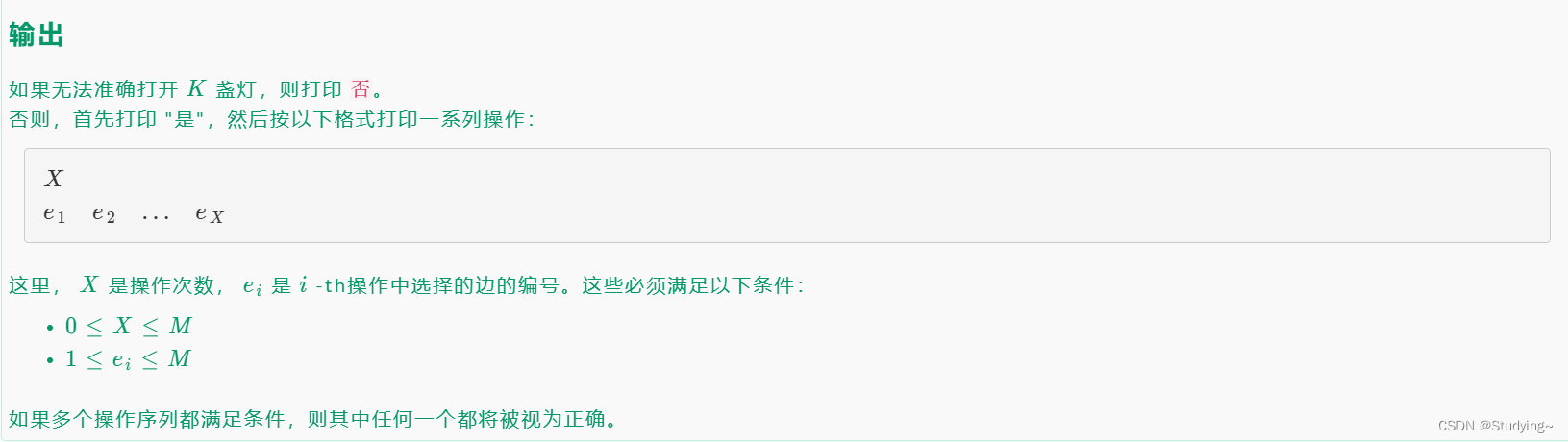
思路解析:
对于每个线只有三种情况
(1) 一个城市亮着灯,另一个城市没亮灯,此时选择这条线路,灯的点亮数不变
(2) 两个城市未亮灯,选择此线路,亮灯数加2
(3)两个城市都亮着灯,选择此线路,亮灯数减2
那么我们可以发现我们无论组合都没法使亮着的灯变为偶数,那么如果我们已知一个灯为亮,此时选择这条线路,要么能使亮灯数增加,要么无变化,那么只要 当前亮灯数小于目标亮灯数就可以选择这条线路,因为这是个无向有环图,所以每遍历一个点做一次记录就好,只遍历没有标记过的点。
这样深搜时,只要有答案便能找到答案。
代码实现:
import java.io.*;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static long inf = (long) 2e18;
static int N;
static int[] vis;
static LinkedList<Integer> ans;
static Vector<Node>[] g;
static int[] lamp;
static int res = 0;
static int K;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
N = f.nextInt();
int M = f.nextInt();
K = f.nextInt();
g = new Vector[N+1];
lamp = new int[N+1];
vis = new int[N+1];
ans = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < N + 1; i++) {
g[i] = new Vector<>();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= M; i++) {
int x = f.nextInt();
int y = f.nextInt();
g[x].add(new Node(y, i));
g[y].add(new Node(x, i));
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
if (vis[i] == 0)
dfs(i);
}
if (res != K){
w.println("No");
}else {
w.println("Yes");
w.println(ans.size());
for (Integer o : ans) {
w.print (o + " ");
}
}
w.flush();
w.close();
br.close();
}
public static void dfs(int x){
vis[x] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < g[x].size(); i++) {
Node cur = g[x].get(i);
int id = cur.id;
int y = cur.to;
if (res == K) return;
if (vis[y] == 1) continue;
dfs(y);
if(lamp[y] == 0 && res < K){
res -= lamp[x] + lamp[y];
lamp[x] ^= 1;
lamp[y] ^= 1;
res += lamp[x] + lamp[y];
ans.add(id);
}
}
}
public static class Node{
int to;
int id;
public Node(int to, int id){
this.to = to;
this.id = id;
}
}
static PrintWriter w = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static Input f = new Input(System.in);
static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static class Input {
public BufferedReader reader;
public StringTokenizer tokenizer;
public Input(InputStream stream) {
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(stream), 32768);
tokenizer = null;
}
public String next() {
while (tokenizer == null || !tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
try {
tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(reader.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
return tokenizer.nextToken();
}
public String nextLine() {
String str = null;
try {
str = reader.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO 自动生成的 catch 块
e.printStackTrace();
}
return str;
}
public int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public Double nextDouble() {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
public BigInteger nextBigInteger() {
return new BigInteger(next());
}
}
}





![每日一题 --- 设计链表[力扣][Go]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/154cf7f5cca64873aefff3651e6b492e.png)