八股文部分来源于网络,例子为原创
OOP(Object-oriented programming)
也就是面向对象编程,继承,封装,多态。
局限性
- 静态语言:类结构一旦定义,不容易被修改(并不是无法修改)。
- 只能侵入性扩展:通过继承和组合组织新的类结构(比如我们继承一个类然后重写法,在子类里面就可以使用super关键字调用父类的方法,同时在子类拓展我们的逻辑。)
AOP 应用场景
- 日志场景:比如log4j或logback中的MDC,比如打印方法的执行时间。
- 统计场景:比如方法执行次数,执行异常次数,数据抽样,
- 安防场景:比如熔断(Hystrix),限流和降级(Sentinel),认证和授权(Spring Security),监控(JMX)
- 性能场景:比如缓存(Spring Cache),超时控制
AOP的术语
AOP主要是拦截OOP中的方法,在Spirng中只支持拦截方法。让我们关注横切面,进行拦截。
1 切面(Aspect)
各个方面都是针对横切问题的模块化单位。它们的行为有点类似于Java类,但也可能包括切入点、建议和类型间声明。也就是把我们关注的公共的东西抽象处来形成一个切面。
2 连接点(Join Point)
程序执行过程中的一个点,例如方法的执行或异常的处理。在Spring AOP中,连接点总是表示方法的执行。
3 切点 Pointcut
用于匹配Joint Point 的条件,决定了我们是不是在这些切入点进行接入。
4 Advice 通知(befroe, after, around需要手动调用)
我们找到了切入点,我们需要执行的动作,在一个特定的Joint Poiont 进行操作。一个Aspect 多应多个JointPoint,一个Join Point对应多个Advice。
AOP的设计模式
- 代理模式 静态代理和动态代理
- 判断模式 类,方法,注解,参数,异常
- 拦截模式 前置,后置,返回,异常
使用方式
添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.6</version>
</dependency>
aspectjweaver包含aspectjrt,所以我们只需要引入aspectjweaver依赖包就可以了
基于注解
1 前置通知
2 后置通知
3 环绕通知
首先我们定义一个切面类
@Aspect
public class AspectDemo {
private String templateStr = "=========================== %s ==============";
@Pointcut("execution(public * *(..))")
private void anyPublicPointCut() {
}
@Before("anyPublicPointCut()")
public void anyPublicBefore() {
System.out.println(String.format(templateStr, "前置拦截"));
}
@After("anyPublicPointCut()")
public void anyPublicAfter() {
System.out.println(String.format(templateStr, "后置拦截"));
}
@Around("anyPublicPointCut()")
public void anyPublicAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
System.out.println(String.format(templateStr, "环绕拦截"));
// 特别注意这里需要我们手动去调用
joinPoint.proceed();
}
}
在客户端进行使用:
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.register(Client.class, AspectDemo.class);
context.refresh();
Client bean = context.getBean(Client.class);
bean.execute();
}
public void execute() {
System.out.println("================== 执行方法内部逻辑 ==============");
}
}
执行结果:
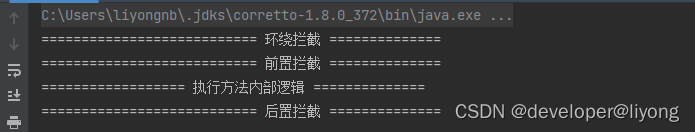
小结:
1 关于顺序问题我们可以看到在同一切面遵循环绕通知 -> 前置通知 -> 后置通知的顺序 当然后置通知里面又有分类,后文会进行介绍。
2 前置通知,后置通知都是框架主动执行,只有环绕通知需要我们手动去调用。
基于xml
1 切面申明
2 前置通知
3 后置通知
4 环绕通知
// 切面的方法
public class InterceptConfig {
private String templateStr = "=========================== xml %s ==============";
public void anyPublicBefore() {
System.out.println(String.format(templateStr, "前置拦截"));
}
public void anyPublicAfter() {
System.out.println(String.format(templateStr, "后置拦截"));
}
public void anyPublicAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
System.out.println(String.format(templateStr, "环绕拦截"));
joinPoint.proceed();
}
}
配置切面
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean id="aspectActionConfig" class="com.liyong.learn.aop.annotation.InterceptConfig"></bean>
<bean id="client" class="com.liyong.learn.aop.annotation.Client"></bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="aspectActionConfig" >
<aop:before method="anyPublicBefore" pointcut="execution(public * *(..))"></aop:before>
<aop:after method="anyPublicAfter" pointcut="execution(public * *(..))"></aop:after>
<aop:around method="anyPublicAround" pointcut="execution(public * *(..))"></aop:around>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aop.xml");
Client bean = context.getBean(Client.class);
bean.execute();
}
public void execute() {
System.out.println("================== 执行方法内部逻辑 ==============");
}
}
可以看到和上面的运行结果一样:
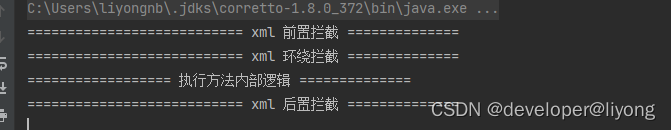
基于API
1 切面申明
2 前置通知
3 后置通知
4 环绕通知
