深度学习-解读GoogleNet深度学习网络
深度学习中,经典网络引领一波又一波的技术革命,从LetNet到当前最火的GPT所用的Transformer,它们把AI技术不断推向高潮。2012年AlexNet大放异彩,它把深度学习技术引领第一个高峰,打开人们的视野。
用pytorch构建CNN经典网络模型GoogleNet,又称为Inception V1 ,还可以用数据进行训练模型,得到一个优化的模型。
深度学习
深度学习-回顾经典AlexNet网络:山高我为峰-CSDN博客
深度学习-CNN网络改进版LetNet5-CSDN博客
深度学习-回顾CNN经典网络LetNet-CSDN博客
GPT实战系列-如何用自己数据微调ChatGLM2模型训练_pytorch 训练chatglm2 模型-CSDN博客
Caffe笔记:python图像识别与分类_python 怎么识别 caffe-CSDN博客
深度学习-Pytorch同时使用Numpy和Tensors各自特效-CSDN博客
深度学习-Pytorch运算的基本数据类型_pytorch支持的训练数据类型-CSDN博客
深度学习-Pytorch如何保存和加载模型
深度学习-Pytorch如何构建和训练模型-CSDN博客
深度学习-Pytorch数据集构造和分批加载-CSDN博客
Python Faster R-CNN 安装配置记录_attributeerror: has no attribute 'smooth_l1_loss-CSDN博客
经典算法-遗传算法的python实现
经典算法-模拟退火算法的python实现
经典算法-粒子群算法的python实现-CSDN博客
GoogleNet概述
GoogLeNet是2014年Christian Szegedy提出的一种全新的深度学习结构,和VGGNet同一年诞生,获得2014年ILSVRC竞赛的第一名。
在这之前的AlexNet、VGG等结构都是通过增大网络的深度(层数)来获得更好的训练效果,但层数的增加会带来很多负作用,比如overfit、梯度消失、梯度爆炸等。
inception的提出则从另一种角度来提升训练结果:能更高效的利用计算资源,在相同的计算量下能提取到更多的特征,从而提升训练结果。
网络结构
Inception结构
inception结构的主要贡献有两个:
一是使用1x1的卷积来进行升降维;
二是在多个尺寸上同时进行卷积再聚合。

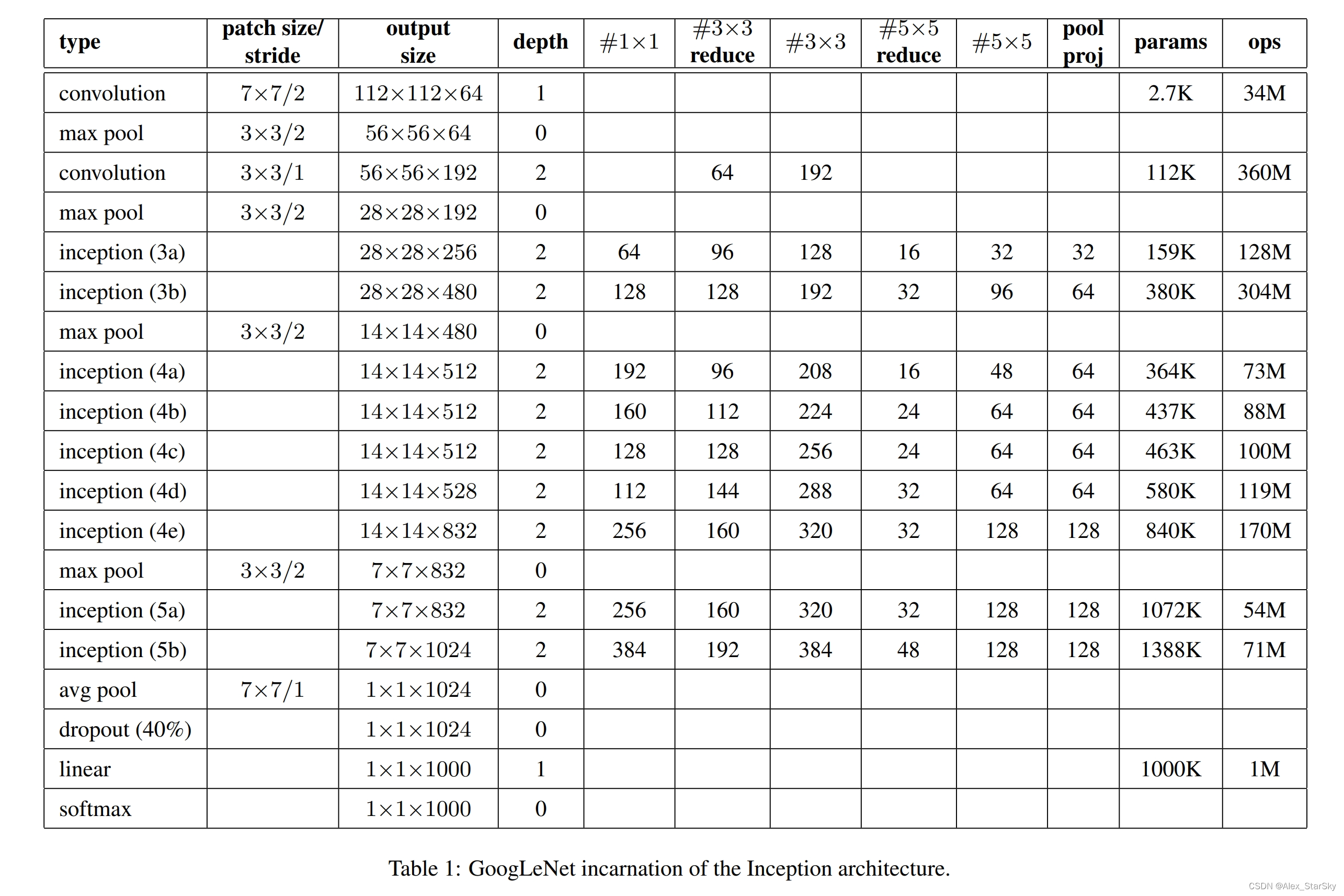
GoogleNet 的结构主要有Inception模块构成,主要有9个Incepion模块,和两个卷积模块构成。Inception也有2个改版。
结构描述
输入图像3通道分辨率:224x224x3
9层:图像输入后,5个卷积层,3个全连接层,1个输出层;
(1)C1:64个conv 7x7,stride=2–> MaxPool 3x3, stride=2 --> 输出 64个56x56;
(2)C2:192个conv 3x3, stride=2 --> MaxPool 3x3, stride=2 --> 输出 192个28x28;
(3)inception(3a) :–> 输出 256个28x28;
(4)inception(3b) :–> 输出 480个28x28;–> MaxPool 3x3, stride=2 --> 输出 480个14x14;
(5)inception(4a) :–> 输出 512个14x14;
(6)inception(4b) :–> 输出 512个14x14;
(7)inception(4c) :–> 输出 512个14x14;
(8)inception(4d) :–> 输出 528个14x14;
(9)inception(4e) :–> 输出 832个14x14;–> MaxPool 3x3, stride=2 --> 输出 832个7x7;
(10)inception(5a) :–> 输出 832个7x7;
(11)inception(5b) :–> 输出 1024个7x7;–> AvgPool 7x1, stride=1 --> 输出 1024个1x1;
(12)Dropout(40%):–> 输出 1024个1x1;
(13)linear --> 输出 1000个1x1;
(14)softmax --> 输出 1000个1x1;
整个GoogleNet 网络包含的参数数量表。
Pytorch实现
以下便是使用Pytorch实现的经典网络结构GoogleNet
class ConvReLU(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding):
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding, bias=True),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.conv(x)
class InceptionModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, c1x1_out, c3x3_in, c3x3_out, c5x5_in, c5x5_out, pool_proj):
super().__init__()
self.branch1 = ConvReLU(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=c1x1_out, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvReLU(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=c3x3_in, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
ConvReLU(in_channels=c3x3_in, out_channels=c3x3_out, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
)
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
ConvReLU(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=c5x5_in, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
