什么是slab分配器?
用户态程序可以使用malloc及其在C标准库中的相关函数申请内存;内核也需要经常分配内存,但无法使用标准库函数;linux内核中,伙伴分配器是一种页分配器,是以页为单位的,但这个单位太大了;如果要分配小块,就需要一个块分配器;slab是内核中一种基本的块分配器;
slab分配器在某些情况下表现不太好,Linux内核提供了两个备用的块分配器。
1)在配备了大量物理内存的大型计算机上,slab分配器的管理数据结构的内存开销比较大,所以设计了slub分配器;
2)在小内存的嵌入式设备上,使用比slab分配器代码更少、更简单的slob分配器。
slab是内核默认的块分配器;本文对slab进行介绍;
slab分配器的作用及原理
slab分配器的主要作用是分配小块内存,并且使用缓存的思想提高系统性能;
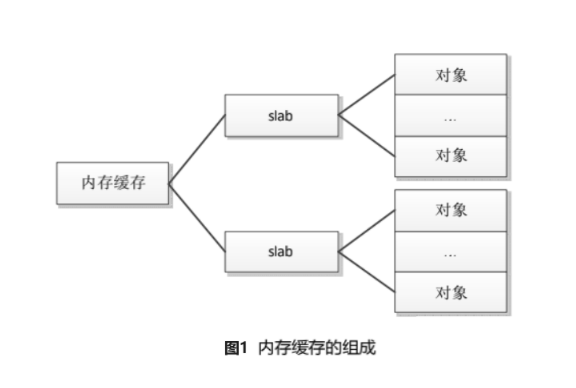
slab分配器的核心思想是:为每种对象类型创建一个内存缓存,每个内存缓存由多个大块(slab)组成,一个slab是一个或多个连续的物理页(物理页是从伙伴分配器申请的),每个slab包含多个对象。slab 采用了面向对象的思想,基于对象类型管理内存,每种对象被划分为一类,例如进程描述符(task_struct)是一个类,每个进程描述符实例是一个对象。
通过伙伴分配器和slab分配器分配的内存在物理内存中是连续的;
内存缓存组成如下:
一般内核代码、伙伴分配器、块分配器及物理页帧的关联如下:
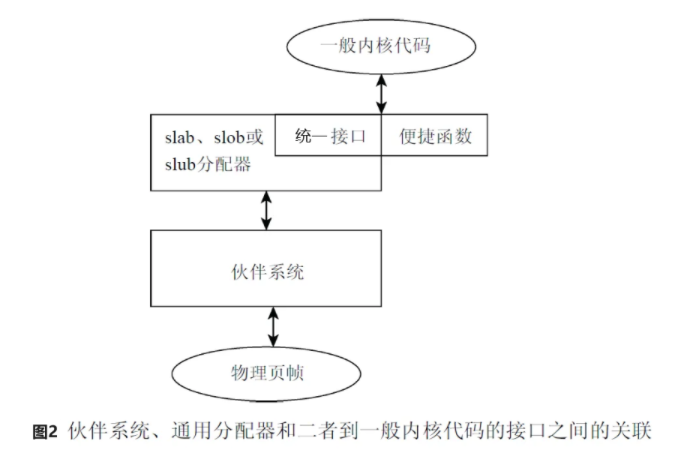
上图中,统一接口即slab、slob、slub分配器提供出来的统一接口,kmalloc、kfree等;
编程接口
slab,slob,slub块分配器提供了统一的编程接口;slab中内存缓存分为两种:通用内存缓存和专用内存缓存;
通用内存缓存编程接口为kmalloc、kfree、krealloc等;
专用内存缓存编程接口为kmem_cache_create、kmem_cache_alloc、kmem_cache_free、kmem_cache_destroy等;
cat /proc/slabinfo可以查看slab信息;第一列为内存缓存名称;
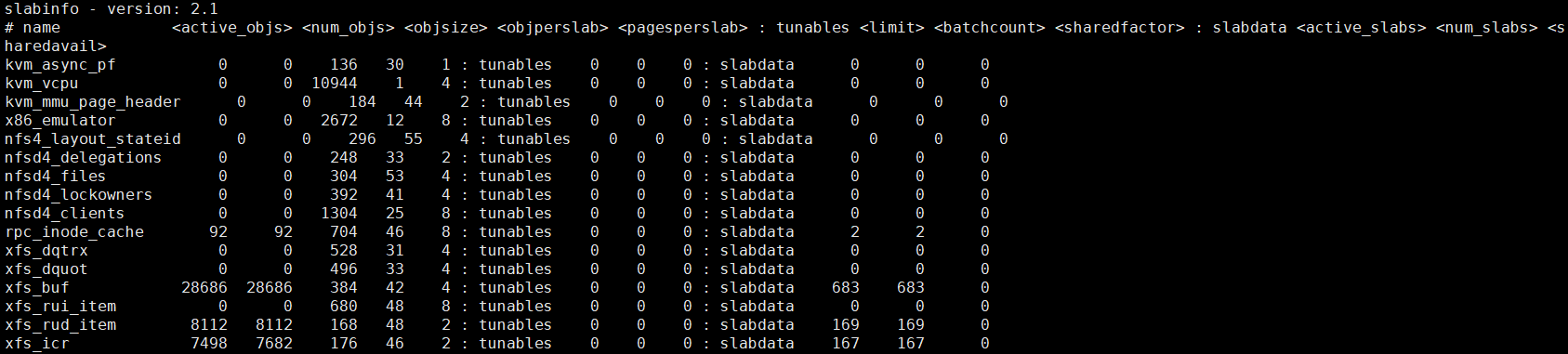
通用内存缓存接口
从普通区域分配页的通用内存缓存的名称是“kmalloc-”(size 是对象的长度),从 DMA 区域分配页的通用内存缓存的名称是“dma-kmalloc-”;通用内存缓存对象的长度是 2^n字节;
通过通用内存缓存申请内存,块分配器需要找到一个对象的长度刚好大于或等于请求的内存长度的通用内存缓存;
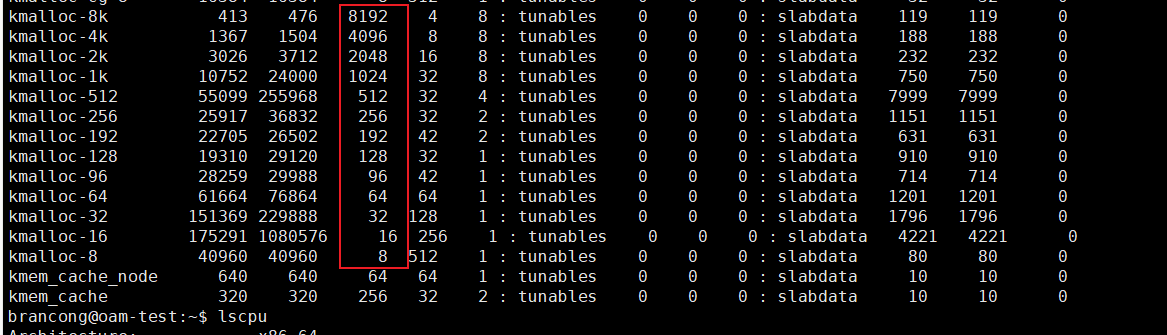
每列含义如下:

kmalloc
分配内存
