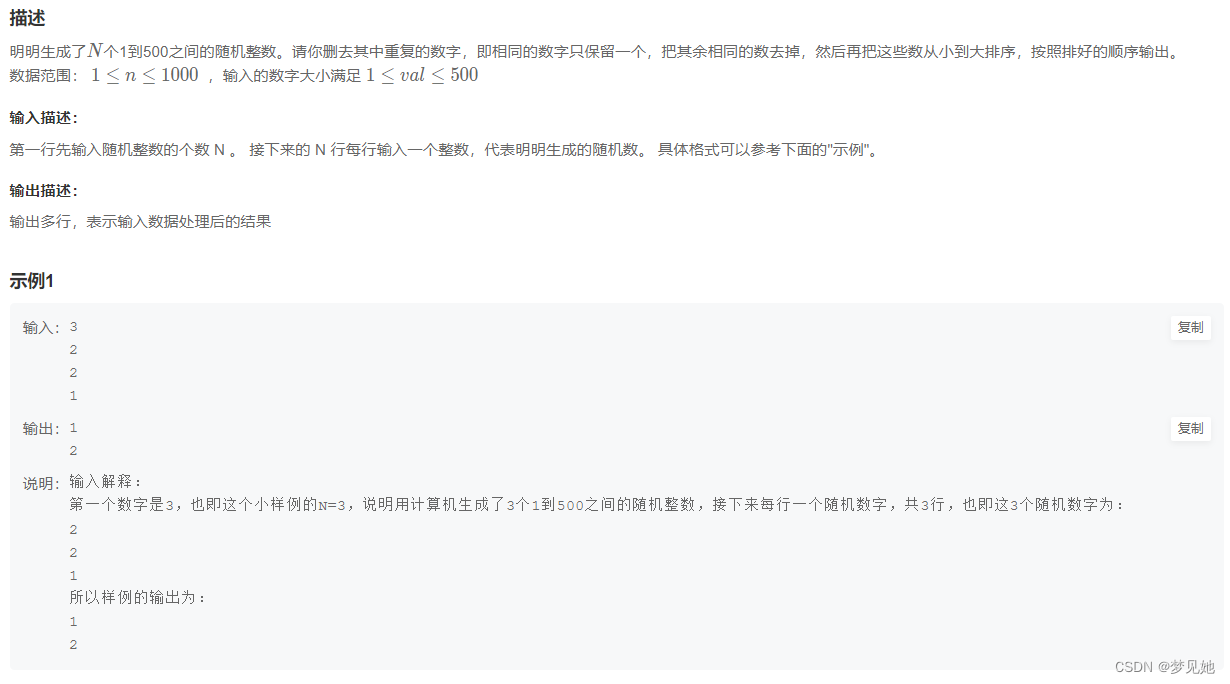
小米
好的公司有年终且在年前发放,一般的公司有(可能打折的)年终且年后分批发放,不好的公司各有操作。
3 月已来,小米的年终也开始热议起来。
最近,一则「传小米年终打折,14薪能保住吗」冲上热搜。
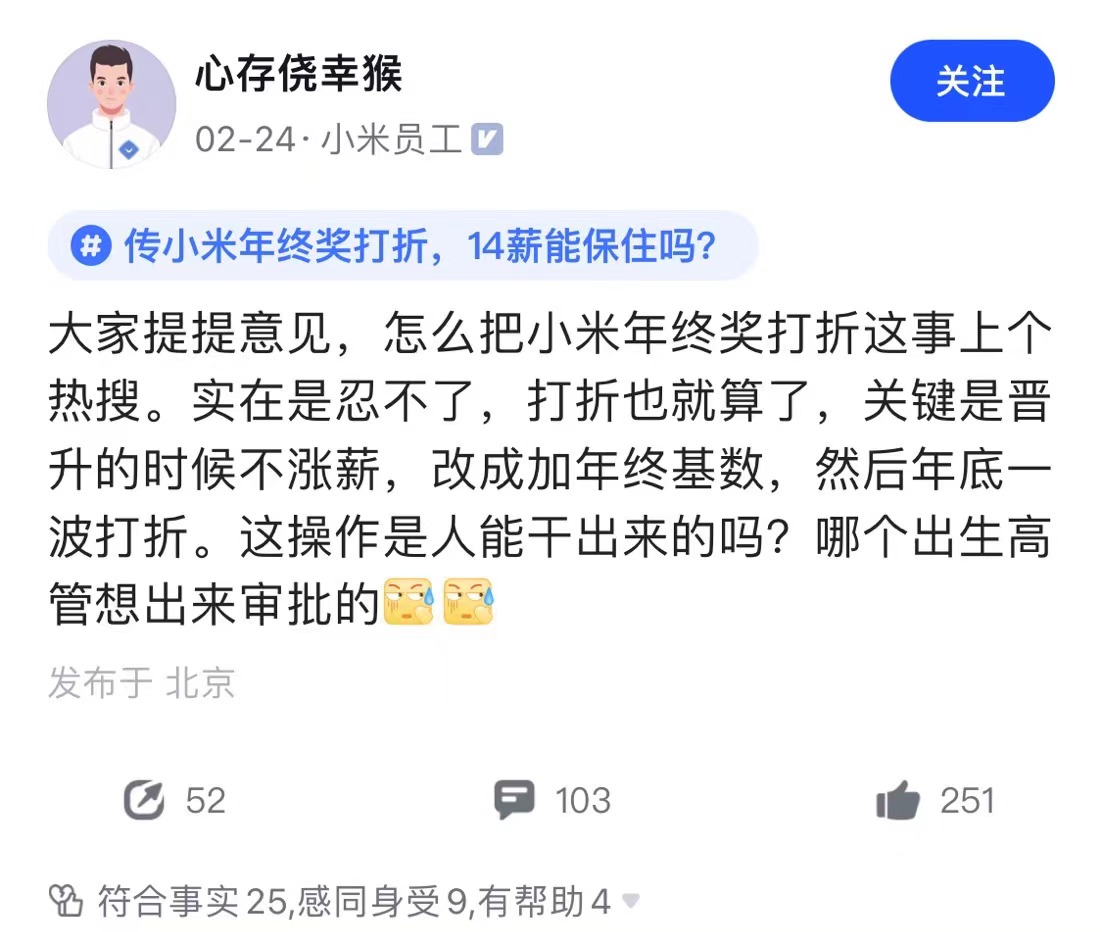
有网友爆料,小米晋升不涨 base,而是涨年终奖基数,结果到了年底,却宣布年终打折。
如果情况属实,并非个例,那确实是逆天操作了。
不涨 base 涨年终,员工以为这是全部,结果高管在年底的第五层等你 ...
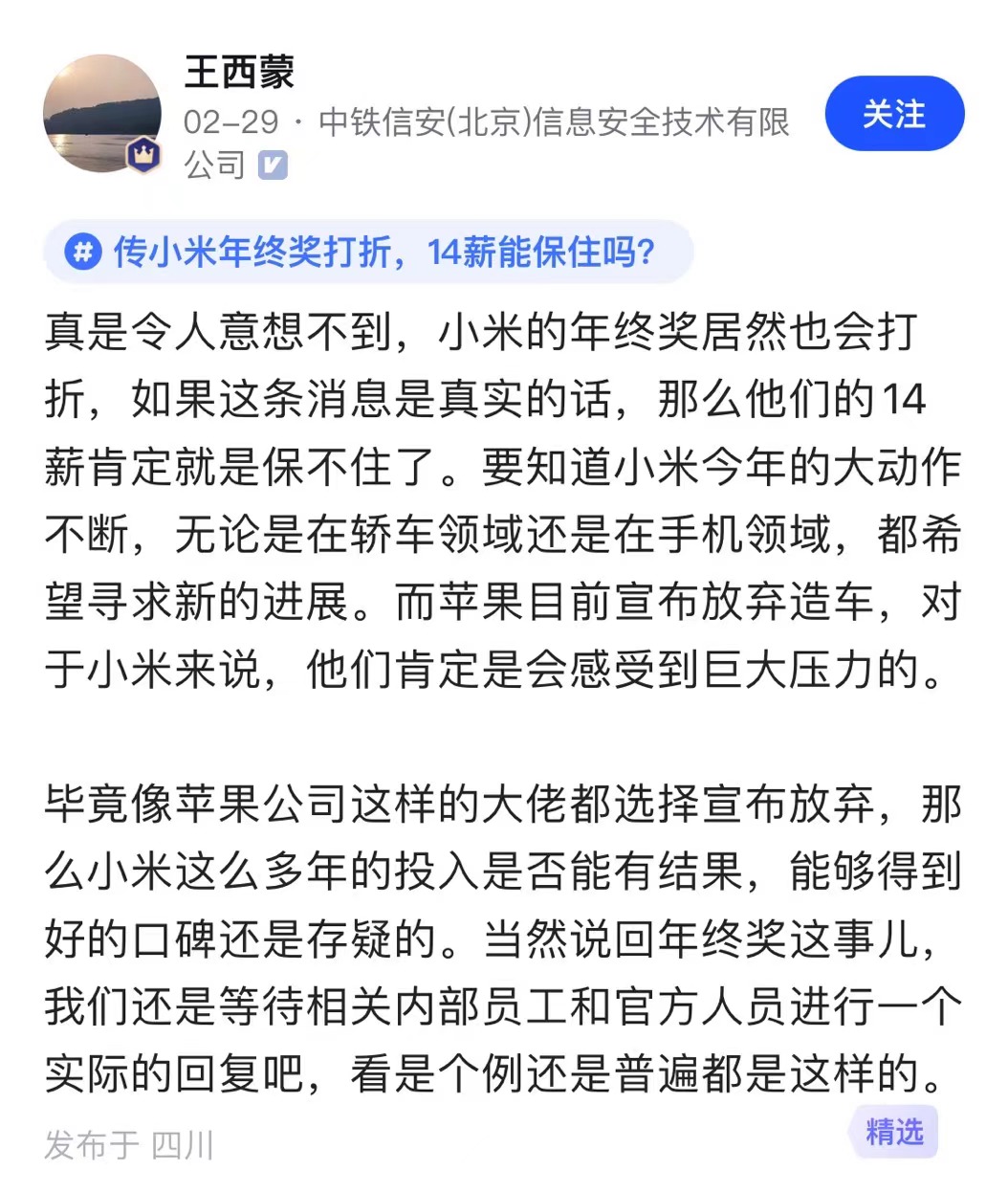
还有网友指出小米这两年动作频繁,可能面临诸多压力和风险,这些才是年终打折的内因。
尤其是小米汽车,花了大力气才实现量产,结果老大哥苹果则直接宣布放弃,可见在这赛道充满不确定性。
除此以外,雷总去年频繁捐钱,上了不少次热搜。对外"大方",对内"抠搜"也成为了被攻击的点之一。
有网友指出雷总宁愿捐钱也不发给自己人,但也有网友反驳道,雷军的捐钱都是个人出资,属于个人行为,而公司决定不发钱,往往公司决策层的行为。
这两方观点都有点"极端",现实情况往往不是非黑即白。
雷军的对外形象就是代表小米,所以说捐款行为没有任何企业形象方面的考虑,显然不可能,反而以雷军个人名义捐款,比以小米公司名义进行捐款,更有宣传效果。
而且雷军目前仍是小米的实控人,同时仍活跃在企业管理的方方面面,因此不发年终或年终打折这样的决策,你说雷军没有参与决策,或者说在决策中没有起到决定性作用,显然也不现实。
对此你怎么看呢?你对小米的印象如何?
...
回归主线。
来做一道和「小米」相关的面试原题。
题目描述
平台:LeetCode
题号:1797
你需要设计一个包含验证码的验证系统。
每一次验证中,用户会收到一个新的验证码,这个验证码在 ct 时刻之后 timeToLive 秒过期。
如果验证码被更新了,那么它会在 ct (可能与之前的 ct 不同)时刻延长 timeToLive 秒。
请你实现 AuthenticationManager 类:
-
AuthenticationManager(int timeToLive)构造AuthenticationManager并设置timeToLive参数。 -
generate(string id, int ct)给定id,在当前时间ct生成一个新的验证码。 -
renew(string id, int ct)将给定id且未过期的验证码在ct时刻更新。如果给定
id对应的验证码不存在或已过期,请你忽略该操作,不会有任何更新操作发生。 -
countUnexpiredTokens(int ct)请返回在给定ct时刻,未过期的验证码数目。
如果一个验证码在时刻 t 过期,且另一个操作恰好在时刻 t 发生(renew 或者 countUnexpiredTokens 操作),过期事件优先于其他操作。
示例 1: 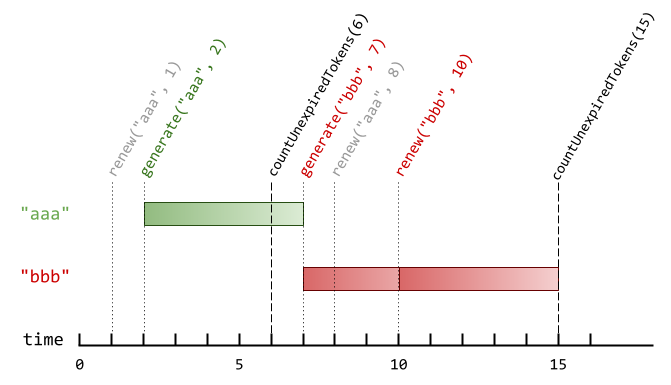
输入:
["AuthenticationManager", "renew", "generate", "countUnexpiredTokens", "generate", "renew", "renew", "countUnexpiredTokens"]
[[5], ["aaa", 1], ["aaa", 2], [6], ["bbb", 7], ["aaa", 8], ["bbb", 10], [15]]
输出:
[null, null, null, 1, null, null, null, 0]
解释:
