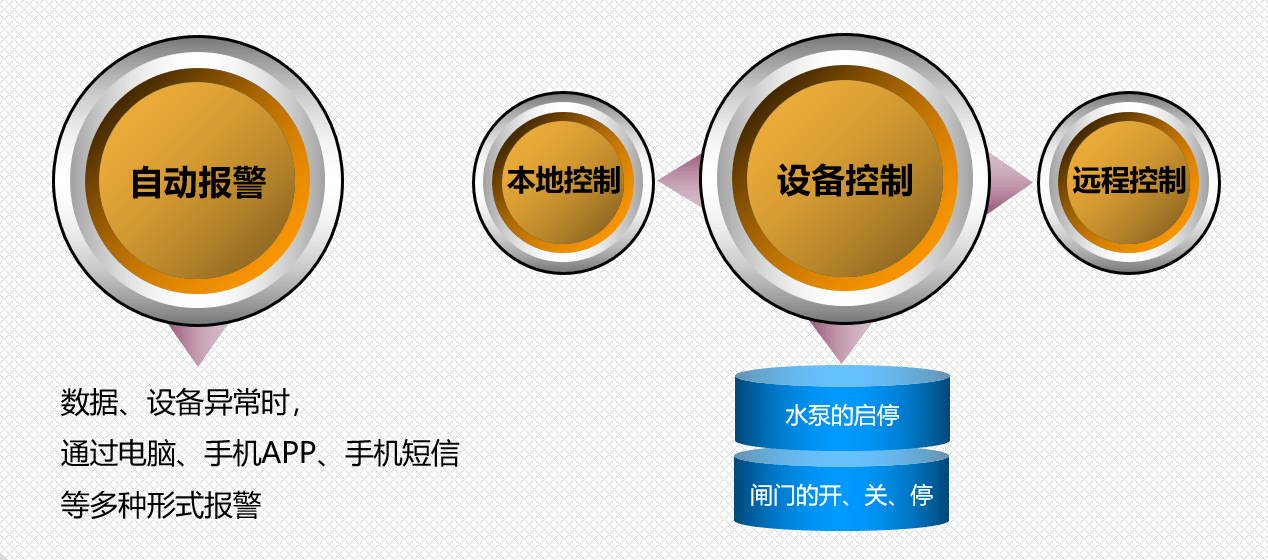
存储方式
- 数组存储方式的分析
优点:通过下标方式访问元素,速度快。对于有序数组,还可使用二分查找提高检索速度。
缺点:如果要检索具体某个值,或者插入值(按一定顺序)会整体移动,效率较低 - 链式存储方式的分析
优点:在一定程度上对数组存储方式有优化(比如:插入一个数值节点,只需要将插入节点,链接到链表中即可,删除效率也很好)。
缺点:在进行检索时,效率仍然较低,比如(检素某个值,需要从头节点开始遍历) - 树存储方式的分析
能提高数据存储,读取的效率,比如利用二叉排序树(Binary Sort Tree),既可以保证数据的检索速度,同时也可以保证数据的插入,删除,修改的速度。
常用术语
- 节点
- 根节点
- 父节点
- 子节点
- 叶子节点(设有子节点的节点)
- 节点的权(节点值)
- 路径(从root节点找到该节点的路线)
- 层
- 子树
- 树的高度(最大层数),初始值为 1
- 森林:多颗子树构成森林
二叉树
每个节点最多这只能有两个子节点的一种形式称为二叉树
-
二叉树的子节点分为左节点和右节点
-
如果该二叉树的所有叶子节点都在最后一层,并且结点总数 = 2 n − 1 =2^n-1 =2n−1,n为层数,则我们称为满二叉树。
-
如果该二叉树的所有叶子节点都在最后一层或者倒数第二层,而且最后一层的叶子节点在左边连续,倒数第二层的叶子节点在右边连续,我们称为完全二叉树
遍历方式
-
深度优先遍历1
- 前序遍历(递归法,迭代法)
- 中序遍历(递归法,迭代法)
- 后序遍历(递归法,迭代法)
-
广度优先遍历2
- 层次遍历(迭代法)
- 通常利用队列的先进先出或者数组顺序遍历来实现
- 层次遍历(迭代法)
前序,中序,后序
- 前序遍历:先输出父节点,再遍历左子树和右子树
- 中序遍历:先遍历左子树,再输出父节点,再遍历右子树
- 后序遍历:先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树,最后输出父节点
- 小结:看输出父节点的顺序,就确定是前序,中序还是后序
1.创建一颗二叉树
2.前序遍历
2.1先输出当前节点(初始的时候是root节点)
2.2如果左子节点不为空,则递归继续前序遍历
2.2如果右子节点不为空,则递归续前序遍历
3.中序遍历
3.1如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,则递归中序遍历,
3.2输出当前节点
3.2如果当前节点的右子节点不为空,则递归中序遍历
4.后序遍历
3.1如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,则递归后序遍历,
3.2如果当前节点的右子节点不为空,则递归后序遍历
3.3输出当前节点
package com.xiaolu.tree;
/**
* @author 林小鹿
* @version 1.0
* 二叉树
*/
public class BinaryTreeMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
HeroNode root = new HeroNode(1, "小米");
HeroNode node2 = new HeroNode(2, "小鹿");
HeroNode node3 = new HeroNode(3, "小红");
HeroNode node4 = new HeroNode(4, "张三");
HeroNode node5 = new HeroNode(5, "李四");
root.setLeft(node2);
root.setRight(node3);
node3.setRight(node4);
node3.setLeft(node5);
binaryTree.setRoot(root);
System.out.println("前序遍历");
binaryTree.preOrder();
System.out.println("中序遍历");
binaryTree.infixOrder();
System.out.println("后序遍历");
binaryTree.postOrder();
}
}
// BinaryTree 二叉树
class BinaryTree {
private HeroNode root;
public void setRoot(HeroNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.postOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
}
// HeroNode结点
class HeroNode {
private int no;
private String name;
private HeroNode left;
private HeroNode right;
public HeroNode(int no, String name) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
// 前序遍历方法
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this); // 先输出父结点
// 递归左子树前序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
// 递归右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
// 先递归左子树中序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
// 输出父结点
System.out.println(this);
// 递归右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
// 先递归左子树中序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.postOrder();
}
// 递归右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.postOrder();
}
// 输出父结点
System.out.println(this);
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public HeroNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(HeroNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public HeroNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(HeroNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
前中后序查找方式
- 前序查找
- 1.先判断当前结点的no是否等于要查找的
2.如果是相等,则返回当前结点
3.如果不等,则判断当前结点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归前序查找
4.如果左递归前序查找,找到结点,则返回,否续判断,当前的结点的右子节点是否为空,如果不空,则续向右递归前序查找
- 1.先判断当前结点的no是否等于要查找的
- 中序查找思路
- 1.判断当前结点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归中序查找
2.如果找到,则返回,如果没有找到,就和当前结点比较,如果是则返回当前结点,否则继续进行右递归的中序查找
3.如果右递归中序查找,找到就返回,否则返回null
- 1.判断当前结点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归中序查找
- 后序查找思路
- 1.判断当前结点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归后序查找
2.如果找到,就返回,如果没有找到,就判断当前结点的右子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则右递归进行后序查找,如果找到,就返回
3.就和当前结点进行,比如,如果是则返回,否则返回null
- 1.判断当前结点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归后序查找
试题
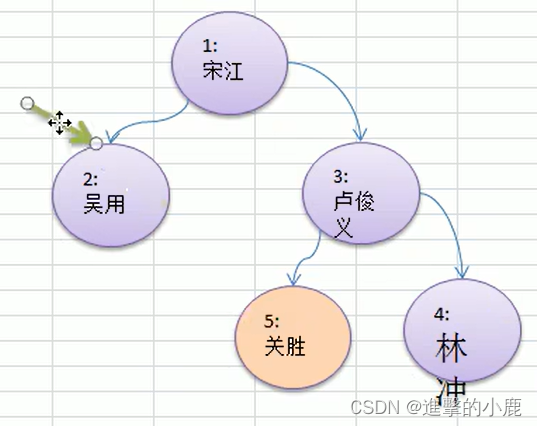
package com.xiaolu.tree;
/**
* @author 林小鹿
* @version 1.0
* 二叉树
*/
public class BinaryTreeMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
HeroNode root = new HeroNode(1, "小米");
HeroNode node2 = new HeroNode(2, "小鹿");
HeroNode node3 = new HeroNode(3, "小红");
HeroNode node4 = new HeroNode(4, "张三");
HeroNode node5 = new HeroNode(5, "李四");
root.setLeft(node2);
root.setRight(node3);
node3.setRight(node4);
node3.setLeft(node5);
binaryTree.setRoot(root);
System.out.println("前序遍历");
binaryTree.preOrder();
System.out.println("中序遍历");
binaryTree.infixOrder();
System.out.println("后序遍历");
binaryTree.postOrder();
// 结果:
// 前序遍历4次(比较4次)
// 中序遍历3次(比较3次)
// 后序遍历2次(比较2次)
System.out.println("前序遍历查找");
HeroNode resNode = binaryTree.preOrderSearch(5);
if (resNode != null) {
System.out.printf("找到了,信息为no=%d name=%s", resNode.getNo(), resNode.getName());
} else {
System.out.printf("没有找到no = %d 的英雄", 5);
}
}
}
// BinaryTree 二叉树
class BinaryTree {
private HeroNode root;
public void setRoot(HeroNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.postOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
// 前序遍历查找
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.preOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 中序遍历查找
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.infixOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 后序遍历查找
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.postOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
// HeroNode结点
class HeroNode {
private int no;
private String name;
private HeroNode left;
private HeroNode right;
public HeroNode(int no, String name) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
// 前序遍历方法
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this); // 先输出父结点
// 递归左子树前序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
// 递归右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
// 先递归左子树中序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
// 输出父结点
System.out.println(this);
// 递归右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
// 先递归左子树中序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.postOrder();
}
// 递归右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.postOrder();
}
// 输出父结点
System.out.println(this);
}
/**
* 前序遍历查找
* @param no 查找的no
* @return 如果找打就返回Node,如果没有找到就返回null
*/
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
System.out.println("进入前序遍历查找");
//比较当前结点
if(this.no == no) {
return this;
}
//1,则判断当前结点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归前序查找
//2,如果左递归前序查找,找到结点,则返回
HeroNode resNode = null; // 结果结点
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.preOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) {// 说明左子树找到
return resNode;
}
//1、左递归前序查找,找到结点,则返回,否继续判断,
//2、当前的结点的右子节点是否为空,如果不空,则继续向右递归前序查找
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.preOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode;
}
// 中序遍历查找
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
//判断当前结点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归中序查找
HeroNode resNode = null;
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("进入中序遍历查找");
//如果找到,则返回,如果没有找到,就和当前结点比较,如果是则返回当前结点
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
// 向右递归中序查找
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode;
}
// 后序遍历查找
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
//判断当前结点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归后序查找
HeroNode resNode = null;
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) { // 左子树找到
return resNode;
}
// 如果左子树没有找到,则向右子树进行后序遍历查找
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) { // 右子树找到
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("进入后遍历查找");
// 如果左右子树都没有找到,就比较当前结点
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
return resNode;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public HeroNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(HeroNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public HeroNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(HeroNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
删除结点(与前序类似)
-
如果删除的节点是叶子节点,则删除该节点
-
如果删除的节点是非叶子节点,则删除该子树
思路
- 因为我们的二叉树是单向的,所以我们是判断当前结点的子结点是否需要删除结点,而不能去判断当前这个结点是不是需要删除结点
- 如果当前结点的左子结点不为空,并且左子结点就是要删除结点,就将this.left=null; 并且就返回(结束递归删除)
- 如果当前结点的右子结点不为空,并且右子结点就是要删除结点,就将this.righta=null; 并且就返回(结束递归删除)
- 如果第2和第3步没有删除结点,那么我们就需要向左子树进行递归删除
- 如果第4步也没有删除结点,则应当向右子树进行递归删除
- 考虑如果树是空树root,如果只有一个root结点,则等价将二叉树置空
在HeroNode中增加了delNode方法
// 递归删除结点
public void delNode(int no) {
// 检查左子节点
if (this.left != null && this.left.no == no) {
this.left = null;
return;
}
// 检查右子节点
if (this.right != null && this.right.no == no) {
this.right = null;
return;
}
// 左子树递归
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.delNode(no);
}
// 右子树递归
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.delNode(no);
}
}
在BinaryTree增加了delNode调用代码
// 删除结点
public void delNode(int no) {
