个人主页 : 个人主页
个人专栏 : 《数据结构》 《C语言》《C++》《Linux》
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、线程的总结
- 1. 线程的优点
- 2. 线程的缺点
- 3. 线程异常
- 4.线程和进程
- 二、线程的控制
- 创建线程
- 线程终止
- 线程等待
- 获取返回值
- 线程分离
- 总结
前言
本文作为我对于线程的简单总结,线程控制的知识总结
一、线程的总结
1. 线程的优点
- 创建一个新线程的代价比创建一个新进程小的多
- 与进程之间的切换相比,线程之间的切换需要操作系统做的工作要小
- 线程占有的资源要比进程少很多
- 能充分利用多处理器的可并行数量(并行,多个执行流在同一时刻拿着不同的CPU继续运算,执行代码)
- 在等待慢速I/O操作结束的同时,程序可执行其他的计算任务
- 计算密集型应用,为了能在多处理器系统上运行,将计算分解到多个线程中实现
- I/O密集型应用(如下载,上传),为了提高性能,将I/O操作重叠。线程可以同时等待不同的I/O操作
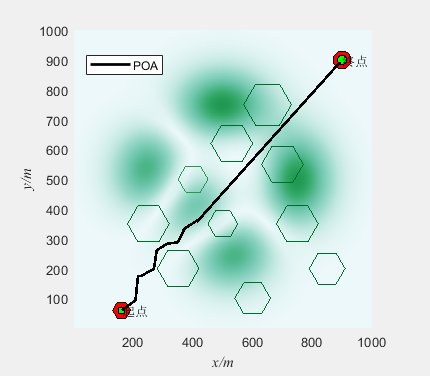
创建线程并不是越多越好,进程的执行效率,一定随着线程的数量增多,效率为正态分布的(线程的切换)。线程的个数最好 = CPU的个数 * CPU的核数
2. 线程的缺点
- 性能损失:一个很少被外部事件阻塞的计算密集型线程往往无法与其他线程共享同一个处理器,如果计算密集型线程的数量比可用的处理器多,那么可能会有较大的性能损失,如增加了额外的同步和调度开销,而可用的资源不变
- 健壮性(鲁棒性)降低:编写多线程需要全面更深入的考虑,在一个多线程程序里,因时间分配的细微偏差或者因共享了不该共享的变量而造成不良影响的可能性是很大的,也就是说线程之间是缺乏保护的
- 缺乏访问控制:因为线程共享地址空间,那一个线程定义的局部变量 or new出的空间,其它线程也能使用,这就导致一个线程可能会不小心修改另一个线程正在使用的数据,导致数据不一致、逻辑错误甚至程序崩溃
- 编程难度提高:编写与调试一个多线程程序比单线程程序困难
3. 线程异常
- 单个线程如果出现除0,野指针问题导致线程崩溃,进程也会崩溃
- 线程是进程的执行分支,线程出异常,就类似进程出异常,进而触发信号机制,终止进程,进程终止,该进程内的所有线程也全部终止
创建5个线程,其中线程thread-4触发除0异常。
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string>
#include <functional>
#include <time.h>
#include <vector>
using func_t = std::function<void()>;
const int threadnum = 5;
class ThreadDate
{
public:
ThreadDate(const std::string &name, const uint64_t &time, func_t f)
: threadname(name), createtime(time), func(f)
{
}
public:
std::string threadname;
uint64_t createtime;
func_t func;
};
void Print()
{
std::cout << "执行的任务..." << std::endl;
}
void *threadRoutine(void *args)
{
ThreadDate *td = static_cast<ThreadDate *>(args);
while (true)
{
std::cout << "new thread "
<< " name: " << td->threadname << " create time: " << td->createtime << std::endl;
td->func();
if(td->threadname == "thread-4")
{