AuthenticationManager authenticationManager = new AuthenticationManager(5); // 构造 AuthenticationManager ,设置 timeToLive = 5 秒。
authenticationManager.renew("aaa", 1); // 时刻 1 时,没有验证码的 tokenId 为 "aaa" ,没有验证码被更新。
authenticationManager.generate("aaa", 2); // 时刻 2 时,生成一个 tokenId 为 "aaa" 的新验证码。
authenticationManager.countUnexpiredTokens(6); // 时刻 6 时,只有 tokenId 为 "aaa" 的验证码未过期,所以返回 1 。
authenticationManager.generate("bbb", 7); // 时刻 7 时,生成一个 tokenId 为 "bbb" 的新验证码。
authenticationManager.renew("aaa", 8); // tokenId 为 "aaa" 的验证码在时刻 7 过期,且 8 >= 7 ,所以时刻 8 的renew 操作被忽略,没有验证码被更新。
authenticationManager.renew("bbb", 10); // tokenId 为 "bbb" 的验证码在时刻 10 没有过期,所以 renew 操作会执行,该 token 将在时刻 15 过期。
authenticationManager.countUnexpiredTokens(15); // tokenId 为 "bbb" 的验证码在时刻 15 过期,tokenId 为 "aaa" 的验证码在时刻 7 过期,所有验证码均已过期,所以返回 0 。
提示:
-
-
-
-
id只包含小写英文字母。 -
所有 generate函数的调用都会包含独一无二的id值。 -
所有函数调用中, ct的值严格递增。 -
所有函数的调用次数总共不超过 2000次。
哈希表
数据范围只有 20,我们使用哈希表记录每个 id 的过期时间 ct,在每次查询时遍历整个哈希表来统计未过期的验证码数量。
Java 代码:
class AuthenticationManager {
int d;
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
public AuthenticationManager(int timeToLive) {
d = timeToLive;
}
public void generate(String id, int ct) {
map.put(id, ct + d);
}
public void renew(String id, int ct) {
if (!map.containsKey(id) || map.get(id) <= ct) return ;
map.put(id, ct + d);
}
public int countUnexpiredTokens(int ct) {
int ans = 0;
for (String id : map.keySet()) {
if (map.get(id) > ct) ans++;
}
return ans;
}
}
C++ 代码:
class AuthenticationManager {
int d;
unordered_map<string, int> map;
public:
AuthenticationManager(int timeToLive) : d(timeToLive){}