if (root != null) {
// 如果只有一个root结点,直接判断
if (root.getNo() == no) {
root = null;
} else {
root.delNode(no);
}
}else {
System.out.println("空树,不能删除");
}
}
总代码
package com.xiaolu.tree;
/**
* @author 林小鹿
* @version 1.0
* 二叉树
*/
public class BinaryTreeMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
HeroNode root = new HeroNode(1, "小米");
HeroNode node2 = new HeroNode(2, "小鹿");
HeroNode node3 = new HeroNode(3, "小红");
HeroNode node4 = new HeroNode(4, "张三");
HeroNode node5 = new HeroNode(5, "李四");
root.setLeft(node2);
root.setRight(node3);
node3.setRight(node4);
node3.setLeft(node5);
binaryTree.setRoot(root);
System.out.println("前序遍历");
binaryTree.preOrder();
System.out.println("中序遍历");
binaryTree.infixOrder();
System.out.println("后序遍历");
binaryTree.postOrder();
// 结果:
// 前序遍历4次(比较4次)
// 中序遍历3次(比较3次)
// 后序遍历2次(比较2次)
System.out.println("前序遍历查找");
HeroNode resNode = binaryTree.preOrderSearch(5);
if (resNode != null) {
System.out.printf("找到了,信息为no=%d name=%s", resNode.getNo(), resNode.getName());
} else {
System.out.printf("没有找到no = %d 的英雄", 5);
}
System.out.println("删除前");
binaryTree.preOrder();
binaryTree.delNode(3);
System.out.println("删除后");
binaryTree.preOrder();
}
}
// BinaryTree 二叉树
class BinaryTree {
private HeroNode root;
public void setRoot(HeroNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
// 删除结点
public void delNode(int no) {
if (root != null) {
// 如果只有一个root结点,直接判断
if (root.getNo() == no) {
root = null;
} else {
root.delNode(no);
}
}else {
System.out.println("空树,不能删除");
}
}
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.postOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
// 前序遍历查找
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.preOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 中序遍历查找
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.infixOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 后序遍历查找
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.postOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
// HeroNode结点
class HeroNode {
private int no;
private String name;
private HeroNode left;
private HeroNode right;
public HeroNode(int no, String name) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
// 递归删除结点
public void delNode(int no) {
// 检查左子节点
if (this.left != null && this.left.no == no) {
this.left = null;
return;
}
// 检查右子节点
if (this.right != null && this.right.no == no) {
this.right = null;
return;
}
// 左子树递归
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.delNode(no);
}
// 右子树递归
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.delNode(no);
}
}
// 前序遍历方法
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this); // 先输出父结点
// 递归左子树前序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
// 递归右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
// 先递归左子树中序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
// 输出父结点
System.out.println(this);
// 递归右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
// 先递归左子树中序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.postOrder();
}
// 递归右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.postOrder();
}
// 输出父结点
System.out.println(this);
}
/**
* 前序遍历查找
* @param no 查找的no
* @return 如果找打就返回Node,如果没有找到就返回null
*/
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
System.out.println("进入前序遍历查找");
//比较当前结点
if(this.no == no) {
return this;
}
//1,则判断当前结点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归前序查找
//2,如果左递归前序查找,找到结点,则返回
HeroNode resNode = null; // 结果结点
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.preOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) {// 说明左子树找到
return resNode;
}
//1、左递归前序查找,找到结点,则返回,否继续判断,
//2、当前的结点的右子节点是否为空,如果不空,则继续向右递归前序查找
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.preOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode;
}
// 中序遍历查找
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
//判断当前结点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归中序查找
HeroNode resNode = null;
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("进入中序遍历查找");
//如果找到,则返回,如果没有找到,就和当前结点比较,如果是则返回当前结点
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
// 向右递归中序查找
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode;
}
// 后序遍历查找
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
//判断当前结点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归后序查找
HeroNode resNode = null;
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) { // 左子树找到
return resNode;
}
// 如果左子树没有找到,则向右子树进行后序遍历查找
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) { // 右子树找到
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("进入后遍历查找");
// 如果左右子树都没有找到,就比较当前结点
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
return resNode;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public HeroNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(HeroNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public HeroNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(HeroNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
顺序存储二叉树
广度优先遍历,数组存储方式和树的存储方式的相互转换,查询仍然可以使用二叉树查询遍历
特点
- 顺序二叉树通常只考虑完全二叉树
- 第n个元素的左子节点为 2 ∗ n + 1 2*n+1 2∗n+1
- 第n个元素的右子节点为 2 ∗ n + 2 2*n+2 2∗n+2
- 第n个元素的父节点为 ( n − 1 ) / 2 (n-1)/2 (n−1)/2
- n表示二叉树中的第几个元素【数组的下标】(按0开始编号)
试题
给你一个数组 {1,2,3,4,5,6,7},要求以二叉树前序遍历的方式进行遍历。
前序遍历
// index 数组的下标n
public void preOrder(int index) {
// 如果数组为空
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
System.out.println("数组为空,不能按照二叉树的前序遍历");
return;
}
// 输出当前元素
System.out.printf("%d ", arr[index]);
// 向左递归遍历
if ((2 * index + 1) < arr.length) {
preOrder(2 * index + 1);
}
// 向右递归遍历
if ((2 * index + 2) < arr.length) {
preOrder(2 * index + 2);
}
}
中序遍历
// 顺序存储二叉树的中序遍历
public void infixOrder(int index) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
System.out.println("数组为空,不能按照二叉树的前序遍历");
return;
}
// 向左
if ((2 * index + 1) < arr.length) {
infixOrder(2 * index + 1);
}
// 当前结点
System.out.printf("%d ", arr[index]);
// 向右
if ((2 * index + 2) < arr.length) {
infixOrder(2 * index + 2);
}
}
后序遍历
// 顺序存储二叉树的后序遍历
public void postOrder(int index) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
System.out.println("数组为空,不能按照二叉树的前序遍历");
return;
}
// 向左
if ((2 * index + 1) < arr.length) {
postOrder(2 * index + 1);
}
// 向右
if ((2 * index + 2) < arr.length) {
postOrder(2 * index + 2);
}
// 当前结点
System.out.printf("%d ", arr[index]);
}
总代码
package com.xiaolu.tree;
/**
* @author 林小鹿
* @version 1.0
* 顺序存储二叉树遍历
* 数组存储转二叉树存储
*/
public class ArrBinaryTreeMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
ArrBinaryTree arrBinaryTree = new ArrBinaryTree(arr);
arrBinaryTree.preOrder(); // 1,2,4,5,3,6,7
arrBinaryTree.infixOrder(); // 4,2,5,1,6,3,7
arrBinaryTree.postOrder(); // 4,5,2,6,7,3,1
}
}
// 实现顺序存储二叉树遍历
class ArrBinaryTree {
private int[] arr; // 存储数据结点的数组
public ArrBinaryTree(int[] arr) {
this.arr = arr;
}
public void preOrder() {
this.preOrder(0);
System.out.println();
}
public void infixOrder() {
this.infixOrder(0);
System.out.println();
}
public void postOrder() {
this.postOrder(0);
System.out.println();
}
// 顺序存储二叉树的前序遍历
// index 数组的下标n
public void preOrder(int index) {
// 如果数组为空
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
System.out.println("数组为空,不能按照二叉树的前序遍历");
return;
}
// 输出当前元素
System.out.printf("%d ", arr[index]);
// 向左递归遍历
if ((2 * index + 1) < arr.length) {
preOrder(2 * index + 1);
}
// 向右递归遍历
if ((2 * index + 2) < arr.length) {
preOrder(2 * index + 2);
}
}
// 顺序存储二叉树的中序遍历
public void infixOrder(int index) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
System.out.println("数组为空,不能按照二叉树的前序遍历");
return;
}
// 向左
if ((2 * index + 1) < arr.length) {
infixOrder(2 * index + 1);
}
// 当前结点
System.out.printf("%d ", arr[index]);
// 向右
if ((2 * index + 2) < arr.length) {
infixOrder(2 * index + 2);
}
}
// 顺序存储二叉树的后序遍历
public void postOrder(int index) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
System.out.println("数组为空,不能按照二叉树的前序遍历");
return;
}
// 向左
if ((2 * index + 1) < arr.length) {
postOrder(2 * index + 1);
}
// 向右
if ((2 * index + 2) < arr.length) {
postOrder(2 * index + 2);
}
// 当前结点
System.out.printf("%d ", arr[index]);
}
}
线索化二叉树
有效利用左右指针
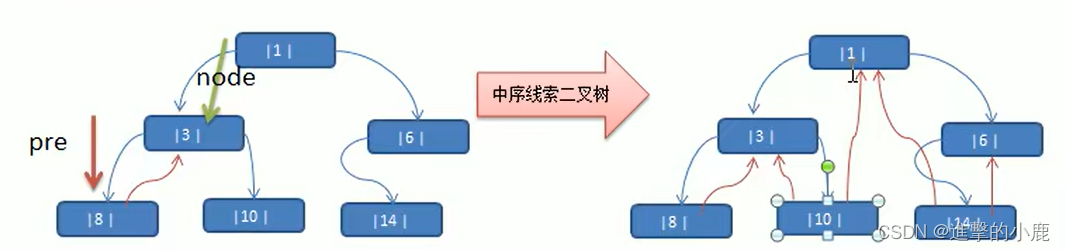
- n个结点的二叉链表中含有n+1【公式3 n + 1 = 2 n − ( n − 1 ) n+1=2n-(n-1) n+1=2n−(n−1)】个空指针域。利用二叉链表中的空指针域,存放指向该结点在某种遍历次序下的前驱和后继结点的指针(这种附加的指针称为"线索")
- 这种加上了线索的二叉链表称为线索链表,相应的二叉树称为线索二叉树(Threaded BinaryTree),根据线索性质的不同,线索二叉树可分为前序线索二叉树、中序线索二叉树和后序线索二叉树三种
- 一个结点的前一个结点,称为前驱结点
- 一个结点的后一个结点,称为后继结点
注意:前后驱结点并不一定等于左右子树
package com.xiaolu.tree.threadedbinarytree;
/**
* @author 林小鹿
* @version 1.0
* 线索化二叉树 --- 中序遍历
*/
public class ThreadedBinaryTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeroNode root = new HeroNode(1, "tom");
HeroNode node2 = new HeroNode(3, "jack");
HeroNode node3 = new HeroNode(6, "smith");
HeroNode node4 = new HeroNode(8, "mary");