std::cout << td->threadname << "触发异常" << std::endl;
int a = 10;
a /= 0;
}
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
std::vector<pthread_t> pthreads;
for (int i = 0; i < threadnum; ++i)
{
char threadname[64];
snprintf(threadname, sizeof(threadname), "%s-%d", "thread", i);
pthread_t tid;
ThreadDate *td = new ThreadDate(threadname, (uint64_t)time(nullptr), Print);
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, (void *)td);
pthreads.push_back(tid);
sleep(1);
}
while (true)
{
std::cout << "main thread" << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
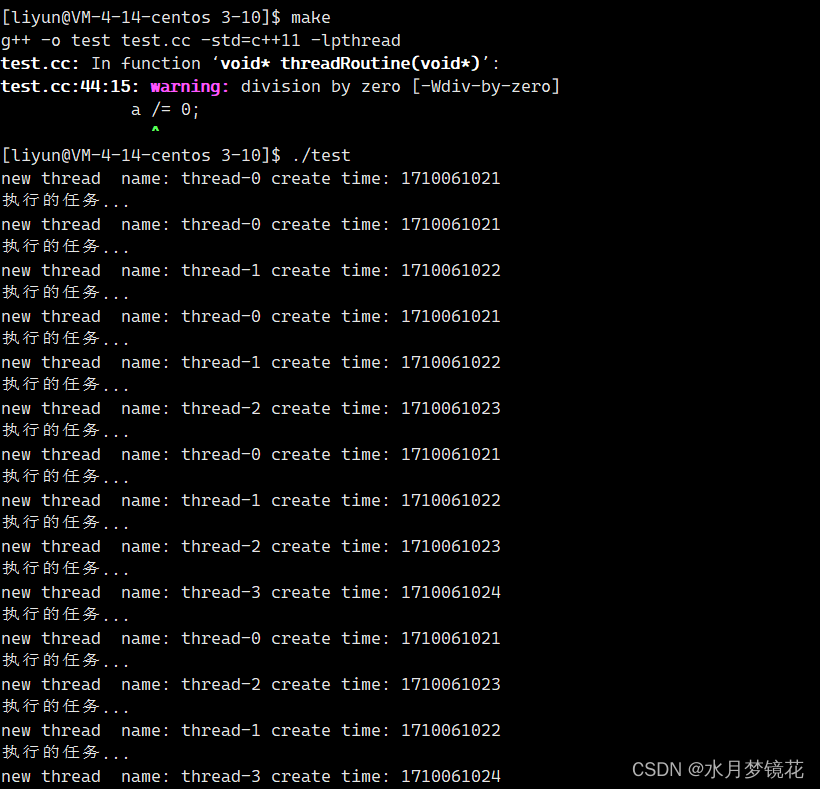
其中thread-4线程触发异常,进程直接终止。
4.线程和进程
- 进程是资源分配的基本单位
- 线程是调度的基本单位
- 线程共享进程数据,但也有自己的一部分独立的数据(线程ID,线程的上下文数据,独立的栈结构(pthread库维护),errno,信号屏蔽字,调度优先级)
- 进程的多个线程共享同一个地址空间,因此地址空间的代码段,数据段都是共享的,线程还共享进程的文件描述符表,每种信号的处理方式(SIG_IGN,SIG_DFL,自定义的信号处理函数),当前工作目录(cwd),用户id和组id
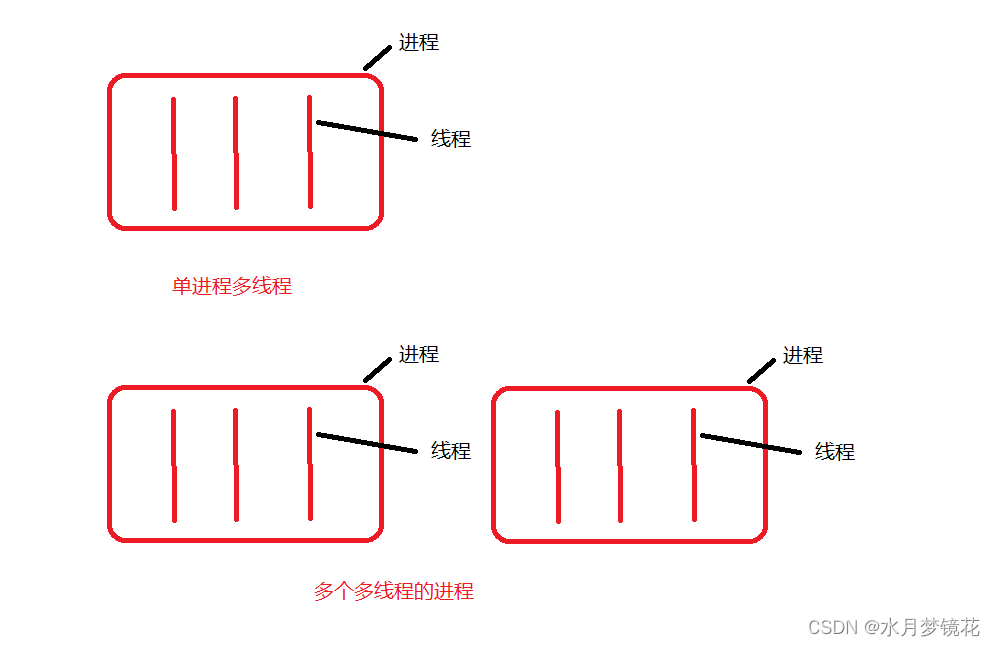
进程和线程的关系如下:
二、线程的控制
创建线程
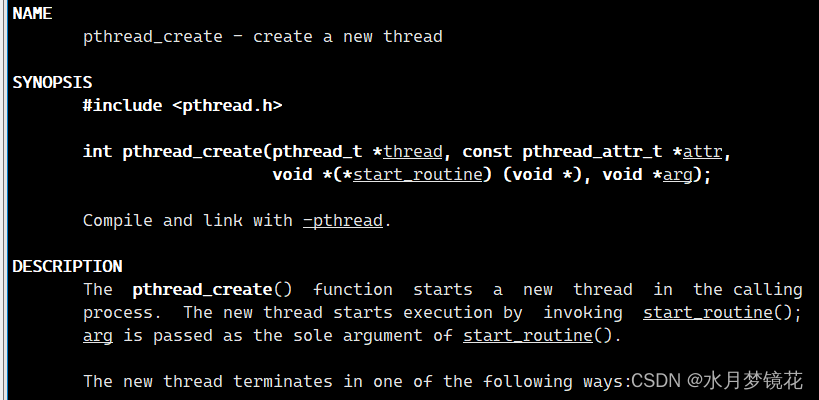
函数原型: int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);
功能:创建一个新的线程
参数:thread:返回线程ID
attr:设置线程属性,attr为nullptr表示使用默认属性
start_routine:是函数指针,为线程启动后要执行的函数
arg:传给线程启动函数的参数
返回值:成功返回0,失败返回错误码
错误检查:传统的一些函数,成功返回0,失败返回-1,并且对全局变量errno赋值以指示错误。pthreads函数出错时不会设置全局变量errno,而是将错误码通过返回值返回。pthreads也同样提供线程内errno变量,以支持其它使用errno的代码。对于pthreads函数的错误,建议通过返回值的判定,因为读取返回值要比读取线程内的errno变量更方便。
下面我们要创建一个新线程循环打印"new thread’,主线程循环打印"main thread"
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void *threadRoutine(void *args)
{
while(true)
{
std::cout << "new thread" << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, nullptr);
while(true)
{
std::cout << "main thread" << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
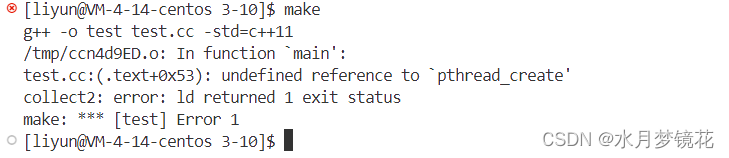
编译时会有报错,编译器不认识pthread_create这个函数,但我们不是加了头文件吗?
