一、Java中的栈
1.常用方法
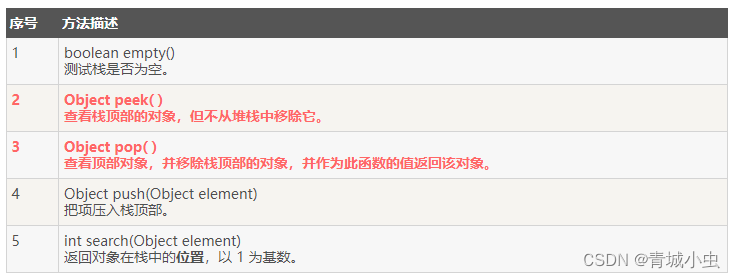
注意上面的peek()方法和pop()方法的区别!
2.实例
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
System.out.println("now the stack is " + isEmpty(stack));
stack.push("1");
stack.push("2");
stack.push("3");
stack.push("4");
stack.push("5");
System.out.println("now the stack is " + isEmpty(stack));
System.out.println(stack.peek());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.search("2"));
}
public static String isEmpty(Stack<String> stack) {
return stack.empty() ? "empty" : "not empty";
}
}
输出:
now the stack is not empty
5
5
4
2
二、Java中的队列
1.常用方法
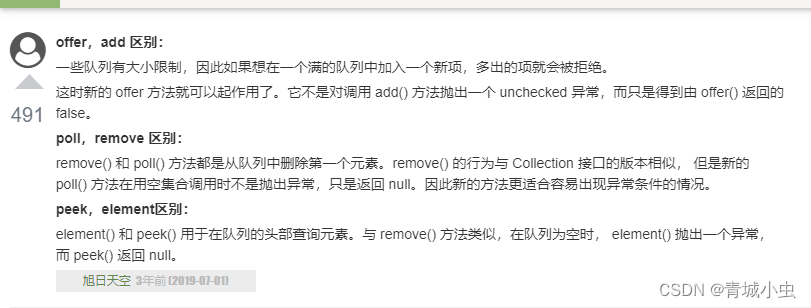
2.实列
队列是一种特殊的线性表,它只允许在表的前端进行删除操作,而在表的后端进行插入操作。
LinkedList类实现了Queue接口,因此我们可以把LinkedList当成Queue来用。
以下实例演示了队列(Queue)的用法:
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//add()和remove()方法在失败的时候会抛出异常(不推荐)
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>();
//添加元素
queue.offer("a");
queue.offer("b");
queue.offer("c");
queue.offer("d");
queue.offer("e");
for(String q : queue){
System.out.println(q);
}
System.out.println("===");
System.out.println("poll="+queue.poll()); //返回第一个元素,并在队列中删除
for(String q : queue){
System.out.println(q);
}
System.out.println("===");
System.out.println("element="+queue.element()); //返回第一个元素
for(String q : queue){
System.out.println(q);
}
System.out.println("===");
System.out.println("peek="+queue.peek()); //返回第一个元素
for(String q : queue){
System.out.println(q);
}
}
}