排序链表
给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
示例 1:
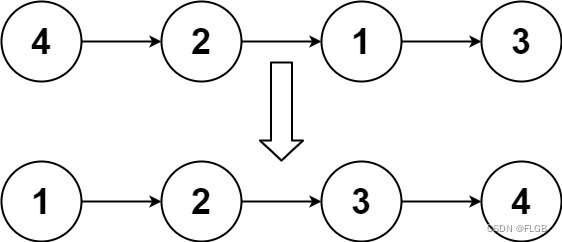
输入:head = [4,2,1,3]
输出:[1,2,3,4]
解题思路
对链表进行升序排序,可以使用归并排序(Merge Sort)的思想。具体步骤如下:
- 分割: 使用快慢指针找到链表的中点,将链表分为两部分。
- 递归: 递归地对两部分链表进行排序。
- 合并: 合并两个有序链表,得到最终的有序链表。合并两个有序链表
Java实现
public class SortLinkedList {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
// 1、递归结束条件
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// 2、找到链表中间节点并断开链表 & 递归下探
ListNode midNode = middleNode(head);
ListNode rightHead = midNode.next;
midNode.next = null;
ListNode left = sortList(head);
ListNode right = sortList(rightHead);
// 3、当前层业务操作(合并有序链表)
return mergeTwoLists(left, right);
}
// 找到链表中间节点(876. 链表的中间结点)
private ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
public static ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) {
return l2;
}
if (l2 == null) {
return l1;
}
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 构造链表 4 -> 2 -> 1 -> 3
ListNode head = new ListNode(4);
head.next = new ListNode(2);
head.next.next = new ListNode(1);
head.next.next.next = new ListNode(3);
// 调用 sortList 方法对链表进行排序
SortLinkedList solution = new SortLinkedList();
ListNode result = solution.sortList(head);
// 打印排序后的链表
while (result != null) {
System.out.print(result.val + " ");
result = result.next;
}
// 输出:1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4
}
}
时间空间复杂度
- 时间复杂度:O(nlogn),其中 n 是链表的长度,每一层归并的时间复杂度为 O(n),总共有 O(logn) 层。
- 空间复杂度:O(logn),递归调用栈的深度为 O(logn)