我们知道linux没有真正的线程,只有轻量级进程的概念,所以操作系统只会提供轻量级进程创建的系统调用,不会直接提供线程创建的接口。linux为了解决这一问题,就在软件层创建了pthread原生线程库对用户提供线程控制接口,在内部将线程与轻量级进程一一对应。
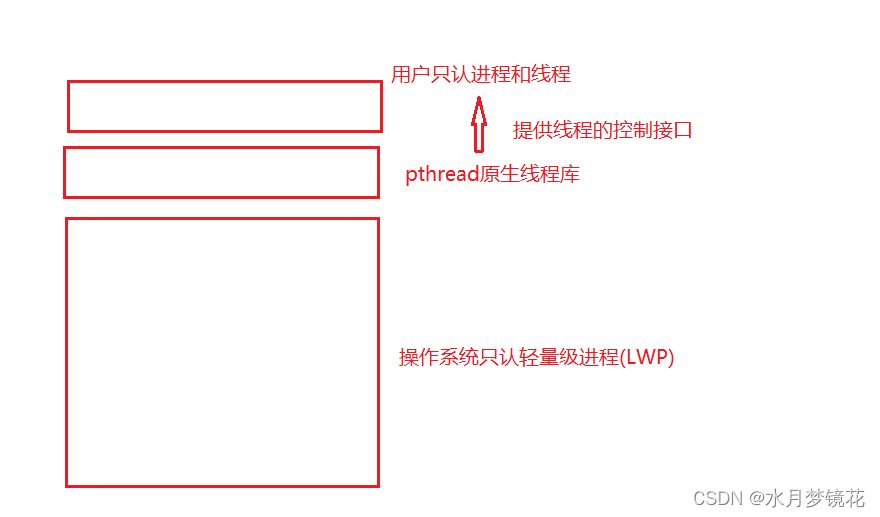
这样有什么好处?标准化和兼容性(pthread编写的多线程应用程序在遵循POSIX标准的各种Unix-like系统上(包括Linux)都具有很高的可移植性),灵活性:pthread库提供了一套丰富的API,用于线程的创建、管理、同步和通信。这使得开发者可以根据应用程序的需求灵活地创建和管理线程,实现复杂的并发和并行计算任务。
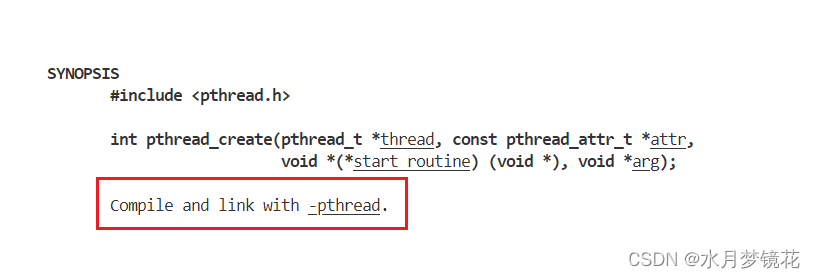

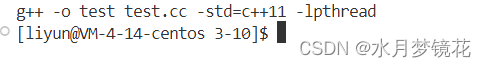
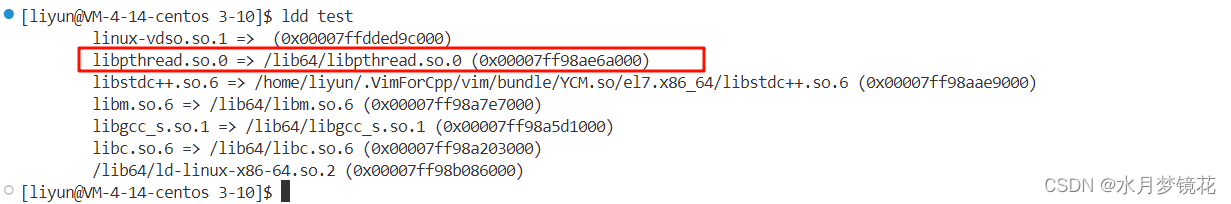

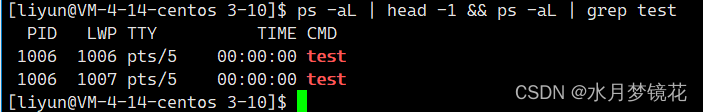
结果如上。
如何给创建的线程传参?
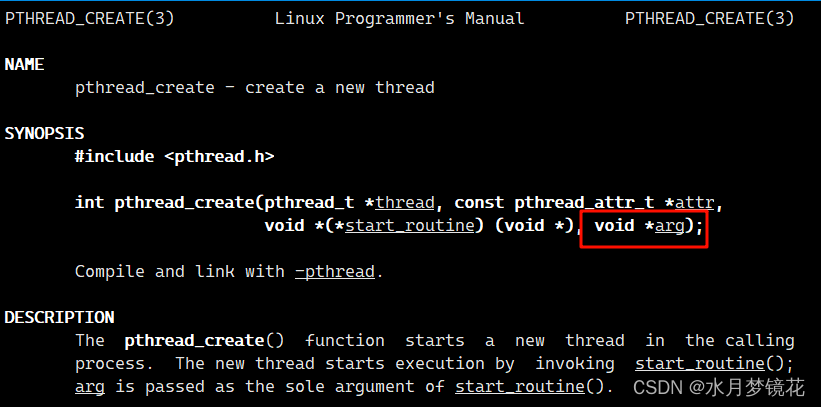
如上,arg的类型是void*类型,表示任意类型的指针。也就是说,我们可以穿一个整形,字符串,结构体对象。如下传递结构体。
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string>
#include <functional>
#include <time.h>
using func_t = std::function<void()>;
class ThreadDate
{
public:
ThreadDate(const std::string &name, const uint64_t &time, func_t f)
:threadname(name), createtime(time), func(f)
{}
public:
std::string threadname;
uint64_t createtime;
func_t func;
};
void Print()
{
std::cout << "执行的任务..." << std::endl;
}
void *threadRoutine(void *args)
{
ThreadDate * td = static_cast<ThreadDate*>(args);
while(true)
{
std::cout << "new thread "<< " name: " << td->threadname << " create time: " << td->createtime<< std::endl;
td->func();
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
ThreadDate * td = new ThreadDate("thread-1", (uint64_t)time(nullptr), Print);
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, (void *)td);
while(true)
{
std::cout << "main thread" << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
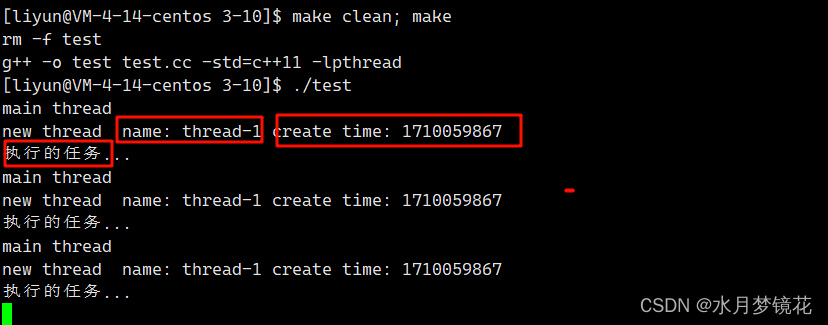
那如何一次创建多个线程?与创建多个子进程类似。
