目录
- 1.背景
- 2.算法原理
- 2.1算法思想
- 2.2算法过程
- 3.代码实现
- 4.参考文献
1.背景
2021年,Abdollahzadeh等人受到非洲秃鹫自然捕食行为启发,提出了非洲秃鹫优化算法(African Vultures Optimization Algorithm, AVOA)。
2.算法原理
2.1算法思想
AVOA模拟了非洲秃鹫在自然界中的捕食过程,是典型的领导者-追随者模式。AVOA通过最优秃鹫和次优秃鹫对整个群体进行引导。
2.2算法过程
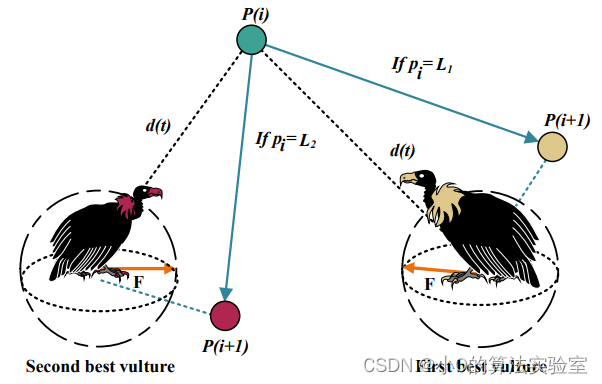
领导者-秃鹰筛选:
R
(
i
)
=
{
B
e
s
t
V
u
l
t
u
r
e
1
i
f
p
i
=
L
1
B
e
s
t
V
u
l
t
u
r
e
2
i
f
p
i
=
L
2
\left.R(i)=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}BestVulture_1ifp_i=L_1\\BestVulture_2ifp_i=L_2\end{array}\right.\right.
R(i)={BestVulture1ifpi=L1BestVulture2ifpi=L2
这里
p
i
p_i
pi是对群体适应度归一化,通过轮盘赌策略选取最佳解策略。
p
i
=
F
i
∑
i
=
1
n
F
i
p_i=\frac{F_i}{\sum_{i=1}^nF_i}
pi=∑i=1nFiFi
饥饿度:
秃鹰的行为受到饥饿水平和能量储备的驱使,成为优化算法中探索和开发阶段转换的关键灵感。饱食时,秃鹰能够飞行更远寻找食物,而饥饿时能量减少,限制了它们的飞行能力。在饥饿时,秃鹰更积极地寻找食物,常常与更强壮的秃鹰一起觅食。
t
=
h
×
(
s
i
n
w
(
π
2
×
i
t
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
i
m
a
x
i
t
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
s
)
+
c
o
s
(
π
2
×
i
t
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
i
m
a
x
i
t
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
s
)
−
1
)
F
=
(
2
×
r
a
n
d
1
+
1
)
×
z
×
(
1
−
i
t
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
i
m
a
x
i
t
e
r
a
t
i
o
n
s
)
+
t
\begin{aligned} &t=h\times\left(sin^{\mathrm{w}}\left(\frac{\pi}{2}\times\frac{iteration_{i}}{maxiterations}\right)+cos\left(\frac{\pi}{2}\times\frac{iteration_{i}}{maxiterations}\right)-1\right) \\ &F=(2\times rand_1+1)\times z\times\left(1-\frac{iteration_i}{maxiterations}\right)+t \end{aligned}
t=h×(sinw(2π×maxiterationsiterationi)+cos(2π×maxiterationsiterationi)−1)F=(2×rand1+1)×z×(1−maxiterationsiterationi)+t
当
∣
F
∣
>
1
|F|>1
∣F∣>1时,全局探索;反之,局部搜索。
探索阶段:
P
(
i
+
1
)
=
{
R
(
i
)
−
D
(
i
)
∗
F
,
i
f
P
1
≥
r
a
n
d
P
1
R
(
i
)
−
F
+
r
a
n
d
2
∗
(
(
u
b
−
l
b
)
∗
r
a
n
d
3
+
l
b
)
,
e
l
s
e
\mathrm{P}\left(\mathrm{i}+1\right)=\begin{cases}\mathrm{R}(\mathrm{i})-\mathrm{D}(\mathrm{i})*\mathrm{F},\mathrm{if}\mathrm{P}_1\ge\mathrm{rand}_{\mathrm{P}1}\\\mathrm{R}(\mathrm{i})-\mathrm{F}+\mathrm{rand}_2*((\mathrm{u}\mathrm{b}-\mathrm{l}\mathrm{b})*\mathrm{rand}_3+\mathrm{l}\mathrm{b}),\mathrm{else}\end{cases}
P(i+1)={R(i)−D(i)∗F,ifP1≥randP1R(i)−F+rand2∗((ub−lb)∗rand3+lb),else
其中,
D
(
i
)
D(i)
D(i)表述为:
D
(
i
)
=
∣
X
∗
R
(
i
)
−
P
(
i
)
∣
\mathrm D(\mathrm i)=|\mathrm X*\mathrm R(\mathrm i)-\mathrm P(\mathrm i)|
D(i)=∣X∗R(i)−P(i)∣
开发阶段:
S
1
=
R
(
i
)
×
(
r
a
n
d
5
×
P
(
i
)
2
π
)
×
c
o
s
(
P
(
i
)
)
S
2
=
R
(
i
)
×
(
r
a
n
d
6
×
P
(
i
)
2
π
)
×
s
i
n
(
P
(
i
)
)