ConvReLU(in_channels=c5x5_in, out_channels=c5x5_out, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2)
)
self.branch4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
ConvReLU(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=pool_proj, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.branch1(x)
x2 = self.branch2(x)
x3 = self.branch3(x)
x4 = self.branch4(x)
x = torch.cat([x1, x2, x3, x4], dim=1)
return x
class AuxClassifier(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, n_classes):
super().__init__()
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(4)
self.conv = ConvReLU(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=128, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.fc1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=128*4*4, out_features=1024, bias=True),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=0.7)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=n_classes, bias=True)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, x):
b, _, _ ,_ = x.shape
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.fc1(x.view(b, -1))
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.softmax(x)
return x
class GooLeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, n_classes) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=1)
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
ConvReLU(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3),
nn.LocalResponseNorm(size=5, k=2, alpha=1e-4, beta=0.75),
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvReLU(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
ConvReLU(in_channels=64, out_channels=192, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.LocalResponseNorm(size=5, k=2, alpha=1e-4, beta=0.75),
)
self.inception3a = InceptionModule(in_channels=192, c1x1_out=64, c3x3_in=96, c3x3_out=128, c5x5_in=16, c5x5_out=32, pool_proj=32)
self.inception3b = InceptionModule(in_channels=256, c1x1_out=128, c3x3_in=128, c3x3_out=192, c5x5_in=32, c5x5_out=96, pool_proj=64)
self.inception4a = InceptionModule(in_channels=480, c1x1_out=192, c3x3_in=96, c3x3_out=208, c5x5_in=16, c5x5_out=48, pool_proj=64)
self.inception4b = InceptionModule(in_channels=512, c1x1_out=160, c3x3_in=112, c3x3_out=224, c5x5_in=24, c5x5_out=64, pool_proj=64)
self.inception4c = InceptionModule(in_channels=512, c1x1_out=128, c3x3_in=128, c3x3_out=256, c5x5_in=24, c5x5_out=64, pool_proj=64)
self.inception4d = InceptionModule(in_channels=512, c1x1_out=112, c3x3_in=144, c3x3_out=288, c5x5_in=32, c5x5_out=64, pool_proj=64)
self.inception4e = InceptionModule(in_channels=528, c1x1_out=256, c3x3_in=160, c3x3_out=320, c5x5_in=32, c5x5_out=128, pool_proj=128)
self.inception5a = InceptionModule(in_channels=832, c1x1_out=256, c3x3_in=160, c3x3_out=320, c5x5_in=32, c5x5_out=128, pool_proj=128)
self.inception5b = InceptionModule(in_channels=832, c1x1_out=384, c3x3_in=192, c3x3_out=384, c5x5_in=48, c5x5_out=128, pool_proj=128)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=0.4)