void generate(string id, int ct) {
map[id] = ct + d;
}
void renew(string id, int ct) {
if (!map.count(id) || map[id] <= ct) return;
map[id] = ct + d;
}
int countUnexpiredTokens(int ct) {
int ans = 0;
for (auto it = map.begin(); it != map.end(); ++it) {
if (it->second > ct) ans++;
}
return ans;
}
};
Python 代码:
class AuthenticationManager:
def __init__(self, timeToLive):
self.d = timeToLive
self.map = {}
def generate(self, id: str, ct: int) -> None:
self.map[id] = ct + self.d
def renew(self, id: str, ct: int) -> None:
if id not in self.map or self.map[id] <= ct:
return
self.map[id] = ct + self.d
def countUnexpiredTokens(self, ct: int) -> int:
ans = 0
for id in self.map:
if self.map[id] > ct:
ans += 1
return ans
TypeScript 代码:
class AuthenticationManager {
d: number;
map: { [id: string]: number } = {};
constructor(timeToLive: number) {
this.d = timeToLive;
}
generate(id: string, ct: number): void {
this.map[id] = ct + this.d;
}
renew(id: string, ct: number): void {
if (!this.map.hasOwnProperty(id) || this.map[id] <= ct) {
return;
}
this.map[id] = ct + this.d;
}
countUnexpiredTokens(ct: number): number {
let ans = 0;
for (const id in this.map) {
if (this.map[id] > ct) {
ans++;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
-
时间复杂度: generate操作和renew操作的复杂度为 ;countUnexpiredTokens操作的复杂度为 -
空间复杂度:
双向链表
在所有函数的调用过程中,timeToLive 都在单调递增。
在哈希表的做法里,我们没有清理旧验证码的操作,同时每次执行 countUnexpiredTokens 时,需要对整个哈希表进行遍历。
实际上,如果我们引入 「双向链表」,并将哈希表的键值对定义从 {验证码:过期时间值} 调整为 {验证码:链表节点} 时(链表节点属性仅包含验证码字符串 id 及其过期时间 t),我们便能实现如下优化:
-
「减少统计未过期验证码时的无效遍历」:由于构建的双向链表严格按照
timeToLive递增,因此可以从尾部出发,从后往前利用链表节点的prev指针进行遍历统计。如此一来,有多少未过期的验证码,我们就会遍历多少个链表节点,其余已过期的节点对象并不会被访问;
