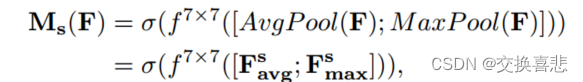Yarn
Yarn 是用来做分布式系统中的资源协调技术
MapReduce 1.x
对于 MapReduce 1.x 的版本上:
由 Client 发起计算请求,Job Tracker 接收请求之后分发给各个TaskTrack进行执行
在这个阶段,资源的管理与请求的计算是集成在 mapreduce 上的,这种架构会导致 mapreduce 的功能过于臃肿,也会衍生出一系列的问题。
而 YARN 的出现及时的对这个问题作出了改变,YARN 就类似于一个操作系统,mapreduce 就类似于运行在 YARN 这个操作系统上的实际程序
YARN 同时也支持 Spark、Flink、Taz 等分布式计算技术,这使得 YARN 进一步被发扬光大
YARN 基础
Yarn 的基础原理就是将资源管理 与 作业调度(监视)功能进行拆分,由 ResourceManager 进行资源管理,由 ApplicationMaster 进行作业调度与监视功能
ResourceManager
NodeManager
NodeManager
…
Client 将作业提交给 ResourceManager 进行资源调度
YARN 基础配置
ResourceManager 会将任务分配给一个个的 NodeManager 每个NodeManager 中都有一个个的Contaniner,这一个个的 Container中就保存着一个个的任务的计算,同时,NodeManager 中也保存着一个个任务的 Application Master、每一个 Container 的计算完成后会汇报给 Application Master 其结束的信息,Application Master 会及时向 Resource Manager 汇报其情况信息。
修改 mapred-site.xml:
在最后添加;
<configuration>
<!-- 指定Mapreduce 的作业执行时,用yarn进行资源调度 -->
<property>
<name>mapreduce.framework.name</name>
<value>yarn</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.app.mapreduce.am.env</name>
<value>HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=/export/server/hadoop-3.3.6</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.map.env</name>
<value>HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=/export/server/hadoop-3.3.6</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.reduce.env</name>
<value>HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=/export/server/hadoop-3.3.6</value>
</property>
</configuration>
修改 yarn-site.xml
<configuration>
<!-- Site specific YARN configuration properties -->
<!-- 设置ResourceManager -->
<property>
<name>yarn.resourcemanager.hostname</name>
<value>node1</value>
</property>
<!--配置yarn的shuffle服务-->
<property>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services</name>
<value>mapreduce_shuffle</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services.mapreduce_shuffle.class</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.mapred.ShuffleHandler</value>
</property>
</configuration>
在 hadoop-env.sh 中添加:
export HDFS_NAMENODE_USER=root
export HDFS_DATANODE_USER=root
export HDFS_SECONDARYNAMENODE_USER=root
export YARN_RESOURCEMANAGER_USER=root
export YARN_NODEMANAGER_USER=root
之后将修改好的这几个文件分发给其他节点
scp mapred-site.xml yarn-site.xml hadoop-env.sh node2:$PWD
scp mapred-site.xml yarn-site.xml hadoop-env.sh node3:$PWD
之后就可以打开 yarn.sh:
start-yarn.sh
之后在对应的 8088 端口就可以找到对应的可视化网页信息了
进行词频统计(wordcount)的测试:
hadoop jar /export/server/hadoop-3.3.6/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-3.3.6.jar wordcount /input /output1
就可以顺利调用对应的东西了。
另外,如果我们希望查看日志信息,还需要再 mapred-site.xml 中继续进行配置:
<property>
<name>MapReduce.jobhistory.address</name>
<value>node1:10020</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>MapReduce.jobhistory.webapp.address</name>
<value>node1:19888</value>
</property>
继续在 yarn.xml 中配置:
<!-- 添加如下配置 -->
<!-- 是否需要开启⽇志聚合 -->