定义切面表达式:
public class ApiPointCut extends StaticMethodMatcherPointcut {
// 要拦截的方法
private final String methodName;
// 要拦截的类
private final Class targetClass;
public ApiPointCut(String methodName, Class targetClass) {
super();
this.methodName = methodName;
this.targetClass = targetClass;
}
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
return Objects.equals(methodName, method.getName())
&& (this.targetClass.isAssignableFrom(targetClass) || this.targetClass == targetClass);
}
}
定义拦截器:
public class CustomMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Method method = invocation.getMethod();
System.out.println("==========执行拦截===" + method);
// 这里一定要调用否则方法不会执行
return invocation.proceed();
}
}
使用方式:
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个切面 里面制定了我们要拦截的方法及我们要拦截的规则
ApiPointCut pointCut = new ApiPointCut("execute", Client.class);
// 定义一个对象
Client client = new Client();
// 这是SpirngAop 给我们提供的生产代理后的对象的工厂 当然这个工厂也可以通过配置的方式配置在xml
ProxyFactory proxy = new ProxyFactory(client);
DefaultPointcutAdvisor advisor = new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointCut, new CustomMethodInterceptor());
proxy.addAdvisor(advisor);
// 通过代理获取对象
Client proxyClient = (Client) proxy.getProxy();
proxyClient.execute();
}
public void execute() {
System.out.println("================== 执行方法内部逻辑 ==============");
}
}
执行结果:
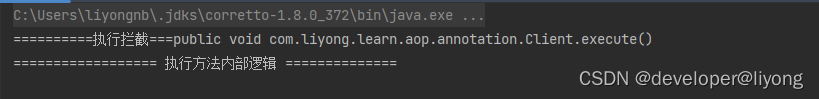
当然我们还可以使用其它的工厂类,通过API的方式来使用AOP:
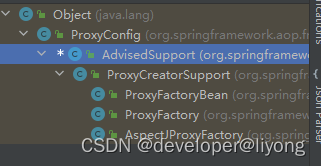
我们可以看到ProxyFactoryBean,ProxyFactory,AspectJProxyFactory都是来源于几类AdviceSupport。所以我们可以通过这几个工厂去创建AOP.
// 这个例子对map的put方法进行拦截
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Object> cache = new HashMap<>();
AspectJProxyFactory aspectJProxyFactory = new AspectJProxyFactory(cache);
aspectJProxyFactory.addAdvice(new MethodBeforeAdvice() {
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
if ("put".equals(method.getName()) && args.length == 2) {
System.out.println("========== 前置拦截 ==========");
}
}
});
Map<String, Object> proxy = aspectJProxyFactory.getProxy();
proxy.put("1", "1");
}
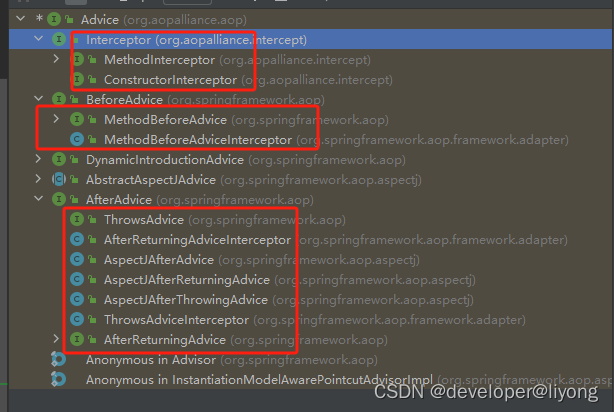
addAdvice可以有很多方式前置后置,环绕等,他们的顶级接口都是Advice:
自动动态代理
1 BeanNameAutoProxyCreator 通过bean名称的方式进行判断是否需要代理
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="aspectActionConfig" class="com.liyong.learn.aop.annotation.InterceptConfig"></bean>
<bean id="client" class="com.liyong.learn.auto.Client"></bean>
<!--定义拦截器-->
<bean id="interceptor" class="com.liyong.learn.aop.annotation.CustomMethodInterceptor"></bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.BeanNameAutoProxyCreator">
<property name="beanNames" value="*"></property>
<property name="interceptorNames" >
<!--指定拦截器-->
<value>interceptor</value>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("auto.xml");
Client bean = context.getBean(Client.class);
bean.execute();
}
public void execute() {
System.out.println("================== 执行方法内部逻辑 ==============");
}
}
2 DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="defaultCreator" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator"></bean>
<bean id="client" class="com.liyong.learn.auto.Client"></bean>
<bean id="clientOne" class="com.liyong.learn.auto.ClientOne"></bean>
<bean id="interceptor" class="com.liyong.learn.aop.annotation.CustomMethodInterceptor"></bean>
<bean id="pointCut" class="com.liyong.learn.aop.annotation.ApiPointCut">
<!-- 指定方法名 -->
<constructor-arg index="0" value="execute"></constructor-arg>
<!-- 指定类名 -->