HeroNode node5 = new HeroNode(10, "king");
HeroNode node6 = new HeroNode(14, "dim");
//二叉树,后面我们要递归创建,目前先手动创建
root.setLeft(node2);
root.setRight(node3);
node2.setLeft(node4);
node2.setRight(node5);
node3.setLeft(node6);
ThreadBinaryTree threadBinaryTree = new ThreadBinaryTree();
threadBinaryTree.setRoot(root);
threadBinaryTree.threadedNodes();
// 测试
HeroNode leftNode = node5.getLeft();
HeroNode rightNode = node5.getRight();
System.out.println("10号结点的前驱结点=" + leftNode);
System.out.println("10号结点的后驱结点=" + rightNode);
}
}
// BinaryTree 实现了线索化功能的二叉树
class ThreadBinaryTree {
private HeroNode root;
// 为了实现线索化,需要创建要给指向当前结点的前驱结点的指针
private HeroNode pre = null;
public void setRoot(HeroNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
public void threadedNodes() {
this.threadedNodes(root);
}
/**
* 对二叉树进行中序线索化
*
* @param node 需要线索化的结点
*/
public void threadedNodes(HeroNode node) {
// 如果 node == null,不能线索化
if (node == null) {
return;
}
// 1.先线索化左子树
threadedNodes(node.getLeft());
// 2.线索化当前结点
if (node.getLeft() == null) {
// 让当前结点的左指针指向前驱结点
node.setLeft(pre);
// 修改当前结点的左指针类型,指向前驱结点
node.setLeftType(1);
}
// 处理后继结点
if (pre != null && pre.getRight() == null) {
// 让前驱结点的右指针指向当前结点
pre.setRight(node);
// 修改前驱结点的右指针类型
pre.setRightType(1);
}
// 每处理一个结点后,让当前结点是下一个结点的前驱结点
pre = node;
// 3.线索化右子树
threadedNodes(node.getRight());
}
// 删除结点
public void delNode(int no) {
if (root != null) {
// 如果只有一个root结点,直接判断
if (root.getNo() == no) {
root = null;
} else {
root.delNode(no);
}
} else {
System.out.println("空树,不能删除");
}
}
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.postOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
// 前序遍历查找
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.preOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 中序遍历查找
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.infixOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 后序遍历查找
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.postOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
// HeroNode结点
class HeroNode {
private int no;
private String name;
private HeroNode left;
private HeroNode right;
//1.如果 leftType==0表示指向的是左子树,如果1则表示指向前驱结点
//2.如果 rightType=0表示指向是右子树,如果1表示指向后继结点
private int leftType;
private int rightType;
public HeroNode(int no, String name) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
// 递归删除结点
public void delNode(int no) {
// 检查左子节点
if (this.left != null && this.left.no == no) {
this.left = null;
return;
}
// 检查右子节点
if (this.right != null && this.right.no == no) {
this.right = null;
return;
}
// 左子树递归
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.delNode(no);
}
// 右子树递归
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.delNode(no);
}
}
// 前序遍历方法
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this); // 先输出父结点
// 递归左子树前序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
// 递归右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
// 先递归左子树中序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
// 输出父结点
System.out.println(this);
// 递归右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
// 先递归左子树中序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.postOrder();
}
// 递归右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.postOrder();
}
// 输出父结点
System.out.println(this);
}
/**
* 前序遍历查找
*
* @param no 查找的no
* @return 如果找打就返回Node,如果没有找到就返回null
*/
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
System.out.println("进入前序遍历查找");
//比较当前结点
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
//1,则判断当前结点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归前序查找
//2,如果左递归前序查找,找到结点,则返回
HeroNode resNode = null; // 结果结点
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.preOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) {// 说明左子树找到
return resNode;
}
//1、左递归前序查找,找到结点,则返回,否继续判断,
//2、当前的结点的右子节点是否为空,如果不空,则继续向右递归前序查找
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.preOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode;
}
// 中序遍历查找
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
//判断当前结点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归中序查找
HeroNode resNode = null;
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("进入中序遍历查找");
//如果找到,则返回,如果没有找到,就和当前结点比较,如果是则返回当前结点
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
// 向右递归中序查找
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode;
}
// 后序遍历查找
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
//判断当前结点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归后序查找
HeroNode resNode = null;
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) { // 左子树找到
return resNode;
}
// 如果左子树没有找到,则向右子树进行后序遍历查找
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) { // 右子树找到
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("进入后遍历查找");
// 如果左右子树都没有找到,就比较当前结点
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
return resNode;
}
public int getLeftType() {
return leftType;
}
public void setLeftType(int leftType) {
this.leftType = leftType;
}
public int getRightType() {
return rightType;
}
public void setRightType(int rightType) {
this.rightType = rightType;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public HeroNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(HeroNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public HeroNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(HeroNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
遍历线索化二叉树
因为线索化后,各个结点指向有变化,因此原来的遍历方式不能使用,这时需要使用新的方式遍历线索化二叉树,各个节点可以通过线型方式遍历,因此无需使用递归方式,这样也提高了遍历的效率。遍历的次序应当和中序遍历保持一致。
ThreadBinaryTree类中写的 中序遍历
// 遍历线索化二叉树 --- 中序遍历
public void threadedList() {
// 定义一个变量,存储当前遍历的结点,从root开始
HeroNode node = root;
while (node != null) {
// 循环的找到leftType == 1的结点,第一个找到就是8结点
// 后面随着遍历而变化,因为当leftType==1时,说明该结点是按照线索化处理后的有效结点
while (node.getLeftType() == 0) {
node = node.getLeft();
}
// 打印当前这个结点
System.out.println(node);
// 如果当前结点的右指针指向的是后继结点,就一直输出
while (node.getRightType() == 1) {
// 获取到当前结点的后继节点
node = node.getRight();
System.out.println(node);
}
// 替换这个遍历的结点
node = node.getRight();
}
}
总代码
package com.xiaolu.tree.threadedbinarytree;
/**
* @author 林小鹿
* @version 1.0
* 线索化二叉树 --- 中序遍历
*/
public class ThreadedBinaryTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeroNode root = new HeroNode(1, "tom");
HeroNode node2 = new HeroNode(3, "jack");
HeroNode node3 = new HeroNode(6, "smith");
HeroNode node4 = new HeroNode(8, "mary");
HeroNode node5 = new HeroNode(10, "king");
HeroNode node6 = new HeroNode(14, "dim");
//二叉树,后面我们要递归创建,目前先手动创建
root.setLeft(node2);
root.setRight(node3);
node2.setLeft(node4);
node2.setRight(node5);
node3.setLeft(node6);
ThreadBinaryTree threadBinaryTree = new ThreadBinaryTree();
threadBinaryTree.setRoot(root);
threadBinaryTree.threadedNodes();
// 测试
HeroNode leftNode = node5.getLeft();
HeroNode rightNode = node5.getRight();
System.out.println("10号结点的前驱结点=" + leftNode);
System.out.println("10号结点的后驱结点=" + rightNode);
System.out.println("使用线索化的方式遍历线索化二叉树");
threadBinaryTree.threadedList();
}
}
// BinaryTree 实现了线索化功能的二叉树
class ThreadBinaryTree {
private HeroNode root;
// 为了实现线索化,需要创建要给指向当前结点的前驱结点的指针
private HeroNode pre = null;
public void setRoot(HeroNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
public void threadedNodes() {
this.threadedNodes(root);
}
// 遍历线索化二叉树 --- 中序
public void threadedList() {
// 定义一个变量,存储当前遍历的结点,从root开始
HeroNode node = root;
while (node != null) {
// 循环的找到leftType == 1的结点,第一个找到就是8结点
// 后面随着遍历而变化,因为当leftType==1时,说明该结点是按照线索化处理后的有效结点
while (node.getLeftType() == 0) {
node = node.getLeft();
}
// 打印当前这个结点
System.out.println(node);
// 如果当前结点的右指针指向的是后继结点,就一直输出
while (node.getRightType() == 1) {
// 获取到当前结点的后继节点
node = node.getRight();
System.out.println(node);
}
// 替换这个遍历的结点
node = node.getRight();
}
}
/**
* 对二叉树进行中序线索化
*
* @param node 需要线索化的结点
*/
public void threadedNodes(HeroNode node) {
// 如果 node == null,不能线索化
if (node == null) {
return;
}
// 1.先线索化左子树
threadedNodes(node.getLeft());
// 2.线索化当前结点
if (node.getLeft() == null) {
// 让当前结点的左指针指向前驱结点
node.setLeft(pre);
// 修改当前结点的左指针类型,指向前驱结点
node.setLeftType(1);
}
// 处理后继结点
if (pre != null && pre.getRight() == null) {
// 让前驱结点的右指针指向当前结点
pre.setRight(node);
// 修改前驱结点的右指针类型
pre.setRightType(1);
}
// 每处理一个结点后,让当前结点是下一个结点的前驱结点
pre = node;
// 3.线索化右子树
threadedNodes(node.getRight());
}
// 删除结点
public void delNode(int no) {
if (root != null) {
// 如果只有一个root结点,直接判断
if (root.getNo() == no) {
root = null;
} else {
root.delNode(no);
}
} else {
System.out.println("空树,不能删除");
}
}
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.postOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
// 前序遍历查找
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.preOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 中序遍历查找
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.infixOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 后序遍历查找