\begin{aligned}S_1&=R(i)\times\left(\frac{rand_5\times P(i)}{2\pi}\right)\times cos(P(i))\\S_2&=R(i)\times\left(\frac{rand_6\times P(i)}{2\pi}\right)\times sin(P(i))\end{aligned}
S1S2=R(i)×(2πrand5×P(i))×cos(P(i))=R(i)×(2πrand6×P(i))×sin(P(i))
A
1
=
B
e
s
t
V
u
l
t
u
r
e
1
(
i
)
−
B
e
s
t
V
u
l
t
u
r
e
1
(
i
)
×
P
(
i
)
B
e
s
t
V
u
l
t
u
r
e
1
(
i
)
−
P
(
i
)
2
×
F
A_1=BestVulture_1(i)-\frac{BestVulture_1(i)\times P(i)}{BestVulture_1(i)-P(i)^2}\times F
A1=BestVulture1(i)−BestVulture1(i)−P(i)2BestVulture1(i)×P(i)×F
A
2
=
B
e
s
t
V
u
l
t
u
r
e
2
(
i
)
−
B
e
s
t
V
u
l
t
u
r
e
2
(
i
)
×
P
(
i
)
B
e
s
t
V
u
l
t
u
r
e
2
(
i
)
−
P
(
i
)
2
×
F
A_2=BestVulture_2(i)-\frac{BestVulture_2(i)\times P(i)}{BestVulture_2(i)-P(i)^2}\times F
A2=BestVulture2(i)−BestVulture2(i)−P(i)2BestVulture2(i)×P(i)×F
3.代码实现
%非洲秃鹫优化算法
function [Best_pos, Best_fitness,Iter_curve, History_pos, History_best]=AVOA(pop, dim, ub, lb, fobj,maxIter)
%input
%pop 种群数量
%dim 问题维数
%ub 变量上边界
%lb 变量下边界
%fobj 适应度函数
%maxIter 最大迭代次数
%output
%Best_pos 最优位置
%Best_fitness 最优适应度值
%Iter_curve 每代最优适应度值
%History_pos 每代种群位置
%History_best 每代最优位置
%% 全局记录
Best_pos=zeros(1,dim);
Best_fitness=inf;
Best_vulture2_X=zeros(1,dim);
Best_vulture2_F=inf;
%% 初始化种群
X=initialization(pop,dim,ub,lb);
%% 控制参数
p1=0.6;
p2=0.4;
p3=0.6;
alpha=0.8;
betha=0.2;
gamma=2.5;
%% 迭代
current_iter=0; % Loop counter
while current_iter < maxIter
for i=1:size(X,1)
% Calculate the fitness of the population
current_vulture_X = X(i,:);
current_vulture_F=fobj(current_vulture_X);
% Update the first best two vultures if needed
if current_vulture_F<Best_fitness
Best_fitness=current_vulture_F; % Update the first best bulture
Best_pos=current_vulture_X;
end
if current_vulture_F>Best_fitness && current_vulture_F<Best_vulture2_F
Best_vulture2_F=current_vulture_F; % Update the second best bulture
Best_vulture2_X=current_vulture_X;
end
end
a=unifrnd(-2,2,1,1)*((sin((pi/2)*(current_iter/maxIter))^gamma)+cos((pi/2)*(current_iter/maxIter))-1);
P1=(2*rand+1)*(1-(current_iter/maxIter))+a;
% Update the location
for i=1:size(X,1)
current_vulture_X = X(i,:); % pick the current vulture back to the population
F=P1*(2*rand()-1);
random_vulture_X=random_select(Best_pos,Best_vulture2_X,alpha,betha);
if abs(F) >= 1 % Exploration:
current_vulture_X = exploration(current_vulture_X, random_vulture_X, F, p1, ub, lb);
elseif abs(F) < 1 % Exploitation:
current_vulture_X = exploitation(current_vulture_X, Best_pos, Best_vulture2_X, random_vulture_X, F, p2, p3, dim, ub, lb);
end
X(i,:) = current_vulture_X; % place the current vulture back into the population
end
current_iter=current_iter+1;
X = boundaryCheck(X, lb, ub);
