文章目录
- 一、apply 标准库函数
- 二、let 标准库函数
Kotlin 语言中 , 在 Standard.kt 源码中 , 为所有类型定义了一批标准库函数 , 所有的 Kotlin 类型都可以调用这些函数 ;
一、apply 标准库函数
Kotlin 标准库函数 中的 apply 函数 ,
该函数可以看作 实例对象 的 配置函数 ,
传入 T.() -> Unit 类型 的 Lambda 表达式 作为参数 ,
该实例对象默认为 Lambda 表达式中的 this 参数 ;
apply 函数 的返回值 是 接收者对象 ,
也就是 调用 apply 函数 的实例对象 ,
同时也是 Lambda 表达式参数中的 this 参数 ;
apply 标准库函数原型 :
/**
* 以' this '值作为接收者调用指定函数[block],并返回' this '值。
*
* 有关详细使用信息,请参阅[scope functions]的文档
* (https://kotlinlang.org/docs/reference/scope-functions.html#apply)。
*/
@kotlin.internal.InlineOnly
public inline fun <T> T.apply(block: T.() -> Unit): T {
contract {
callsInPlace(block, InvocationKind.EXACTLY_ONCE)
}
block()
return this
}
代码示例 : 创建 File 文件对象 , 并为该文件设置 可读 , 可写 , 可执行 权限 ;
import java.io.File
fun main() {
val file = File("hello.txt")
file.setReadable(true)
file.setWritable(true)
file.setExecutable(true)
}
apply 函数代码示例 : 后面设置 可读 , 可写 , 可执行 权限的配置操作 , 可以在 apply 标准库函数中完成 , 代码如下 :
import java.io.File
fun main() {
val file = File("hello.txt").apply {
this.setReadable(true)
this.setWritable(true)
this.setExecutable(true)
}
}
二、let 标准库函数
Kotlin 标准库函数 中的 let 函数 ,
可以传入 (T) -> R 类型 的 Lambda 表达式 作为参数 ,
该 匿名函数 中 使用 it 默认变量 获取 调用者 实例对象 ;
apply 函数与 let 函数的区别 :
- apply 函数的 返回值是 调用者 ;
