AVL树
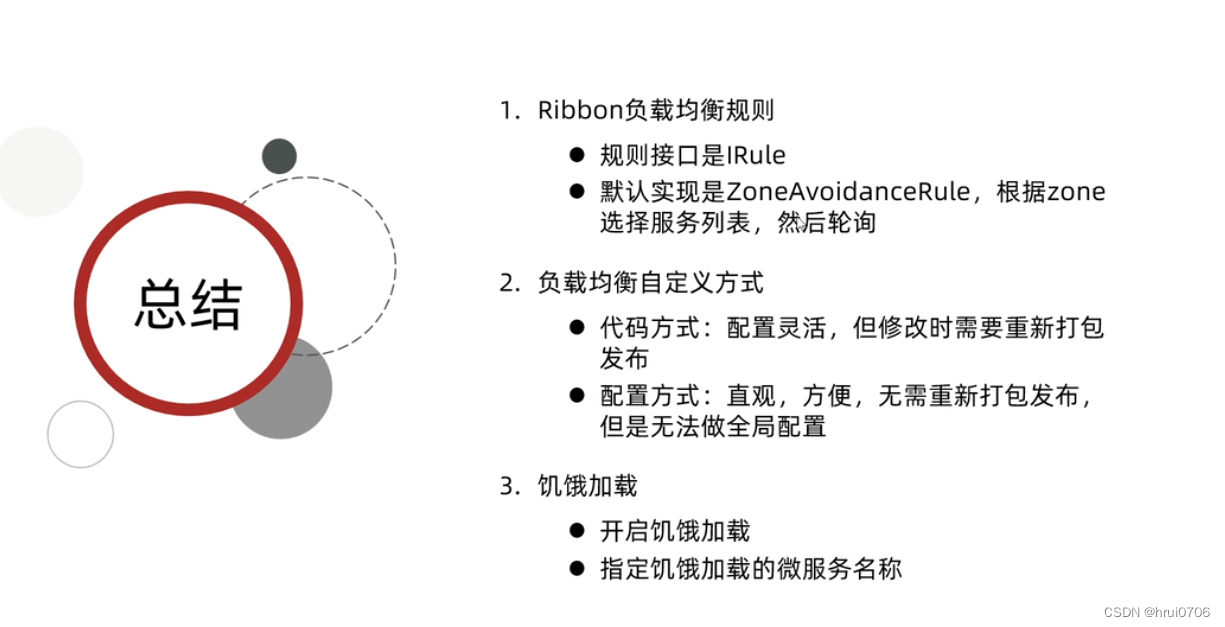
- 1. 概念
- 2. AVL节点的定义
- 3. AVL树插入
- 3.1 旋转
- 4.AVL树的验证
1. 概念
- AVL树是一种自平衡二叉搜索树。它的每个节点的左子树和右子树的高度差(平衡因子,我们这里按右子树高度减左子树高度)的绝对值不超过1。
- AVL的左子树和右子树都是AVL树。
- 比起二叉搜索树AVL树可以很好的优化二叉搜索树最坏的情况,使查询的效率达到O(log2 N)。
2. AVL节点的定义
和搜索二叉树节点相比,AVL树节点多了一个父节点和平衡因子(不是必要)需要维护。
template<class T>
typedef struct AVLTreeNode
{
AVLTreeNode(const T& data)
:_pLeft(nullptr)
,_pRight(nullptr)
,_pParent(nullptr)
,_data(data)
,_bf(0)
{};
//左节点、右节点、父节点
AVLTreeNode<T>* _pLeft;
AVLTreeNode<T>* _pRight;
AVLTreeNode<T>* _pParent;
T _data;
//平衡因子
int bf;
};
3. AVL树插入
和搜索二叉树的插入操作相比较,AVL树的插入需要多维护父节点和平衡因子。维护父节点比较简单,我们需要学习的是维护平衡因子。
当我们按照搜索二叉树的逻辑插入一个节点后,在插入这个节点之前父节点的平衡因子可能是-1/0/1这三种,如果该节点插入到父节点的左边需要将平衡因子减1,插入到右边则加1。所以插入之后平衡因子有这几种情况±1/0/±2。如果是±1,那么需要继续判断上面节点的平衡因子、如果是0,那么不需要判断了、如果是±2,那么就需要进行旋转操作。
3.1 旋转
我们先说结论:1、旋转之后节点所在子树的高度会回到插入之前。2、旋转不会对上面节点平衡因子产生影响。
- 右单旋
初始情况:
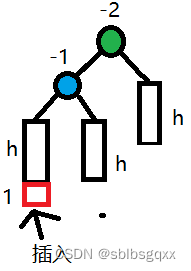
// 右单旋
void RotateR(Node* pParent)
{
Node* parent = pParent->_parent;
//变成局部的根
Node* pParentL = pParent->_left;
Node* pParentR = pParentL->_right;
if (pParent == _proot)
_proot = pParentL;
pParent->_left = pParentR;
if (pParentR)
pParentR->_parent = pParent;
pParentL->_left = pParent;
pParent->_parent = pParentL;
pParentL->_parent = parent;
//只需要修改pParent和pParentL的平衡因子
pParent->_bf = 0;
pParentL->_bf = 0;
return;
}
旋转之后情况

- 左单旋
初始情况:
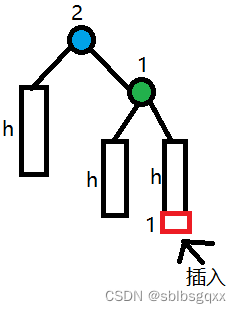
// 左单旋
void RotateL(Node* pParent)
{
Node* parent = pParent->_parent;
//变成局部的根
Node* pParentR = pParent->_right;
Node* pParentL = pParentR->_left;
//如果pParnet为根,则要修改根
if (pParent == _proot)
_proot = pParentR;
pParent->_right = pParentL;
if (pParentL)
pParentL->_parent = pParent;
pParentR->_left = pParent;
pParent->_parent = pParentR;
pParentR->_parent = parent;
//只需要修改pParent和pParentR的平衡因子
pParent->_bf = 0;
pParentR->_bf = 0;
return;
