目录
实验要求:
实验过程:
一:首先设计实验
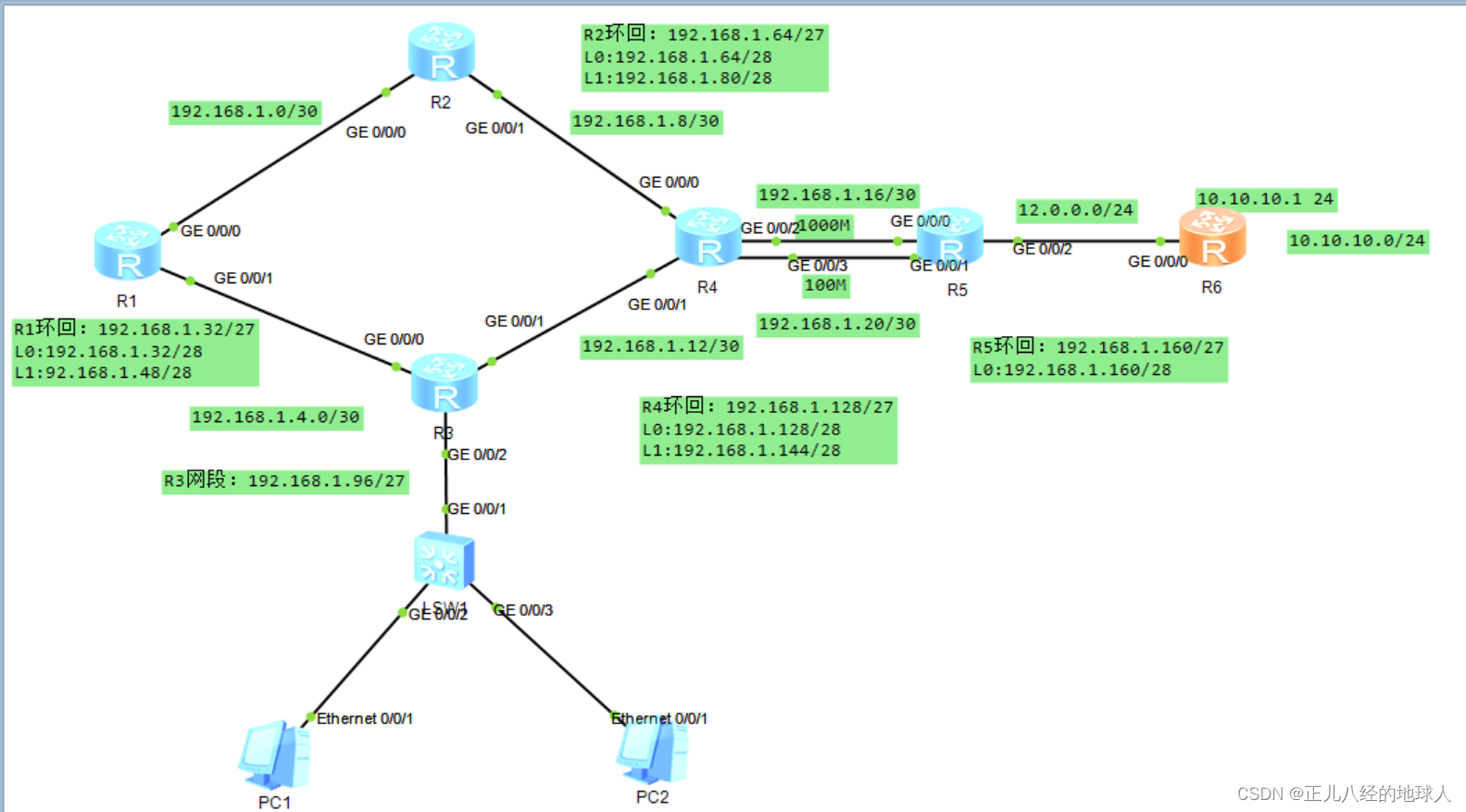
二:IP地址的划分(基于192.168.1.0/24)
在ensp中对路由器的相关命令进行配置:
三:配IP地址
(1)首先给所有设备配置环回IP(用户网段)地址:
(2)配置路由之间骨干链路的IP:
(3)给PC端配置IP地址(使用dhcp服务):
四:配置缺省路由(R6为公网处于该网络的边界位置)
(1)手动配置缺省
(2)添加路由(预防路由环路,便于部署管理路由)
五:避免环路(要求5、选路最佳,路由表尽量小,避免环路;)
六:实现NAT连接(要求6、R1-R5均可以访问R6的环回;)
七:Telnet远程连接,端口映射(要求:7、R6 telnet R5的公有地址时,实际登录到R1上;)
八:修改链路优先级(要求8、R4与R5正常通过1000M链路,故障时通过100m链路)
实验要求:
1、R6为ISP,接口IP地址均为公有地址,该设备只能配置IP地址,之后不能再对其进行任何配置;
2、R1-R5为局域网,私有IP地址192.168.1.0/24,请合理分配;
3、R1、R2、R4,各有两个环回IP地址;R5,R6各有一个环回地址;所有路由器上环回均代表连接用户的接口;
4、R3下面的两台PC通过DHCP自动获取IP地址;
5、选路最佳,路由表尽量小,避免环路;
6、R1-R5均可以访问R6的环回;
7、R6 telnet R5的公有地址时,实际登录到R1上;
8、R4与R5正常通过1000M链路,故障时通过100m链路;
实验过程:
一:首先设计实验
从图中和实验要求12中我们可以看出这个拓扑结构是一个从R5开始局域网(公网)和公网,在做实验的过程中我们要考虑一些拓扑结构的省略,比如我们配好IP地址过后可以将我们的R4到R5的100M的连线和R5与R6的连线先down了,减少我们实验的复杂性(尽可能的去简化我们的拓扑结构)。
二:IP地址的划分(基于192.168.1.0/24)
为了我们实验的便利性,在配置IP地址的时候我们要考虑以下几个方面:
- 要尽可能的节省IP地址;
- 要便于我们进行汇总减少我们的出错情况;
- 网段的划分要合理,如该实验中我们需要划分14个网段,但是实际划分的网段要比我们需要的网段要稍多一些(作为保留地址)避免故障发生。
路由器之间的网段划分:
192.168.1.000 00000 /27 ----- 总线链路(骨干链路)
192.168.1.000 000 00 /30 ---- 192.168.1.0/3
192.168.1.000 001 00 /30 --- 192.168.1.4/30
192.168.1.000 010 00 /30 ---- 192.168.1.8/30
192.168.1.000 011 00 /30 ---- 192.168.1.12/30
192.168.1.000 100 00 /30 ---- 192.168.1.16/30
192.168.1.000 101 00 /30 ---- 192.168.1.20/30
# 192.168.1.000 110 00 /30 ----192.168.1.25/30
# 192.168.1.000 111 00 /30 ----192.168.1.31/30 (多余的的2条网段备用)
R1-R5上环回地址的分配:
192.168.1.001 00000 /27 ---- R1 192.168.1.32/27 [R1环回(2)]
192.168.1.001 0 0000 /28 --- 192.168.1.32/28
192.168.1.001 1 0000 /28 --- 192.168.1.48/28
192.168.1.010 00000 /27 ---- R2 192.168.1.64/27 [R2环回(2)]
192.168.1.010 0 0000 /28 ---- 192.168.1.64/28
192.168.1.010 1 0000 /28 ---- 192.168.1.80/28
192.168.1.011 00000 /27 ---- R3 192.168.1.96/27 [R3,(下面PC由dhcp服务获取ip地址)]
192.168.1.100 00000 /27 ---- R4 192.168.1.128/27 [R4环回(2)]
192.168.1.100 0 0000 /28 ---- 192.168.1.128/28
192.168.1.100 1 0000 /28 ---- 192.168.1.144/28
192.168.1.101 00000 /27 ---- R5 192.168.1.160/27 [R5环回(1)]
192.168.1.101 0 0000 ---- 192.168.1.160/28
192.168.1.110 00000 /27
192.168.1.111 00000 /27(多余的2条IP地址,为预留备用)
R5 与R6上的链路网段:12.0.0.0/24
R6的环回地址为10.10.10.0/24
所有的网段和IP地址分配如下图:
在ensp中对路由器的相关命令进行配置:
三:配IP地址
(1)首先给所有设备配置环回IP(用户网段)地址:
R1:
<Huawei>sys
<Huawei>system-view
[Huawei]sysname R1
[R1]
[R1]interface LoopBack 0
[R1-LoopBack0]
[R1-LoopBack0]ip address 192.168.1.33 28{32为网络号,可用ip要加1}
[R1-LoopBack0]q
[R1]interface LoopBack 1
[R1-LoopBack1]ip address 192.168.1.49 28
[R1-LoopBack1]q
[R1]R2:
<Huawei>sys
[Huawei]sysname R2
[R2]
[R2]interface LoopBack 0
[R2-LoopBack0]ip add 192.168.1.65 28
[R2-LoopBack0]q
[R2]interface LoopBack 1
[R2-LoopBack1]ip add 192.168.1.81 28
[R2-LoopBack1]q
[R2]R3:
<Huawei>sys
[Huawei]sysname R3
[R3]
[R3]un info en
Info: Information center is disabled.
