语法
expect [选项] [ -c cmds ] [ [ -[f|b] ] cmdfile ] [ args ]
选项
-c:从命令行执行expect脚本,默认expect是交互地执行的
示例:expect -c 'expect "\n" {send "pressed enter\n"}'
-d:输出调试信息
示例:expect -d ssh.exp
expect中的相关命令
spawn:启动新的进程
send:向进程发送字符串
expect:从进程接收字符串
interact:允许用户交互
exp_continue 匹配多个字符串时在执行动作后加此命令
expect最常用的语法(tcl语言:模式-动作)
单一分支模式的语法:
expect "hi" { send "You said hi\n" } 匹配到 hi 后,会输出"you said hi",并换行
多分支模式的语法:
expect "hi" { send "You said hi\n" } \ "hehe" { send “Hehe yourself\n" } \ "bye" { send "Goodbye\n" }
匹配 hi, hehe, bye 中的任意字符串时, 发送相应字符串。等同于:
expect { "hi" { send "You said hi\n" } "hehe" { send "Hehe yourself\n" } "bye" { send "Goodbye\n" } }
样例
准备测试环境
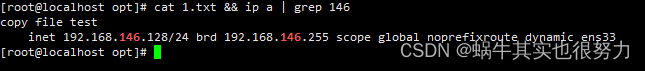
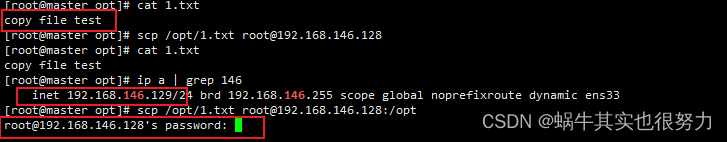
如图显示,一个txt文件,源主机192.168.146.129拷贝至目的主机192.168.146.128,会提示输入密码
安装expect
源主机安装即可
yum -y install expect安装好的expect的命令在 /usr/bin目录下
![]()
编写测试代码
[root@master opt]# vim copyfile.sh
#!/bin/bash
source_file_name="1.txt"
dst_host_name="192.168.146.128"
RED='\E[1;31m'
GREEN='\E[1;32m'
YELOW='\E[1;33m'
SHAN='\E[1;31;5m'
RES='\E[0m'
# 使用expect -c '...'的方式直接在脚本中嵌入了Expect的代码块
expect -c '
# set 方式设置所需要用到的环境变量
set source_file "/opt/1.txt"
set dst_host "192.168.146.128"
set dst_dir "/opt/"
set dst_user "root"
set dst_password "123456"
# spawn启动某个命令的子进程
spawn scp -r $source_file $dst_user@$dst_host:$dst_dir
# except的匹配,匹配到yes 就用send输入yes然后继续,匹配到password字样,就send密码
expect {
"(yes/no)?" {
send "yes\n"
exp_continue
}
"password" {
send "$dst_password\n"
}
}
# 等待命令结束
expect eof
# 输出一个提示语
puts "File transfer successful!"
# 允许用户交互spawn的子进程命令
interact
'
if [[ $? -eq 0 ]];then
echo -e "${GREEN}[+]File: $source_file_name copy to $dst_host_name completed!${RES}"
else
echo -e "${RED}[-]File: $source_file_name copy to $dst_host_name failed!${RES}"
fi
exit 0
执行
全程无交互,文件拷贝成功
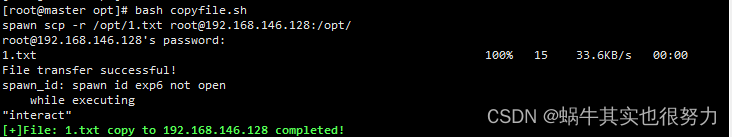
目标主机查看
目标主机192.168.146.128上已有了1.txt文件。