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.postOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
// HeroNode结点
class HeroNode {
private int no;
private String name;
private HeroNode left;
private HeroNode right;
//1.如果 leftType==0表示指向的是左子树,如果1则表示指向前驱结点
//2.如果 rightType=0表示指向是右子树,如果1表示指向后继结点
private int leftType;
private int rightType;
public HeroNode(int no, String name) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
// 递归删除结点
public void delNode(int no) {
// 检查左子节点
if (this.left != null && this.left.no == no) {
this.left = null;
return;
}
// 检查右子节点
if (this.right != null && this.right.no == no) {
this.right = null;
return;
}
// 左子树递归
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.delNode(no);
}
// 右子树递归
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.delNode(no);
}
}
// 前序遍历方法
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this); // 先输出父结点
// 递归左子树前序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
// 递归右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
// 先递归左子树中序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
// 输出父结点
System.out.println(this);
// 递归右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
// 先递归左子树中序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.postOrder();
}
// 递归右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.postOrder();
}
// 输出父结点
System.out.println(this);
}
/**
* 前序遍历查找
*
* @param no 查找的no
* @return 如果找打就返回Node,如果没有找到就返回null
*/
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
System.out.println("进入前序遍历查找");
//比较当前结点
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
//1,则判断当前结点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归前序查找
//2,如果左递归前序查找,找到结点,则返回
HeroNode resNode = null; // 结果结点
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.preOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) {// 说明左子树找到
return resNode;
}
//1、左递归前序查找,找到结点,则返回,否继续判断,
//2、当前的结点的右子节点是否为空,如果不空,则继续向右递归前序查找
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.preOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode;
}
// 中序遍历查找
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
//判断当前结点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归中序查找
HeroNode resNode = null;
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("进入中序遍历查找");
//如果找到,则返回,如果没有找到,就和当前结点比较,如果是则返回当前结点
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
// 向右递归中序查找
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode;
}
// 后序遍历查找
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
//判断当前结点的左子节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归后序查找
HeroNode resNode = null;
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) { // 左子树找到
return resNode;
}
// 如果左子树没有找到,则向右子树进行后序遍历查找
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) { // 右子树找到
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("进入后遍历查找");
// 如果左右子树都没有找到,就比较当前结点
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
return resNode;
}
public int getLeftType() {
return leftType;
}
public void setLeftType(int leftType) {
this.leftType = leftType;
}
public int getRightType() {
return rightType;
}
public void setRightType(int rightType) {
this.rightType = rightType;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public HeroNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(HeroNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public HeroNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(HeroNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
数据结构实际应用
堆排序
以数组的方式进行存储,但是实际上还是树结构,以树结构的方式进行查询遍历,速度非常快,平均时间复杂度均为 O ( n log 2 n ) O(n\log_2n) O(nlog2n)
- 堆排序是利用堆这种数据结构而设计的一种排序算法,堆排序是一种选择排序,它的最坏,最好,平均时间复杂度均为 O ( n log 2 n ) O(n\log_2n) O(nlog2n),它也是不稳定排序。
- 堆是具有以下性质的完全二叉树:每个结点的值都大于或等于其左右孩子结点的值,称为大顶堆,注意:没有要求结点的左孩子的值和右孩子的值的大小关系。
- 每个结点的值都小于或等于其左右孩子结点的值,称为小顶堆
- 大顶堆特点: a r r [ i ] > = a r r [ 2 ∗ i + 1 ] arr[i]>=arr[2*i+1] arr[i]>=arr[2∗i+1] && $ arr[i]>=arr[2*i+2]$ // i 对应第几个节点,i 从0开始编号
- 小顶堆特点: a r r [ i ] < = a r r [ 2 ∗ i + 1 ] arr[i]<=arr[2*i+1] arr[i]<=arr[2∗i+1] && $ arr[i]<=arr[2*i+2]$ // i 对应第几个节点,i 从0开始编号
- 一般升序采用大顶堆,降序采用小顶堆
- (arr.length / 2 - 1) 4:能够定位到顺序存储二叉树的倒数第二层索引
- 规则:从左至右,从下至上
基本思想:
- 将待排序序列构造成一个大顶堆
- 此时,整个序列的最大值就是堆顶的根节点。
- 将其与末尾元素进行交换,此时末尾就为最大值。
- 然后将剩余n-1个元素重新构造成一个堆,这样会得到n个元素的次小值。如此反复执行,便能得到一个有序序列了。
可以看到在构建大顶堆的过程中,元素的个数逐渐减少,最后就得到一个有序序列了
流程
从左至右,从下至上
- 将无序序列构建城一个堆,根据升序降序需求选择大顶堆或小顶堆
- 将堆顶元素与末尾元素交换,将最大元素 “沉” 到数组末端
- 重新调整结构,使其满足堆定义,然后继续交换堆顶元素与当前末尾元素,反复执行调整 + 交换步骤,直到整个序列有序。
package com.xiaolu.tree;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author 林小鹿
* @version 1.0
* 堆排序 --- 升序
*/
public class HeapSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 升序排序
int[] arr = {4, 6, 8, 5, 9};
heapSort(arr);
}
// 编写一个堆排序的方法
public static void heapSort(int[] arr) {
int temp = 0;
System.out.println("堆排序!!");
// // 分布完成
// adjustHeap(arr, 1, arr.length);
// System.out.println("第一次" + Arrays.toString(arr)); // [4, 9, 8, 5, 6]
// adjustHeap(arr, 0, arr.length);
// System.out.println("第二次" + Arrays.toString(arr)); // [9, 6, 8, 5, 4]
// arr.length / 2 - 1 定位到顺序二叉树的倒数第二层坐标索引
for (int i = arr.length / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
adjustHeap(arr, i, arr.length);
}
// 将堆顶元素与末尾元素交换,将最大元素 “沉” 到数组末端
// 重新调整结构,使其满足堆定义,然后继续交换堆顶元素与当前末尾元素,反复执行调整 + 交换步骤,直到整个序列有序。
for (int j = arr.length - 1; j > 0; j--) {
// 交换
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[0];
arr[0] = temp;
adjustHeap(arr, 0, j);
}
System.out.println("数组=" + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
/**
* 将一个数组(二叉树),调整成一个大顶堆
* 将以 i 对应的非叶子结点的树调整成大顶堆 此时的arr为一颗顺序存储二叉树
* 举例int arr[] = {4,6,8,5,9} => i=1 => adjustHeap => 得到 {4,9,8,5,6}
* 如果我们再次调用 adjustHeap 传入的是 i=0 => 得到{4,9,8,5,6} => {9,6,8,5,4}
*
* @param arr 待调整的数组
* @param i 表示非叶子结点在数组中索引
* @param length 表示对多少个元素继续调整
*/
public static void adjustHeap(int[] arr, int i, int length) {
int temp = arr[i];
// 开始调整
// k = i * 2 + 1 k是i结点的左子结点
for (int k = i * 2 + 1; k < length; k = k * 2 + 1) {
if (k + 1 < length && arr[k] < arr[k + 1]) {// 左子节点的值小于右子结点的值
k++;
}
if (arr[k] > temp) { // 如果子结点大于父结点
arr[i] = arr[k];
i = k; // i 指向 k,继续循环比较
} else {
break; // !
}
}
// 当 for 循环结束后,已经将i 为父结点的树的最大值放在了最顶(局部)
arr[i] = temp; // 将temp值放到调整后的位置
}
}
赫夫曼树
叶子才是有效数值
-
给定n个权值作为n个叶子结点,构造一棵二叉树,若该树的带权路径长度(wpl)达到最小,称这样的二叉树为最优二叉树,也称为哈夫曼树Huffman Tree),还有的书翻译为霍夫曼树。
-
赫夫曼树是带权路径长度最短的树,权值较大的结点离根较近。
-
路径和路径长度:在一棵树中,从一个结点往下可以达到的孩子或孙子结点之间的通路,称为路径。通路中分支的数目称为路径长度。若规定根结点的层数为1,则从根结点到第L层结点的路径长度为 L-1
-
结点的权及带权路径长度:若将树中结点赋给一个有着某种含义的数值,则这个数值称为该结点的权。结点的带权路径长度为:从根结点到该结点之间的路径长度与该结点的权的乘积
-
树的带权路径长度:树的带权路径长度规定为所有叶子结点的带权路径长度之和,记为WPL(weighted path length),权值越大的结点离根结点越近的二叉树才是最优二叉树。
-
WPL最小的就是赫夫曼树
步骤思路
- 从小到大进行排序,将每一个数据,每个数据都是一个节点,每个节点可以看成是一颗最简单的二叉树
- 取出根节点权值最小的两颗二叉树
- 组成一颗新的二叉树,该新的二叉树的根节点的权值是前面两颗二叉树根节点权值的和
- 再将这颗新的二叉树,以根节点的权值大小再次排序,不断重复1-2-3-4的步骤,直到数列中,所有的数据都被处理,就得到一颗赫夫曼树
package com.xiaolu.huffmantree;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 林小鹿
* @version 1.0
*/
public class HuffmanTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {13, 7, 8, 3, 29, 6, 1};
Node root = createHuffmanTree(arr);
// 前序遍历二叉树
System.out.println("前序遍历二叉树");
preOrder(root);
}
// 调用前序遍历
public static void preOrder(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
root.preOrder(root);
} else {
System.out.println("空树,无法遍历");
}
}
// 创建赫夫曼树的方法
/**
*
* @param arr 需要创建成哈夫曼树的数组
* @return 创建好后的赫夫曼树的 root结点
*/
public static Node createHuffmanTree(int[] arr) {
// 1.遍历arr数组
// 2.将arr的每个元素构成一个Node
// 3.将Node 放入到ArrayList中
List<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<Node>();
for (int value : arr) {
nodes.add(new Node(value));
}
// 开始循环处理
while (nodes.size() > 1) {
// 排序
Collections.sort(nodes);
System.out.println("nodes = " + nodes);
// 取出根节点权值最小的两颗二叉树
Node leftNode = nodes.get(0);
Node rightNode = nodes.get(1);
// 构建一颗新的二叉树
Node parent = new Node(leftNode.value + rightNode.value);
parent.left = leftNode;
parent.right = rightNode;
// 从ArrayList中删除处理过的二叉树
nodes.remove(leftNode);
nodes.remove(rightNode);
// 将parent加入到nodes
nodes.add(parent);
// 重新排序
Collections.sort(nodes);
}
// 返回赫夫曼树的root结点
return nodes.get(0);
}
}
// 为了让Node 对象支持排序Collections集合排序
// 让Node 实现Comparable接口
class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
int value; // 结点权值
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder(Node node) {
// System.out.println(this);
// if (this.left != null) {
// this.left.preOrder();
// }
// if (this.right != null) {
// this.right.preOrder();
// }
// 另一种写法
if (node == null) {
return;
}
System.out.println(node);
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"value=" + value +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
// 从小到大
return this.value - o.value;
}
}
赫夫曼编码
- 赫夫曼编码也翻译为 哈夫曼编码(Huffman Coding),又称霍夫曼编码,是一种编码方式,属于一种程序算法
- 赫夫曼编码是赫哈夫曼树在电讯通信中的经典的应用之一。
- 赫夫曼编码广泛地用于数据文件压缩。其**压缩率通常在20%~90%**之间
