目录
题目传送门
算法解析
最终代码
提交结果
尾声
题目传送门
[CSP-J 2022] 上升点列 - 洛谷![]() https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P8816
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P8816
算法解析
k = 0 且 xi, yi 值域不大时,这题是非常简单的 DP,类似「数字三角形」。
记 dp(x,y) 为「以 (x,y) 为终点,最长合法序列的长度」。
则对于所有(已经存在的)整点,有:
dp(x,y) = max {dp(x − 1, y), dp(x, y − 1)} + 1
xi, yi 值域比较大时:
可以考虑记 dp(n) 表示「以 n 号点结尾的合法序列,最长能有多长」。
dp(n) = max {dp(i) + 1}
i → n ✓
不会存在环状结构——因为合法序列必须向右、上方发展。
把刚刚的DP改造一下,就是本题正解:
记 dp(n, k) 表示「以 n 号点结尾,已经使用掉了 k 个自由点,获得的收益」。
dp(n,k) = max {dp(i, k − cost) + cost + 1}
i → n ✓
实现细节:本题的求值顺序值得注意,合法路径可能形如 P1 → P3 → P2。
有两种解决方法:
- 记忆化搜索(记忆化搜索最擅长解决求值顺序混乱的 DP)
- 预先按 x, y 排序,使得编号大的点一定是从编号小的点转移过来
这里记忆化搜索比较好写一些,我这里就只讲记忆化搜索了
先写一下求 a 到 b 需要补多少个点的函数,即两点曼哈顿距离再减一(a 在左下,b 在右上,否则返回无穷)
代码中 x[u] 表示 u 点的横坐标,y[u] 表示 u 点的纵坐标
int dis(int a, int b) {
if(x[a] > x[b])
return inf;
if(y[a] > y[b])
return inf;
return x[b] - x[a] + y[b] - y[a] - 1;
}然后是 dp 函数,定义上面已经说过了
int dp(int now, int k)首先判断如果自由点已经用完了,即 k < 0,那么返回负无穷(因为最后是取最大值)
int dp(int now, int k) {
if(k < 0)
return -inf;
}既然是记忆化,那么就需要记忆
用 vis[n][k] 数组记录 dp(n, k) 是否访问过,val[n][k] 数组记录如果访问过的 dp(n, k) 的值
这样如果 vis[now][k] == true(访问过),则返回 val[now][k]
int dp(int now, int k) {
if(k < 0)
return -inf;
if(vis[now][k])
return val[now][k];
}然后就该枚举它的前驱(代码中的 to),然后取里面最大的收益
这个记录最大收益的变量(代码中的 res)的初值一定要是 1,因为如果哪也去不了,那么就只能走到现在这一个点,也就是 now
int dp(int now, int k) {
if(k < 0)
return -inf;
if(vis[now][k])
return val[now][k];
int res = 1;
for(int to = 1; to <= n; ++to)
return res;
}接下来需要判断 to != now,然后计算出 to 到 now 需要补多少个点(代码中的 cost)
int dp(int now, int k) {
if(k < 0)
return -inf;
if(vis[now][k])
return val[now][k];
int res = 1;
for(int to = 1; to <= n; ++to)
if(to != now) {
int cost = dis(to, now);
}
return res;
}再判断费用超出运算,就 contunue(如果走不到,dis 就会返回无穷,一定大于 k,所以不用特判走不到)
int dp(int now, int k) {
if(k < 0)
return -inf;
if(vis[now][k])
return val[now][k];
int res = 1;
for(int to = 1; to <= n; ++to)
if(to != now) {
int cost = dis(to, now);
if(cost > k)
continue;
}
return res;
}接着就是往下递归了,now 变成了 to,预算费用还剩 k - cost,所以传进去是