<constructor-arg index="1" value="com.liyong.learn.auto.Client"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- 配置一个通知 就需要配置pointCut 以及要执行的动作 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultPointcutAdvisor" name="advice">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="pointCut"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" ref="interceptor"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("auto.xml");
Client bean = context.getBean(Client.class);
bean.execute();
}
public void execute() {
System.out.println("================== 执行方法内部逻辑 ==============");
}
}
DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator读取了上下文环境,发现配置的又AOP于是自动代理了,我们得到的是道理以后的对象
3 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 这是基于注解的形式来实现AOP我们只需要注解就能够成功的对我们们关心的地方进行拦截。
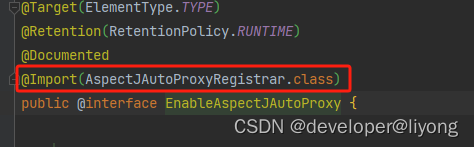
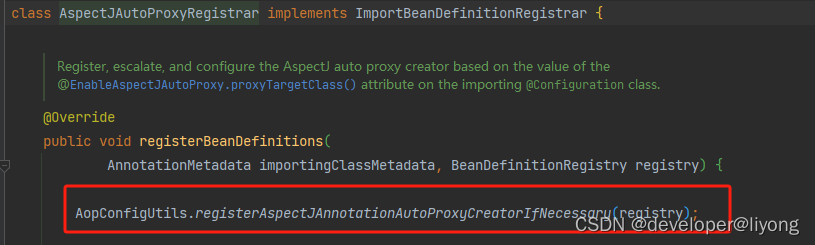
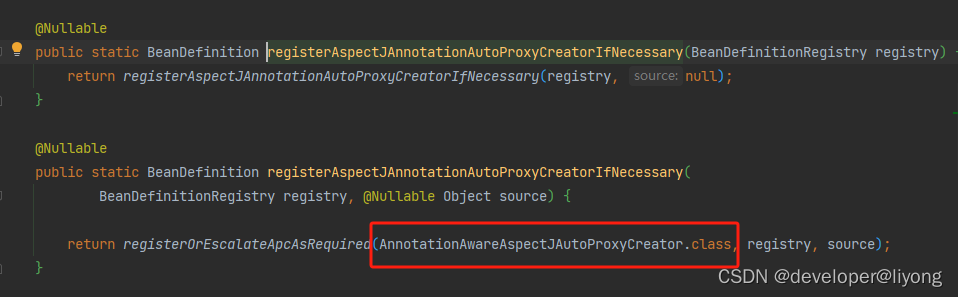
before,after 与 Around 的执行顺序
1 在同一个Aspect里面Around优先于before
2 如果不在同一个Aspect里面,则是通过Order来控制的
@Aspect
public class AspectOne implements Ordered {
@Pointcut("execution(public * *(..))")
private void anyPublicOperation() {
}
@Before("anyPublicOperation()")
public void beforeAnyPublicMethod() {
System.out.println("====== before one ==========");
}
@Around("anyPublicOperation()")
public Object aroundAnyPublicMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("=========== around one ====== ");
// 主动调用
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 1;
}
}
@Aspect
public class AspectTwo implements Ordered {
@Pointcut("execution(public * *(..))")
private void anyPublicOperation() {
}
@Before("anyPublicOperation()")
public void beforeAnyPublicMethod() {
System.out.println("====== before two ==========");
}
@After("anyPublicOperation()")
public void afterAnyPublicMethod(){
System.out.println("====== after two ==========");
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 2;
}
}
@Configuration // 标注以后会有增强提升
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy // 激活自动代理
public class AspectDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.register(AspectOne.class, AspectTwo.class, AspectDemo.class);
context.refresh();
AspectDemo bean = context.getBean(AspectDemo.class);
bean.execute();
context.close();
}
public void execute() {
System.out.println(111);
}
}
可以看到同一个aspect里面Around会先执行,然后就是数字越低越优先执行:
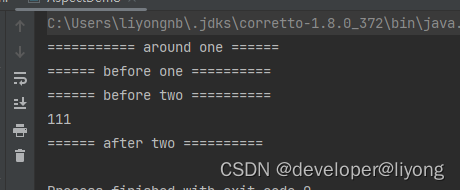
三种After 的关系
1 AfterReturning
2 AfterThrowing
3 After
@Aspect
public class AfterConfig {
@Pointcut("execution(public * *(..))")
private void anyPublicOperation() {
}
@After("anyPublicOperation()")
public void after(){
System.out.println("====== after=========");
}
@AfterReturning("anyPublicOperation()")
public void afterReturning(){
System.out.println("====== afterReturning =========");
}
@AfterThrowing("anyPublicOperation()")
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("====== afterThrowing =========");
}
}
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AfterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.register(AfterConfig.class, AfterDemo.class);
context.refresh();
AfterDemo bean = context.getBean(AfterDemo.class);
bean.execute();
}
public void execute() {
Random random = new Random();
boolean flag = random.nextBoolean();
if (flag) {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
System.out.println("execute");
}
}
可以看到我们三种After的执行顺序是先after类似于finally,然后是afterReturing,如果是有异常的话就是after和afterThrowing.通过配置的方式参考前面的配置。