什么是自连接?
自连接可以理解为自己连接自己,在一张表上面所进行的操作;将一张表分成两张结构和数据完全一样的表,相当于克隆了一张跟自己长得一模一样的表;
但是既然是两张一模一样的表,数据库怎么去区分出那张表是哪张表呢?这时候最重要的一个知识点就来了,那就是给两张表分别取个别名。
自连接语法
自连接我所知道有以下几种语法,有遗漏的话也欢迎大家在评论区给我补充出来。
1、内连接
1.1隐式内连接
select 字段列表 from 表 [as] 表别名1,表 [as] 表别名2 where 条件...;
1.2.显式内连接
select 字段列表 from 表 [as] 表别名1 [inner] join 表 [as] 表别名2 on 条件...;
2、外连接
2.1.左外连接
select 字段列表 from 表 [as] 表别名1 left [outer] join 表 [as] 表别名2 on 条件...;
2.2.右外连接
select 字段列表 from 表 [as] 表别名1 right [outer] join 表 [as] 表别名2 on 条件...;
温馨提示:[]里面的单词可以写,也可以省略不写。
案例演示1
商品表:
create table tb_goods(
id int primary key auto_increment comment '主键ID',
goods varchar(50) not null comment '商品',
price decimal(7,2) default 0.00 comment '商品价格'
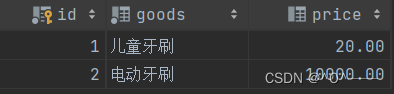
) comment '商品表';给商品表插入数据:
insert into tb_goods(goods,price) values('儿童牙刷',20),
('电动牙刷',10000),
('拼多多牙刷',9.9);
insert into tb_goods(goods) values('妈妈给买的牙刷');数据展示:
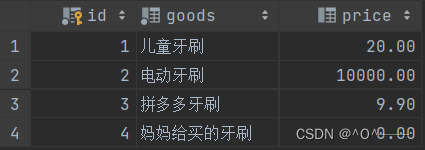
需求:
查询比“拼多多牙刷”的价格贵的牙刷有哪些?
思路解析(用的是隐式内连接):
select 字段列表 from 表 [as] 表别名1,表 [as] 表别名2 where 条件...;
第一步:把 tb_goods(商品表)取两个别名,把它们连接起来;
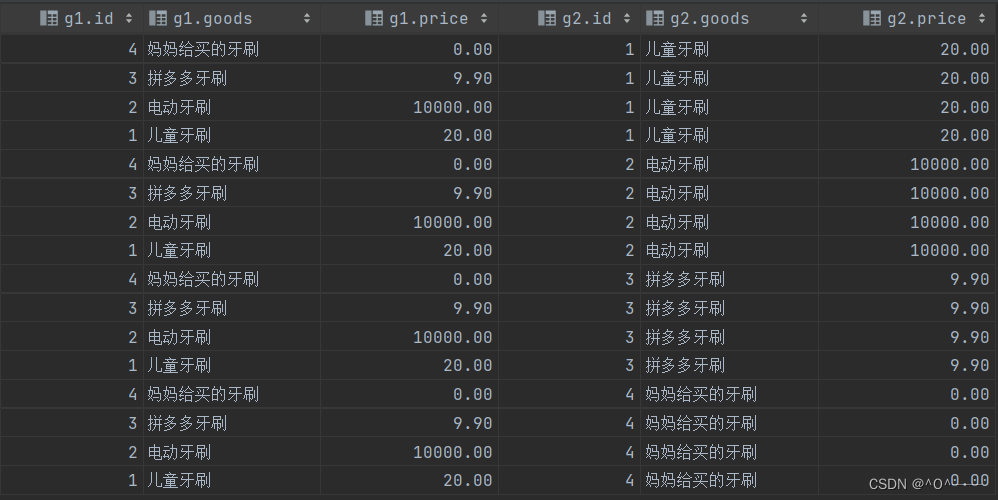
select * from tb_goods as g1,tb_goods as g2;
查询结果如下:它会列出每条数据的组合情况,如下,每一种牙刷都能组成四种组合。
第二步:从 g1 表里面把所有“拼多多牙刷”找出来;
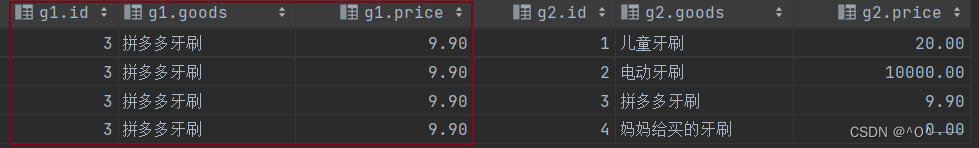
select * from tb_goods as g1,tb_goods as g2 where g1.goods = '拼多多牙刷';
查询结果如下:在 g1 表中找出了所有的“拼多多牙刷”。
可以看到 g2 表里面的 g2.price 已经把每个牙刷的价格都已经查询出来了;
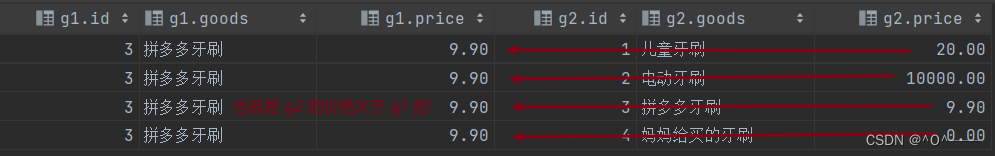
第三步:这时候只要查询出 g2 的价格大于 g1 价格的数据就可以了,也就是大于“拼多多牙刷”的数据
select * from tb_goods as g1,tb_goods as g2 where g1.goods = '拼多多牙刷' and g2.price > g1.price;
查询结果如下:已经查出了 g2 的价格大于 g1 价格的数据。