self.fc = nn.Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=n_classes, bias=True)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
self.aux_classfier1 = AuxClassifier(in_channels=512, n_classes=n_classes)
self.aux_classfier2 = AuxClassifier(in_channels=528, n_classes=n_classes)
def forward(self, x):
b, _, _, _ = x.shape
x = self.conv1(x)
print('# Conv1 output shape:', x.shape)
x = self.maxpool(x)
print('# Pool1 output shape:', x.shape)
x = self.conv2(x)
print('# Conv2 output shape:', x.shape)
x = self.maxpool(x)
print('# Pool2 output shape:', x.shape)
x = self.inception3a(x)
print('# Inception3a output shape:', x.shape)
x = self.inception3b(x)
print('# Inception3b output shape:', x.shape)
x = self.maxpool(x)
print('# Pool3 output shape:', x.shape)
x = self.inception4a(x)
print('# Inception4a output shape:', x.shape)
aux1 = self.aux_classfier1(x)
print('# aux_classifier1 output shape:', aux1.shape)
x = self.inception4b(x)
print('# Inception4b output shape:', x.shape)
x = self.inception4c(x)
print('# Inception4c output shape:', x.shape)
x = self.inception4d(x)
print('# Inception4d output shape:', x.shape)
aux2 = self.aux_classfier2(x)
print('# aux_classifier2 output shape:', aux2.shape)
x = self.inception4e(x)
print('# Inception4e output shape:', x.shape)
x = self.maxpool(x)
print('# Pool4 output shape:', x.shape)
x = self.inception5a(x)
print('# Inception5a output shape:', x.shape)
x = self.inception5b(x)
print('# Inception5b output shape:', x.shape)
x = self.avgpool(x)
print('# Avgpool output shape:', x.shape)
x = self.dropout(x.view(b, -1))
print('# dropout output shape:', x.shape)
x = self.fc(x)
print('# FC output shape:', x.shape)
x = self.softmax(x)
print('# Softmax output shape:', x.shape)
return x, aux1, aux2
inputs = torch.randn(4, 3, 224, 224)
cnn = GooLeNet(in_channels = 3, n_classes = 1000)
outputs = cnn(inputs)
大家可以和前面的对照差异,也可以一窥DeepLearning技术的突破点。
在VGGNet 是一大创举,DeepMind团队更闻名的是在围棋开创一片天地,AlphaGo风靡一时,把人工智能推向又一个高潮,CNN网络引领的深度学习蓬勃发展,造就人工智能技术革命的起点。
觉得有用 收藏 收藏 收藏
点个赞 点个赞 点个赞
End
GPT专栏文章:
GPT实战系列-实战Qwen通义千问在Cuda 12+24G部署方案_通义千问 ptuning-CSDN博客
GPT实战系列-ChatGLM3本地部署CUDA11+1080Ti+显卡24G实战方案
GPT实战系列-Baichuan2本地化部署实战方案
GPT实战系列-让CodeGeeX2帮你写代码和注释_codegeex 中文-CSDN博客
GPT实战系列-ChatGLM3管理工具的API接口_chatglm3 api文档-CSDN博客
GPT实战系列-大话LLM大模型训练-CSDN博客
GPT实战系列-LangChain + ChatGLM3构建天气查询助手
GPT实战系列-大模型为我所用之借用ChatGLM3构建查询助手
GPT实战系列-P-Tuning本地化训练ChatGLM2等LLM模型,到底做了什么?(二)
GPT实战系列-P-Tuning本地化训练ChatGLM2等LLM模型,到底做了什么?(一)
GPT实战系列-ChatGLM2模型的微调训练参数解读
GPT实战系列-如何用自己数据微调ChatGLM2模型训练
GPT实战系列-ChatGLM2部署Ubuntu+Cuda11+显存24G实战方案
GPT实战系列-Baichuan2等大模型的计算精度与量化
GPT实战系列-GPT训练的Pretraining,SFT,Reward Modeling,RLHF
GPT实战系列-探究GPT等大模型的文本生成-CSDN博客





![[VulnHub靶机渗透] BNE0x03 Simple](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/8c62878a23eb49798c29677da6b81981.png)