目录
- 1. 单链表相关练习题
- 1.1 移除链表元素
- 1.2 反转链表
- 1.3 链表的中间结点
- 1.4 链表的倒数第k个结点
- 1.5 合并两个有序链表
- 1.6 链表分割
- 1.7 链表的回文结构
- 1.8 相交链表
- 1.9 判断一个链表中是否有环
- 1.10 寻找环状链表相遇点
- 1.11 链表的深度拷贝
1. 单链表相关练习题
注:单链表结构上存在一定缺陷,所以链表相关的题目一般都针对与单链表。
1.1 移除链表元素
题目要求:
题目信息:
- 头节点head
- 移除值val
题目链接:
移除链表元素
方法(顺序处理法):
思路:分析链表结构与结点所处的位置(是否为空链表,结点是否为头结点),分情况依次处理。
过程演示:
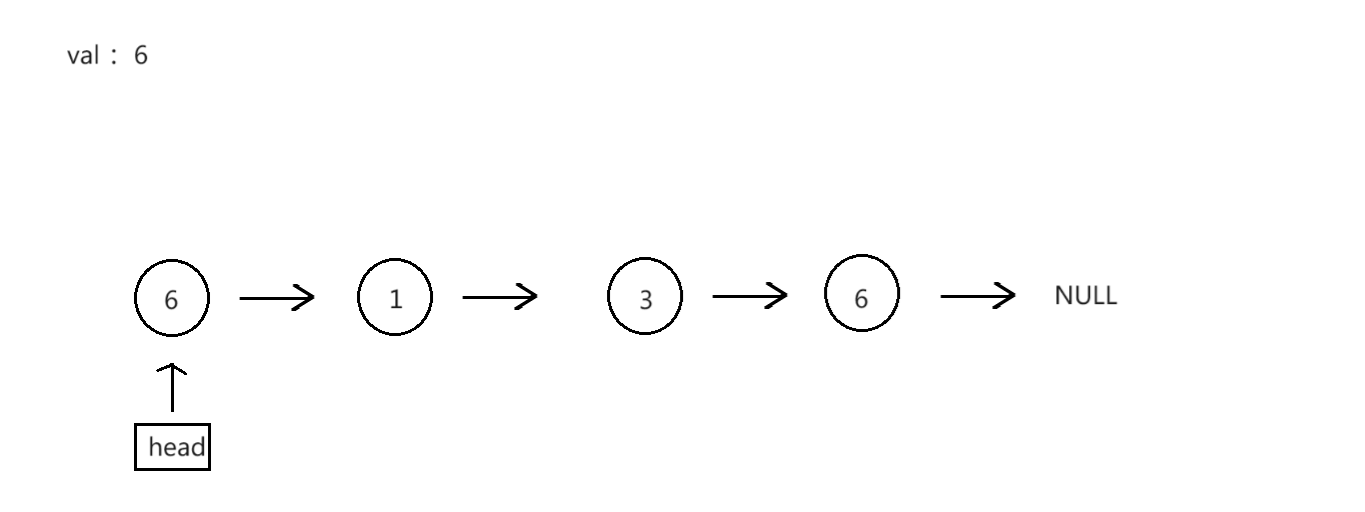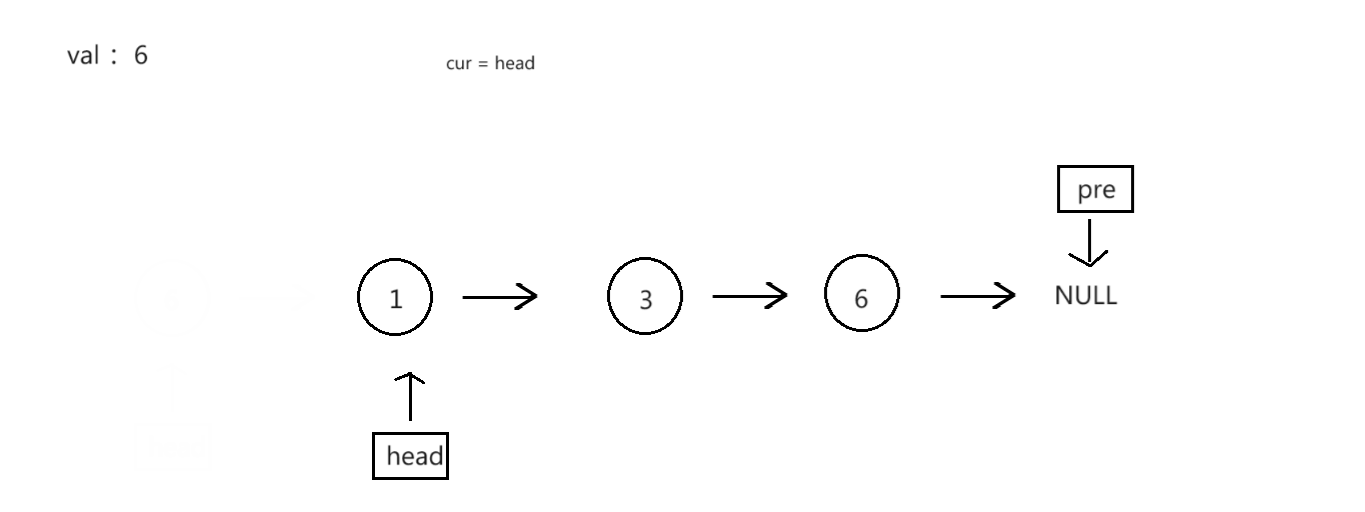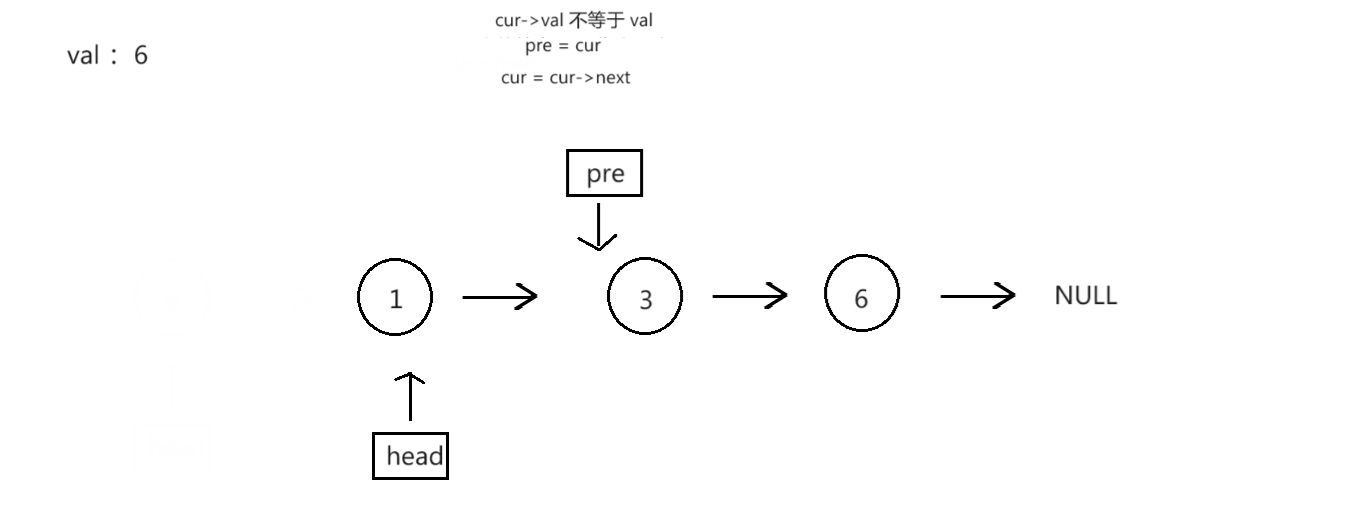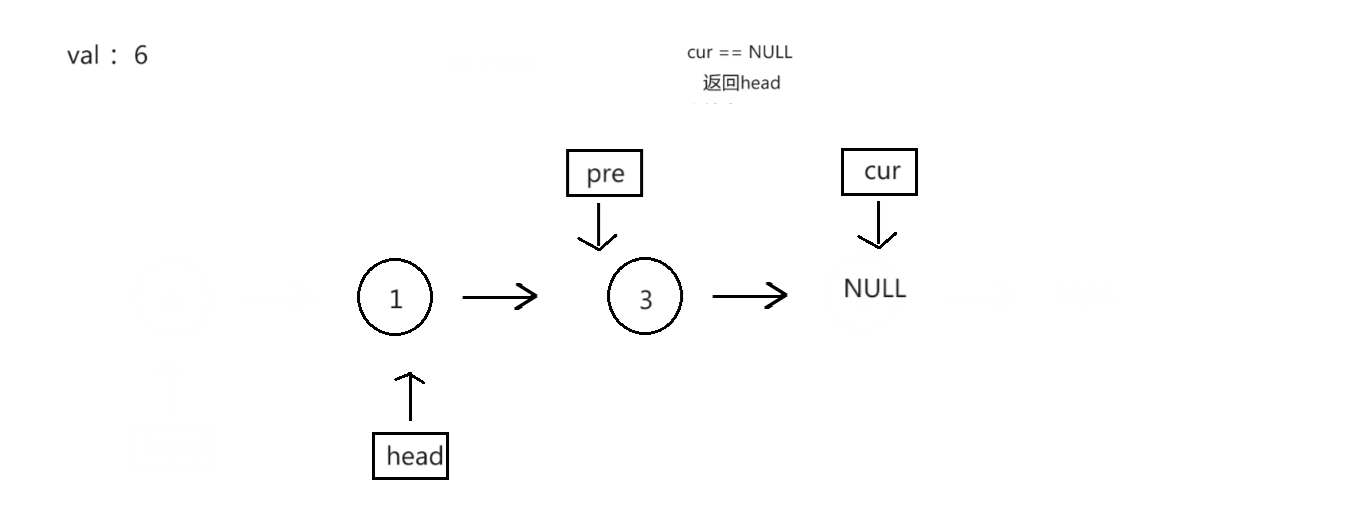
struct ListNode* removeElements4(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
struct ListNode* pre = NULL;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->val == val)
{
//头删
if (cur == head)
{
head = head->next;
free(cur);
cur = head;
}
else//中间删
{
pre->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = pre->next;
}
}
else
{
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return head;
}
1.2 反转链表
题目要求:
题目链接:
反转链表
过程演示:
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* pre = NULL;
struct ListNode* mid = head;
struct ListNode* cur = NULL;
if(head)
{
cur = head->next;
}
while(mid)
{
mid->next = pre;
pre = mid;
mid = cur;
if(cur)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return pre;
}
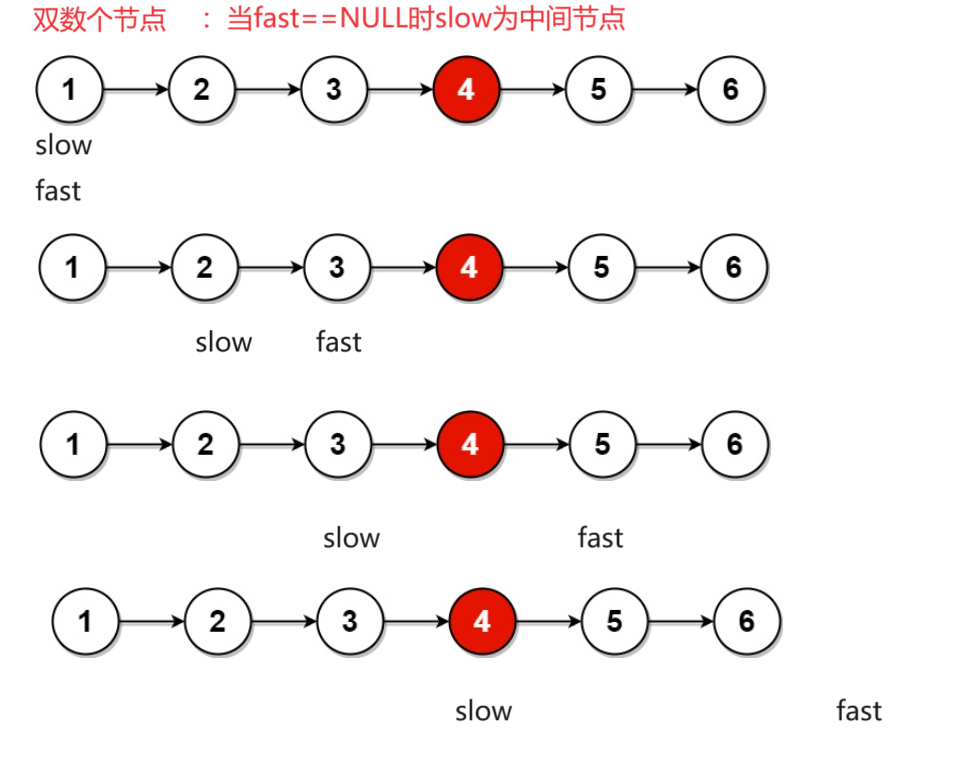
1.3 链表的中间结点
题目要求:
题目链接:
链表的中间结点
过程演示(快慢指针法):
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* fast = head;
struct ListNode* slow = head;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