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string>
#include <functional>
#include <time.h>
#include <vector>
using func_t = std::function<void()>;
const int threadnum = 5;
class ThreadDate
{
public:
ThreadDate(const std::string &name, const uint64_t &time, func_t f)
: threadname(name), createtime(time), func(f)
{
}
public:
std::string threadname;
uint64_t createtime;
func_t func;
};
void Print()
{
std::cout << "执行的任务..." << std::endl;
}
void *threadRoutine(void *args)
{
ThreadDate *td = static_cast<ThreadDate *>(args);
while (true)
{
std::cout << "new thread "
<< " name: " << td->threadname << " create time: " << td->createtime << std::endl;
td->func();
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
std::vector<pthread_t> pthreads;
for (int i = 0; i < threadnum; ++i)
{
char threadname[64];
snprintf(threadname, sizeof(threadname), "%s-%d", "thread", i);
pthread_t tid;
ThreadDate *td = new ThreadDate(threadname, (uint64_t)time(nullptr), Print);
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, (void *)td);
pthreads.push_back(tid);
sleep(1);
}
while (true)
{
std::cout << "main thread" << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}

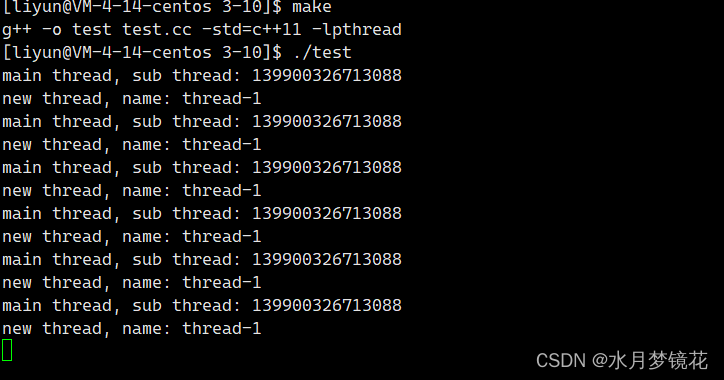
下面代码,创建线程并通过返回值打印其线程id。
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
void *threadRoutine(void *args)
{
std::string name = static_cast<const char*>(args);
while(true)
{
std::cout << "new thread, name: " << name << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, (void*)"thread-1");
while(true)
{
std::cout << "main thread, sub thread: " << tid << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