[R3]int g0/0/2
[R3-GigabitEthernet0/0/2]ip add 192.168.1.97 27
[R3-GigabitEthernet0/0/2]q
[R3]R4:
<Huawei>sys
[Huawei]sysname
[Huawei]sysname R4
[R4]interface LoopBack 0
[R4-LoopBack0]ip add 192.168.1.129 28
[R4-LoopBack0]q
[R4]interface LoopBack 1
[R4-LoopBack1]ip add 192.168.1.145 28
[R4-LoopBack1]q
[R4]R5:
<Huawei>sys
[Huawei]sysname R5
[R5]interface LoopBack 0
[R5-LoopBack0]ip add 192.168.1.161 27
[R5-LoopBack0]q
[R5]R6:
<Huawei>sys
[Huawei]sysname R6
[R6]interface LoopBack 0
[R6-LoopBack0]ip add 10.10.10.1 24
[R6-LoopBack0]q
[R6](2)配置路由之间骨干链路的IP:
R1:
<R1>sys
[R1]interface g0/0/0
[R1-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 192.168.1.1 30
[R1-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]q
[R1]int g0/0/1
[R1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]ip add 192.168.1.5 30
[R1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]q
[R1]R2:
<R2>sys
[R2]int g0/0/1
[R2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]ip add 192.168.1.9 30
[R2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]q
[R2]int g0/0/0
[R2-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 192.168.1.2 30
[R2-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]q
[R2]R3:
<R3>sys
[R3]int g0/0/0
[R3-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 192.168.1.6 30
[R3-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]q
[R3]int g0/0/1
[R3-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]ip add 192.168.1.13 30
[R3-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]q
[R3]R4:
<R4>sys
[R4]int g0/0/0
[R4-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 192.168.1.10 30
[R4-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]q
[R4]int g0/0/1
[R4-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]ip add 192.168.1.14 30
[R4-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]q
[R4]int g0/0/2
[R4-GigabitEthernet0/0/2]ip add 192.168.1.17 30
[R4-GigabitEthernet0/0/2]q
[R4]int g0/0/3
[R4-GigabitEthernet0/0/3]ip add 192.168.1.21 30
[R4-GigabitEthernet0/0/3]q
[R4]R5:
<R5>
<R5>sys
[R5]int g0/0/0
[R5-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 192.168.1.18 30
[R5-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]q
[R5]int g0/0/1
[R5-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]ip add 192.168.1.22 30
[R5-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]q
[R5]int g0/0/2
[R5-GigabitEthernet0/0/2]ip add 12.0.0.1 24
[R5-GigabitEthernet0/0/2]q
[R5]R6:
<R6>sys
[R6]int g0/0/0
[R6-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 12.0.0.2 24
[R6-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]q
[R6](3)给PC端配置IP地址(使用dhcp服务):
<R3>sys
[R3]dhcp ena
[R3]dhcp enable
[R3]ip pool a
[R3-ip-pool-a]network 192.168.1.96 mask 27
[R3-ip-pool-a]gateway-list 192.168.1.97
[R3-ip-pool-a]dns-list 114.114.114.114 8.8.8.8
[R3-ip-pool-a]q
[R3]int g0/0/2
[R3-GigabitEthernet0/0/2]dhcp select global然后在实验拓扑图中对PC1与PC2启动dhcp服务,再在命令行中ipconfig查看动态分配的ip地址


PC1:192.168.1.126
PC2:192.168.1.125
PS:配置好这些后要检查一下ip有没有配错的,网段之间是否能够ping通,以防马虎而导致影响了后面的实验进程,再一个就是后面实验过程中出错了排错就很是麻烦。
举例:
检查下R1所有网段用户的ip是否正确:
[R1]display ip interface brief
(这里只保留需要检查的信息)
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 192.168.1.1/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 192.168.1.5/30 up up
LoopBack0 192.168.1.33/28 up up(s)
LoopBack1 192.168.1.49/28 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
[R1]
Ping测试:
R1对R2:
[R1]ping 192.168.1.2
PING 192.168.1.2: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