/**
* kmalloc - allocate memory
* @size: how many bytes of memory are required.
* @flags: the type of memory to allocate.
*
* kmalloc is the normal method of allocating memory
* for objects smaller than page size in the kernel.
*/
void *kmalloc(size_t size, gfp_t flags);
size,申请的内存字节数;
flags,页分配器的分配标志位;当内存缓存没有空闲对象,向页分配器请求分配页的时候使用这个标志位;
块分配器找到一个合适的通用内存缓存:对象的长度刚好大于或等于请求的内存长度,然后从这个内存缓存分配对象;如果分配成功,返回对象的地址,否则返回空指针;
krealloc
重新分配内存
/**
* krealloc - reallocate memory. The contents will remain unchanged.
* @p: object to reallocate memory for.
* @new_size: how many bytes of memory are required.
* @flags: the type of memory to allocate.
*
* The contents of the object pointed to are preserved up to the
* lesser of the new and old sizes. If @p is %NULL, krealloc()
* behaves exactly like kmalloc(). If @new_size is 0 and @p is not a
* %NULL pointer, the object pointed to is freed.
*/
void *krealloc(const void *p, size_t new_size, gfp_t flags);
p,需要重新分配内存的对象的指针;
new_size,新的长度;
flags,页分配器的分配标志位;
kfree
释放内存
/**
* kfree - free previously allocated memory
* @objp: pointer returned by kmalloc.
*
* If @objp is NULL, no operation is performed.
*
* Don't free memory not originally allocated by kmalloc()
* or you will run into trouble.
