文章目录
- 1.原理简介
- 2. 注意事项
- 3. 功能实现
- 代码实现部分
- 4.可视化
- 5.与GSEA比较
1.原理简介
Gene Set Variation Analysis (GSVA) 基因集变异分析。可以简单认为是样本数据中的基因根据表达量排序后形成了一个rank list,这个rank list 与 预设的gene sets(a set of genes forming a pathway or some other functional unit)进行比较,用KS test计算分布差异(GSVA enrichment score is either the difference between the two sums or the maximum deviation from zero),最大差异作为enrichment score。
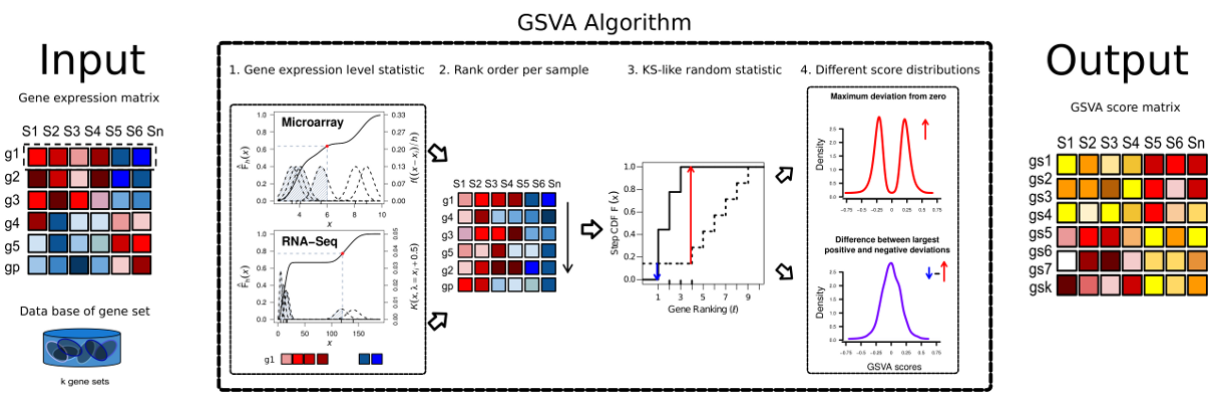
算法主要做了四件事:
1.Kernel estimation of the cumulative density function (kcdf). 实现基因表达量的非参估计,使得样本间基因表达量高低可比。或者就简单认为是一种 rank,只不过rank方法是KS分布计算出来的数值决定的。
2.The expression-level statistic is rank ordered for each sample。同上述,进行样本内gene rank
3.For every gene set, the Kolmogorov-Smirnov-like rank statistic is calculated. rank 后的样本gene set 与预设的gene set 计算分布差异。
4.The GSVA enrichment score is either the difference between the two sums or the maximum deviation from zero. 将第三步计算的分布差异转换成 GSVA enrichment score。
2. 注意事项
-
基因表达量的数值影响gsva的参数设置:
while microarray data, transform values to log2(values) and set paramseter kcdf=“Poisson”
while RNAseq values of expression data is integer count, set paramseter kcdf=“Poisson”
whlie RNAseq values of expression data is log-CPMs, log-RPKMs or log-TPMs , set paramseter kcdf=“Gaussian” -
gsva 函数执行的默认过滤操作:
- matches gene identifiers between gene sets and gene expression values,gene expression matrix中无法match的gene会被剔除
- it discards gene sets that do not meet minimum and maximumgene set size requirements specified with the arguments min.sz and max.sz 。我没搞清楚这个是样本内的gene set 还是预设的gene set大小不符合设置会被过滤掉。
-
得到GSVA ES后如果想进行差异分析时,该如何操作:
unchanged the default argument mx.diff=TRUE to obtain approximately normally distributed ES
and use limma on the resulting GSVA enrichment scores,finally get plots. -
变异分的计算:
two approaches for turning the KS like random walk statistic into an enrichment statistic (ES) (also called GSVA score), the classical maximum deviation method & a normalized ES。classical maximum deviation method的含义 : the maximum deviation from zero of the random walk of the j-th sample with respect to the k-th gene set (gsva函数参数设置: mx.diff =TRUE)
a normalized ES 的含义: 零假设下(no change in pathway activity throughout the sample population)enrichment scores 应该是个正态分布。(个人还是觉得第一种算分方法靠谱)(gsva函数参数设置: mx.diff =FALSE)
3. 功能实现
大致可以实现如下两个目的:
- 单样本内的gene sets 识别,也可以认为得到 gene signatures。
- 多样本ES 比较,识别差异 gene sets,然后聚类,根据gene sets标识样本生物学属性。(单细胞分析中有些人就是这样干的,他们不是基于图的聚类方法 去细胞聚类然后再找DE,最后注释细胞类群。他们让每个细胞与预设的gene sets比较得到 GSVA ES,然后根据ES聚类,从而划分出来细胞类群,然后说这类细胞特化/极化出了啥表型,有啥用,巴拉巴拉一个故事)。
代码实现部分
# 准备表达矩阵
list.files("G:/20240223-project-HY0007-GSVA-analysis-result/")
expr <- read.table("../TPM_DE.filter.txt",sep = "\t",header = T,row.names = 1)
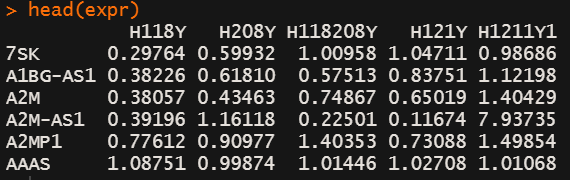
head(expr)
expr <- as.matrix(expr) # 需要转换成matrix或者 ExpressionSet object
# 准备预设的gene sets
# install.packages("msigdbr")
library(msigdbr)
## msigdbr包提取下载 先试试KEGG和GO做GSVA分析
##KEGG
KEGG_df_all <- msigdbr(species = "Homo sapiens", # Homo sapiens or Mus musculus