- 赫夫曼码是可变字长编码(VLC)的一种。Huffman于1952年提出一种编码方法,称之为最佳编码
通信领域中对数据处理方式
-
定长编码:将数据一字不差全部编码转换成二进制
-
变长编码:有着自身的一套规则编码达到高效通信
-
前缀编码:字符的编码都不能是其他字符编码的前缀,符合此要求的编码叫做前缀编码,即不能匹配到重复的编码
-
赫夫曼编码:按照字符出现的次数构建一颗赫夫曼树,次数作为权值
步骤
-
按照字符出现的次数构建一颗赫夫曼树,次数作为权值
-
根据赫夫曼树,给各个字符规定编码(前缀编码),向左的路径为0 向右的路径为1
- 例如:u:10010
-
此编码满足前缀编码,即字符的编码都不能是其他字符编码的前缀。不会造成匹配的多义性
注意:这个赫夫曼树根据排序方法不同,也可能不太一样,这样对应的赫夫曼编码也不完全一样,但是wpl 是一样的,都是最小的,比如:如果我们让每次生成的新的二叉树总是排在权值相同的二叉树的最后一个,则生成的二叉树为:
代码
实现赫夫曼编码压缩数据的原理,创建 “i like like like java do you like a java” 对应的赫夫曼树
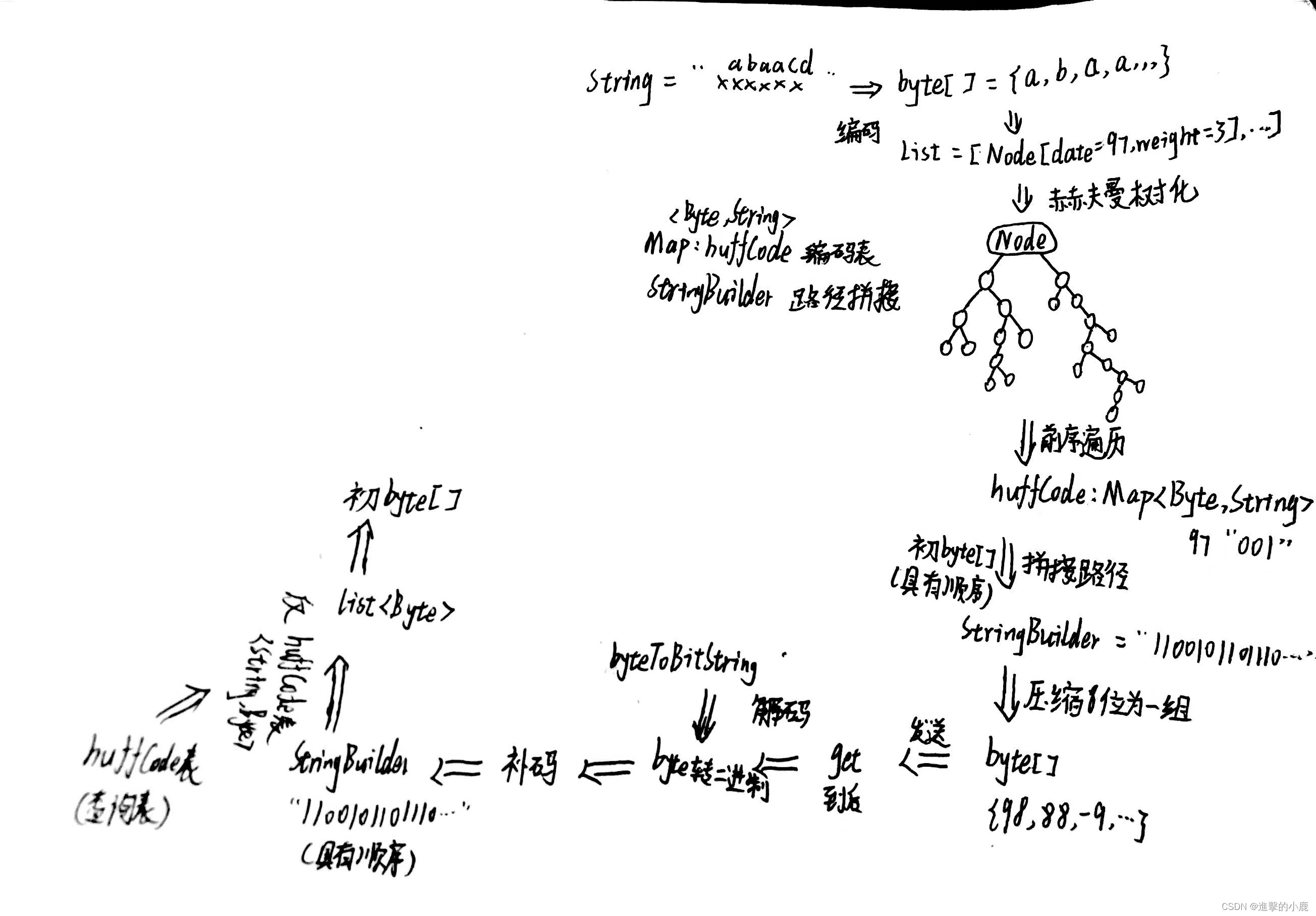
- Node {data(存放数据),weight(权值),left和right}
- 得到"i like like like java do you like a java’”对应的byte[] 数组
- 编写一个方法,将准备构建赫夫曼树的Node 节点放到List,形式[Node[date=97,weight=5], Node[date=32,weight=9]…],体现d:1 y:1 u:1 j:2 v:2 o:2 l:4 k:4 e:4 i:5 a:5 :9
- 可以通过List创建对应的赫夫曼树
- 生成赫夫曼树对应的赫夫曼编码(路径)【将传入的node结点的所有叶子结点的赫夫曼编码得到,并放入到HashMap<Byte, String>集合中】
- 根据生成的赫夫曼编码,压缩得到处理后的赫夫曼编码【字节数组】
- 从HashMap<Byte, String> 中获取路径并存储到StringBuilt中
- StringBuilt字符串 “101010001011111111001000101…” 压缩【八位为一字节】 转成byte[] 数组
package com.xiaolu.huffmantree.huffmancode;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author 林小鹿
* @version 1.0
*/
public class HuffmanCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "i like like like java do you like a java"; // 长度:40
byte[] contentBytes = content.getBytes();
System.out.println("压缩前长度:"+contentBytes.length);
// 调用封装的赫夫曼编码方法,得到一个压缩后的赫夫曼编码字节数组
byte[] huffmanCodeBytes = huffmanZip(contentBytes);
System.out.println("huffmanCodeBytes= " + Arrays.toString(huffmanCodeBytes));
System.out.println("压缩后长度:"+huffmanCodeBytes.length);
// 分布过程
/*
// 创建List集合
List<Node> node = getNode(contentBytes);
System.out.println(node);
System.out.println("赫夫曼树");
// 根据node 生成赫夫曼树
Node huffmanTreeRoot = createHuffmanTree(node);
preOrder(huffmanTreeRoot);
// 根据赫夫曼树生成对应的赫夫曼编码
Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes = getCodes(huffmanTreeRoot);
System.out.println("生成的赫夫曼编码表:" + huffmanCodes);
// 根据生成的赫夫曼编码,压缩得到处理后的赫夫曼编码
byte[] huffmanCodeBytes = zip(contentBytes, huffmanCodes);
System.out.println("压缩后");
System.out.println("huffmanCodeBytes= " + Arrays.toString(huffmanCodeBytes));// 长度:17
System.out.println("压缩后长度:"+huffmanCodeBytes.length); */
}
/**
* 封装赫夫曼编码步骤代码
* @param bytes 原始字符串对应的字节数组
* @return 经过赫夫曼编码处理后的字节数组 (压缩后的数组)
*/
private static byte[] huffmanZip(byte[] bytes) {
// 创建List集合
List<Node> node = getNode(bytes);
// 根据node 生成赫夫曼树
Node huffmanTreeRoot = createHuffmanTree(node);
// 根据赫夫曼树生成对应的赫夫曼编码
Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes = getCodes(huffmanTreeRoot);
// 根据生成的赫夫曼编码,压缩得到处理后的赫夫曼编码
return zip(bytes, huffmanCodes);
}
// 生成赫夫曼树对应的赫夫曼编码
// 1.将赫夫曼编码表存放在Map<Byte,String>形式
// 32->01 97->100 100->11000等等[形式]
static Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes = new HashMap<Byte, String>();
//2.在生成赫夫曼编码表示,需要去拼接路径,定义一个StringBuilder存储某个叶子结点的路径
static StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
// 将字符串对应的byte[]数组,通过生成的赫夫曼编码表,返回一个赫夫曼编码压缩后的byt[]
/**
* @param bytes 原始的字符串对应的byte[]
* @param huffmanCodes 生成的赫夫曼编码map
* @return 赫夫曼编码处理后的byte[]
* 举例:String content="i like like like java do you like a java"; =》byte[] contentBytes = content.getBytes()
* 返回的是字符串"1010100010111111110010001011111111001000101111111100100"
* => 对应的byte[] huffmanCodeBytes,即 8位对应一个byte,放入到huffmanCodeBytes
* huffmanCodeBytes[0] = 10101000(补) => byte[推导10101000 => 10101000 - 1 => 10100111(反码) => 11011000(原码)
* => -88
*/
private static byte[] zip(byte[] bytes, Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes) {
// 1.利用huffmanCodes 将 bytes 转成赫夫曼编码对应的字符串
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
// 遍历bytes 数组
for (byte b : bytes) {
stringBuilder.append(huffmanCodes.get(b));
}
// 将stringBuilder 转成byte[] 数组
int len = (stringBuilder.length() + 7) / 8; // 统计stringBuilder 的长度
// 等效于以下代码
/*
int len;
if (stringBuilder.length() % 8 == 0) {
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8;
} else {
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8 + 1;
}
*/
// 创建存储压缩后的byte数组
byte[] huffmanCodeBytes = new byte[len];
for (int i = 0, index = 0; i < stringBuilder.length(); i += 8, index++) {
String strByte;
// 8位为一字节
if (i + 8 > stringBuilder.length()) {
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i);
} else {
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i, i + 8);
}
// 将strByte 转成一个byte,放到 huffmanCodeBytes 中
huffmanCodeBytes[index] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(strByte, 2);
}
return huffmanCodeBytes;
}
// 为了调用方便,重载getCodes
private static Map<Byte, String> getCodes(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
// 处理左子树
getCodes(root.left, "0", stringBuilder);
// 处理右子树
getCodes(root.right, "1", stringBuilder);
return huffmanCodes;
}
/**
* 功能:将传入的node结点的所有叶子结点的赫夫曼编码得到,并放入到huffmanCodes集合
*
* @param node 传入的结点
* @param code 路径:左子节点是 0,右子节点是 1
* @param stringBuilder 用于拼接路径
*/
private static void getCodes(Node node, String code, StringBuilder stringBuilder) {
// 用于拼接路径
StringBuilder stringBuilder2 = new StringBuilder(stringBuilder);
// 将code 加入到 stringBuilder2
stringBuilder2.append(code);
if (node != null) {// 如果 node == null不处理
// 判断当前node是否为叶子结点
if (node.data == null) {// 非叶子结点
// 向左递归
getCodes(node.left, "0", stringBuilder2);
// 向右递归
getCodes(node.right, "1", stringBuilder2);
} else {// 叶子结点
// 存入
huffmanCodes.put(node.data, stringBuilder2.toString());
}
}
}
/**
* @param bytes 接收字节数组
* @return 返回 List 形式 [Node[date=97,weight=5], Node[date=32,weight=9]......],
*/
public static List<Node> getNode(byte[] bytes) {
List<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<>();
// 遍历bytes,统计每个byte出现的次数 -> map[key, value]
HashMap<Byte, Integer> counts = new HashMap<>();
for (byte b : bytes) {
Integer count = counts.get(b);
if (count == null) { // 第一次将字符加入到map中
counts.put(b, 1);
} else {// 出现次数 +1
counts.put(b, count + 1);
}
}
// 把每一个键值对转成一个Node 对象,并加入到nodes集合
// 遍历map
for (Map.Entry<Byte, Integer> entry : counts.entrySet()) {
nodes.add(new Node(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()));
}
return nodes;
}
private static Node createHuffmanTree(List<Node> nodes) {
while (nodes.size() > 1) {
// 排序
Collections.sort(nodes);
// 取出第一颗最小的二叉树
Node leftNode = nodes.get(0);
// 取出第二颗最小的二叉树
Node rightNode = nodes.get(1);
// 创建一颗新的二叉树,它的根节点 没有data,只有权值
Node parentNode = new Node(null, leftNode.weight + rightNode.weight);
parentNode.left = leftNode;
parentNode.right = rightNode;
// 从nodes中移除已经处理过的两颗二叉树
nodes.remove(leftNode);
nodes.remove(rightNode);
// 将新的二叉树添加到nodes
nodes.add(parentNode);
}
// 返回赫夫曼树的根节点
return nodes.get(0);
}
private static void preOrder(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("赫夫曼树为空");
}
}
}
class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
Byte data; // 存放数据(字符) 'a' --> 97
int weight; // 权值,表示字符出现的次数
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(Byte data, int weight) {
this.data = data;
this.weight = weight;
}
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this);
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
// 从小到大
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node[" +
"data=" + data +
", weight=" + weight +
']';
}
}
赫夫曼解码
步骤
- 将huffmanCodeBytes[-88,-65,-56,-65,-56,-65,-55,77E,-57,6,-24,-14,-117,-4,-60,-90,28]
重写先转成赫夫曼编码对应的二进制的字符串"1010100010111。。。" - 赫夫曼编码对应的二进制的字符串"1010100010111…" => 对照 赫夫曼编码 =》“i like like like java do you like a java”
package com.xiaolu.huffmantree.huffmancode;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author 林小鹿
* @version 1.0
*/
public class HuffmanCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "i like like like java do you like a java"; // 长度:40
byte[] contentBytes = content.getBytes();
System.out.println("压缩前长度:" + contentBytes.length);
// 调用封装的赫夫曼编码方法,得到一个压缩后的赫夫曼编码字节数组
byte[] huffmanCodeBytes = huffmanZip(contentBytes);
System.out.println("huffmanCodeBytes= " + Arrays.toString(huffmanCodeBytes));
System.out.println("压缩后长度:" + huffmanCodeBytes.length);
// 解码
byte[] sourceBytes = decode(huffmanCodes, huffmanCodeBytes);
System.out.println("原来的字符串=" + new String(sourceBytes));
// 分布过程
/*
// 创建List集合
List<Node> node = getNode(contentBytes);
System.out.println(node);
System.out.println("赫夫曼树");
// 根据node 生成赫夫曼树
Node huffmanTreeRoot = createHuffmanTree(node);
preOrder(huffmanTreeRoot);
// 根据赫夫曼树生成对应的赫夫曼编码
Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes = getCodes(huffmanTreeRoot);
System.out.println("生成的赫夫曼编码表:" + huffmanCodes);
// 根据生成的赫夫曼编码,压缩得到处理后的赫夫曼编码
byte[] huffmanCodeBytes = zip(contentBytes, huffmanCodes);
System.out.println("压缩后");
System.out.println("huffmanCodeBytes= " + Arrays.toString(huffmanCodeBytes));// 长度:17
System.out.println("压缩后长度:"+huffmanCodeBytes.length); */
}
// 1. 将huffmanCodeBytes[-88,-65,-56,-65,-56,-65,-55,77E,-57,6,-24,-14,-117,-4,-60,-90,28]