*/
void kfree(const void *objp);
objp,kmalloc返回的对象的地址;
kfree函数怎么知道objp是属于哪个内存缓存(kmem_cahce)的?后面解答这个问题;
专用内存缓存

使用通用的内存缓存的缺点是:块分配器需要找到一个对象的长度刚好大于或等于请求的内存长度的通用内存缓存,如果请求的内存长度和内存缓存的对象长度相差很远,浪费比较大,例如申请 36 字节,实际分配的内存长度是 64 字节,浪费了 28 字节。所以有时候使用者需要创建专用的内存缓存,编程接口如下。
kmem_cache_create
创建内存缓存
/*
* kmem_cache_create - Create a cache.
* @name: A string which is used in /proc/slabinfo to identify this cache.
* @size: The size of objects to be created in this cache.
* @align: The required alignment for the objects.
* @flags: SLAB flags
* @ctor: A constructor for the objects.
*
* Returns a ptr to the cache on success, NULL on failure.
* Cannot be called within a interrupt, but can be interrupted.
* The @ctor is run when new pages are allocated by the cache.
*
* The flags are
*
* %SLAB_POISON - Poison the slab with a known test pattern (a5a5a5a5)
* to catch references to uninitialised memory.
*
* %SLAB_RED_ZONE - Insert `Red' zones around the allocated memory to check
* for buffer overruns.
*
* %SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN - Align the objects in this cache to a hardware
* cacheline. This can be beneficial if you're counting cycles as closely
* as davem.
*/
struct kmem_cache *
kmem_cache_create(const char *name, size_t size, size_t align,
unsigned long flags, void (*ctor)(void *))
kmem_cache_alloc
/**
* kmem_cache_alloc - Allocate an object
* @cachep: The cache to allocate from.
* @flags: See kmalloc().
*
* Allocate an object from this cache. The flags are only relevant
* if the cache has no available objects.
*/
void *kmem_cache_alloc(struct kmem_cache *cachep, gfp_t flags);
kmem_cache_free
/**
* kmem_cache_free - Deallocate an object
* @cachep: The cache the allocation was from.
* @objp: The previously allocated object.
*
* Free an object which was previously allocated from this
* cache.
*/
void kmem_cache_free(struct kmem_cache *cachep, void *objp);
kmem_cache_destroy
void kmem_cache_destroy(struct kmem_cache *s);
kmem_cache初始化
start_kernel()–>mm_init–>kmem_cache_init();
第一个 kmem_cache 结构体实例是定义的全局变量kmem_cache_boot(mm/slab.c)。
kmem_cache_init()函数在初始化过程中调用create_boot_cache()对 kmem_cache_boot进行了进一步初始化。第一个kmem_cache实例用于为创建其他kmem cache实例分配空间,其name是kmem_cache。
之后初始化通用内存缓存的kmem_cache实例;
/*
* kmalloc_info[] is to make slub_debug=,kmalloc-xx option work at boot time.
* kmalloc_index() supports up to 2^26=64MB, so the final entry of the table is
* kmalloc-67108864.
*/
const struct kmalloc_info_struct kmalloc_info[] __initconst = {
{NULL, 0}, {"kmalloc-96", 96},
{"kmalloc-192", 192}, {"kmalloc-8", 8},
{"kmalloc-16", 16}, {"kmalloc-32", 32},
{"kmalloc-64", 64}, {"kmalloc-128", 128},
{"kmalloc-256", 256}, {"kmalloc-512", 512},
{"kmalloc-1024", 1024}, {"kmalloc-2048", 2048},
{"kmalloc-4096", 4096}, {"kmalloc-8192", 8192},
{"kmalloc-16384", 16384}, {"kmalloc-32768", 32768},
{"kmalloc-65536", 65536}, {"kmalloc-131072", 131072},
{"kmalloc-262144", 262144}, {"kmalloc-524288", 524288},
{"kmalloc-1048576", 1048576}, {"kmalloc-2097152", 2097152},
{"kmalloc-4194304", 4194304}, {"kmalloc-8388608", 8388608},
{"kmalloc-16777216", 16777216}, {"kmalloc-33554432", 33554432},
{"kmalloc-67108864", 67108864}
};
/* internal cache of cache description objs */
static struct kmem_cache kmem_cache_boot = {
.batchcount = 1,
.limit = BOOT_CPUCACHE_ENTRIES,
.shared = 1,
.size = sizeof(struct kmem_cache),
.name = "kmem_cache",
};
/*
* Initialisation. Called after the page allocator have been initialised and
* before smp_init().