第四步:此时就可以对这两个数据进行查询;
select g2.goods,g2.price from tb_goods as g1,tb_goods as g2 where g1.goods = '拼多多牙刷' and g2.price > g1.price;
查询结果如下:得到了比“拼多多牙刷”的价格贵的牙刷,已经完成了需求。
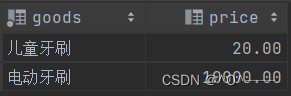
最后,如果要查询的数据更清晰的话,可以给查询的字段取别名;
select g2.goods as '商品',g2.price as '商品价格' from tb_goods as g1,tb_goods as g2 where g1.goods = '拼多多牙刷' and g2.price > g1.price;
查询结果如下:
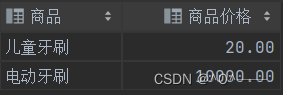
同样的,用显示内连接也可以完成该需求:
select g2.* from tb_goods as g1 inner join tb_goods as g2 on g1.goods = '拼多多牙刷' and g2.price > g1.price;
查询结果如下:
案例演示2
学生表:
create table tb_student(
id int primary key auto_increment comment '主键ID',
student_id char(2) not null unique comment '学号',
name varchar(50) not null comment '姓名',
age tinyint unsigned not null comment '年龄',
parent_id char(2) comment '监护人ID'
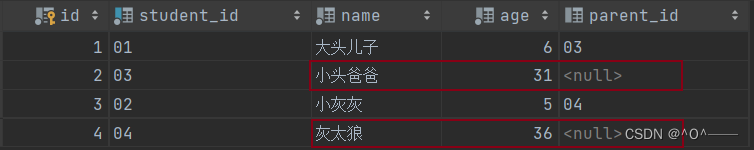
)comment '学生表';给学生表插入数据:
insert into tb_student(student_id, name, age,parent_id) VALUES('01','大头儿子',6,'03'),
('03','小头爸爸',31,null),
('02','小灰灰',5,'04'),
('04','灰太狼',36,null);数据展示:
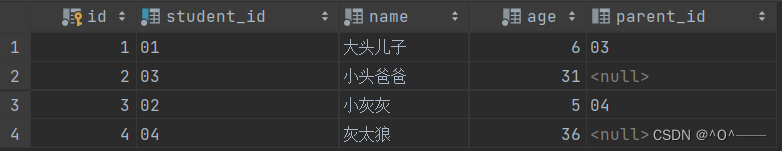
需求:
1、查询 学生姓名 及 学生的监护人 姓名。
思路解析(用的是隐式内连接):
select 字段列表 from 表 [as] 表别名1,表 [as] 表别名2 where 条件...;
第一步:把 tb_student(学生表)取两个别名,把它们连接起来;
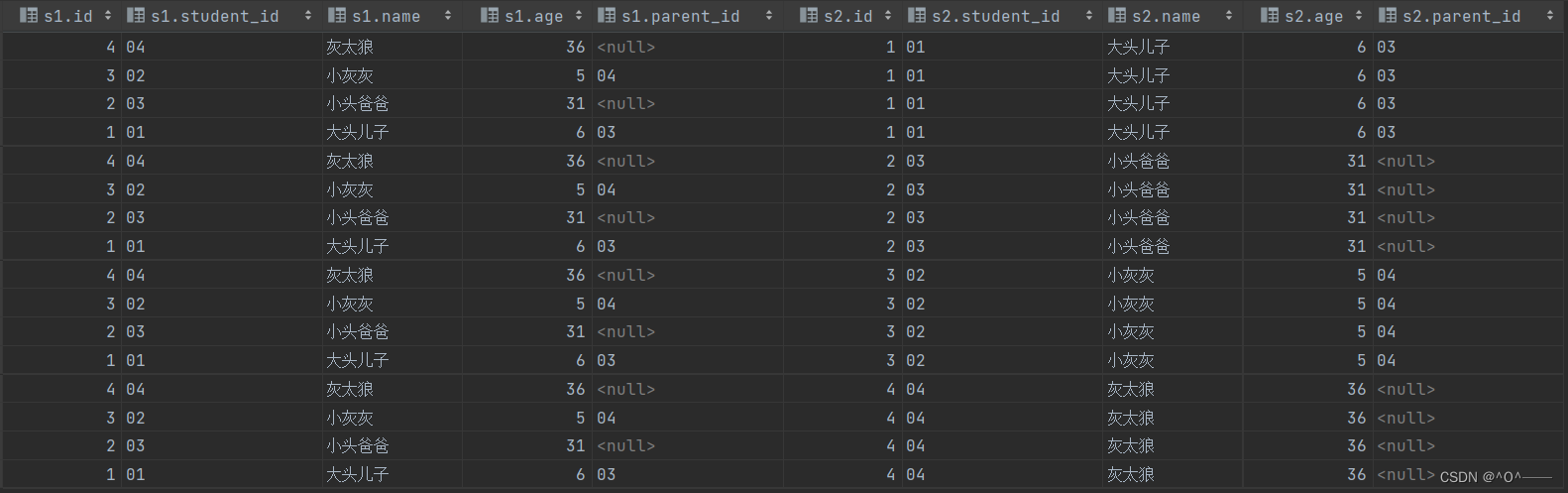
select * from tb_student as s1,tb_student as s2;
第二步:看到这个需求,你可能会觉得奇怪,为什么都没有 学生的监护人 这个字段,而只有 学生监护人ID ;
那是因为我们可以通过 学生监护人ID(parent_id) 关联 学生学号(student_id),找到该学生的学生监护人(student_id)。比如:大头儿子的 学生监护人ID(parent_id)是 03,此时 03 学生学号(student_id)的家长为 小头爸爸;