category = "C2",
subcategory = "CP:KEGG")
KEGG_df <- dplyr::select(KEGG_df_all,gs_name,gs_exact_source,gene_symbol)
kegg_list <- split(KEGG_df$gene_symbol, KEGG_df$gs_name) ##按照gs_name给gene_symbol分组
##GO
GO_df_all <- msigdbr(species = "Homo sapiens",
category = "C5")
GO_df <- dplyr::select(GO_df_all, gs_name, gene_symbol, gs_exact_source, gs_subcat)
GO_df <- GO_df[GO_df$gs_subcat!="HPO",]
go_list <- split(GO_df$gene_symbol, GO_df$gs_name) ##按照gs_name给gene_symbol分组
## manual operation
list.files("../")
library(GSEABase) # 读取 Gmt文件
myself_geneset <- getGmt("../my_signature.symbols.gmt.txt")
#### GSVA ####
# geneset 1
geneset <- go_list
gsva_mat <- gsva(expr=expr,
gset.idx.list=geneset,
kcdf="Gaussian" ,#"Gaussian" for logCPM,logRPKM,logTPM, "Poisson" for counts
verbose=T,
mx.diff =TRUE,# 下游做limma得到差异通路
min.sz = 10 # gene sets 少于10个gene的过滤掉
)
write.csv(gsva_mat,"gsva_go_matrix.csv")
# geneset 2
geneset <- kegg_list
gsva_mat <- gsva(expr=expr,
gset.idx.list=geneset,
kcdf="Gaussian" ,#"Gaussian" for logCPM,logRPKM,logTPM, "Poisson" for counts
verbose=T,
mx.diff =TRUE,# 下游做limma得到差异通路
min.sz = 10 # gene sets 少于10个gene的过滤掉
)
write.csv(gsva_mat,"gsva_kegg_matrix.csv")
# geneset 3
geneset <- myself_geneset
gsva_mat <- gsva(expr=expr,
gset.idx.list=geneset,
kcdf="Gaussian" ,#"Gaussian" for logCPM,logRPKM,logTPM, "Poisson" for counts
verbose=T,
mx.diff =TRUE,# 下游做limma得到差异通路
min.sz = 10 # gene sets 少于10个gene的过滤掉
)
write.csv(gsva_mat,"gsva_myself_matrix.csv")
# 拿到结果后做可视化分析 一般是火山图和柱状偏差图或者热图
4.可视化
# 先整体来张热图
pheatmap::pheatmap(gsva_mat,cluster_rows = T,show_rownames = F,cluster_cols = F)

# KEGG条目或者GO条目太多了,做个差异分析过滤掉一些不显著差异的
#### 进行limma差异处理 ####
##设定 实验组exp / 对照组ctr
# 不需要进行 limma-trend 或 voom的步骤
library(limma)
group_list <- colnames(expr)
design <- model.matrix(~0+factor(group_list))
design
colnames(design) <- levels(factor(group_list))
rownames(design) <- colnames(gsva_mat)
contrast.matrix <- makeContrasts(contrasts=paste0(exp,'-',ctr), #"exp/ctrl"
levels = design)
fit1 <- lmFit(gsva_mat,design) #拟合模型
fit2 <- contrasts.fit(fit1, contrast.matrix) #统计检验
efit <- eBayes(fit2) #修正
summary(decideTests(efit,lfc=1, p.value=0.05)) #统计查看差异结果
tempOutput <- topTable(efit, coef=paste0(exp,'-',ctr), n=Inf)
degs <- na.omit(tempOutput)
write.csv(degs,"gsva_go_degs.results.csv")
#### 对GSVA的差异分析结果进行热图可视化 ####
##设置筛选阈值
padj_cutoff=0.05
log2FC_cutoff=log2(2)
keep <- rownames(degs[degs$adj.P.Val < padj_cutoff & abs(degs$logFC)>log2FC_cutoff, ])
length(keep)
dat <- gsva_mat[keep[1:50],] #选取前50进行展示
degs$significance <- as.factor(ifelse(degs$adj.P.Val < padj_cutoff & abs(degs$logFC) > log2FC_cutoff,
ifelse(degs$logFC > log2FC_cutoff ,'UP','DOWN'),'NOT'))
# 火山图
this_title <- paste0(' Up : ',nrow(degs[degs$significance =='UP',]) ,
'\n Down : ',nrow(degs[degs$significance =='DOWN',]),
'\n adj.P.Val <= ',padj_cutoff,
'\n FoldChange >= ',round(2^log2FC_cutoff,3))
g <- ggplot(data=degs,
aes(x=logFC, y=-log10(adj.P.Val),
color=significance)) +