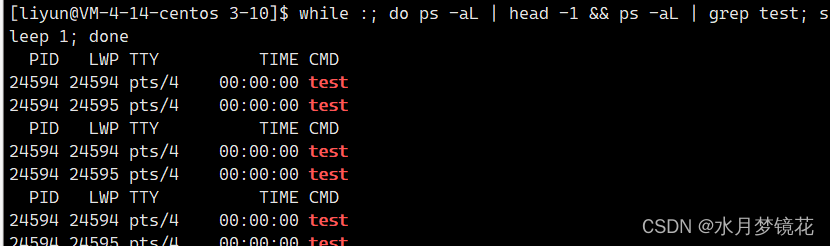
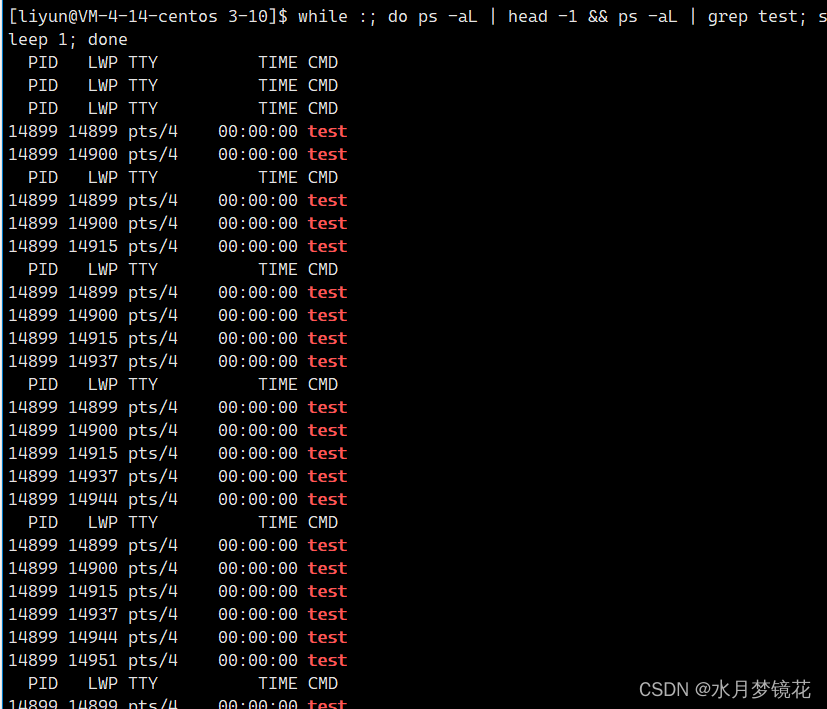
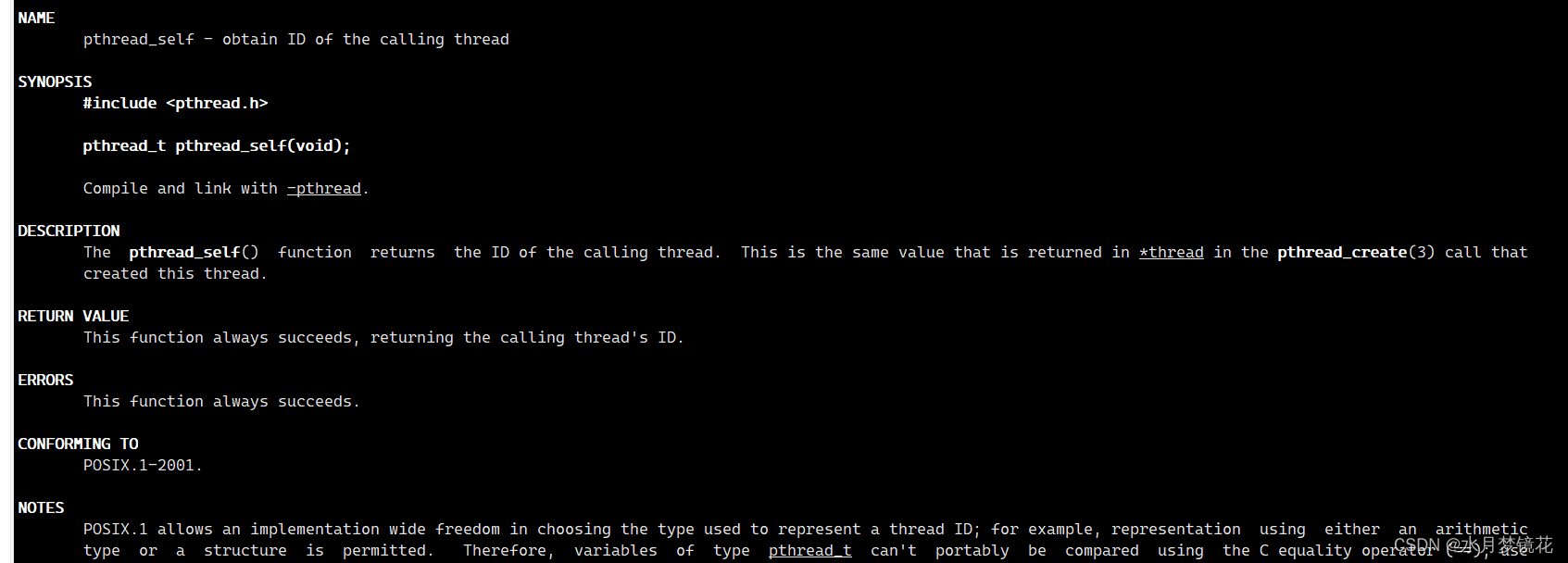
很明显,创建出来的线程id与LWP并不同,那主线程的id值是否也与LWP不同?这我们就要了解一个接口pthread_self(线程获取自己的id)
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
void *threadRoutine(void *args)
{
std::string name = static_cast<const char*>(args);
while(true)
{
std::cout << "new thread, name: " << name << "thread id is " << pthread_self() << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, (void*)"thread-1");
while(true)
{
std::cout << "main thread id " << pthread_self() << "sub thread id " << tid << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
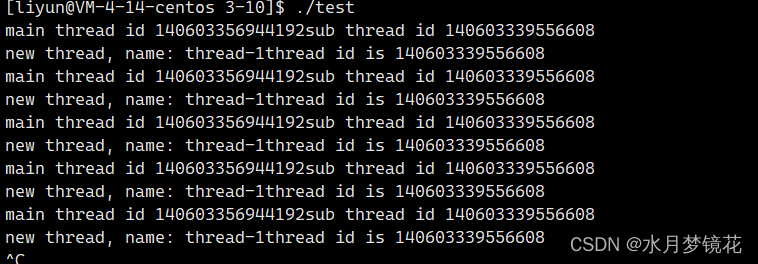
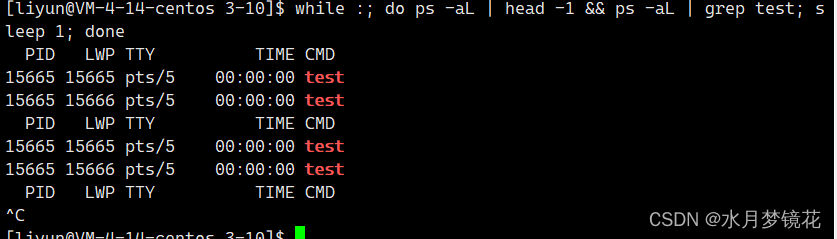
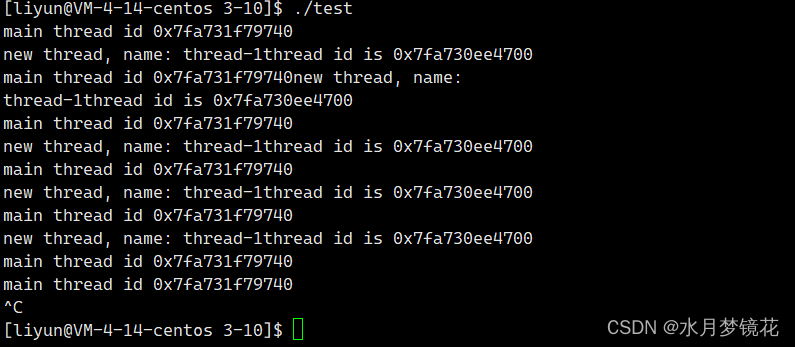
主线程的id与新线程的id明显不是LWP,那是什么呢?我们以十六进制打印看看。
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
// 转换为十六进制
std::string ToHex(pthread_t tid)
{
char id[64];
snprintf(id, sizeof(id), "0x%lx", tid);
return id;
}
void *threadRoutine(void *args)
{
std::string name = static_cast<const char*>(args);
while(true)
{
std::cout << "new thread, name: " << name << "thread id is " << ToHex(pthread_self()) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, (void*)"thread-1");
while(true)
{
std::cout << "main thread id " << ToHex(pthread_self()) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
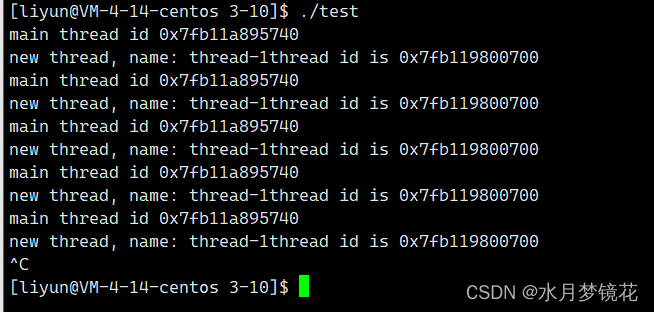
现在,这个线程id是不是很像地址? 没错,线程id就是地址。
线程终止
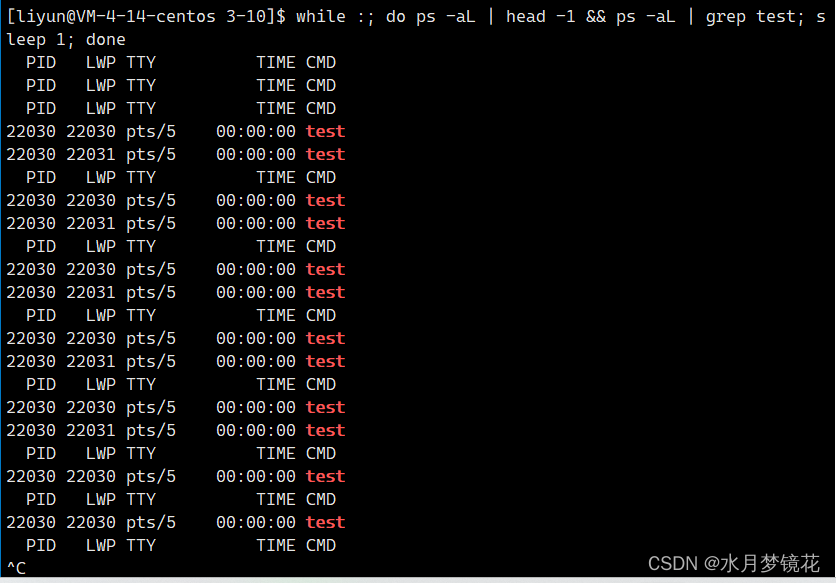
如果需要只终止某个线程而不终止整个进程,可以有三个方法:
- 从线程函数return。这种方法对主线程不适用,从main函数return相当于调用exit函数
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