0.00% packet loss
R1对R3:
[R1]ping 192.168.1.6
PING 192.168.1.6: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
0.00% packet loss
R4对R2:
[R4]ping 192.168.1.9
PING 192.168.1.9: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
0.00% packet loss
R4对R3:
[R4]ping 192.168.1.13
PING 192.168.1.13: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
0.00% packet loss
R4对R5:
[R4]ping 192.168.1.18
PING 192.168.1.18: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
0.00% packet loss
[R4]ping 192.168.1.22
PING 192.168.1.22: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
0.00% packet loss
R5对R6:
[R5]ping 12.0.0.2
PING 12.0.0.2: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
0.00% packet loss所以由以上的测试我们可以得知各路由网段之间是互通的
四:配置缺省路由(R6为公网处于该网络的边界位置)
(1)手动配置缺省
R1:
[R1]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 192.168.1.2
[R1]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 192.168.1.6
R2:
[R2]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 192.168.1.10
R3:
[R3]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 192.168.1.14
R4:
[R4]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 192.168.1.18
R5:
[R5]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 12.0.0.2(2)添加路由(预防路由环路,便于部署管理路由)
R1:
[R1]ip route-static 192.168.1.64 27 192.168.1.2
[R1]ip route-static 192.168.1.8 30 192.168.1.2
[R1]ip route-static 192.168.1.96 27 192.168.1.6
[R1]ip route-static 192.168.1.12 30 192.168.1.6
R2:
[R2]ip route-static 192.168.1.32 27 192.168.1.1
[R2]ip route-static 192.168.1.4 30 192.168.1.1
[R2]ip route-static 192.168.1.96 27 192.168.1.1
[R2]ip route-static 192.168.1.96 27 192.168.1.10
R3:
[R3]ip route-static 192.168.1.32 27 192.168.1.5
[R3]ip route-static 192.168.1.0 30 192.168.1.5
[R3]ip route-static 192.168.1.64 27 192.168.1.5
[R3]ip route-static 192.168.1.64 27 192.168.1.14
R4:
[R4]ip route-static 192.168.1.64 27 192.168.1.9
[R4]ip route-static 192.168.1.0 30 192.168.1.9
[R4]ip route-static 192.168.1.32 27 192.168.1.9
[R4]ip route-static 192.168.1.32 27 192.168.1.13
[R4]ip route-static 192.168.1.4 30 192.168.1.13
[R4]ip route-static 192.168.1.96 27 192.168.1.13
R5:
[R5]ip route-static 192.168.1.32 27 192.168.1.17
[R5]ip route-static 192.168.1.64 27 192.168.1.17
[R5]ip route-static 192.168.1.96 27 192.168.1.17
[R5]ip route-static 192.168.1.128 27 192.168.1.17
[R5]ip route-static 192.168.1.0 30 192.168.1.17
[R5]ip route-static 192.168.1.4 30 192.168.1.17
[R5]ip route-static 192.168.1.8 30 192.168.1.17
[R5]ip route-static 192.168.1.12 30 192.168.1.17在此简单的使用R1去测试一下网络连接是否通
举例:1、R1去ping R5上面的环回地址
[R1]ping 192.168.1.161
PING 192.168.1.161: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
0.00% packet loss
R5去ping PC2
[R5]ping 192.168.1.125
PING 192.168.1.125: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
0.00% packet loss测试通过!!!
到此我们已经完成了要求中的1~4啦!!
五:避免环路(要求5、选路最佳,路由表尽量小,避免环路;)
[R1]ip route-static 192.168.1.32 27 NULL 0
[R2]ip route-static 192.168.1.64 27 NULL 0
[R4]ip route-static 192.168.1.128 27 NULL 0六:实现NAT连接(要求6、R1-R5均可以访问R6的环回;)
[R5]acl 2000
[R5-acl-basic-2000]rule permit source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
[R5-acl-basic-2000]q
[R5]int g0/0/2
[R5-GigabitEthernet0/0/2]nat outbound 2000七:Telnet远程连接,端口映射(要求:7、R6 telnet R5的公有地址时,实际登录到R1上;)
[R1-aaa]display user-interface (查看我的用户权限为3)
Idx Type Tx/Rx Modem Privi ActualPrivi Auth Int
+ 0 CON 0 9600 - 3 3 N -
设置aaa模式:
[R1]aaa
[R1-aaa]local-user gxc privilege level 3 password cipher 123456
Info: Add a new user.