SQL 语句编写:找到 s1 表的 学生监护人ID(parent_id)和 s2 表的 学生学号(student_id),把它们用 = 关联起来,意思就是:通过 学生监护人ID(parent_id)找到 学生学号(student_id);
select * from tb_student as s1,tb_student as s2 where s1.parent_id = s2.student_id;
查询结果如下:此时就可以看到对应的 学生姓名(s1.name) 及 学生监护人姓名(s2.name) 都已经被找到了。

第三步:此时就可以对这两个数据进行查询;
select s1.name,s2.name from tb_student as s1,tb_student as s2 where s1.parent_id = s2.student_id;
查询结果如下:

最后,如果要查询的数据更清晰的话,可以给查询的字段取别名;
select s1.name as '学生姓名',s2.name as '学生监护人姓名' from tb_student as s1,tb_student as s2 where s1.parent_id = s2.student_id;
查询结果如下:

同样的,用显示内连接也可以完成该需求:
select s1.name '学生姓名',s2.name as '学生监护人姓名' from tb_student as s1 inner join tb_student s2 on s1.parent_id = s2.student_id;
查询结果如下:

还有一种情况,在这个学生表(tb_student)里面,还有人没有学生归属人,也就是学生归属人ID(parent_id)为 null 的情况;
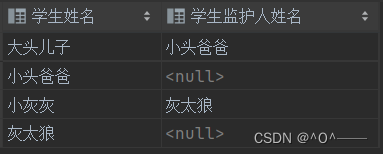
此时,我提出了一个需求:我希望查询 学生姓名 及 学生的监护人 姓名,如果学生没有学生的监护人, 也要查询出来。
此时就不能使用内连接了,要使用外连接,内连接只能查出它们相互交集的数据;
select s1.name '学生姓名',s2.name '学生监护人姓名' from tb_student as s1 left join tb_student as s2 on s1.parent_id = s2.student_id;
查询结果如下:

完。。。
![[ 数据结构 ] 汉诺塔--------分治算法最佳实践](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/7d96447a7fb433347f93cdf2b2e4a2cb.png)