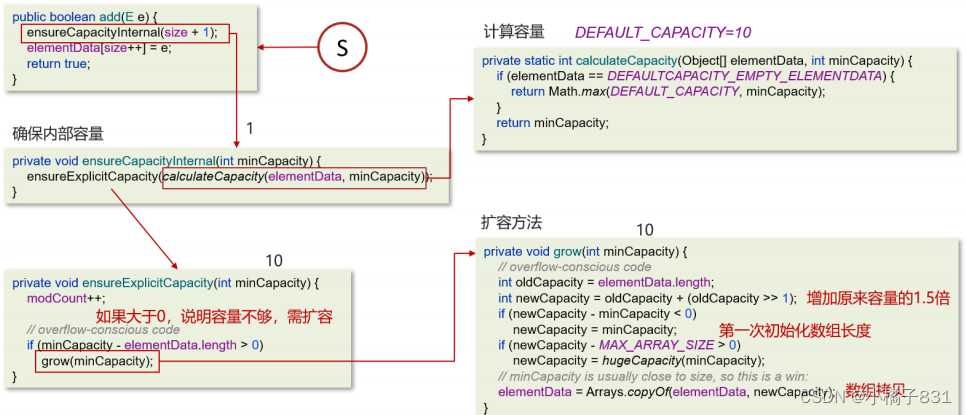
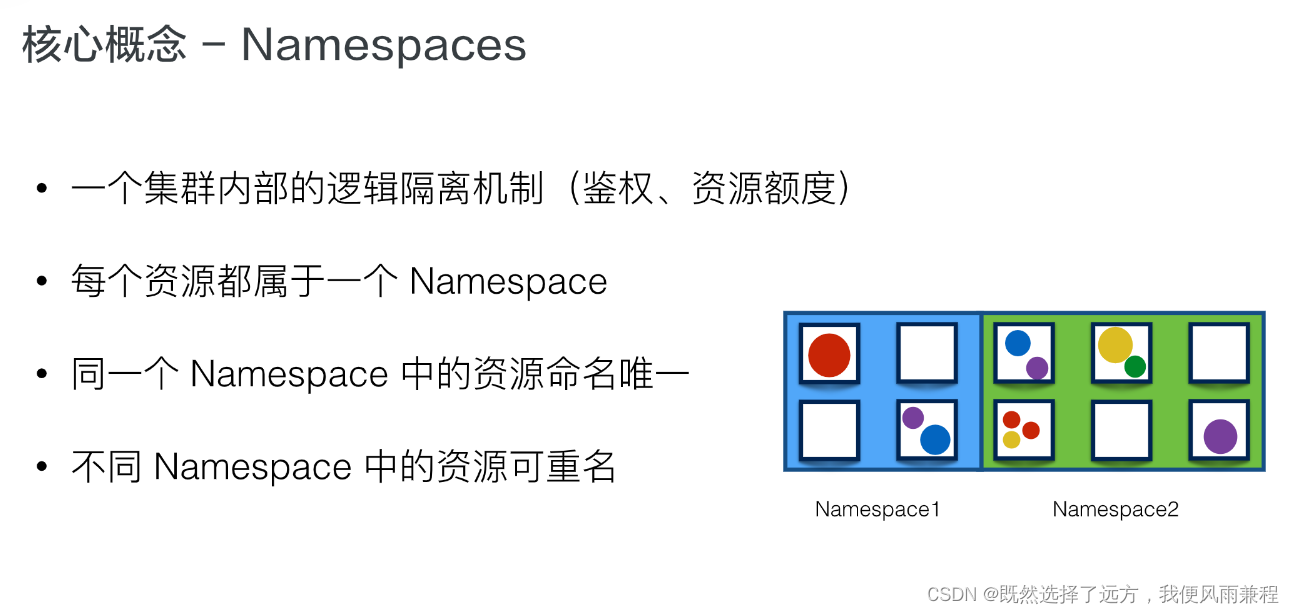
解题思路
满足 若图上有环,则代价为0 若无环,则在图上已有的边在添加一条回边可形成环 对所有的点由小到大排序 由于环的大小可以为2 通过拓扑排序找环,在找环的过程中,看能否添一条边,代价更小 若拓扑不能访问到所有的点则有环 添边,则按照拓扑顺序,维护每个点能被访问的点中,值最小的与其连边形成环,判断代价
import java.io.*;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.BitSet;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import java.util.Vector;
public class Main{
static long md=(long)998244353;
static long Linf=Long.MAX_VALUE/2;
static int inf=Integer.MAX_VALUE/2;
static
class Edge{
int fr,to,nxt;
public Edge(int u,int v) {
fr=u;
to=v;
}
}
static Edge[] e;
static int[] head;
static int cnt=0;
static void addEdge(int fr,int to) {
cnt++;
e[cnt]=new Edge(fr, to);
e[cnt].nxt=head[fr];
head[fr]=cnt;
}
static
class Node{
int x;
long y;
public Node(int X,long Y) {
x=X;
y=Y;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
AReader input=new AReader();
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int n=input.nextInt();
int m=input.nextInt();
e=new Edge[m+1];
head=new int[n+1];
cnt=0;
long[] a=new long[n+1];
long[] b=new long[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) {
long y=input.nextLong();
a[i]=y;
b[i]=y;
}
Arrays.sort(a,1,n+1);
//拓扑排序
int[] in=new int[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i) {
int u=input.nextInt();
int v=input.nextInt();
addEdge(u, v);
in[v]++;
}
Queue<Integer> q=new LinkedList<Integer>();
int tot=0;
long[] c=new long[n+1];
Arrays.fill(c, Linf);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) {
if(in[i]==0) {
q.add(i);
}
}
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int x=q.peek();
q.poll();
tot++;
for(int i=head[x];i>0;i=e[i].nxt) {
int v=e[i].to;
c[v]=Math.min(Math.min(c[x], b[x]), c[v]);
//维护每个点能被访问点中最小的值、
//c[x]不包含自己,在更新其连边时要加上
in[v]--;
if(in[v]==0) {
q.add(v);
}
}
}
if(tot<n) {//判环
out.println(0);
}else {//无环
long ans=(a[1]+a[2])*2;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) {
long res=b[i]+c[i];
ans=Math.min(ans, res);
}
out.print(ans);
}
out.flush();
out.close();
}
//System.out.println();
//out.println();
static
class AReader{
BufferedReader bf;
StringTokenizer st;
BufferedWriter bw;
public AReader(){
