目录
- 1.背景
- 2.算法原理
- 2.1算法思想
- 2.2算法过程
- 3.代码实现
- 4.参考文献
1.背景
2022年,Braik 等人受到白鲨捕食行为启发,提出了非洲秃鹫优化算法(White Shark Optimizer, WSO)。
2.算法原理
2.1算法思想
海洋中白鲨拥有敏锐的感知、听觉和嗅觉,WSO模拟了白鲨探索整个搜索空间来追踪、定位和捕获猎物,并通过白鲨位置的不断更新来达到求解优化问题。
2.2算法过程
速度更新:
这里很像PSO更新方式,作者对控制参数进行了更为复杂的设置。
v
k
+
1
i
=
μ
[
v
k
i
+
p
1
(
w
gbest
k
−
w
k
i
)
×
c
1
+
p
2
(
w
best
v
k
i
−
w
k
i
)
×
c
2
]
v_{k+1}^i=\mu\left[v_k^i+p_1\right.\left(w_{\text{gbest }_k}-w_k^i\right)\times c_1+\left.p_2\left(w_{\text{best}}^{v_k^i}-w_k^i\right)\times c_2\right]
vk+1i=μ[vki+p1(wgbest k−wki)×c1+p2(wbestvki−wki)×c2]
其中,参数
p
1
,
p
2
p_1,p_2
p1,p2表述如下:
p
1
=
p
m
a
x
+
(
p
m
a
x
−
p
m
i
n
)
×
e
−
(
4
k
/
K
)
2
p
2
=
p
m
i
n
+
(
p
m
a
x
−
p
m
i
n
)
×
e
−
(
4
k
/
K
)
2
\begin{aligned}p_1&=p_{max}+(p_{max}-p_{min})\times e^{-(4k/K)^2}\\p_2&=p_{min}+(p_{max}-p_{min})\times e^{-(4k/K)^2}\end{aligned}
p1p2=pmax+(pmax−pmin)×e−(4k/K)2=pmin+(pmax−pmin)×e−(4k/K)2
位置更新:
大白鲨常常在不断寻找潜在猎物,可能位于最佳或次优位置。它们会通过听到猎物移动引起的波浪声或闻到猎物的气味来确定位置。
w
k
+
1
i
=
{
w
k
i
⋅
¬
⊕
w
o
+
u
⋅
a
+
l
⋅
b
R
<
m
v
w
k
i
+
v
k
i
/
f
R
⩾
m
v
\left.w_{k+1}^i=\left\{\begin{array}{cc}w_k^i\cdot\neg\oplus w_o+u\cdot a+l\cdot b&R<m_v\\w_k^i+v_k^i/f&R\geqslant m_v\end{array}\right.\right.
wk+1i={wki⋅¬⊕wo+u⋅a+l⋅bwki+vki/fR<mvR⩾mv
其中,
¬
,
⊕
\lnot, \oplus
¬,⊕分别为否定运算和异或运算。其余参数表述为:
a
=
s
g
n
(
w
k
i
−
u
)
>
0
b
=
sgn
(
w
k
i
−
l
)
<
0
w
o
=
⊕
(
a
,
b
)
a=\mathrm{sgn}(w_{k}^{i}-u)>0 \\ b=\operatorname{sgn}(w_k^i-l)<0 \\ w_o=\oplus(a,b)
a=sgn(wki−u)>0b=sgn(wki−l)<0wo=⊕(a,b)
向猎物移动:
w
k
+
1
i
=
w
g
best
k
+
r
1
D
⃗
w
sgn
(
r
2
−
0.5
)
r
3
<
s
s
w_{k+1}^i=w_{g\text{best}_k}+r_1\vec{D}_w\text{sgn}(r_2-0.5)\quad r_3<s_s
wk+1i=wgbestk+r1Dwsgn(r2−0.5)r3<ss
最优解保留:
w
k
+
1
i
=
w
k
i
+
w
k
+
1
i
2
×
R
w_{k+1}^i=\frac{w_k^i+w_{k+1}^i}{2\times R}
wk+1i=2×Rwki+wk+1i
伪代码:

3.代码实现
% 白鲨优化算法
function [Best_pos, Best_fitness, Iter_curve, History_pos, History_best] = WSO(pop, maxIter, lb, ub, dim,fobj)
%input
%pop 种群数量
%dim 问题维数
%ub 变量上边界
%lb 变量下边界
%fobj 适应度函数
%maxIter 最大迭代次数
%output
%Best_pos 最优位置
%Best_fitness 最优适应度值
%Iter_curve 每代最优适应度值
%History_pos 每代种群位置
%History_best 每代最优个体位置
%% Convergence curve
Iter_curve=zeros(1,maxIter);
%% 初始化
WSO_Positions = zeros(pop, dim);
for i = 1:pop
for j = 1:dim
WSO_Positions(i,j) = (ub(j) - lb(j)) * rand() + lb(j);
end
end
% initial velocity
v=0.0*WSO_Positions;
%% 计算适应度
fit=zeros(pop,1);
for i=1:pop
fit(i,1)=fobj(WSO_Positions(i,:));
end
%% 记录
fitness=fit; % Initial fitness of the random positions of the WSO
[Best_fitness,index]=min(fit);
wbest = WSO_Positions; % Best position initialization
Best_pos = WSO_Positions(index,:); % initial global position
%% WSO Parameters
fmax=0.75; % Maximum frequency of the wavy motion
fmin=0.07; % Minimum frequency of the wavy motion
tau=4.11;
mu=2/abs(2-tau-sqrt(tau^2-4*tau));
pmin=0.5;
pmax=1.5;
a0=6.250;
a1=100;
a2=0.0005;
%% 迭代
for ite=1:maxIter
mv=1/(a0+exp((maxIter/2.0-ite)/a1));
s_s=abs((1-exp(-a2*ite/maxIter))) ;
p1=pmax+(pmax-pmin)*exp(-(4*ite/maxIter)^2);
p2=pmin+(pmax-pmin)*exp(-(4*ite/maxIter)^2);
%% Update the speed of the white sharks in water
nu=floor((pop).*rand(1,pop))+1;
for i=1:size(WSO_Positions,1)
rmin=1; rmax=3.0;
rr=rmin+rand()*(rmax-rmin);
wr=abs(((2*rand()) - (1*rand()+rand()))/rr);
v(i,:)= mu*v(i,:) + wr *(wbest(nu(i),:)-WSO_Positions(i,:));
%% or
% v(i,:)= mu*(v(i,:)+ p1*(gbest-WSO_Positions(i,:))*rand+....