*/
void __init kmem_cache_init(void)
{
int i;
BUILD_BUG_ON(sizeof(((struct page *)NULL)->lru) <
sizeof(struct rcu_head));
kmem_cache = &kmem_cache_boot;
if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_NUMA) || num_possible_nodes() == 1)
use_alien_caches = 0;
for (i = 0; i < NUM_INIT_LISTS; i++)
kmem_cache_node_init(&init_kmem_cache_node[i]);
/*
* Fragmentation resistance on low memory - only use bigger
* page orders on machines with more than 32MB of memory if
* not overridden on the command line.
*/
if (!slab_max_order_set && totalram_pages > (32 << 20) >> PAGE_SHIFT)
slab_max_order = SLAB_MAX_ORDER_HI;
/* Bootstrap is tricky, because several objects are allocated
* from caches that do not exist yet:
* 1) initialize the kmem_cache cache: it contains the struct
* kmem_cache structures of all caches, except kmem_cache itself:
* kmem_cache is statically allocated.
* Initially an __init data area is used for the head array and the
* kmem_cache_node structures, it's replaced with a kmalloc allocated
* array at the end of the bootstrap.
* 2) Create the first kmalloc cache.
* The struct kmem_cache for the new cache is allocated normally.
* An __init data area is used for the head array.
* 3) Create the remaining kmalloc caches, with minimally sized
* head arrays.
* 4) Replace the __init data head arrays for kmem_cache and the first
* kmalloc cache with kmalloc allocated arrays.
* 5) Replace the __init data for kmem_cache_node for kmem_cache and
* the other cache's with kmalloc allocated memory.
* 6) Resize the head arrays of the kmalloc caches to their final sizes.
*/
/* 1) create the kmem_cache */
/*
* struct kmem_cache size depends on nr_node_ids & nr_cpu_ids
*/
create_boot_cache(kmem_cache, "kmem_cache",
offsetof(struct kmem_cache, node) +
nr_node_ids * sizeof(struct kmem_cache_node *),
SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN);
list_add(&kmem_cache->list, &slab_caches);
slab_state = PARTIAL;
/*
* Initialize the caches that provide memory for the kmem_cache_node
* structures first. Without this, further allocations will bug.
*/
kmalloc_caches[INDEX_NODE] = create_kmalloc_cache(
kmalloc_info[INDEX_NODE].name,
kmalloc_size(INDEX_NODE), ARCH_KMALLOC_FLAGS);
slab_state = PARTIAL_NODE;
setup_kmalloc_cache_index_table();
slab_early_init = 0;
/* 5) Replace the bootstrap kmem_cache_node */
{
int nid;
for_each_online_node(nid) {
init_list(kmem_cache, &init_kmem_cache_node[CACHE_CACHE + nid], nid);
init_list(kmalloc_caches[INDEX_NODE],
&init_kmem_cache_node[SIZE_NODE + nid], nid);
}
}
create_kmalloc_caches(ARCH_KMALLOC_FLAGS);
}
slab分配器数据结构
struct keme_cache
/*
* Definitions unique to the original Linux SLAB allocator.
*/
struct kmem_cache {
struct array_cache __percpu *cpu_cache;
/* 1) Cache tunables. Protected by slab_mutex */
unsigned int batchcount;
unsigned int limit;
unsigned int shared;
unsigned int size;
struct reciprocal_value reciprocal_buffer_size;
/* 2) touched by every alloc & free from the backend */
unsigned int flags; /* constant flags */
unsigned int num; /* # of objs per slab */
/* 3) cache_grow/shrink */
/* order of pgs per slab (2^n) */
unsigned int gfporder;
/* force GFP flags, e.g. GFP_DMA */
gfp_t allocflags;
size_t colour; /* cache colouring range */
unsigned int colour_off; /* colour offset */
struct kmem_cache *freelist_cache;
unsigned int freelist_size;
/* constructor func */
void (*ctor)(void *obj);
/* 4) cache creation/removal */
const char *name;
struct list_head list;
int refcount;
int object_size;
int align;
/* 5) statistics */
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_SLAB
unsigned long num_active;
unsigned long num_allocations;
unsigned long high_mark;
unsigned long grown;
unsigned long reaped;
unsigned long errors;
unsigned long max_freeable;
unsigned long node_allocs;
unsigned long node_frees;
unsigned long node_overflow;
atomic_t allochit;
atomic_t allocmiss;
atomic_t freehit;
atomic_t freemiss;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_SLAB_LEAK
atomic_t store_user_clean;
#endif
/*
* If debugging is enabled, then the allocator can add additional
* fields and/or padding to every object. size contains the total
* object size including these internal fields, the following two
* variables contain the offset to the user object and its size.