bf=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
st=new StringTokenizer("");
bw=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
}
public String nextLine() throws IOException{
return bf.readLine();
}
public String next() throws IOException{
while(!st.hasMoreTokens()){
st=new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public char nextChar() throws IOException{
//确定下一个token只有一个字符的时候再用
return next().charAt(0);
}
public int nextInt() throws IOException{
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException{
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public double nextDouble() throws IOException{
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
public float nextFloat() throws IOException{
return Float.parseFloat(next());
}
public byte nextByte() throws IOException{
return Byte.parseByte(next());
}
public short nextShort() throws IOException{
return Short.parseShort(next());
}
public BigInteger nextBigInteger() throws IOException{
return new BigInteger(next());
}
public void println() throws IOException {
bw.newLine();
}
public void println(int[] arr) throws IOException{
for (int value : arr) {
bw.write(value + " ");
}
println();
}
public void println(int l, int r, int[] arr) throws IOException{
for (int i = l; i <= r; i ++) {
bw.write(arr[i] + " ");
}
println();
}
public void println(int a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
bw.newLine();
}
public void print(int a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
}
public void println(String a) throws IOException{
bw.write(a);
bw.newLine();
}
public void print(String a) throws IOException{
bw.write(a);
}
public void println(long a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
bw.newLine();
}
public void print(long a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
}
public void println(double a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
bw.newLine();
}
public void print(double a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
}
public void print(char a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
}
public void println(char a) throws IOException{
bw.write(String.valueOf(a));
bw.newLine();
}
}
}

的序列即为环
初值设为
,先不管最小点之间是否有边,反正不会更劣