// 重写先转成赫夫曼编码对应的二进制的字符串"1010100010111。。。"
//2. 赫夫曼编码对应的二进制的字符串"1010100010111..." => 对照 赫夫曼编码 =》"i like like like java do you like a java"
/**
* 完成对压缩数据的解码
*
* @param huffmanCodes 赫夫曼编码表 map
* @param huffmanBytes 赫夫曼彪马得到的字节数组
* @return 原来字符串对应的数组
*/
private static byte[] decode(Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes, byte[] huffmanBytes) {
// 1.先得到 huffmanBytes对应的二进制的字符串,形式 1010100010111
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
// 将byte数组转成二进制字符串
for (int i = 0; i < huffmanBytes.length; i++) {
byte b = huffmanBytes[i];
// 判断是不是最后一个字节
boolean flag = (i == huffmanBytes.length - 1);
stringBuilder.append(byteToBitString(!flag, b));
}
// 把字符串按照指定的赫夫曼编码进行解码
// 把赫夫曼编码表进行调换,因为反向查询a->100 100->a
Map<String, Byte> map = new HashMap<>();
for (Map.Entry<Byte, String> entry : huffmanCodes.entrySet()) {
map.put(entry.getValue(), entry.getKey());
}
// 创建集合存放byte
List<Byte> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 扫描 stringBuilder
for (int i = 0; i < stringBuilder.length(); ) {
int count = 1; // 小的计数器
boolean flag = true;
Byte b = null;
while (flag) {
// 1010100010111...
// 递增的取出 key
String key = stringBuilder.substring(i, i + count);
b = map.get(key);
if (b == null) { // 说明没有匹配到
count++;
} else { // 匹配到
flag = false;
}
}
list.add(b);
i += count; // i 增长到count的位置
}
byte[] b = new byte[list.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
b[i] = list.get(i);
}
return b;
}
/**
* 将一个byte 转成一个二进制的字符串
*
* @param flag 标志是否需要补高位,如果是true,表示需要补高位
* @param b 传入的byte
* @return 该 byte对应的二进制字符串,注意是按补码返回的
*/
private static String byteToBitString(boolean flag, byte b) {
// 使用变量保存b
int temp = b;
// int对应的二进制的是32位(4个字节)
// 正数则会自动删除前面的无效0 ==> 需要补高位
// byte最后的一位长度是多少就是多少,不需要补零
if (flag) {// 判断是否需要补高位(是否为 byte最后的一位)
// 补高位
temp |= 256; // 按位或 256对应的二进制 1 0000 0000 | 0000 0001 => 1 0000 0001
}
String str = Integer.toBinaryString(temp); // 返回的是temp对应的二进制的补码
if (flag) {
return str.substring(str.length() - 8); // 取后八位
} else {// byte最后一位 => 直接返回
return str;
}
}
/**
* 封装赫夫曼编码步骤代码,方便调用
*
* @param bytes 原始字符串对应的字节数组
* @return 经过赫夫曼编码处理后的字节数组 (压缩后的数组)
*/
private static byte[] huffmanZip(byte[] bytes) {
// 创建List集合
List<Node> node = getNode(bytes);
// 根据node 生成赫夫曼树
Node huffmanTreeRoot = createHuffmanTree(node);
// 根据赫夫曼树生成对应的赫夫曼编码(路径)
Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes = getCodes(huffmanTreeRoot);
// 根据生成的赫夫曼编码,压缩得到处理后的赫夫曼编码
return zip(bytes, huffmanCodes);
}
// 生成赫夫曼树对应的赫夫曼编码
// 1.将赫夫曼编码表存放在Map<Byte,String>形式
// 32->01 97->100 100->11000等等[形式]
static Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes = new HashMap<Byte, String>();
//2.在生成赫夫曼编码表示,需要去拼接路径,定义一个StringBuilder存储某个叶子结点的路径
static StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
// 将字符串对应的byte[]数组,通过生成的赫夫曼编码表,返回一个赫夫曼编码压缩后的byt[]
/**
* @param bytes 原始的字符串对应的byte[]
* @param huffmanCodes 生成的赫夫曼编码map
* @return 赫夫曼编码处理后的byte[]
* 举例:String content="i like like like java do you like a java"; =》byte[] contentBytes = content.getBytes()
* 返回的是字符串"1010100010111111110010001011111111001000101111111100100"
* => 对应的byte[] huffmanCodeBytes,即 8位对应一个byte,放入到huffmanCodeBytes
* huffmanCodeBytes[0] = 10101000(补) => byte[推导10101000 => 10101000 - 1 => 10100111(反码) => 11011000(原码)
* => -88
*/
private static byte[] zip(byte[] bytes, Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes) {
// 1.利用huffmanCodes 将 bytes 转成赫夫曼编码对应的字符串
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
// 遍历bytes 数组
for (byte b : bytes) {
stringBuilder.append(huffmanCodes.get(b));
}
// 将stringBuilder 转成byte[] 数组
int len = (stringBuilder.length() + 7) / 8; // 统计stringBuilder 的长度
// 等效于以下代码
/*
int len;
if (stringBuilder.length() % 8 == 0) {
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8;
} else {
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8 + 1;
}
*/
// 创建存储压缩后的byte数组
byte[] huffmanCodeBytes = new byte[len];
for (int i = 0, index = 0; i < stringBuilder.length(); i += 8, index++) {
String strByte;
// 8位为一字节
if (i + 8 > stringBuilder.length()) {
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i);
} else {
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i, i + 8);
}
// 将strByte 转成一个byte,放到 huffmanCodeBytes 中
huffmanCodeBytes[index] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(strByte, 2);
}
return huffmanCodeBytes;
}
// 为了调用方便,重载getCodes
private static Map<Byte, String> getCodes(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
// 处理左子树
getCodes(root.left, "0", stringBuilder);
// 处理右子树
getCodes(root.right, "1", stringBuilder);
return huffmanCodes;
}
/**
* 功能:将传入的node结点的所有叶子结点的赫夫曼编码得到,并放入到huffmanCodes集合
*
* @param node 传入的结点
* @param code 路径:左子节点是 0,右子节点是 1
* @param stringBuilder 用于拼接路径
*/
private static void getCodes(Node node, String code, StringBuilder stringBuilder) {
// 用于拼接路径
StringBuilder stringBuilder2 = new StringBuilder(stringBuilder);
// 将code 加入到 stringBuilder2
stringBuilder2.append(code);
if (node != null) {// 如果 node == null不处理
// 判断当前node是否为叶子结点
if (node.data == null) {// 非叶子结点
// 向左递归
getCodes(node.left, "0", stringBuilder2);
// 向右递归
getCodes(node.right, "1", stringBuilder2);
} else {// 叶子结点
// 存入
huffmanCodes.put(node.data, stringBuilder2.toString());
}
}
}
/**
* @param bytes 接收字节数组
* @return 返回 List 形式 [Node[date=97,weight=5], Node[date=32,weight=9]......],
*/
public static List<Node> getNode(byte[] bytes) {
List<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<>();
// 遍历bytes,统计每个byte出现的次数 -> map[key, value]
HashMap<Byte, Integer> counts = new HashMap<>();
for (byte b : bytes) {
Integer count = counts.get(b);
if (count == null) { // 第一次将字符加入到map中
counts.put(b, 1);
} else {// 出现次数 +1
counts.put(b, count + 1);
}
}
// 把每一个键值对转成一个Node 对象,并加入到nodes集合
// 遍历map
for (Map.Entry<Byte, Integer> entry : counts.entrySet()) {
nodes.add(new Node(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()));
}
return nodes;
}
private static Node createHuffmanTree(List<Node> nodes) {
while (nodes.size() > 1) {
// 排序
Collections.sort(nodes);
// 取出第一颗最小的二叉树
Node leftNode = nodes.get(0);
// 取出第二颗最小的二叉树
Node rightNode = nodes.get(1);
// 创建一颗新的二叉树,它的根节点 没有data,只有权值
Node parentNode = new Node(null, leftNode.weight + rightNode.weight);
parentNode.left = leftNode;
parentNode.right = rightNode;
// 从nodes中移除已经处理过的两颗二叉树
nodes.remove(leftNode);
nodes.remove(rightNode);
// 将新的二叉树添加到nodes
nodes.add(parentNode);
}
// 返回赫夫曼树的根节点
return nodes.get(0);
}
private static void preOrder(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("赫夫曼树为空");
}
}
}
class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
Byte data; // 存放数据(字符) 'a' --> 97
int weight; // 权值,表示字符出现的次数
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(Byte data, int weight) {
this.data = data;
this.weight = weight;
}
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this);
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
// 从小到大
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node[" +
"data=" + data +
", weight=" + weight +
']';
}
}
使用赫夫曼完成对文件的压缩解压操作
压缩
将数据和赫夫曼编码表存入到文件中
/**
* 对文件进行压缩
*
* @param srcFile 待压缩的文件全路径
* @param dstFile 压缩后文件存放的全路径
*/
public static void zipFile(String srcFile, String dstFile) {
// 创建输入、输出流
FileInputStream is = null;
FileOutputStream os = null;
// 创建对象流,为以后恢复源文件时使用
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
// 创建一个和源文件大小一样的byte[]数组
byte[] b = new byte[is.available()];
is.read(b);
// 直接对源文件进行压缩
byte[] huffmanBytes = huffmanZip(b);
// 存放压缩文件
os = new FileOutputStream(dstFile);
// 创建一个和文件输出流关联的ObjectOutputStream
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
// 把赫夫曼编码后的字节数组写入到压缩文件
oos.writeObject(huffmanBytes);
// 注意一定要把赫夫曼编码也写入到压缩文件里,不然恢复不了
oos.writeObject(huffmanCodes);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally {
try {
is.close();
oos.close();
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
解压
读取压缩文件(数据和赫夫曼编码表)-> 完成解压(文件恢复)
/**
* 完成对压缩文件的解压
*
* @param zipFile 准备解压的文件路径
* @param dstFile 解压后的文件存储路径
*/
public static void unZipFile(String zipFile, String dstFile) {
// 创建输入、输出流
FileInputStream is = null;
FileOutputStream os = null;
// 创建对象流,为恢复源文件时使用
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream(zipFile);
// 创建一个和 is 关联的对象输入流
ois = new ObjectInputStream(is);
// 读取byte数组 huffmanBytes
byte[] huffmanBytes = (byte[]) ois.readObject();
// 读取赫夫曼编码表
Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes = (Map<Byte, String>) ois.readObject();
// 解码
byte[] bytes = decode(huffmanCodes, huffmanBytes);
// 写入到目标文件
os = new FileOutputStream(dstFile);
os.write(bytes);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
os.close();
ois.close();
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
注意事项
- 如果文件本身就是经过压缩处理的,那么使用赫夫曼编码再压缩效率不会有明显变化,比如视频,ppt等等文件
- 赫夫曼编码是按字节来处理的,因此可以处理所有的文件(二进制文件、文本文件)
- 如果一个文件中的内容,重复的数据不多,压缩效果也不会很明显.