% + p2*(wbest(nu(i),:)-WSO_Positions(i,:))*rand);
end
%% Update the white shark position
for i=1:size(WSO_Positions,1)
f =fmin+(fmax-fmin)/(fmax+fmin);
a=sign(WSO_Positions(i,:)-ub)>0;
b=sign(WSO_Positions(i,:)-lb)<0;
wo=xor(a,b);
% locate the prey based on its sensing (sound, waves)
if rand<mv
WSO_Positions(i,:)= WSO_Positions(i,:).*(~wo) + (ub.*a+lb.*b); % random allocation
else
WSO_Positions(i,:) = WSO_Positions(i,:)+ v(i,:)/f; % based on the wavy motion
end
end
%% Update the position of white sharks consides_sng fishing school
for i=1:size(WSO_Positions,1)
for j=1:size(WSO_Positions,2)
if rand<s_s
Dist=abs(rand*(Best_pos(j)-1*WSO_Positions(i,j)));
if(i==1)
WSO_Positions(i,j)=Best_pos(j)+rand*Dist*sign(rand-0.5);
else
WSO_Pos(i,j)= Best_pos(j)+rand*Dist*sign(rand-0.5);
WSO_Positions(i,j)=(WSO_Pos(i,j)+WSO_Positions(i-1,j))/2*rand;
end
end
end
end
%
%% Update global, best and new positions
for i=1:pop
% Handling boundary violations
if WSO_Positions(i,:)>=lb & WSO_Positions(i,:)<=ub%
% Find the fitness
fit(i)=fobj(WSO_Positions(i,:));
% Evaluate the fitness
if fit(i)<fitness(i)
wbest(i,:) = WSO_Positions(i,:); % Update the best positions
fitness(i)=fit(i); % Update the fitness
end
%% Finding out the best positions
if (fitness(i)<Best_fitness)
Best_fitness=fitness(i);
Best_pos = wbest(index,:); % Update the global best positions
end
end
end
Iter_curve(ite) = Best_fitness;
History_pos{ite} = WSO_Positions;
History_best{ite} = Best_pos;
end
end
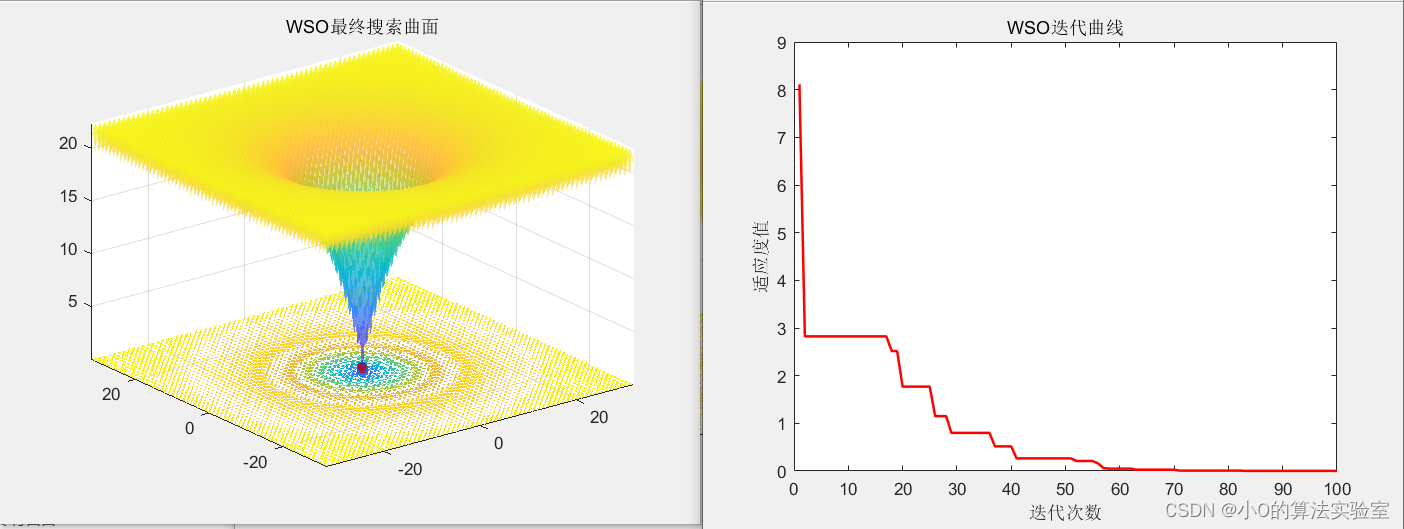
4.参考文献
[1] Braik M, Hammouri A, Atwan J, et al. White Shark Optimizer: A novel bio-inspired meta-heuristic algorithm for global optimization problems[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2022, 243: 108457.