🧧🧧🧧🧧🧧个人主页🎈🎈🎈🎈🎈
🧧🧧🧧🧧🧧数据结构专栏🎈🎈🎈🎈🎈
🧧🧧🧧🧧🧧上一篇文章:特殊的线性表——栈🎈🎈🎈🎈🎈
文章目录
- 前言
- 1.队列(Queue)
- 1.1队列的概念
- 2.2 队列的使用
- 2.3 队列模拟实现
- 2.4 循环队列
- 3. 双端队列 (Deque)
前言
上一章我们讲了一种特殊的线性表只能在表尾进行插入和删除操作,接下来我们讲一个和栈很相似的数据结构,它也是一种特殊且所限制的线性表,它是只能在表头删除操作在表尾进行插入操作。
1.队列(Queue)
1.1队列的概念
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾(Tail/Rear) 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
2.2 队列的使用
在Java中,Queue是个接口,底层是通过链表实现的。
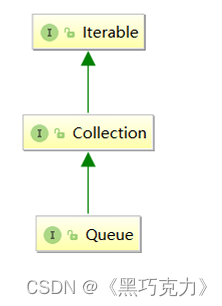
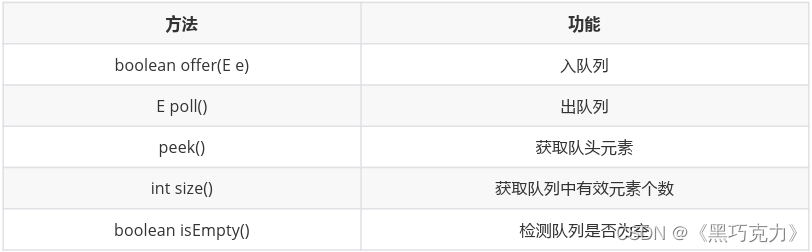
注意:Queue是个接口,在实例化时必须实例化LinkedList的对象,因为LinkedList实现了Queue接口。
2.3 队列模拟实现
我们这里通过链表来实现队列:
1.我们先将链表的框架搭建一下,代码如下:
public class MyQueue {
static class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode prev;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public ListNode head;
public ListNode last;
}
2.方法的实现:
2.1入队(offer)
//offer 入队
public void offer(int val) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(val);
//1.空节点
if(head == null) {
head = node;
last = node;
} else {
//2.不为空节点,尾插法。
last.next = node;
node.prev = last;
last = node;
}
}
2.2 出队(poll)
//poll 出队
public int poll() {
//1.判断队是否为空
if(isEmpty()) {
//1.1队为空,抛出队为空的异常
throw new QueueEmptyException("队空异常!!!!");
} else {