-
「引入清理时机」:由于上述的统计过程,我们会找到最靠前的一个未过期节点。可以将其作为新的双向链表新头结点,从而将整段的过期节点从双向链表中删除
最后,我们像对其他链表题目一样,为了方便,引入 he 和 ta 的头尾链表哨兵节点以减少边界处理。
Java 代码:
class AuthenticationManager {
class Node {
String id;
int t;
Node prev, next;
Node (String _id, int _t) {
id = _id; t = _t;
}
}
int d;
Node he, ta;
Map<String, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
public AuthenticationManager(int timeToLive) {
he = new Node("", -1); ta = new Node("", (int)1e9);
he.next = ta; ta.prev = he;
d = timeToLive;
}
public void generate(String id, int ct) {
Node node = new Node(id, ct + d);
node.prev = ta.prev;
node.next = ta;
ta.prev.next = node;
ta.prev = node;
map.put(id, node);
}
public void renew(String id, int ct) {
if (!map.containsKey(id) || map.get(id).t <= ct) return ;
Node node = map.get(id);
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
generate(id, ct);
}
public int countUnexpiredTokens(int ct) {
int ans = 0;
Node cur = ta.prev;
while (cur.t > ct && ++ans >= 0) cur = cur.prev;
he.next = cur.next;
cur.next.prev = he;
return ans;
}
}
C++ 代码:
class AuthenticationManager {
struct Node {
string id;
int t;
Node *prev, *next;
Node (string _id, int _t) : id(_id), t(_t), prev(nullptr), next(nullptr) {}
};
int d;
Node *he, *ta;
unordered_map<string, Node*> map;
public:
AuthenticationManager(int timeToLive) : d(timeToLive) {
he = new Node("", -1);
ta = new Node("", (int)1e9);
he->next = ta;
ta->prev = he;
}
void generate(string id, int ct) {
Node* node = new Node(id, ct + d);
node->prev = ta->prev;
node->next = ta;
ta->prev->next = node;
ta->prev = node;