启动R1 telnet服务:
[R1-aaa]local-user gxc service-type telnet
[R1]user-interface vty 0 4
[R1-ui-vty0-4]authentication-mode aaa
R5的端口映射:
[R5]int g0/0/2
[R5-GigabitEthernet0/0/2]nat static protocol tcp global current-interface 23 ins
ide 192.168.1.33 23
Warning:The port 23 is well-known port. If you continue it may cause function fa
ilure.
Are you sure to continue?[Y/N]:y
启动R5 telnet服务:
[R5]aaa
[R5-aaa]local-user gxc privilege level 3 password cipher 123456
Info: Add a new user.
[R5-aaa]local-user gxc service-type telnet
[R5-aaa]q
[R5]user-interface vty 0 4
[R5-ui-vty0-4]authentication-mode aaa
R6进行远程登录测试八:修改链路优先级(要求8、R4与R5正常通过1000M链路,故障时通过100m链路)
[R4]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 192.168.1.22
[R4]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 192.168.1.22 preference 61
[R5]ip route-static 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.252 192.168.1.21 pre 61
[R5]ip route-static 192.168.1.4 255.255.255.252 192.168.1.21 pre 61
[R5]ip route-static 192.168.1.8 255.255.255.252 192.168.1.21 pre 61
[R5]ip route-static 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.252 192.168.1.21 pre 61
[R5]ip route-static 192.168.1.32 255.255.255.224 192.168.1.21 pre 61
[R5]ip route-static 192.168.1.64 255.255.255.224 192.168.1.21 pre 61
[R5]ip route-static 192.168.1.96 255.255.255.224 192.168.1.21 pre 61
[R5]ip route-static 192.168.1.128 255.255.255.224 192.168.1.21 pre 61
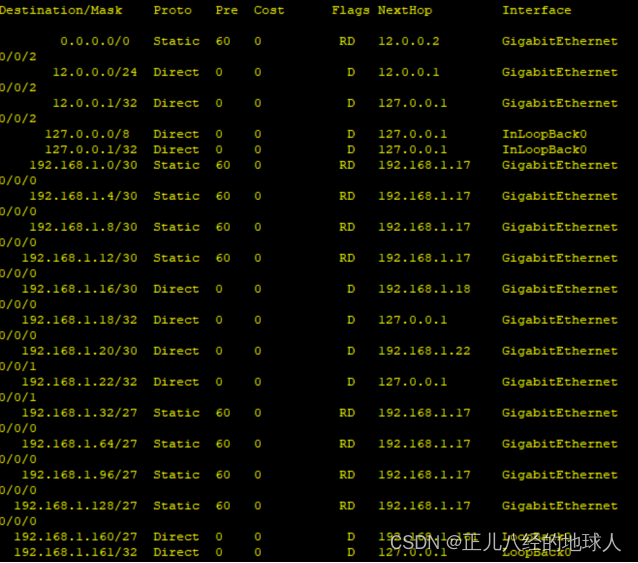
[R5]display ip routing-table这是没有故障时连接走上面1000M的链路
(现在路由表中只显示优先级为60)
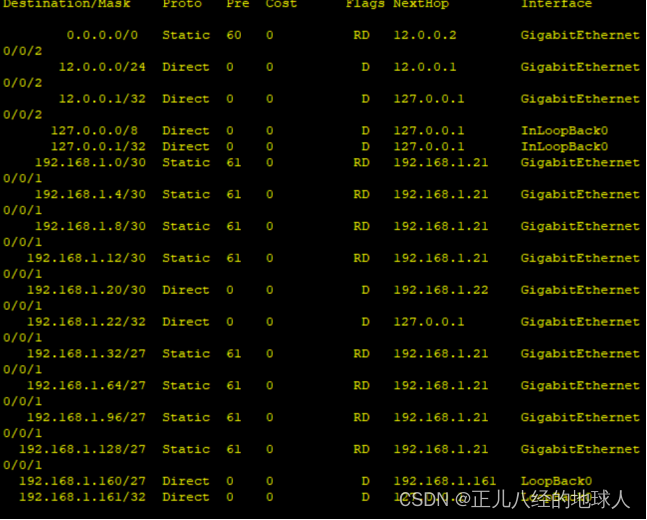
[R5-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]shutdown现在关闭R5 g0/0/0接口假设出现故障了,只能走下面100M的链路
(现在路由表中到R4的优先级为61)

![[HackMyVM] Quick](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/6c324b3fe0d343f3bb8aad1d2f86219d.png)