<!-- 开启⽇志聚合后,将会将各个Container的⽇志保存在yarn.nodemanager.remote-app-logdir的位置 -->
<!-- 默认保存在/tmp/logs -->
<property>
<name>yarn.log-aggregation-enable</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
<!-- 历史⽇志在HDFS保存的时间,单位是秒 -->
<!-- 默认的是-1,表示永久保存 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.log-aggregation.retain-seconds</name>
<value>604800</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.log.server.url</name>
<value>http://node1:19888/jobhistory/logs</value>
</property>
YARN 的任务提交流程

-
MapReduce 程序运行 Job 任务,创建出一个 JobCommiter,再由 JobCommiter 进行任务提交等工作。
-
JobCommiter 会将自己要执行的任务提交给 ResourceManager,申请一个应用ID
-
若资源足够,ResourceManager 会分配给 MapReduce 一个应用ID,这个时候,Mapreduce 会将自己的程序上传到 HDFS,再由需要程序的节点下载对应的程序来进行运算
-
JobCommitter 正式向 ResourceManager 提交作业任务,
-
ResourceManager 会找到一个负载较小的 NodeManager,指定其完成这个任务
-
这个被指定的 NodeManager 会创建一个 Container,并创建一个 AppMaster 用来监控这个任务并调度资源(这个 AppMaster 会从 HDFS 上接收对应的信息(分片信息、任务程序)对应每一个分片都对应一个 MapTask)
-
在明确了需要的空间之后,这个 AppMaster 会向 ResourceManager 申请资源,ResourceManager 会根据 NodeManager 上的负载情况为其分配对应的 NodeManager
-
对应的 Node Manager 会向 HDFS 上下载对应的程序,进行真正的任务计算,并在执行的时候向 APPMaster 进行汇报,例如在成功的时候向 appMaster 进行报告。
YARN 的命令
查看当前在 yarn 中运行的任务:
yarn top
测试一下执行:
hadoop jar /export/server/hadoop-3.3.6/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-3.3.6.jar pi 10 10
使用 yarn application 可以查看运行的任务信息
yarn application -list -appStates ALL # 查看所有任务信息
yarn application -list -appStates FINISHED / RUNNING # 查看所有已完成的 / 正在运行的
我们也可以根据查看出来的 APPID 直接杀死进程:
yarn application -kill xxxxxxxxxxx
被杀死的任务会被标记为 KILLED,我们可以使用 yarn application -list -appStates KILLED 来进行查看
YARN 调度器
先进先出调度器
如题,先来的先处理,存在饥饿问题哪怕你只需要一毫秒的运行也需要一直等
容量调度器
会开辟两个空间,其中 80% 的资源会用来像 FIFO 一样进行处理,另有 20% 等待处理其他问题,这样就在一定程度上规避了小型任务饥饿问题,但其存在资源浪费问题,因为可能有 20% 的资源始终没有使用
公平调度器
公平调度器会为每个任务分配相同的资源,当有任务执行结束时,其会将其所占有的资源分配给其他任务
YARN 的队列
YARN 默认使用的是 只有一个队列的容量调度器,其实也就是 FIFO,但这里我们可以进行配置,一般情况下,会创建两个队列,一个用来处理主任务,另一个用来处理小任务
这里需要修改配置文件:
修改 etc/hadoop 中的 capacity-scheduler.xml:
<!--
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License. See accompanying LICENSE file.
-->
<configuration>
<!-- yarn 允许的提交任务的最大数量 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.maximum-applications</name>
<value>10000</value>
<description>
Maximum number of applications that can be pending and running.
</description>
</property>
<!-- Application Master 允许占集群的资源比例,0.1 代表 10% -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.maximum-am-resource-percent</name>
<value>0.1</value>
<description>
Maximum percent of resources in the cluster which can be used to run
application masters i.e. controls number of concurrent running
applications.
</description>
</property>
<!-- 队列类型 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.resource-calculator</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.yarn.util.resource.DefaultResourceCalculator</value>
<description>
The ResourceCalculator implementation to be used to compare
Resources in the scheduler.
