1、Linux RPATH & $ORIGIN
许多现代C / C ++项目都利用Autotools创建GNU构建系统,例如 根据平台生成make文件。 可执行文件(二进制文件)在生成/编译过程中生成,并且可以在执行编译的计算机上本地执行。 但是,如果将同一可执行文件移动到另一台计算机上,或者只是移到同一台计算机上的其他文件夹,则在运行该可执行文件时可能会遇到“找不到库”错误。
2、什么是RPATH和$ORIGIN?
RPATH代表运行时搜索路径。 根据Wikipedia的说法,“rpath指定在可执行文件或库中硬编码的运行时搜索路径。 动态链接加载程序使用rpath查找所需的库” 动态链接是所需共享库的一种“惰性”链接,不是在编译阶段,而是在运行一个可执行文件的后期。 如果设置了rpath,覆盖或补充系统默认的共享库搜索路径,则共享库的路径将被编码到可执行文件的头中,就像扩展PATH系统变量链一样。
$ORIGIN是一个特殊的变量,指示实际的可执行文件名。它在运行时解析到可执行文件的位置,在设置RPATH时非常有用。
示例
编写libhello.so动态库文件
hello.h
#pragma once
void HelloFunc();
hello.cpp
#include <iostream>
void HelloFunc()
{
std::cout << "hello function \n";
}编译
g++ -fPIC -shared -o libhello.so hello.c
main.c
#include <iostream>
#include "hello.h"
int main()
{
HelloFunc();
std::cout << "hello world \n";
return 0;
}
正常编译
g++ main.c -o main -L. -lhello运行结果
./main: error while loading shared libraries: libhello.so: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
我们需要解决找到libhello.so的问题才可以使main运行起来,可以通过以下两种方式
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=yourpath/lib
将libhello.so拷贝到/usr/local/lib,然后运行ldconfig
使用RPATH
编译期
编译命令改为
g++ main.c -o main -L. -lhello -Wl,-rpath='$ORIGIN/'运行
./main
hello function
hello world 程序正常运行
在编译之后,执行之前
使用chrpath
chrpath -r "\$\ORIGIN/path/to/library" <executable>—如果之前没有为可执行文件设置rpath,上述命令可能会失败。使用patchelf实用程序尝试下面的命令,它不会抱怨没有设置rpath,并且会设置RUNPATH来实现类似的目标。
使用patchelf
patchelf — set-rpath ‘$ORIGIN/path/to/library’ <executable>
如何检查RPATH的值?
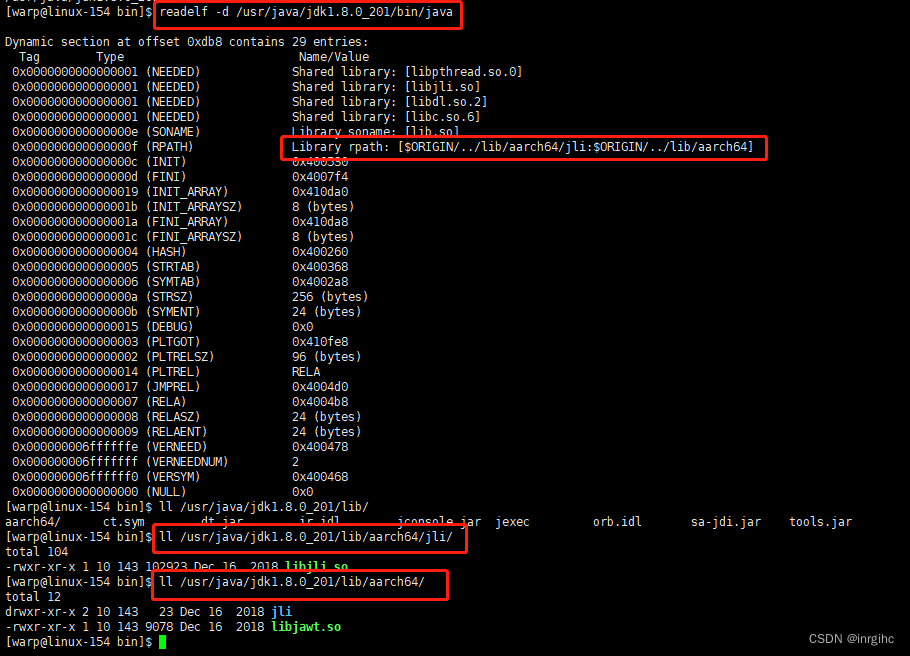
有多种方法可以检查可执行文件或库的RPATH值。objdump、readelf和chrpath是3个常用的实用程序。
- objdump -x path/to/executable | grep RPATH
- readelf -d path/to/executable | head -20
- chrpath -l path/to/executable
使用readelf结果