总代码
package com.xiaolu.huffmantree.huffmancode;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author 林小鹿
* @version 1.0
*/
public class HuffmanCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// // 测试压缩文件
// String srcFile = "E:\\code\\java\\aa.bmp";
// String dstFile = "E:\\code\\java\\aa.zip";
// zipFile(srcFile, dstFile);
// System.out.println("压缩成功");
// 测试解压文件
String zipFile = "E:\\code\\java\\aa.zip";
String dstFile = "E:\\code\\java\\aa2.bmp";
unZipFile(zipFile, dstFile);
System.out.println("解压完成");
/*
String content = "i like like like java do you like a java"; // 长度:40
byte[] contentBytes = content.getBytes();
System.out.println("压缩前长度:" + contentBytes.length);
// 调用封装的赫夫曼编码方法,得到一个压缩后的赫夫曼编码字节数组
byte[] huffmanCodeBytes = huffmanZip(contentBytes);
System.out.println("huffmanCodeBytes= " + Arrays.toString(huffmanCodeBytes));
System.out.println("压缩后长度:" + huffmanCodeBytes.length);
// 解码
byte[] sourceBytes = decode(huffmanCodes, huffmanCodeBytes);
System.out.println("原来的字符串=" + new String(sourceBytes));
*/
// 分布过程
/*
// 创建List集合
List<Node> node = getNode(contentBytes);
System.out.println(node);
System.out.println("赫夫曼树");
// 根据node 生成赫夫曼树
Node huffmanTreeRoot = createHuffmanTree(node);
preOrder(huffmanTreeRoot);
// 根据赫夫曼树生成对应的赫夫曼编码
Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes = getCodes(huffmanTreeRoot);
System.out.println("生成的赫夫曼编码表:" + huffmanCodes);
// 根据生成的赫夫曼编码,压缩得到处理后的赫夫曼编码
byte[] huffmanCodeBytes = zip(contentBytes, huffmanCodes);
System.out.println("压缩后");
System.out.println("huffmanCodeBytes= " + Arrays.toString(huffmanCodeBytes));// 长度:17
System.out.println("压缩后长度:"+huffmanCodeBytes.length); */
}
/**
* 完成对压缩文件的解压
*
* @param zipFile 准备解压的文件路径
* @param dstFile 解压后的文件存储路径
*/
public static void unZipFile(String zipFile, String dstFile) {
// 创建输入、输出流
FileInputStream is = null;
FileOutputStream os = null;
// 创建对象流,为恢复源文件时使用
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream(zipFile);
// 创建一个和 is 关联的对象输入流
ois = new ObjectInputStream(is);
// 读取byte数组 huffmanBytes
byte[] huffmanBytes = (byte[]) ois.readObject();
// 读取赫夫曼编码表
Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes = (Map<Byte, String>) ois.readObject();
// 解码
byte[] bytes = decode(huffmanCodes, huffmanBytes);
// 写入到目标文件
os = new FileOutputStream(dstFile);
os.write(bytes);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
os.close();
ois.close();
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 对文件进行压缩
*
* @param srcFile 待压缩的文件全路径
* @param dstFile 压缩后文件存放的全路径
*/
public static void zipFile(String srcFile, String dstFile) {
// 创建输入、输出流
FileInputStream is = null;
FileOutputStream os = null;
// 创建对象流,为以后恢复源文件时使用
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
// 创建一个和源文件大小一样的byte[]数组
byte[] b = new byte[is.available()];
is.read(b);
// 直接对源文件进行压缩
byte[] huffmanBytes = huffmanZip(b);
// 存放压缩文件
os = new FileOutputStream(dstFile);
// 创建一个和文件输出流关联的ObjectOutputStream
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
// 把赫夫曼编码后的字节数组写入到压缩文件
oos.writeObject(huffmanBytes);
// 注意一定要把赫夫曼编码也写入到压缩文件里,不然恢复不了
oos.writeObject(huffmanCodes);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally {
try {
is.close();
oos.close();
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
// 1. 将huffmanCodeBytes[-88,-65,-56,-65,-56,-65,-55,77E,-57,6,-24,-14,-117,-4,-60,-90,28]
// 重写先转成赫夫曼编码对应的二进制的字符串"1010100010111。。。"
//2. 赫夫曼编码对应的二进制的字符串"1010100010111..." => 对照 赫夫曼编码 =》"i like like like java do you like a java"
/**
* 完成对压缩数据的解码
*
* @param huffmanCodes 赫夫曼编码表 map
* @param huffmanBytes 赫夫曼编码得到的字节数组
* @return 原来字符串对应的数组
*/
private static byte[] decode(Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes, byte[] huffmanBytes) {
// 1.先得到 huffmanBytes对应的二进制的字符串,形式 1010100010111
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
// 将byte数组转成二进制字符串
for (int i = 0; i < huffmanBytes.length; i++) {
byte b = huffmanBytes[i];
// 判断是不是最后一个字节
boolean flag = (i == huffmanBytes.length - 1);
stringBuilder.append(byteToBitString(!flag, b));
}
// 把字符串按照指定的赫夫曼编码进行解码
// 把赫夫曼编码表进行调换,因为反向查询a->100 100->a
Map<String, Byte> map = new HashMap<>();
for (Map.Entry<Byte, String> entry : huffmanCodes.entrySet()) {
map.put(entry.getValue(), entry.getKey());
}
// 创建集合存放byte
List<Byte> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 扫描 stringBuilder
for (int i = 0; i < stringBuilder.length(); ) {
int count = 1; // 小的计数器
boolean flag = true;
Byte b = null;
while (flag) {
// 1010100010111...
// 递增的取出 key
String key = stringBuilder.substring(i, i + count);
b = map.get(key);
if (b == null) { // 说明没有匹配到
count++;
} else { // 匹配到
flag = false;
}
}
list.add(b);
i += count; // i 增长到count的位置
}
byte[] b = new byte[list.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
b[i] = list.get(i);
}
return b;
}
/**
* 将一个byte 转成一个二进制的字符串
*
* @param flag 标志是否需要补高位,如果是true,表示需要补高位
* @param b 传入的byte
* @return 该 byte对应的二进制字符串,注意是按补码返回的
*/
private static String byteToBitString(boolean flag, byte b) {
// 使用变量保存b
int temp = b;
// int对应的二进制的是32位(4个字节)
// 正数则会自动删除前面的无效0 ==> 需要补高位
// byte最后的一位长度是多少就是多少,不需要补零
if (flag) {// 判断是否需要补高位(是否为 byte最后的一位)
// 补高位
temp |= 256; // 按位或 256对应的二进制 1 0000 0000 | 0000 0001 => 1 0000 0001
}
String str = Integer.toBinaryString(temp); // 返回的是temp对应的二进制的补码
if (flag) {
return str.substring(str.length() - 8); // 取后八位
} else {// byte最后一位 => 直接返回
return str;
}
}
/**
* 封装赫夫曼编码步骤代码,方便调用
*
* @param bytes 原始字符串对应的字节数组
* @return 经过赫夫曼编码处理后的字节数组 (压缩后的数组)
*/
private static byte[] huffmanZip(byte[] bytes) {
// 创建List集合
List<Node> node = getNode(bytes);
// 根据node 生成赫夫曼树
Node huffmanTreeRoot = createHuffmanTree(node);
// 根据赫夫曼树生成对应的赫夫曼编码(路径)
Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes = getCodes(huffmanTreeRoot);
// 根据生成的赫夫曼编码,压缩得到处理后的赫夫曼编码
return zip(bytes, huffmanCodes);
}
// 生成赫夫曼树对应的赫夫曼编码
// 1.将赫夫曼编码表存放在Map<Byte,String>形式
// 32->01 97->100 100->11000等等[形式]
static Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes = new HashMap<Byte, String>();
//2.在生成赫夫曼编码表示,需要去拼接路径,定义一个StringBuilder存储某个叶子结点的路径
static StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
// 将字符串对应的byte[]数组,通过生成的赫夫曼编码表,返回一个赫夫曼编码压缩后的byt[]
/**
* @param bytes 原始的字符串对应的byte[]
* @param huffmanCodes 生成的赫夫曼编码map
* @return 赫夫曼编码处理后的byte[]
* 举例:String content="i like like like java do you like a java"; =》byte[] contentBytes = content.getBytes()
* 返回的是字符串"1010100010111111110010001011111111001000101111111100100"
* => 对应的byte[] huffmanCodeBytes,即 8位对应一个byte,放入到huffmanCodeBytes
* huffmanCodeBytes[0] = 10101000(补) => byte[推导10101000 => 10101000 - 1 => 10100111(反码) => 11011000(原码)
* => -88
*/
private static byte[] zip(byte[] bytes, Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes) {
// 1.利用huffmanCodes 将 bytes 转成赫夫曼编码对应的字符串
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
// 遍历bytes 数组
for (byte b : bytes) {
stringBuilder.append(huffmanCodes.get(b));
}
// 将stringBuilder 转成byte[] 数组
int len = (stringBuilder.length() + 7) / 8; // 统计stringBuilder 的长度
// 等效于以下代码
/*
int len;
if (stringBuilder.length() % 8 == 0) {
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8;
} else {
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8 + 1;
}
*/
// 创建存储压缩后的byte数组
byte[] huffmanCodeBytes = new byte[len];
for (int i = 0, index = 0; i < stringBuilder.length(); i += 8, index++) {
String strByte;
// 8位为一字节
if (i + 8 > stringBuilder.length()) {
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i);
} else {
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i, i + 8);
}
// 将strByte 转成一个byte,放到 huffmanCodeBytes 中
huffmanCodeBytes[index] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(strByte, 2);
}
return huffmanCodeBytes;
}
// 为了调用方便,重载getCodes
private static Map<Byte, String> getCodes(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
// 处理左子树
getCodes(root.left, "0", stringBuilder);
// 处理右子树
getCodes(root.right, "1", stringBuilder);
return huffmanCodes;
}
/**
* 功能:将传入的node结点的所有叶子结点的赫夫曼编码得到,并放入到huffmanCodes集合
*
* @param node 传入的结点
* @param code 路径:左子节点是 0,右子节点是 1
* @param stringBuilder 用于拼接路径
*/
private static void getCodes(Node node, String code, StringBuilder stringBuilder) {
// 用于拼接路径