The default i.e. DefaultResourceCalculator only uses Memory while
DominantResourceCalculator uses dominant-resource to compare
multi-dimensional resources such as Memory, CPU etc.
</description>
</property>
<!-- 默认只有一个 default 队列,这里再添加一个 small 队列来处理小任务 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.queues</name>
<value>default,small</value>
<description>
The queues at the this level (root is the root queue).
</description>
</property>
<!-- 这里是每个队列占用的资源百分比 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.capacity</name>
<value>70</value>
<description>Default queue target capacity.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.small.capacity</name>
<value>30</value>
<description>Default queue target capacity.</description>
</property>
<!-- 用户可以占用的资源的比例 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.user-limit-factor</name>
<value>1</value>
<description>
Default queue user limit a percentage from 0.0 to 1.0.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.small.user-limit-factor</name>
<value>1</value>
<description>
Default queue user limit a percentage from 0.0 to 1.0.
</description>
</property>
<!-- 每个队列最多占用整体资源的比例 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.maximum-capacity</name>
<value>100</value>
<description>
The maximum capacity of the default queue.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.small.maximum-capacity</name>
<value>100</value>
<description>
The maximum capacity of the default queue.
</description>
</property>
<!-- 队列的状态 RUNNING 表示该队列是启用的状态 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.state</name>
<value>RUNNING</value>
<description>
The state of the default queue. State can be one of RUNNING or STOPPED.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.small.state</name>
<value>RUNNING</value>
<description>
The state of the default queue. State can be one of RUNNING or STOPPED.
</description>
</property>
<!-- 权限管理 允许哪些用户向队列中提交任务 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.acl_submit_applications</name>
<value>*</value>
<description>
The ACL of who can submit jobs to the default queue.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.small.acl_submit_applications</name>
<value>*</value>
<description>
The ACL of who can submit jobs to the default queue.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.acl_administer_queue</name>
<value>*</value>
<description>
The ACL of who can administer jobs on the default queue.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.small.acl_administer_queue</name>
<value>*</value>
<description>
The ACL of who can administer jobs on the default queue.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.acl_application_max_priority</name>
<value>*</value>
<description>
The ACL of who can submit applications with configured priority.
For e.g, [user={name} group={name} max_priority={priority} default_priority={priority}]
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.small.acl_application_max_priority</name>
<value>*</value>
<description>
The ACL of who can submit applications with configured priority.
For e.g, [user={name} group={name} max_priority={priority} default_priority={priority}]
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.maximum-application-lifetime
</name>
<value>-1</value>
<description>
Maximum lifetime of an application which is submitted to a queue
in seconds. Any value less than or equal to zero will be considered as
disabled.
This will be a hard time limit for all applications in this
queue. If positive value is configured then any application submitted
to this queue will be killed after exceeds the configured lifetime.
User can also specify lifetime per application basis in
application submission context. But user lifetime will be
overridden if it exceeds queue maximum lifetime. It is point-in-time
configuration.
Note : Configuring too low value will result in killing application
sooner. This feature is applicable only for leaf queue.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.small.maximum-application-lifetime
</name>
<value>-1</value>
<description>
Maximum lifetime of an application which is submitted to a queue
in seconds. Any value less than or equal to zero will be considered as
disabled.
This will be a hard time limit for all applications in this
queue. If positive value is configured then any application submitted
to this queue will be killed after exceeds the configured lifetime.
User can also specify lifetime per application basis in
application submission context. But user lifetime will be
overridden if it exceeds queue maximum lifetime. It is point-in-time
configuration.
Note : Configuring too low value will result in killing application
sooner. This feature is applicable only for leaf queue.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.default-application-lifetime
</name>
<value>-1</value>
<description>
Default lifetime of an application which is submitted to a queue
in seconds. Any value less than or equal to zero will be considered as
disabled.