*/
int obj_offset;
#endif /* CONFIG_DEBUG_SLAB */
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMCG
struct memcg_cache_params memcg_params;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_KASAN
struct kasan_cache kasan_info;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SLAB_FREELIST_RANDOM
unsigned int *random_seq;
#endif
struct kmem_cache_node *node[MAX_NUMNODES];
};
一个slab分配器对应一个内存缓存,即一个kmem_cache实例;
kmem_cache数据结构如图3所示;
gfporder表示slab的阶数,即一个slab块包含2^gfporder个页;
num,表示每个slab中的对象数量;
cpu_cache,每个处理器对应一个数组缓存;对于释放的对象,并不是立即回收,而是放到当前CPU的数组缓存中;
node,每个numa节点对应一个kmem_cache_node实例,提升numa节点中CPU的访问性能;
kmem_cache中,其他成员都是管理数据,node和cpu_cache是真正存储对象的;
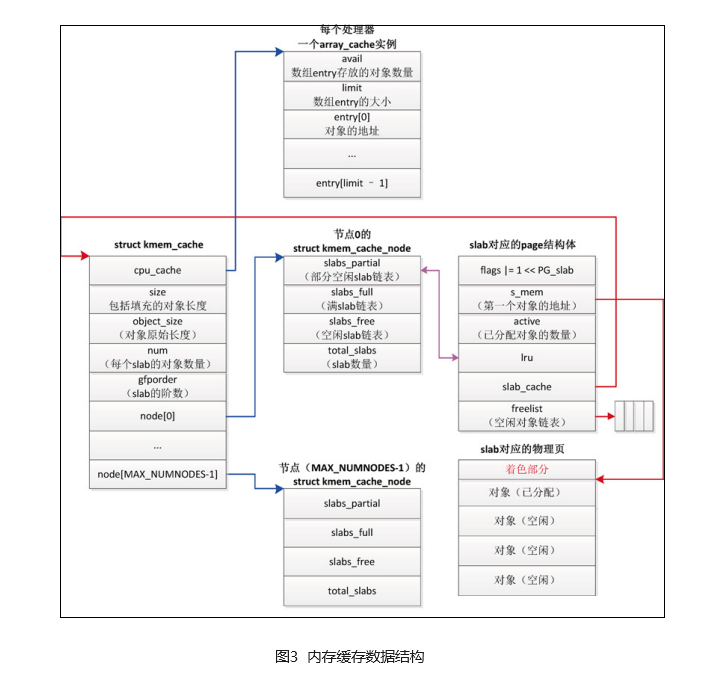
struct kmem_cache_node
在kmem_cache中,每个numa节点对应一个kmem_cache_node实例;
kmem_cache_node 实例包含 3 条 slab 链表:链表 slabs_partial 把部分对象空闲的 slab链接起来,链表 slabs_full 把没有空闲对象的 slab 链接起来,链表 slabs_free 把所有对象空闲的 slab 链接起来。成员 total_slabs 是 slab 数量。
/*
* The slab lists for all objects.
