5.1 网页的状态页
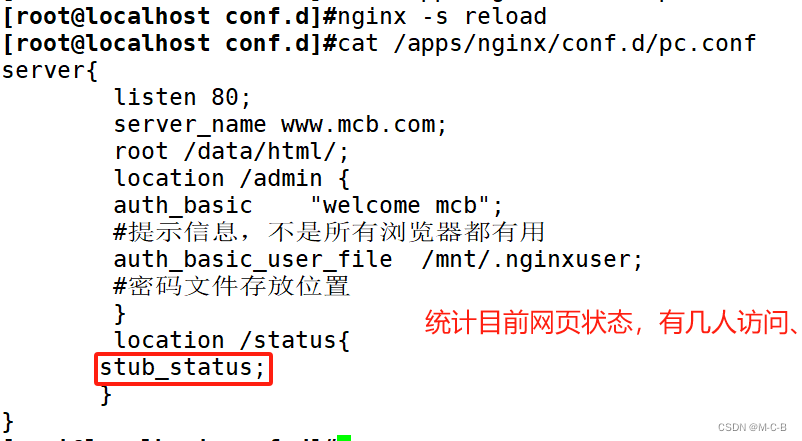
基于nginx 模块 ngx_http_stub_status_module 实现,在编译安装nginx的时候需要添加编译参数 --with-http_stub_status_module,否则配置完成之后监测会是提示语法错误注意: 状态页显示的是整个服务器的状态,而非虚拟主机的状态
server{
listen 80;
server_name www.lucky.com;
root /data/html/;
location /admin {
auth_basic "welcome cxk";
#提示信息,不是所有浏览器都有用
auth_basic_user_file /mnt/.nginxuser;
#密码文件存放位置
}
location /status{
stub_status;
}
}
真机访问
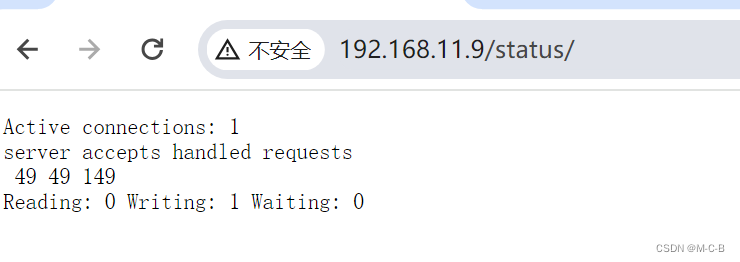
#状态页用于输出nginx的基本状态信息:
#输出信息示例:
Active connections: 291
server accepts handled requests
16630948 16630948 31070465
上面三个数字分别对应accepts,handled,requests三个值
Reading: 6 Writing: 179 Waiting: 106
Active connections:
#当前处于活动状态的客户端连接数,包括连接等待空闲连接数=reading+writing+waiting
accepts:
#统计总值,Nginx自启动后已经接受的客户端请求的总数。
handled:
#统计总值,Nginx自启动后已经处理完成的客户端请求总数,通常等于accepts,除非有因worker_connections限制等被拒绝的连接
requests:
#统计总值,Nginx自启动后客户端发来的总的请求数。
Reading:
#当前状态,正在读取客户端请求报文首部的连接的连接数,数值越大,说明排队现象严重,性能不足
Writing:
#当前状态,正在向客户端发送响应报文过程中的连接数,数值越大,说明访问量很大
Waiting:
#当前状态,正在等待客户端发出请求的空闲连接数,开启 keep-alive的情况下,这个值等于active – (reading+writing)提取数字学习下

还没有结束,报错
配置文件
验证
5.2 Nginx 第三方模块
5.2.1 ehco 模块
开源的echo模块 https://github.com/openresty/echo-nginx-module
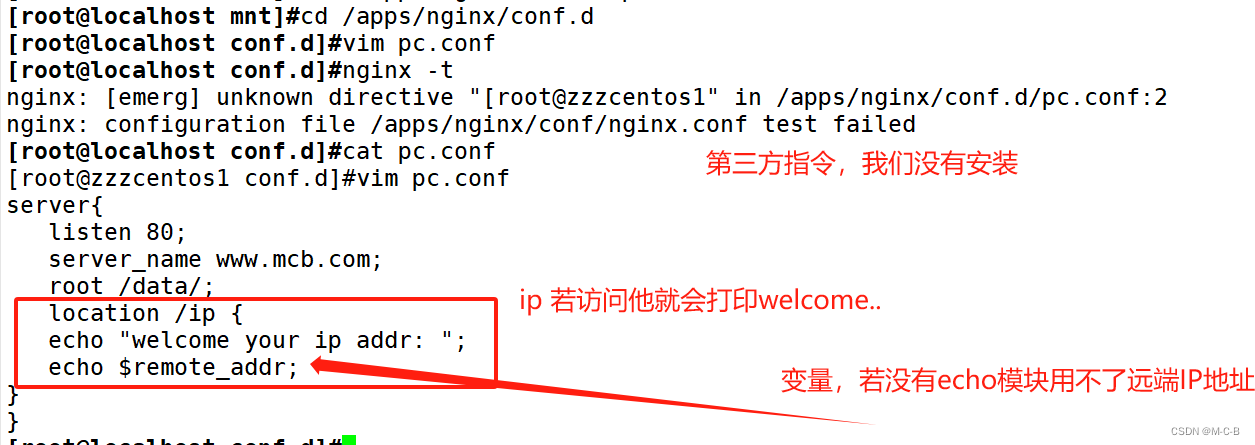
[root@zzzcentos1 conf.d]#vim pc.conf