// 转换为十六进制
std::string ToHex(pthread_t tid)
{
char id[64];
snprintf(id, sizeof(id), "0x%lx", tid);
return id;
}
void *threadRoutine(void *args)
{
std::string name = static_cast<const char*>(args);
int cnt = 5;
while(cnt--)
{
std::cout << "new thread, name: " << name << "thread id is " << ToHex(pthread_self()) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return nullptr; // 线程终止
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, (void*)"thread-1");
while(true)
{
std::cout << "main thread id " << ToHex(pthread_self()) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
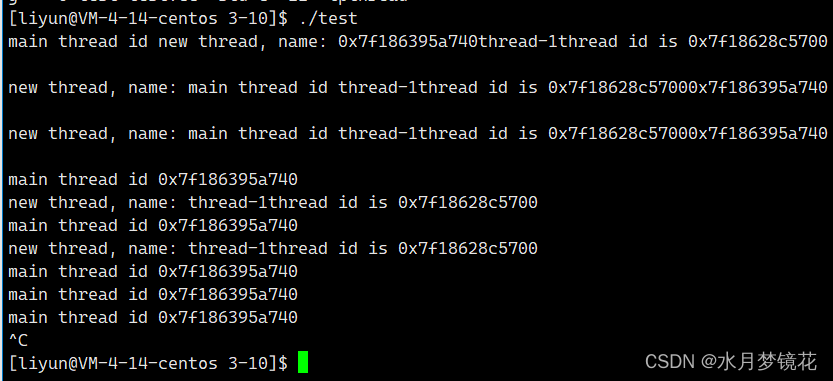
- 线程可以调用pthread_exit终止自己
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
// 转换为十六进制
std::string ToHex(pthread_t tid)
{
char id[64];
snprintf(id, sizeof(id), "0x%lx", tid);
return id;
}
void *threadRoutine(void *args)
{
std::string name = static_cast<const char*>(args);
int cnt = 5;
while(cnt--)
{
std::cout << "new thread, name: " << name << "thread id is " << ToHex(pthread_self()) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
//return nullptr; // 线程终止
pthread_exit(nullptr);
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, (void*)"thread-1");
while(true)
{
std::cout << "main thread id " << ToHex(pthread_self()) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
- 一个线程可以调用pthread_cancel终止同一进程中的另一个线程
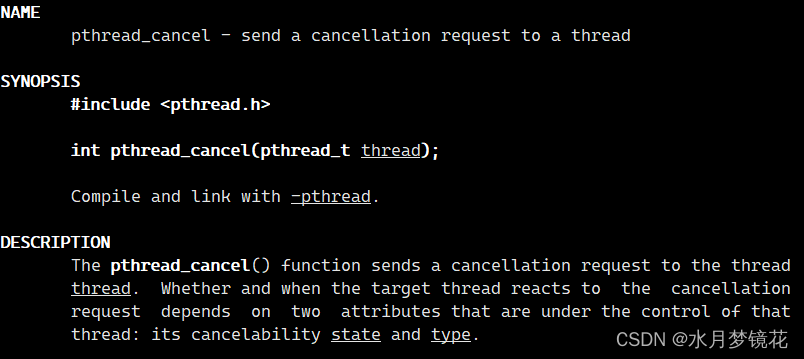
- 功能:取消一个执行中的线程
- 参数 thread:线程id
- 返回值:成功返回0,失败返回错误码
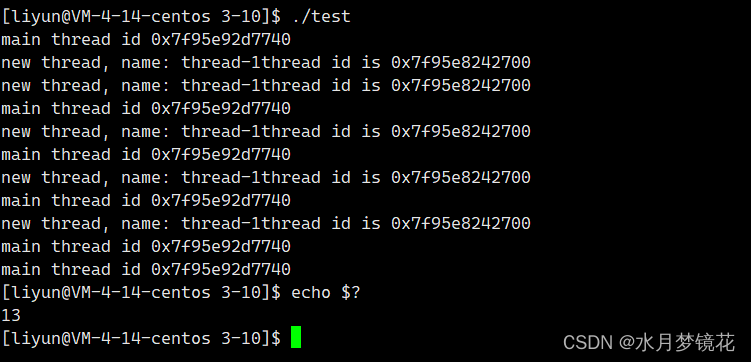
不能用exit函数来终止线程,这会导致这个进程被终止。
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
// 转换为十六进制
std::string ToHex(pthread_t tid)