1.4 链表的倒数第k个结点
题目要求:
题目链接:
倒数第k个结点
过程演示:
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k )
{
struct ListNode* cur = pListHead;
struct ListNode* pre = pListHead;
while(cur && k--)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
if(k > 0)
{
pre = NULL;
}
while(cur)
{
pre = pre->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
return pre;
}
1.5 合并两个有序链表
题目要求:
题目链接:
合并两个链表
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
struct ListNode* newhead = NULL;
struct ListNode* cur = NULL;
struct ListNode* newnode = NULL;
if(list1 == NULL)
return list2;
if(list2 == NULL)
return list1;
while(list1 != NULL && list2 != NULL)
{
if(list1->val <= list2->val)
{
newnode = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
}
else
{
newnode = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
if(newhead == NULL)
{
newhead = newnode;
newnode->next = NULL;
cur = newhead;
}
else
{
//在遍历过程中,list1 或 list2 会等于 NULL
cur->next = newnode;
if(newnode != NULL)
{
newnode->next = NULL;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
}
//有一个链表本就为空
if(list1)
{
cur->next = list1;
}
if(list2)
{
cur->next = list2;
}
return newhead;
}
1.6 链表分割
题目要求:
题目链接:
合并两个链表
ListNode* BuyNewNode(int val)
{
ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
newnode->val = val;
newnode->next = nullptr;
return newnode;
}
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x)
{
ListNode* newhead1 = nullptr;