- let 函数的 返回值是 Lambda 表达式的最后一行 ;
let 函数原型 :
/**
* 调用以' this '值作为参数的指定函数[block],并返回其结果。
*
* 有关详细使用信息,请参阅[scope functions]的文档
* (https://kotlinlang.org/docs/reference/scope-functions.html#let)。
*/
@kotlin.internal.InlineOnly
public inline fun <T, R> T.let(block: (T) -> R): R {
contract {
callsInPlace(block, InvocationKind.EXACTLY_ONCE)
}
return block(this)
}
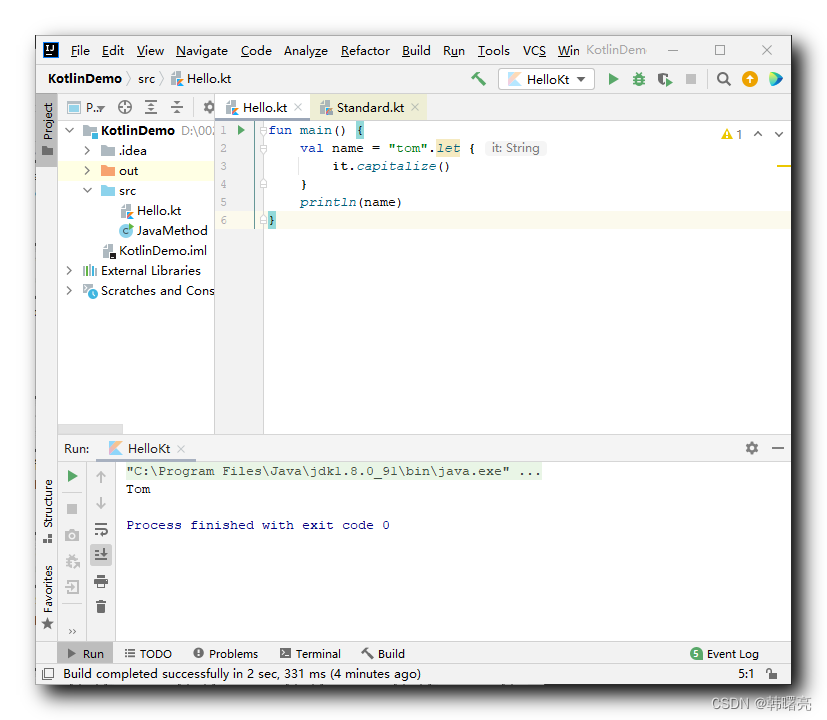
代码示例 :
fun main() {
val name = "tom".let {
it.capitalize()
}
println(name)
}
上述代码中 , 调用 字符串 “tom” 的 let 函数 ,
在 let 函数中 , 将首字母变为大写 , 并返回 ,
let 函数返回的是 匿名函数 的最后一行 , 因此将 “Tom” 字符串 返回了 ;
如果将 let 函数换成 apply 函数 , 则返回的就是 “tom” 字符串本身 , 不是 Lambda 表达式的最后一行 ;
执行结果 :
Tom
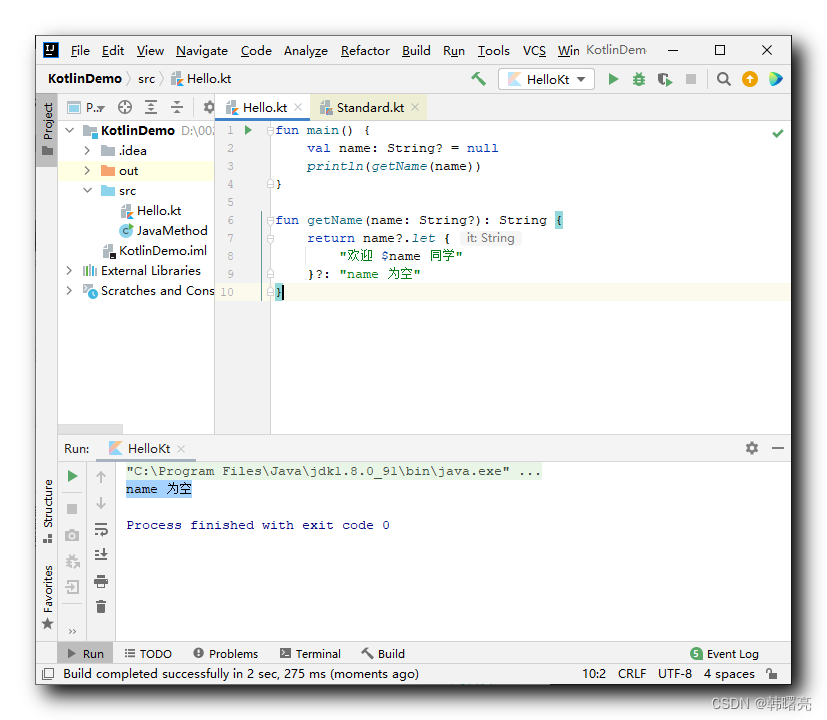
let 函数与 空安全操作符 ?. , 空合并操作符 ?: 结合使用 , 可替代 if 语句效果 ;
代码示例 :
fun main() {
val name: String? = null
println(getName(name))
}
fun getName(name: String?): String {
return name?.let {
"欢迎 $name 同学"
}?: "name 为空"
}
在上述函数中 , 首先确定 name 变量是否为空 ,
如果 name 为空 , 则 name?.let {...} 为空 , 后面的 let 函数根本不会执行 ,
此时会取 空合并操作符 ?: 后面的值作为整个表达式的值 ;
如果 name 不为空 , 则 执行 let 函数 , 整个表达式的值 就是 let 函数的最后一行 返回值 ;
执行结果 :
name 为空









![[笔记]Windows Cyswin ssh配置及远程控制](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/21dd145284ec4d96853150a702cce0b2.png)