}
旋转之后的情况:
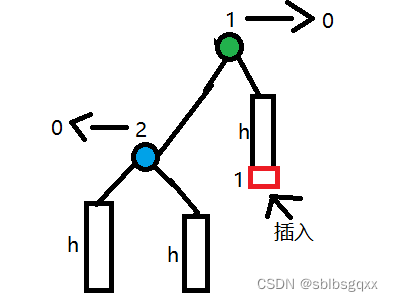
- 左右双旋
初始情况(插入可以插入到左边或右边,情况不同平衡因子也会不同):
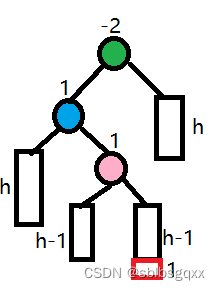
// 左右双旋
void RotateLR(Node* pParent)
{
Node* pParentL = pParent->_left;
Node* pParentLR = pParentL->_right;
int bf = pParentLR->_bf;
RotateL(pParentL);
RotateR(pParent);
if (bf == 0)
{
pParent->_bf = 0;
pParentL->_bf = 0;
pParentLR->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == 1)
{
pParentL->_bf = -1;
pParentLR->_bf = 0;
pParent->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == -1)
{
pParentL->_bf = 0;
pParent->_bf = 1;
pParentLR->_bf = 0;
}
return;
}
旋转之后的情况:
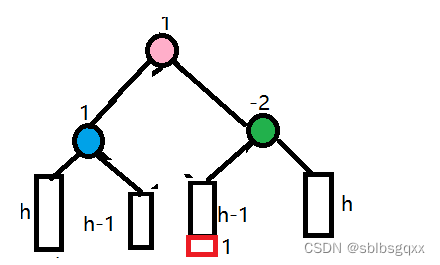
- 右左双旋转
初始情况:
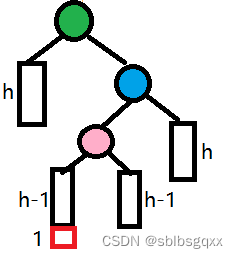
// 右左双旋
void RotateRL(Node* pParent)
{
Node* pParnetR = pParent->_right;
Node* pParentRL = pParnetR->_left;
int bf = pParentRL->_bf;
RotateR(pParnetR);
RotateL(pParent);
if (bf == 0)
{
pParent->_bf = 0;
pParnetR->_bf = 0;
pParentRL->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == -1)
{
pParent->_bf = 0;
pParnetR->_bf = 1;
pParentRL->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == 1)
{
pParent->_bf = -1;
pParnetR->_bf = 0;
pParentRL->_bf = 0;
}
return;
}
旋转之后的情况:
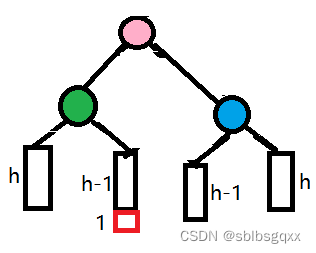
4.AVL树的验证
- 验证为二叉搜索树
中序遍历得到有序的序列就可以证明为二叉搜索树。 - 验证为平衡树
看平衡因子
bool _IsBalance(Node* root, int& height)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
height = 0;
return true;
}
int leftHeight = 0, rightHeight = 0;
if (!_IsBalance(root->_left, leftHeight)
|| !_IsBalance(root->_right, rightHeight))
{
return false;
}
if (abs(rightHeight - leftHeight) >= 2)
{
cout <<root->_kv.first<<"不平衡" << endl;
return false;
}
if (rightHeight - leftHeight != root->_bf)
{
cout << root->_kv.first <<"平衡因子异常" << endl;
return false;
}
height = leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
return true;
}