#点和背景
geom_point(alpha=0.4, size=1) +
theme_classic()+ #无网格线
#坐标轴
xlab("log2 ( FoldChange )") +
ylab("-log10 ( adj.P.Val )") +
#标题文本
ggtitle( this_title ) +
#分区颜色
scale_colour_manual(values = c('blue','grey','red'))+
#辅助线
geom_vline(xintercept = c(-log2FC_cutoff,log2FC_cutoff),lty=4,col="grey",lwd=0.8) +
geom_hline(yintercept = -log10(padj_cutoff),lty=4,col="grey",lwd=0.8) +
#图例标题间距等设置
theme(plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.5),
plot.margin=unit(c(2,2,2,2),'lines'), #上右下左
legend.title = element_blank(),
legend.position="right")
ggsave(g,filename = 'GSVA_go_volcano_padj.pdf',width =8,height =7.5)
#### 发散条形图绘制 ####
# install.packages("ggthemes")
# install.packages("ggprism")
library(ggthemes)
library(ggprism)
p_cutoff=0.001
degs <- gsva_kegg_degs #载入gsva的差异分析结果
Diff <- rbind(subset(degs,logFC>0)[1:20,], subset(degs,logFC<0)[1:20,]) #选择上下调前20通路
dat_plot <- data.frame(id = row.names(Diff),
p = Diff$P.Value,
lgfc= Diff$logFC)
dat_plot$group <- ifelse(dat_plot$lgfc>0 ,1,-1) # 将上调设为组1,下调设为组-1
dat_plot$lg_p <- -log10(dat_plot$p)*dat_plot$group # 将上调-log10p设置为正,下调-log10p设置为负
dat_plot$id <- str_replace(dat_plot$id, "KEGG_","");dat_plot$id[1:10]
dat_plot$threshold <- factor(ifelse(abs(dat_plot$p) <= p_cutoff,
ifelse(dat_plot$lgfc >0 ,'Up','Down'),'Not'),
levels=c('Up','Down','Not'))
dat_plot <- dat_plot %>% arrange(lg_p)
dat_plot$id <- factor(dat_plot$id,levels = dat_plot$id)
## 设置不同标签数量
low1 <- dat_plot %>% filter(lg_p < log10(p_cutoff)) %>% nrow()
low0 <- dat_plot %>% filter(lg_p < 0) %>% nrow()
high0 <- dat_plot %>% filter(lg_p < -log10(p_cutoff)) %>% nrow()
high1 <- nrow(dat_plot)
p <- ggplot(data = dat_plot,aes(x = id, y = lg_p,
fill = threshold)) +
geom_col()+
coord_flip() +
scale_fill_manual(values = c('Up'= '#36638a','Not'='#cccccc','Down'='#7bcd7b')) +
geom_hline(yintercept = c(-log10(p_cutoff),log10(p_cutoff)),color = 'white',size = 0.5,lty='dashed') +
xlab('') +
ylab('-log10(P.Value) of GSVA score') +
guides(fill="none")+
theme_prism(border = T) +
theme(
axis.text.y = element_blank(),
axis.ticks.y = element_blank()
) +
geom_text(data = dat_plot[1:low1,],aes(x = id,y = 0.1,label = id),
hjust = 0,color = 'black') + #黑色标签
geom_text(data = dat_plot[(low1 +1):low0,],aes(x = id,y = 0.1,label = id),
hjust = 0,color = 'grey') + # 灰色标签
geom_text(data = dat_plot[(low0 + 1):high0,],aes(x = id,y = -0.1,label = id),
hjust = 1,color = 'grey') + # 灰色标签
geom_text(data = dat_plot[(high0 +1):high1,],aes(x = id,y = -0.1,label = id),
hjust = 1,color = 'black') # 黑色标签
ggsave("GSVA_barplot_pvalue.pdf",p,width = 15,height = 15)
5.与GSEA比较
GSEA与GSVA 计算enrichment scores 方法类似,都是一个gene list 然后和预设的gene sets 比较,计算两者的距离。
距离计算公式都是max distance from zero of KS test.
不同的是GSEA得到的gene list 一般是根据样本间的logFC或者ratio of signal to noise 或者 样本内的relative expression,排序得到 sorted gene list 再与gene sets 计算 enrichment scores。
GSVA 得到gene list 的方法是根据kcdf累积分布计算样本内gene relative expression,然后排序得到 sorted gene list 再与gene sets 计算 enrichment scores。