//2.队中是否只有一个元素
int val = head.val;
if(head.next == null) {
//2.1只有一个元素
head = null;
last = null;
return val;
} else {
//2.2队中不只一个元素,删头节点
head = head.next;
head.prev = null;
return val;
}
}
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
2.3 peek
//peek
public int peek() {
//1.判断队是否为空
if(isEmpty()) {
//1.1队为空,抛出队为空的异常
throw new QueueEmptyException("队空异常!!!!");
} else {
//1.2队不空,直接返回队头元素
return head.val;
}
}
2.4 判断队列空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
3.我这写一个队满报异常的代码
public class QueueEmptyException extends RuntimeException{
public QueueEmptyException() {
}
public QueueEmptyException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
2.4 循环队列
在实现队列可以通过链表来实现,还可以通过顺序表来实现,但在用顺序表来实现的时候,我们会发现,当队中在一边出队一边入队,会出现空间浪费的情况。
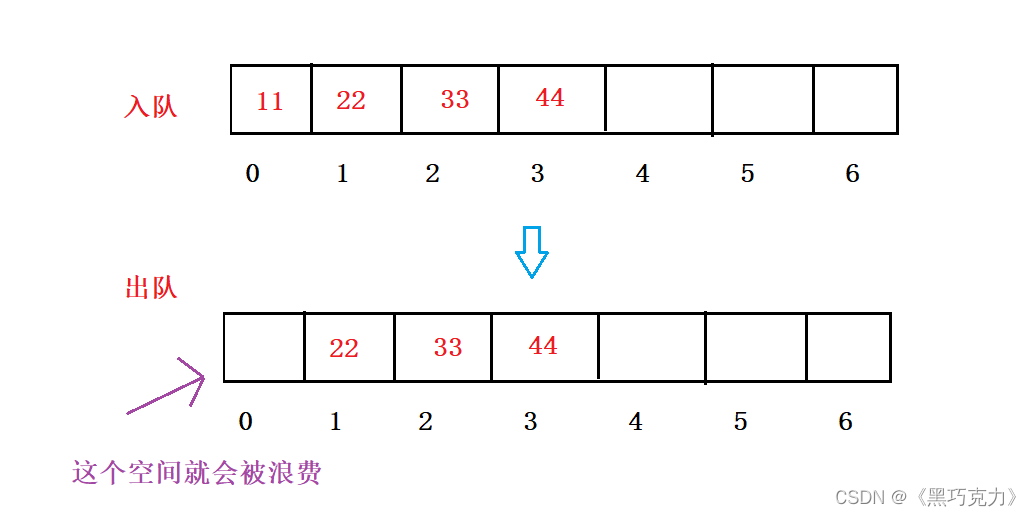
那我们怎么解决这个问题? 我们就提出将一个数组围成一个圆圈的样子,那么这么就不会把空间给浪费,像这样似的:
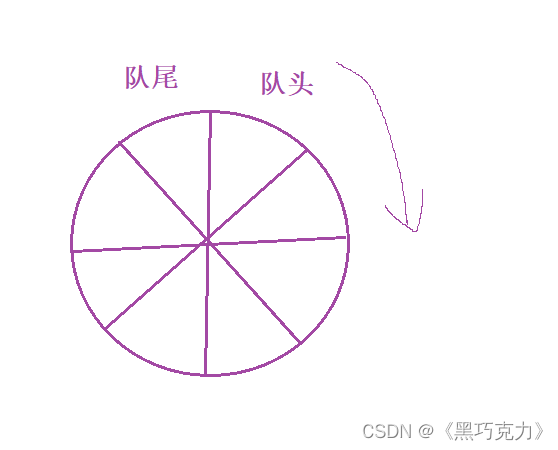
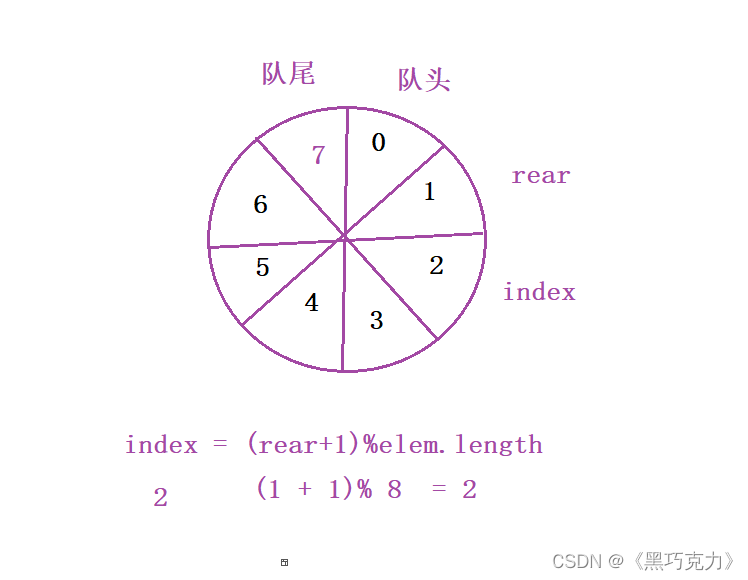
这时候会出现一个问题那就是怎么去区分这个队中是满还是空,在解决这个问题之前我先分享一个很有趣的方法:关于数组下标在循环的一个小tip 下一个下标等于(此时的下标+1)%数组的长度
用公式表示:index =(rear+1)%elem.length
我们就这个问题有三种方式去解决分别为:
1.size计数法
我们定义一个变量usedSize来记录队中的元素个数,当usedSize等于0,说明队中为空,当usedSize等于数组的长度,那么队满。
在入队的时候每入队一个元素usedSize就加1,在出队的时候usedSize就减1.