server{
listen 80;
server_name www.mcb.com;
root /data/;
location /ip {
echo "welcome your ip addr: ";
echo $remote_addr;
}
}
①修改子配置文件
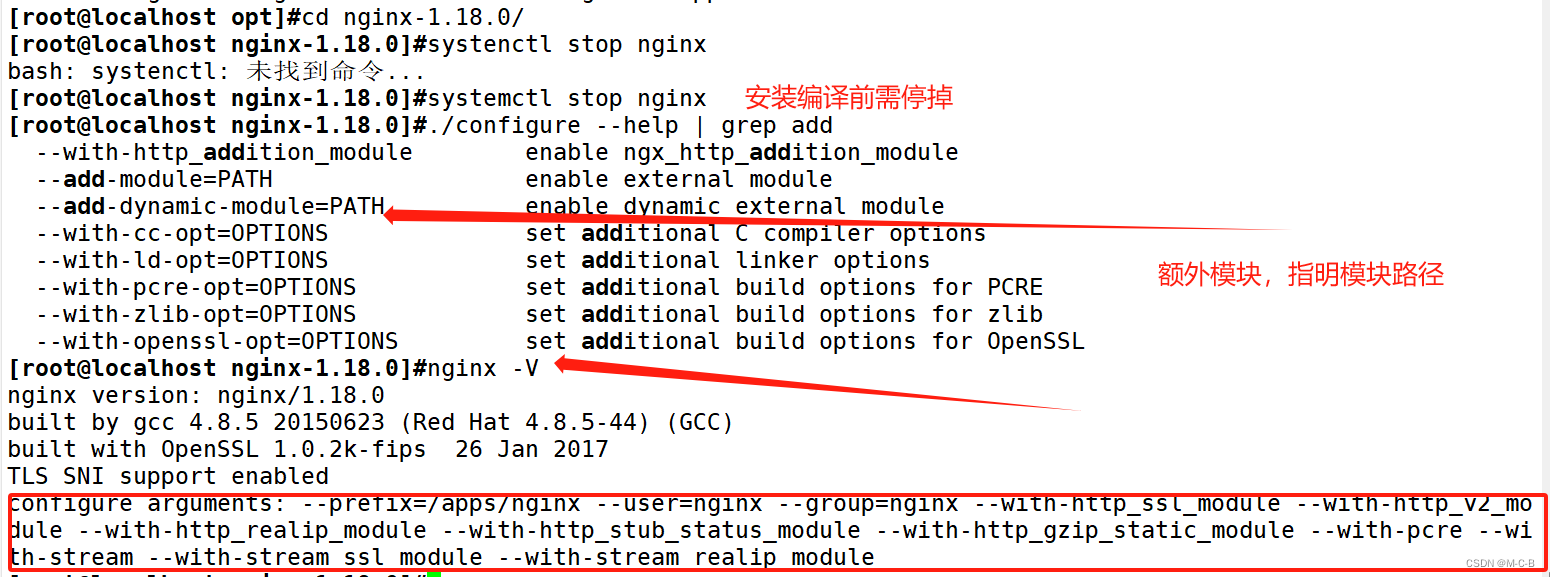
②依赖nginx编译echo模块
[root@mcb-11-9 conf.d]#cd /opt/
[root@mvb-11-9 opt]#unzip echo-nginx-module-master.zip
[root@mcb-11-9 opt]#cd nginx-1.18.0/
[root@mcb-11-9 nginx-1.18.0]#systemctl stop nginx
[root@mcb-11-9 nginx-1.18.0]#./configure --help | grep add
[root@mcb-11-9 nginx-1.18.0]#nginx -V
[root@mcb-11-9 nginx-1.18.0]#./configure --prefix=/apps/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_realip_module --add-module=/opt/echo-nginx-module-master
[root@zzzcentos1 nginx-1.18.0]#make && make install③添加echo模块后检查语法会不会报错
④浏览页面
5.3 变量
官方文档 http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html
5.3.1 常用内置变量
$remote_addr;
#存放了客户端的地址,注意是客户端的公网IP
$proxy_add_x_forwarded_for
#此变量表示将客户端IP追加请求报文中X-Forwarded-For首部字段,多个IP之间用逗号分隔,如果请求中没有X-Forwarded-For,就使用$remote_addrthe “X-Forwarded-For” client request header field with the $remote_addr variable appended to it, separated by a comma. If the “X-Forwarded-For” field is not present in the client request header, the $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for variable is equal to the $remote_addr variable.