ListNode* end1 = nullptr;
ListNode* newhead2 = nullptr;
ListNode* end2 = nullptr;
ListNode* cur = pHead;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val < x)
{
if(newhead1 == nullptr)
{
newhead1 = BuyNewNode(cur->val);
end1 = newhead1;
}
else
{
end1->next = BuyNewNode(cur->val);
end1 = end1->next;
}
}
else
{
if(newhead2 == nullptr)
{
newhead2 = BuyNewNode(cur->val);
end2 = newhead2;
}
else
{
end2->next = BuyNewNode(cur->val);
end2 = end2->next;
}
}
cur = cur->next;
}
if(newhead1 == nullptr)
{
newhead1 = newhead2;
}
else
{
end1->next = newhead2;
}
return newhead1;
}
1.7 链表的回文结构
题目要求:
题目链接:
回文串
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* head)
{
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
ListNode* mid = head;
ListNode* cur = head->next;
while (mid)
{
mid->next = pre;
pre = mid;
mid = cur;
if (cur)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return pre;
}
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A)
{
//找相同,逆置
//逐点比较
//回文结构存在奇数个结点
//获取中间结点
ListNode* fast = A;
ListNode* slow = A;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
if(fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
}
}
//表1
ListNode* newhead2 = slow->next;
//表2
slow->next = nullptr;
ListNode* newhead1 = reverse(A);
if(fast)
{
newhead1 = newhead1->next;
}
while (newhead1 && newhead2 && newhead1->val == newhead2->val)
{
newhead1 = newhead1->next;
newhead2 = newhead2->next;
}
