题目大意
在ICPCCamp中,有n个方便编号的城镇,编号为1,2,...,n,它们之间通过(n-1)条道路相连。连接第i个城镇a_i和b_i的道路的长度为c_i。保证任意两座城市之间只能通过道路到达。
Bobo希望修建(n-1)条高速公路,这样任意两个城镇之间可以仅通过高速公路到达。 在城镇x和y之间修建一条高速公路对他的费用为δ(x,y)美分, 其中δ(x,y)是使用道路连接城镇x和y之间的最短路径的长度。
由于Bobo很有钱,他希望找到修建(n-1)条高速公路的最昂贵方式。
输入包含零个或多个测试用例,并以文件结束符结束。对于每个测试用例
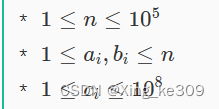
解题思路
- 最大生成树
- 找出最长路径,即树的直径
- 然后对于每个点看离谁远连谁
- 求和即为答案
- 具体来讲
- 先找出不是叶子的一点,从这点跑最短路(题目要求代价为最短路径),找到最远点
- (最远点和次远点在一个子树时,不为树的直径)
- 再从最远点跑最短路,找到离它最远的点,这两点即为直径端点
- 然后从这两点分别跑最短路,比较其他点离哪个点更远,计算答案
import java.io.*;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
//implements Runnable
public class Main{
static long md=(long)998244353;
static long Linf=Long.MAX_VALUE/2;
static int inf=Integer.MAX_VALUE/2;
static int N=2000000;
static int n=0;
static int m=0;
static
class Edge{
int fr,to,nxt;
long val;
public Edge(int u,int v,long w) {
fr=u;
to=v;
val=w;
}
}
static Edge[] e;
static int[] head;
static int cnt=0;
static void addEdge(int fr,int to,long val) {
cnt++;
e[cnt]=new Edge(fr, to, val);
e[cnt].nxt=head[fr];
head[fr]=cnt;
}
static
class Node{
int x;
long y;
public Node(int u,long v) {
x=u;
y=v;
}
}
static void Dij(int s,long[] dis) {
Arrays.fill(dis, Linf);
boolean[] vis=new boolean[n+1];
PriorityQueue<Node> q=new PriorityQueue<Node>((o1,o2)->{
if(o1.y-o2.y>0)return 1;
else if(o1.y-o2.y<0)return -1;
else return 0;
});
q.add(new Node(s, 0));
dis[s]=0;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
Node now=q.peek();q.poll();
int x=now.x;
if(vis[x])continue;
vis[x]=true;
for(int i=head[x];i>0;i=e[i].nxt) {
int v=e[i].to;
if(vis[v])continue;
long w=e[i].val;
if(dis[v]>dis[x]+w) {
dis[v]=dis[x]+w;
q.add(new Node(v, dis[v]));
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// AReader input=new AReader();
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
while(input.hasNext()) {
n=input.nextInt();
e=new Edge[2*n+1];
head=new int[n+1];
cnt=0;
for(int i=1;i<n;++i) {
int u=input.nextInt();
int v=input.nextInt();
long w=input.nextLong();
addEdge(u, v, w);
addEdge(v, u, w);
}
long[] dis=new long[n+1];
int s=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) {
if(e[head[i]].nxt!=0) {
s=i;
break;
}
}
Dij(s, dis);
long mx=0;
int mxi=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) {
if(mx<dis[i]) {
mx=dis[i];
mxi=i;
}
}
int a=mxi;
Dij(mxi, dis);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) {
if(mx<dis[i]) {
mx=dis[i];
mxi=i;
}
}
int b=mxi;
long[] dis1=new long[n+1];
long[] dis2=new long[n+1];
Dij(a, dis1);
Dij(b, dis2);
long ans=0;
ans+=dis1[b];
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) {
if(i==a||i==b)continue;
ans+=Math.max(dis1[i], dis2[i]);
}
out.println(ans);
out.flush();
}
out.flush();
out.close();
}
// public static final void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// new Thread(null, new Main(), "线程名字", 1 << 27).start();
// }
// @Override
// public void run() {
// try {
// //原本main函数的内容
// solve();
//
// } catch (Exception e) {
// }
// }
static
class AReader{
BufferedReader bf;
StringTokenizer st;
BufferedWriter bw;
public AReader(){
bf=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
st=new StringTokenizer("");
bw=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException{
return bf.readLine();
}
public String next() throws IOException{
while(!st.hasMoreTokens()){
st=new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public char nextChar() throws IOException{
//确定下一个token只有一个字符的时候再用
return next().charAt(0);
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException{
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException{
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public double nextDouble() throws IOException{
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
public float nextFloat() throws IOException{
return Float.parseFloat(next());
}
public byte nextByte() throws IOException{
return Byte.parseByte(next());
}
public short nextShort() throws IOException{
return Short.parseShort(next());
}
public BigInteger nextBigInteger() throws IOException{
return new BigInteger(next());
}
public void println() throws IOException {
bw.newLine();
}
public void println(int[] arr) throws IOException{
for (int value : arr) {
bw.write(value + " ");
}
println();
}
public void println(int l, int r, int[] arr) throws IOException{
for (int i = l; i <= r; i ++) {
bw.write(arr[i] + " ");
}
println();
}
public void println(int a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
bw.newLine();
}
public void print(int a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
}
public void println(String a) throws IOException{
bw.write(a);
bw.newLine();
}
public void print(String a) throws IOException{
bw.write(a);
}
public void println(long a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
bw.newLine();
}
public void print(long a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
}
public void println(double a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
bw.newLine();
}
public void print(double a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
}
public void print(char a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
}
public void println(char a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
bw.newLine();
}
}
}