代码实现:
public class CircularQueueSize {
public int[] elem;
public int front;
public int rear;
public int usedSize;
public CircularQueueSize() {
elem = new int[8];
}
//入队
public void offer(int val) {
if(isFull()) {
throw new CircularQueueSizeFullException("队满异常!!!");
} else {
elem[rear] = val;
rear = (rear+1) % elem.length;
usedSize++;
}
}
//出队
public int poll() {
//1.判断队空不空
if(isEmpty()) {
//1.1队空
throw new CircularQueueSizeEmptyException("循环队列空异常!!!");
} else {
//1.2队不空
int val = elem[front];
front = (front+1) % elem.length;
usedSize--;
return val;
}
}
//判断队中是否空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return usedSize == 0;
}
//判断循环队列已满
public boolean isFull() {
return usedSize == elem.length;
}
//Front 获取队头元素
public int Front () {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return elem[front];
}
//Rear 获取队尾元素
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
int ret = (rear == 0) ? elem.length : rear-1;
return elem[ret];
}
}
2.flg标志法
我们定义一个boolean类型的flg标志位,一开始为false,每入队一个元素flg就置为true,每出队一个元素flg置为false。
判断队满队空的条件
队满:队头等于队尾并且flg等于ture
队空:队头等于队尾并且flg等于false
代码实现:
public class CircularQueueFlg {
public int[] elem;
public int front;
public int rear;
public boolean flg;
public int usedSize;
public CircularQueueFlg() {
elem = new int[8];
}
//入队
public void offer(int val) {
if(isFull()) {
throw new CircularQueueSizeFullException("队满异常!!!");
}
elem[rear] = val;
flg = true;
rear = (rear+1) % elem.length;
}
//出队
public int poll() {
//1.判断队空不空
if(isEmpty()) {
//1.1队空
throw new CircularQueueSizeEmptyException("循环队列空异常!!!");
} else {
//1.2队不空
int val = elem[front];
flg = false;
front = (front+1) % elem.length;
return val;
}
}
//判断队中是否空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (front == rear) && (flg == false);
}
//判断循环队列已满
public boolean isFull() {
return (front == rear) && (flg == true);
}
//Front 获取队头元素
public int Front () {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return elem[front];
}
//Rear 获取队尾元素
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
int ret = (rear == 0) ? elem.length : rear-1;
return elem[ret];
}
}
3.空间牺牲法
我们牺牲一个空间来实现循环队列判断队满和队空
队满:index = 队头 index (队尾此刻的下标+1)%数组的长度
队空:队尾等于队头
代码实现:
public class CircularQueueSpace {
public int[] elem;
public int front;
public int rear;
public CircularQueueSpace() {
elem = new int[8];
}
//入队
public void offer(int val) {
if(isFull()) {
throw new CircularQueueSizeFullException("队满异常!!!");
} else {
elem[rear] = val;
rear = (rear+1) % elem.length;
}
}
//出队
public int poll() {
//1.判断队空不空
if(isEmpty()) {
//1.1队空
throw new CircularQueueSizeEmptyException("循环队列空异常!!!");
} else {
//1.2队不空
int val = elem[front];
front = (front+1) % elem.length;
return val;
}
}
//判断队中是否空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == rear;
}
//判断循环队列已满
public boolean isFull() {
return front == (rear+1) % elem.length;
}
//Front 获取队头元素
public int Front () {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return elem[front];
}
//Rear 获取队尾元素
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
int ret = (rear == 0) ? elem.length-1 : rear-1;
return elem[ret];
}
}
3. 双端队列 (Deque)
双端队列(deque)是指允许两端都可以进行入队和出队操作的队列,deque 是 “double ended queue” 的简称。那就说明元素可以从队头出队和入队,也可以从队尾出队和入队。

eque是一个接口,使用时必须创建LinkedList的对象。
在实际工程中,使用Deque接口是比较多的,栈和队列均可以使用该接口。
Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();//双端队列的线性实现
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();//双端队列的链式实现
希望大家可以给我点点关注,点点赞,并且在评论区发表你们的想法和意见,我会认真看每一条评论,你们的支持就是我的最大鼓励。🌹🌹🌹🌹🌹🌹🌹🌹🌹🌹🌹🌹🌹🌹