if (newhead1 == nullptr && newhead2 == nullptr)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
1.8 相交链表
题目要求:
题目链接:
相交链表
void swap(struct ListNode** node1, struct ListNode** node2)
{
struct ListNode* tmp = *node1;
*node1 = *node2;
*node2 = tmp;
}
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
struct ListNode* short_list1 = headA;
struct ListNode* short_list2 = headA;
struct ListNode* long_list1 = headB;
struct ListNode* long_list2 = headB;
while(short_list1 && long_list1)
{
short_list1 = short_list1->next;
long_list1 = long_list1->next;
}
if(short_list1)
{
swap(&short_list1, &long_list1);
swap(&short_list2, &long_list2);
}
while(long_list1)
{
long_list1 = long_list1->next;
long_list2 = long_list2->next;
}
//while((short_list2 && long_list2) || short_list2 != long_list2)
while(short_list2 && long_list2 && short_list2 != long_list2)
{
long_list2 = long_list2->next;
short_list2 = short_list2->next;
}
return short_list2;
}
1.9 判断一个链表中是否有环
题目要求:
题目链接:
判断是否有环
//逻辑步骤存疑
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
struct ListNode* fast = head;
struct ListNode* slow = head;
//err: while(fast && slow != fast)
while(fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(slow == fast)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
1.10 寻找环状链表相遇点
题目要求:
题目链接:
寻找环状链表相遇点
思路依靠结论:一个结点从起始点,一个结点从相遇点(快慢指针相遇点),以同速行走(一次走一步),当他们再一次初次相遇时,此相遇结点即为入环点。
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
//快慢指针确定首次相遇点