If the user has not submitted application with lifetime value then this
value will be taken. It is point-in-time configuration.
Note : Default lifetime can't exceed maximum lifetime. This feature is
applicable only for leaf queue.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.small.default-application-lifetime
</name>
<value>-1</value>
<description>
Default lifetime of an application which is submitted to a queue
in seconds. Any value less than or equal to zero will be considered as
disabled.
If the user has not submitted application with lifetime value then this
value will be taken. It is point-in-time configuration.
Note : Default lifetime can't exceed maximum lifetime. This feature is
applicable only for leaf queue.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.node-locality-delay</name>
<value>40</value>
<description>
Number of missed scheduling opportunities after which the CapacityScheduler
attempts to schedule rack-local containers.
When setting this parameter, the size of the cluster should be taken into account.
We use 40 as the default value, which is approximately the number of nodes in one rack.
Note, if this value is -1, the locality constraint in the container request
will be ignored, which disables the delay scheduling.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.rack-locality-additional-delay</name>
<value>-1</value>
<description>
Number of additional missed scheduling opportunities over the node-locality-delay
ones, after which the CapacityScheduler attempts to schedule off-switch containers,
instead of rack-local ones.
Example: with node-locality-delay=40 and rack-locality-delay=20, the scheduler will
attempt rack-local assignments after 40 missed opportunities, and off-switch assignments
after 40+20=60 missed opportunities.
When setting this parameter, the size of the cluster should be taken into account.
We use -1 as the default value, which disables this feature. In this case, the number
of missed opportunities for assigning off-switch containers is calculated based on
the number of containers and unique locations specified in the resource request,
as well as the size of the cluster.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.queue-mappings</name>
<value></value>
<description>
A list of mappings that will be used to assign jobs to queues
The syntax for this list is [u|g]:[name]:[queue_name][,next mapping]*
Typically this list will be used to map users to queues,
for example, u:%user:%user maps all users to queues with the same name
as the user.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.queue-mappings-override.enable</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
If a queue mapping is present, will it override the value specified
by the user? This can be used by administrators to place jobs in queues
that are different than the one specified by the user.
The default is false.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.per-node-heartbeat.maximum-offswitch-assignments</name>
<value>1</value>
<description>
Controls the number of OFF_SWITCH assignments allowed
during a node's heartbeat. Increasing this value can improve
scheduling rate for OFF_SWITCH containers. Lower values reduce
"clumping" of applications on particular nodes. The default is 1.
Legal values are 1-MAX_INT. This config is refreshable.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.application.fail-fast</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether RM should fail during recovery if previous applications'
queue is no longer valid.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.workflow-priority-mappings</name>
<value></value>
<description>
A list of mappings that will be used to override application priority.
The syntax for this list is
[workflowId]:[full_queue_name]:[priority][,next mapping]*
where an application submitted (or mapped to) queue "full_queue_name"
and workflowId "workflowId" (as specified in application submission
context) will be given priority "priority".
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.workflow-priority-mappings-override.enable</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
If a priority mapping is present, will it override the value specified
by the user? This can be used by administrators to give applications a
priority that is different than the one specified by the user.
The default is false.
</description>
</property>
</configuration>
若我们在提交任务时不指定队列,默认会被提交到 default 队列里,另外我们也可以指定我们将队列提交到哪里:
# 默认:
hadoop jar /export/server/hadoop-3.3.6/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-3.3.6.jar pi 10 10
# 指定队列:
hadoop jar /export/server/hadoop-3.3.6/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-3.3.6.jar wordcount -Dmapreduce.job.queuename=small /input /output3
另外,如果我们希望修改默认提交到的队列,需要在 mapred-site.xml 文件中添加如下配置:
<property>
<name>mapreduce.job.queuename</name>
<value>small</value>
</property>

![练习 12 Web [极客大挑战 2019]BabySQL](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/5113a2a048944a268af0e16ae3460cdb.png)