map[id] = node;
}
void renew(string id, int ct) {
if (!map.count(id) || map[id]->t <= ct) return;
Node* node = map[id];
node->prev->next = node->next;
node->next->prev = node->prev;
generate(id, ct);
}
int countUnexpiredTokens(int ct) {
int ans = 0;
Node* cur = ta->prev;
while (cur->t > ct && ++ans >= 0) cur = cur->prev;
he->next = cur->next;
cur->next->prev = he;
return ans;
}
};
TypeScript 代码:
class Node {
id: string;
t: number;
prev: Node | null;
next: Node | null;
constructor(_id: string, _t: number) {
this.id = _id;
this.t = _t;
this.prev = null
this.next = null
}
}
class AuthenticationManager {
d: number;
he: Node;
ta: Node;
map: {[id: string]: Node};
constructor(timeToLive: number) {
this.d = timeToLive;
this.he = new Node("", -1)
this.ta = new Node("", 1e9)
this.he.next = this.ta
this.ta.prev = this.he
this.map = {};
}
generate(id: string, ct: number) {
let node : Node = new Node(id, ct + this.d) ;
node.prev = this.ta.prev;
node.next = this.ta;
this.ta.prev!.next = node;
this.ta.prev = node;
this.map[id] = node;
}
renew(id: string, ct: number) {
if (!this.map.hasOwnProperty(id) || this.map[id].t <= ct) {
return;
}
var node : Node = this.map[id];
node.prev!.next = node.next;
node.next!.prev = node.prev;
this.generate(id, ct);
}
countUnexpiredTokens(ct: number) {
let ans = 0;
let cur : Node = this.ta.prev!;
while (cur.t > ct && ++ans >= 0)
cur = cur.prev!;
this.he.next = cur.next;
cur.next!.prev = this.he;
return ans;
}
}
-
时间复杂度: generate操作和renew操作的复杂度为 ;countUnexpiredTokens操作的复杂度为 -
空间复杂度:
我是宫水三叶,每天都会分享算法知识,并和大家聊聊近期的所见所闻。
欢迎关注,明天见。
更多更全更热门的「笔试/面试」相关资料可访问排版精美的 合集新基地 🎉🎉