给定单个链表的头 head ,使用 插入排序 对链表进行排序,并返回 排序后链表的头 。
插入排序 算法的步骤:
- 插入排序是迭代的,每次只移动一个元素,直到所有元素可以形成一个有序的输出列表。
- 每次迭代中,插入排序只从输入数据中移除一个待排序的元素,找到它在序列中适当的位置,并将其插入。
- 重复直到所有输入数据插入完为止。
下面是插入排序算法的一个图形示例。部分排序的列表(黑色)最初只包含列表中的第一个元素。每次迭代时,从输入数据中删除一个元素(红色),并就地插入已排序的列表中。
对链表进行插入排序。

示例 1:
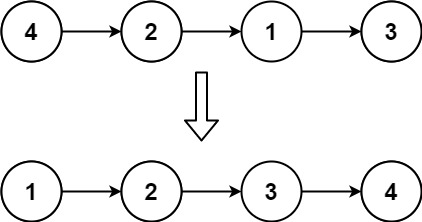
输入: head = [4,2,1,3] 输出: [1,2,3,4]
示例 2:
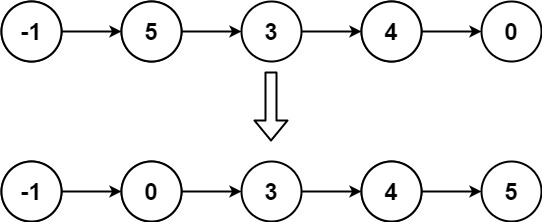
输入: head = [-1,5,3,4,0] 输出: [-1,0,3,4,5]
解法一
所谓的插入排序,就是一次拿一个数把它插入到正确的位置。
举个例子。
4 2 1 3
res = []
拿出 4
res = [4]
拿出 2
res = [2 4]
拿出 1
res = [1 2 4]
拿出 3
res = [1 2 3 4]
用代码的实现的话,因为要拿出一个要插入到已经排好序的链表中,首先肯定是依次遍历链表,找到第一个比要插入元素大的位置,把它插到前边。
至于插入的话,我们需要知道插入位置的前一个节点,所以我们可以用 node.next 和要插入的节点比较,node 就是插入位置的前一个节点了。
而 head 指针已经是最前了,所以我们可以用一个 dummy 指针,来将头指针的情况统一。
public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
//拿出的节点
while (head != null) {
ListNode tempH = dummy;
ListNode headNext = head.next;
head.next = null;
while (tempH.next != null) {
//找到大于要插入的节点的位置
if (tempH.next.val > head.val) {
head.next = tempH.next;
tempH.next = head;
break;
}
tempH = tempH.next;
}
//没有执行插入,将当前节点加到末尾
if (tempH.next == null) {
tempH.next = head;
}
head = headNext;
}
return dummy.next;
}
这里-space-) 还有另一种写法,分享一下。
public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) {
if( head == null ){
return head;
}
ListNode helper = new ListNode(0); //new starter of the sorted list
ListNode cur = head; //the node will be inserted
ListNode pre = helper; //insert node between pre and pre.next
ListNode next = null; //the next node will be inserted
//not the end of input list
while( cur != null ){
next = cur.next;
//find the right place to insert
while( pre.next != null && pre.next.val < cur.val ){
pre = pre.next;
}
//insert between pre and pre.next
cur.next = pre.next;
pre.next = cur;
pre = helper;
cur = next;
}
return helper.next;
}