{
char id[64];
snprintf(id, sizeof(id), "0x%lx", tid);
return id;
}
void *threadRoutine(void *args)
{
std::string name = static_cast<const char*>(args);
int cnt = 5;
while(cnt--)
{
std::cout << "new thread, name: " << name << "thread id is " << ToHex(pthread_self()) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
//return nullptr; // 线程终止
exit(13);
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, (void*)"thread-1");
while(true)
{
std::cout << "main thread id " << ToHex(pthread_self()) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
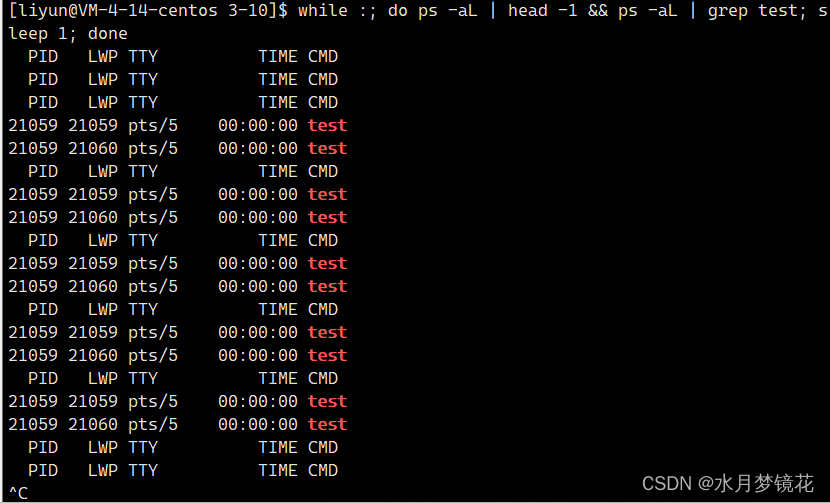
线程等待
获取返回值
我们知道子进程退出时会有僵尸状态,需要父进程来等待子进程。那线程也要被等待吗?是的,线程也要被等待。线程退出没有等待,也会导致类似进程的僵尸问题。线程通过等待获取新线程的返回值。
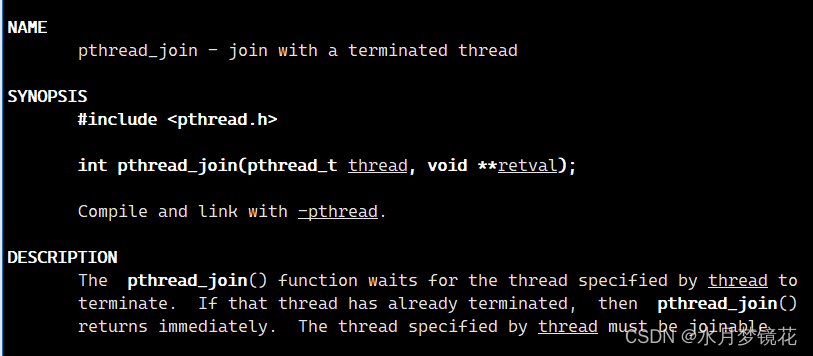
- thread:线程id
- retval:指向一个指针,后者指向返回值
- 返回值:等待成功返回0,失败返回错误码
调用该函数的线程将以阻塞的方式等待,直到id为thread的线程终止。thread线程以不同的方法终止,通过pthread_join的终止状态是不同的: - 如果thread线程通过return返回,retval所指向的单元存放的是thread线程函数的返回值
- 如果thread线程被别的线程调用pthread_cancel异常终止,retval所指向的单元存放的是常数PTHREAD_CANCELED
- 如果thread线程是自己调用pthread_exit终止的,retval所指向的单元存放的是传给pthread_exit的参数
- 如果不想获取thread的返回值,可以将nullptr传给retval
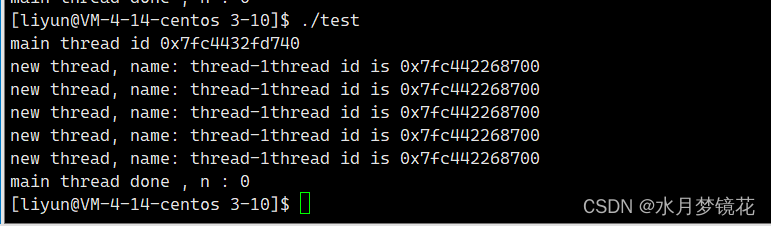
以从线程return为例。
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
// 转换为十六进制
std::string ToHex(pthread_t tid)
{
char id[64];
snprintf(id, sizeof(id), "0x%lx", tid);
return id;
}
void *threadRoutine(void *args)
{
std::string name = static_cast<const char *>(args);
int cnt = 5;
while (cnt--)
{
std::cout << "new thread, name: " << name << "thread id is " << ToHex(pthread_self()) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return nullptr; // 线程终止