StringBuilder stringBuilder2 = new StringBuilder(stringBuilder);
// 将code 加入到 stringBuilder2
stringBuilder2.append(code);
if (node != null) {// 如果 node == null不处理
// 判断当前node是否为叶子结点
if (node.data == null) {// 非叶子结点
// 向左递归
getCodes(node.left, "0", stringBuilder2);
// 向右递归
getCodes(node.right, "1", stringBuilder2);
} else {// 叶子结点
// 存入
huffmanCodes.put(node.data, stringBuilder2.toString());
}
}
}
/**
* @param bytes 接收字节数组
* @return 返回 List 形式 [Node[date=97,weight=5], Node[date=32,weight=9]......],
*/
public static List<Node> getNode(byte[] bytes) {
List<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<>();
// 遍历bytes,统计每个byte出现的次数 -> map[key, value]
HashMap<Byte, Integer> counts = new HashMap<>();
for (byte b : bytes) {
Integer count = counts.get(b);
if (count == null) { // 第一次将字符加入到map中
counts.put(b, 1);
} else {// 出现次数 +1
counts.put(b, count + 1);
}
}
// 把每一个键值对转成一个Node 对象,并加入到nodes集合
// 遍历map
for (Map.Entry<Byte, Integer> entry : counts.entrySet()) {
nodes.add(new Node(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()));
}
return nodes;
}
private static Node createHuffmanTree(List<Node> nodes) {
while (nodes.size() > 1) {
// 排序
Collections.sort(nodes);
// 取出第一颗最小的二叉树
Node leftNode = nodes.get(0);
// 取出第二颗最小的二叉树
Node rightNode = nodes.get(1);
// 创建一颗新的二叉树,它的根节点 没有data,只有权值
Node parentNode = new Node(null, leftNode.weight + rightNode.weight);
parentNode.left = leftNode;
parentNode.right = rightNode;
// 从nodes中移除已经处理过的两颗二叉树
nodes.remove(leftNode);
nodes.remove(rightNode);
// 将新的二叉树添加到nodes
nodes.add(parentNode);
}
// 返回赫夫曼树的根节点
return nodes.get(0);
}
private static void preOrder(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("赫夫曼树为空");
}
}
}
class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
Byte data; // 存放数据(字符) 'a' --> 97
int weight; // 权值,表示字符出现的次数
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(Byte data, int weight) {
this.data = data;
this.weight = weight;
}
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this);
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
// 从小到大
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node[" +
"data=" + data +
", weight=" + weight +
']';
}
}
二叉排序树 (BST树)
二叉排序树:BST:(Binary Sort(Search)Tree),对于二叉排序树的任何一个非叶子节点,要求左子节点的值比当前节点的值小,右子节点的值比当前节点的值大。
特别说明:如果有相同的值,可以将该节点放在左子节点或右子节点
二叉树的创建
// 按二叉排序树的形式递归添加结点
public void add(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
// 判断传入的结点的值与当前子树的根结点的值关系
if (node.value < this.value) {
if (this.left == null) {
this.left = node;
} else {
// 递归得向左子树添加 node
this.left.add(node);
}
} else { // 添加的结点的值大于当前结点的值
if (this.right == null) {
this.right = node;
} else {
// 递归得向右子树添加 node
this.right.add(node);
}
}
}
二叉树的删除
分三种情况
- 删除叶子结点
- 需求先去找到要删除的结点targetNode
- 找到targetNode的父结点parent
- 确定targetNode是parent的左子结点 还是右子结点
- 根据前面的情况来对应删除
- 删除只有一颗子树的结点
- (1)需求先去找到要删除的结点targetNode
- (2)找到targetNode的父结点parent
- (3)确定targetNode的子结点是左子结点还是右子结点
- (4)targetNode是parent的左子结点还是右子结点
- (5)如果targetNode有左子结点
- 如果targetNode是parent的左子结点
parent.left = targetNode.left; - 如果targetNode是parent的右子结点
parent.right = targetNode.left;
- 如果targetNode是parent的左子结点
- (6)如果targetNode有右子结点
- 如果targetNode是parent的左子结点
parent.left = targetNode.right; - 如果targetNode是parent的右子结点
parent.right = targetNode.right
- 如果targetNode是parent的左子结点
- 删除有两颗子树的结点
- (1)需求先去找到要删除的结点targetNode
- (2)找到targetNode的父结点parent
- (3)从targetNode的右子树找到最小的结点【如果是从targetNode的左子树找的话应该找最大的结点】
- (4)用一个临时变量temp,将最小结点的值保存
- (5)删除该最小结点
- (6)targetNode.value = temp
总代码
package com.xiaolu.binarysorttree;
/**
* @author 林小鹿
* @version 1.0
*/
public class BinarySortTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {7, 3, 10, 12, 5, 1, 9, 2};
BinarySortTree binarySortTree = new BinarySortTree();
// 循环添加结点到二叉排序树中
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
binarySortTree.add(new Node(arr[i]));
}
System.out.println("中序遍历:");
binarySortTree.infixOrder();
// 删除叶子结点
binarySortTree.delNode(2);
binarySortTree.delNode(5);
binarySortTree.delNode(9);
binarySortTree.delNode(12);
binarySortTree.delNode(7);
binarySortTree.delNode(3);
binarySortTree.delNode(10);
binarySortTree.delNode(1);
System.out.println("第二次中序遍历:");
binarySortTree.infixOrder();
}
}
// 创建二叉排序树
class BinarySortTree {
private Node root;
// 查找要删除的结点
public Node search(int value) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
} else {
return root.search(value);
}
}
// 查找要删除的父结点
public Node searchParent(int value) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
} else {
return root.searchParent(value);
}
}
/**
* 删除node 为根结点的二叉排序树的最小结点的值的同时返回以node 为根结点的二叉排序树的最小结点
* @param node 传入的结点 (当做二叉排序树的根结点)
* @return 返回以node 为根结点的二叉排序树的最小结点的值
*/
public int delRightTreeMin(Node node) {
Node target = node;
// 循环的查找左结点,就会找到最小值
while (target.left != null) {
target = target.left;
}
// 这是target就指向了最小结点
// 删除最小结点
delNode(target.value);
return target.value;
}
// 删除结点
public void delNode(int value) {
if (root == null) {
return;
} else {
// 找到需要删除的结点 targetNode
Node targetNode = search(value);
// 如果没有找到要删除的结点
if (targetNode == null) {
return;
}
// 如果这颗二叉排序树只有一个结点 (即本身就是父节点)
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
root = null;
return;
}
// 查询父节点
Node parent = searchParent(value);
// 如果待删除的结点是叶子结点
if (targetNode.left == null && targetNode.right == null) {// 删除叶子结点
// 判断 targetNode 是父节点的左子结点还是右子节点
if (parent.left != null && parent.left.value == value) {
parent.left = null;
} else if (parent.right != null && parent.right.value == value) {
parent.right = null;
}
}else if (targetNode.left != null && targetNode.right != null) {// 删除有两颗子树的结点
int minVal = delRightTreeMin(targetNode.right);
targetNode.value = minVal;
} else {// 删除只有一颗子树的结点
// 如果要删除的结点有左子结点
if (targetNode.left != null) {
if (parent != null) {
// 如果targetNode 是parent 的左子结点
if (parent.left.value == value) {
parent.left = targetNode.left;
} else {// 如果targetNode 是parent 的右子结点
parent.right = targetNode.left;
}
} else {
root = targetNode.left;
}
} else {
if (parent != null) {
// 如果要删除的结点有右子结点
if (parent.left.value == value) {// 如果targetNode 是parent 的左子结点
parent.left = targetNode.right;
} else {// 如果targetNode 是parent 的右子结点
parent.right = targetNode.right;
}
} else {
root = targetNode.right;
}
}
}
}
}
// 添加结点
public void add(Node node) {
if (root == null) {
// 如果root为空则直接让root指向node
root = node;
} else {
root.add(node);
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (root == null) {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
} else {
root.infixOrder();
}
}
}
// 创建Node结点
class Node {
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
/**
* 查找要删除的结点
*
* @param value 待删除的结点的值
* @return 如果找到则返回该结点,否则返回空
*/
public Node search(int value) {
if (value == this.value) {
return this;
} else if (value < this.value) {// 如果查找的值小于当前结点,就向左子树递归查找
if (this.left == null) {// 如果左子树为空
return null;
}
return this.left.search(value);
} else {// 如果查找的值不小于当前结点,向右子树递归查找
if (this.right == null) {// 如果右子树为空
return null;
}
return this.right.search(value);
}
}
/**
* 查找要删除结点的父结点
*
* @param value 要找到的结点的值
* @return 返回的是要删除的结点的父结点,如果没有就返回null
*/
public Node searchParent(int value) {
// 如果当前结点就是要删除的结点的父节点,就返回
if ((this.left != null && this.left.value == value)
|| (this.right != null && this.right.value == value)) {
return this;
} else {
// 如果查找的值小于或大于当前结点的值,并且当前结点的左子节点不为空
if (value < this.value && this.left != null) {
return this.left.searchParent(value); // 向左子树递归查找
} else if (value > this.value && this.right != null) {
return this.right.searchParent(value); // 向右子树递归查找
} else {
return null; // 没有找到父节点
}
}
}
// 按二叉排序树的形式递归添加结点
public void add(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
// 判断传入的结点的值与当前子树的根结点的值关系
if (node.value < this.value) {
if (this.left == null) {
this.left = node;
} else {
// 递归得向左子树添加 node
this.left.add(node);
}
} else { // 添加的结点的值大于当前结点的值
if (this.right == null) {
this.right = node;
} else {
// 递归得向右子树添加 node
this.right.add(node);
}
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
System.out.println(this);
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node[" +
"value=" + value +
']';
}
}
先往深走,遇到叶子节点再往回走 ↩︎
一层一层的去遍历 ↩︎
n个结点一共有 2 ∗ n 2*n 2∗n个指针域,除去根结点,每个结点用去 n − 1 n-1 n−1个指针域 ↩︎
利用奇偶数特征推出 ↩︎