*/
struct kmem_cache_node {
spinlock_t list_lock;
#ifdef CONFIG_SLAB
struct list_head slabs_partial; /* partial list first, better asm code */
struct list_head slabs_full;
struct list_head slabs_free;
unsigned long total_slabs; /* length of all slab lists */
unsigned long free_slabs; /* length of free slab list only */
unsigned long free_objects;
unsigned int free_limit;
unsigned int colour_next; /* Per-node cache coloring */
struct array_cache *shared; /* shared per node */
struct alien_cache **alien; /* on other nodes */
unsigned long next_reap; /* updated without locking */
int free_touched; /* updated without locking */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SLUB
unsigned long nr_partial;
struct list_head partial;
#ifdef CONFIG_SLUB_DEBUG
atomic_long_t nr_slabs;
atomic_long_t total_objects;
struct list_head full;
#endif
#endif
};
struct page
每个 slab 由一个或多个连续的物理页组成,页的阶数是 kmem_cache.gfporder,如果阶数大于 0,组成一个复合页。
page 结构体的slab相关成员如下,struct page定义在include/linux/mm_types.h
1)flags 设置标志位 PG_slab,表示该page属于 SLAB 分配器。
2)s_mem,表示slab 第一个对象。
3)active,表示已分配对象的数量。
4)slab_cache,表示该slab所属kmem_cache 实例。
5)freelist,slab中的第一个空闲对象。
这里解答思考题:kfree 函数怎么知道对象属于哪个通用的内存缓存(kmem_cache)?分为 5 步。
- 根据对象的虚拟地址得到物理地址,因为块分配器使用的虚拟地址属于直接映射的内核虚拟地址空间,虚拟地址=物理地址+常量,把虚拟地址转换成物理地址很方便。
- 根据物理地址得到物理页号。
- 根据物理页号得到 page 实例。
- 如果是复合页,需要得到首页的 page 实例。
- 根据 page 实例的成员 slab_cache 得到 kmem_cache 实例。
struct array_cache
内存缓存(kmem_cache)为每个处理器创建了一个数组缓存(结构体 array_cache)。释放对象时,把对象存放到当前处理器对应的数组缓存中;分配对象的时候,先从当前处理器的数组缓存分配对象,采用后进先出(Last In First Out,LIFO)的原则,这种做法可以提高性能,避免从slab分配。
(1)刚释放的对象很可能还在处理器的缓存中,可以更好地利用处理器的缓存。
(2)减少链表操作,避免遍历slab中的链表;
(3)避免处理器之间的互斥,减少自旋锁操作。
每处理器数组缓存
/*
* struct array_cache
*
* Purpose:
* - LIFO ordering, to hand out cache-warm objects from _alloc
* - reduce the number of linked list operations
* - reduce spinlock operations
*
* The limit is stored in the per-cpu structure to reduce the data cache
* footprint.
*
*/
struct array_cache {
unsigned int avail;
unsigned int limit;
unsigned int batchcount;
unsigned int touched;
void *entry[]; /*
* Must have this definition in here for the proper
* alignment of array_cache. Also simplifies accessing
* the entries.
*/
};
(1)成员 entry 是存放对象地址的数组。
(2)成员 avail 是数组存放的对象的数量。
(3)成员 limit 是数组的大小,和结构体 kmem_cache 的成员 limit 的值相同,是根据对象长度猜测的一个值。
(4)成员 batchcount 是批量值,和结构体 kmem_cache 的成员 batchcount 的值相同,批量值是数组大小的一半。
分配对象的时候,先从当前处理器的数组缓存分配对象。如果数组缓存是空的,那么批量分配对象以重新填充数组缓存,批量值就是数组缓存的成员 batchcount;
释放对象的时候,如果数组缓存是满的,那么先把数组缓存中的对象批量归还给 slab,批量值就是数组缓存的成员 batchcount,然后把正在释放的对象存放到数组缓存中。
回收内存
对于所有对象空闲的 slab,没有立即释放,而是放在空闲 slab 链表中。只有内存节点上空闲对象的数量超过限制,才开始回收空闲 slab,直到空闲对象的数量小于或等于限制。
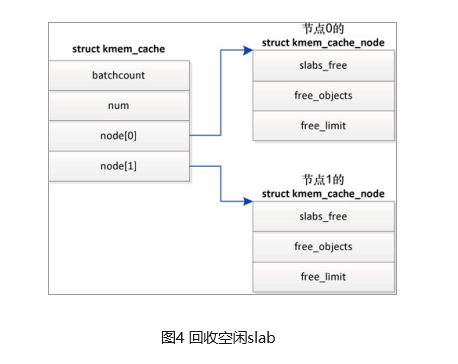
如图4所示,struct kmem_cache_node的成员slabs_free是空闲slab链表的头节点,成员 free_objects 是空闲对象的数量,成员free_limit是空闲对象的数量限制;
节点 n 的空闲对象的数量限制(free_limit) = (1 + 节点的处理器数量)* kmem_cache.batchcount +kmem_cache.num;
SLAB 分配器定期回收对象和空闲 slab,实现方法是在每个处理器上向全局工作队列添加 1 个延迟工作项,工作项的处理函数是 cache_reap。
/**
* cache_reap - Reclaim memory from caches.
* @w: work descriptor
*
* Called from workqueue/eventd every few seconds.
* Purpose:
* - clear the per-cpu caches for this CPU.
* - return freeable pages to the main free memory pool.
*
* If we cannot acquire the cache chain mutex then just give up - we'll try
* again on the next iteration.
*/
static void cache_reap(struct work_struct *w);
参考文献
- 《linux内核深度解析》,余华兵著
- 《professional linux kernel architecture》,Wolfgang Mauerer 著,郭旭 译