dp(to, k - cost)然后长度还需要加上 to 到 now 的距离,即 cost + 1,然后更新最大值(代码里的 res)
代码中的 bemax 函数是把第一个参数赋成两个参数的最大值用的,具体实现方法就是用一个三目运算符
void bemax(int &a, int b) {
a = a > b ? a : b;
}int dp(int now, int k) {
if(k < 0)
return -inf;
if(vis[now][k])
return val[now][k];
int res = 1;
for(int to = 1; to <= n; ++to)
if(to != now) {
int cost = dis(to, now);
if(cost > k)
continue;
bemax(res, dp(to, k - cost) + cost + 1);
}
return res;
}最后再将 vis[now][k] 设成 true,val[now][k] 设成 res
最后 return res 就行了
int dp(int now, int k) {
if(k < 0)
return -inf;
if(vis[now][k])
return val[now][k];
int res = 1;
for(int to = 1; to <= n; ++to)
if(to != now) {
int cost = dis(to, now);
if(cost > k)
continue;
bemax(res, dp(to, k - cost) + cost + 1);
}
vis[now][k] = true;
val[now][k] = res;
return res;
}主函数里需要枚举 i = 1 ~ n,j = 0 ~ k,然后传进去(n 为点的个数,k 为自由点的个数)
注意长度还需要加上没用的 k - j 个点,然后更新答案(代码中的 ans)
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j <= k; ++j)
bemax(ans, dp(i, j) + k - j);最后输出 ans 即可
最终代码
#include <cstdio>
#define N 1005
using namespace std;
const int inf = 0x7fffffff;
int n, k;
int x[N], y[N];
bool vis[N][N];
int val[N][N];
int ans;
void bemax(int &a, int b) {
a = a > b ? a : b;
}
int dis(int a, int b) {
if(x[a] > x[b])
return inf;
if(y[a] > y[b])
return inf;
return x[b] - x[a] + y[b] - y[a] - 1;
}
int dp(int now, int k) {
if(k < 0)
return -inf;
if(vis[now][k])
return val[now][k];
int res = 1;
for(int to = 1; to <= n; ++to)
if(to != now) {
int cost = dis(to, now);
if(cost > k)
continue;
bemax(res, dp(to, k - cost) + cost + 1);
}
vis[now][k] = true;
val[now][k] = res;
return res;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &k);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
scanf("%d%d", &x[i], &y[i]);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j <= k; ++j)
bemax(ans, dp(i, j) + k - j);
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}提交结果
提交一下哈
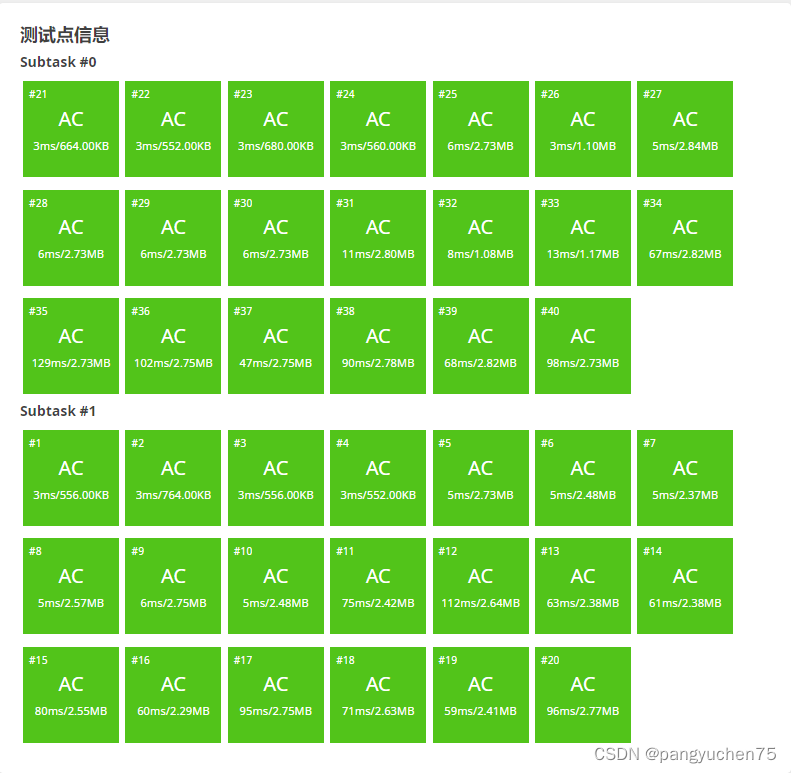
㇏(〃'▽'〃)㇀ AC ! ! !
尾声
如果这篇博客对您(您的团队)有帮助的话,就帮忙点个赞,加个关注!
最后,祝您(您的团队)在 OI 的路上一路顺风!!!
┬┴┬┴┤・ω・)ノ Bye~Bye~