Iter_curve(current_iter)=Best_fitness;
History_pos{current_iter} = X;
History_best{current_iter} = Best_pos;
end
end
%% 初始化函数
function [ X ]=initialization(N,dim,ub,lb)
Boundary_no= size(ub,2);
if Boundary_no==1
X=rand(N,dim).*(ub-lb)+lb;
end
if Boundary_no>1
for i=1:dim
ub_i=ub(i);
lb_i=lb(i);
X(:,i)=rand(N,1).*(ub_i-lb_i)+lb_i;
end
end
end
%%
function [current_vulture_X] = exploitation(current_vulture_X, Best_vulture1_X, Best_vulture2_X, ...
random_vulture_X, F, p2, p3, variables_no, upper_bound, lower_bound)
% phase 1
if abs(F)<0.5
if rand<p2
A=Best_vulture1_X-((Best_vulture1_X.*current_vulture_X)./(Best_vulture1_X-current_vulture_X.^2))*F;
B=Best_vulture2_X-((Best_vulture2_X.*current_vulture_X)./(Best_vulture2_X-current_vulture_X.^2))*F;
current_vulture_X=(A+B)/2;
else
current_vulture_X=random_vulture_X-abs(random_vulture_X-current_vulture_X)*F.*levyFlight(variables_no);
end
end
% phase 2
if abs(F)>=0.5
if rand<p3
current_vulture_X=(abs((2*rand)*random_vulture_X-current_vulture_X))*(F+rand)-(random_vulture_X-current_vulture_X);
else
s1=random_vulture_X.* (rand()*current_vulture_X/(2*pi)).*cos(current_vulture_X);
s2=random_vulture_X.* (rand()*current_vulture_X/(2*pi)).*sin(current_vulture_X);
current_vulture_X=random_vulture_X-(s1+s2);
end
end
end
%%
function [current_vulture_X] = exploration(current_vulture_X, random_vulture_X, F, p1, upper_bound, lower_bound)
if rand<p1
current_vulture_X=random_vulture_X-(abs((2*rand)*random_vulture_X-current_vulture_X))*F;
else
current_vulture_X=(random_vulture_X-(F)+rand()*((upper_bound-lower_bound)*rand+lower_bound));
end
end
%% 随机选择
function [random_vulture_X]=random_select(Best_vulture1_X,Best_vulture2_X,alpha,betha)
probabilities=[alpha, betha ];
if (rouletteWheelSelection( probabilities ) == 1)
random_vulture_X=Best_vulture1_X;
else
random_vulture_X=Best_vulture2_X;
end
end
%% 飞行
function [ o ]=levyFlight(d)
beta=3/2;
sigma=(gamma(1+beta)*sin(pi*beta/2)/(gamma((1+beta)/2)*beta*2^((beta-1)/2)))^(1/beta);
u=randn(1,d)*sigma;
v=randn(1,d);
step=u./abs(v).^(1/beta);
o=step;
end
%% 边界检查
function [ X ] = boundaryCheck(X, lb, ub)
for i=1:size(X,1)
FU=X(i,:)>ub;
FL=X(i,:)<lb;
X(i,:)=(X(i,:).*(~(FU+FL)))+ub.*FU+lb.*FL;
end
end
%% 轮盘赌策略
function [index] = rouletteWheelSelection(x)
index=find(rand() <= cumsum(x) ,1,'first');
end
4.参考文献
[1] Abdollahzadeh B, Gharehchopogh F S, Mirjalili S. African vultures optimization algorithm: A new nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for global optimization problems[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2021, 158: 107408.