//起始点与相遇点出发,同速移动,最后的相遇的点即为环的进入点
struct ListNode* fast = head;
struct ListNode* slow = head;
//遍历寻找相遇点
while(fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(fast == slow)
{
break;
}
}
//判断是否为环状链表
if(fast == NULL || fast->next == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
slow = head;
while(fast != slow)
{
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return fast;
}
1.11 链表的深度拷贝
题目要求:
>题目链接:
链表的深度拷贝
//思路:
//生成拷贝结点
//调整拷贝结点的指针
//还原原链表,链接拷贝结点
struct Node* BuyNewNode(int val)
{
struct Node* newnode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newnode->val = val;
newnode->next = NULL;
newnode->random = NULL;
return newnode;
}
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head)
{
struct Node* node1 = head;
//判断是否为空链表
if(head == NULL)
{
return head;
}
//创建新节点
while (node1)
{
struct Node* newnode = BuyNewNode(node1->val);
newnode->next = node1->next;
node1->next = newnode;
node1 = node1->next->next;
}
//调整新节点的随机指针
struct Node* node2 = head->next;
node1 = head;
while (node2)
{
if (node1->random)
{
node2->random = node1->random->next;
}
node1 = node1->next->next;
if (node2->next)
{
node2 = node2->next->next;
}
else
{
node2 = node2->next;
}
}
//还原链表,链接新链表
node1 = head;
node2 = head->next;
struct Node* newhead = head->next;
while (node1)
{
node1->next = node1->next->next;
if (node2->next)
{
node2->next = node2->next->next;
}
node1 = node1->next;
node2 = node2->next;
}
return newhead;
}