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, (void *)"thread-1");
std::cout << "main thread id " << ToHex(pthread_self()) << std::endl;
int n = pthread_join(tid, nullptr);
std::cout << "main thread done , n : " << n << std::endl;
return 0;
}
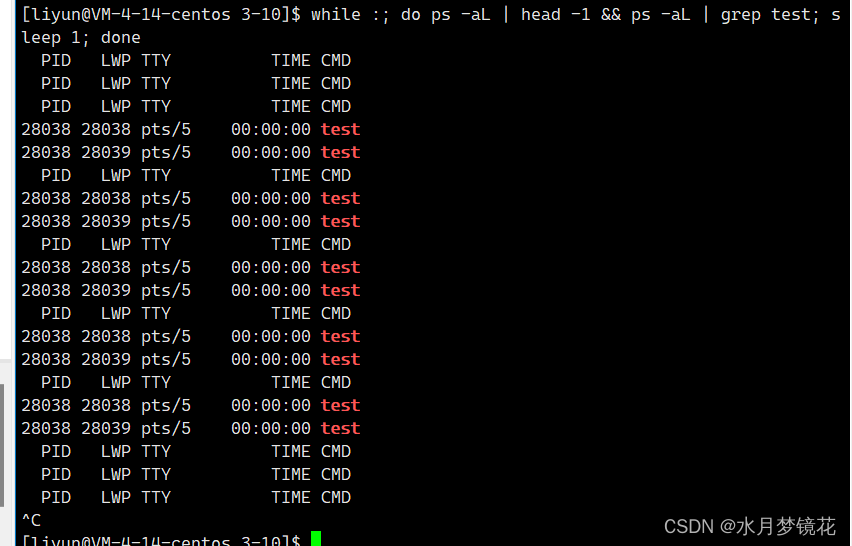
线程分离
对于一个线程,如果主线程要等待它,则会阻塞等待导致主线程自己的任务效率低。如果主线程不等待它,则可能导致类似僵尸进程的状态,使资源泄漏。这时我们就可以将线程分离。
线程可以设置为分离属性,一个线程如果被设置为分离属性,则该线程在退出之后,不需要其它执行流回收该线程资源,而是由操作系统进行回收。
- 默认情况下,新创建的线程是joinable的,线程退出后,需要对其进行pthread_join操作,否则无法释放资源,从而造成资源泄漏
- 如果不关心线程的返回值,join是一种负担,我们可以告诉系统,当线程退出时,自动释放线程资源。
- joinable和分离是冲突的,一个线程不能既是joinable又是分离的。如果等待一个分离的线程,函数会立即返回错误,错误码通常为EINVAL
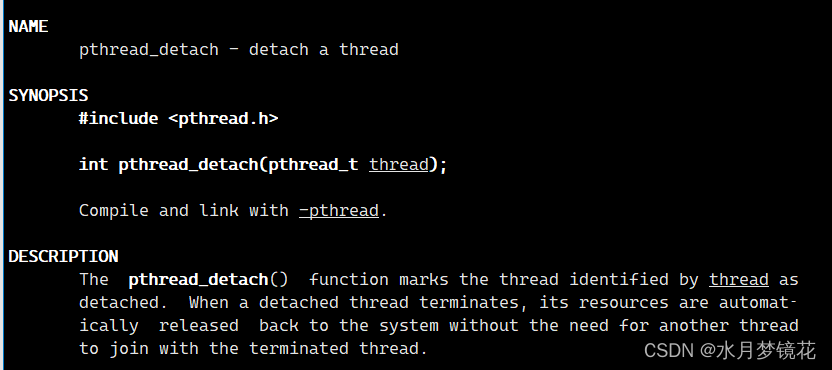
- thread:线程id
- 返回值:成功返回0,失败返回错误码
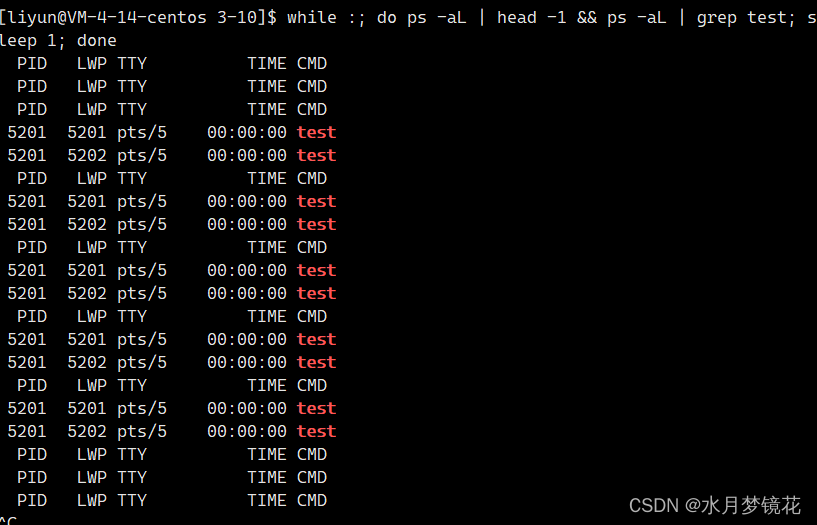
分离的线程在同一个进程地址空间,相互的线程不会相互干扰,但是如果分离的线程崩溃,进程也会崩溃。
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
// 转换为十六进制
std::string ToHex(pthread_t tid)
{
char id[64];
snprintf(id, sizeof(id), "0x%lx", tid);
return id;
}
void *threadRoutine(void *args)
{
std::string name = static_cast<const char *>(args);
int cnt = 5;
while (cnt--)
{
std::cout << "new thread, name: " << name << "thread id is " << ToHex(pthread_self()) << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
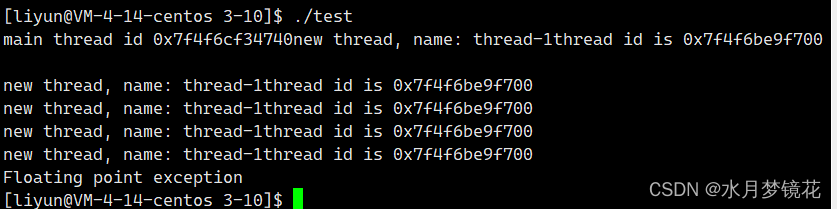
int a = 10;
a /= 0; // 除0异常
return nullptr; // 线程终止
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, (void *)"thread-1");
std::cout << "main thread id " << ToHex(pthread_self()) << std::endl;
sleep(10);
pthread_cancel(tid);
// int n = pthread_join(tid, nullptr);
// std::cout << "main thread done , n : " << n << std::endl;
return 0;
}
总结
以上就是我对于线程控制的总结。