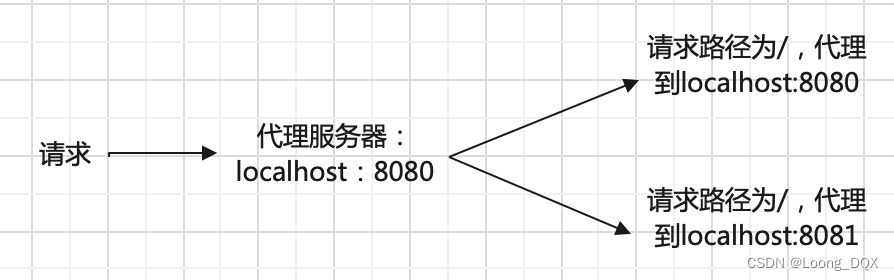
客户机 代理1 代理2 nginx服务器
$proxy_add_x_forwarded_for: 在代理1 上存的是 客户机的ip
$proxy_add_x_forwarded_for: 在代理2 上存的是 客户机的ip,代理1的ip 用逗号隔开
$proxy_add_x_forwarded_for: nginx 上存的是 客户机的ip,代理1的ip,代理2的ip
$args;
#变量中存放了URL中的参数,例如:http://www.kgc.org/main/index.do?id=20190221&partner=search
#返回结果为: id=20190221&partner=search 存放的就是这个
select * from table where id=20190221
$document_root;
#保存了针对当前资源的请求的系统根目录,例如:/apps/nginx/html
$document_uri;
#保存了当前请求中不包含参数的URI,注意是不包含请求的指令,比
如:http://www.kgc.org/main/index.do?id=20190221&partner=search会被定义为/main/index.do
#返回结果为:/main/index.do
$host;
#存放了请求的host名称
limit_rate 10240;
echo $limit_rate;
#如果nginx服务器使用limit_rate配置了显示网络速率,则会显示,如果没有设置, 则显示0
$remote_port;
#客户端请求Nginx服务器时随机打开的端口,这是每个客户端自己的端口
$remote_user;
#已经经过Auth Basic Module验证的用户名
$request_body_file;
#做反向代理时发给后端服务器的本地资源的名称
$request_method;
#请求资源的方式,GET/PUT/DELETE等
$request_filename;
#当前请求的资源文件的磁盘路径,由root或alias指令与URI请求生成的文件绝对路径,如:/apps/nginx/html/main/index.html
$request_uri; https:// www.baidu.com/main/index.do?id=20190221&partner=search
#包含请求参数的原始URI,不包含主机名,相当于:$document_uri?$args,例如:/main/index.do?id=20190221&partner=search
$scheme;
#请求的协议,例如:http,https,ftp等
$server_protocol;
#保存了客户端请求资源使用的协议的版本,例如:HTTP/1.0,HTTP/1.1,HTTP/2.0等
$server_addr;
#保存了服务器的IP地址
$server_name;
#请求的服务器的主机名
$server_port; 443 https
#请求的服务器的端口号
$http_<name>
#name为任意请求报文首部字段,表示记录请求报文的首部字段
arbitrary request header field; the last part of a variable name is the field name converted to lower case with dashes replaced by underscores
#用下划线代替横线
#示例: echo $http_User_Agent;
$http_user_agent;
#客户端浏览器的详细信息
$http_cookie;
#客户端的cookie信息
$cookie_<name>
#name为任意请求报文首部字部cookie的key名
$http_<name>
#name为任意请求报文首部字段,表示记录请求报文的首部字段,ame的对应的首部字段名需要为小写,如果有
横线需要替换为下划线
arbitrary request header field; the last part of a variable name is the field
name converted to lower case with dashes replaced by underscores #用下划线代替横线
#示例:
echo $http_user_agent;
echo $http_host;
$sent_http_<name>
#name为响应报文的首部字段,name的对应的首部字段名需要为小写,如果有横线需要替换为下划线,此变量有问题
echo $sent_http_server;
$arg_<name>
#此变量存放了URL中的指定参数,name为请求url中指定的参数
#对比 变量 $arg 是全部, 如果 要id 如下
echo $arg_id;
实验:变量
server{
listen 80;
server_name www.lucky.com;
root /data/;
location /ip {
echo "welcome,your ip addr: ";
echo $remote_addr;
}
location /main {
index index.html;
default_type text/html;
echo "hello world,main-->";
echo $remote_addr;
echo $args;
echo $arg_user;
echo $document_root;
echo $document_uri;
echo $host;
echo $http_user_agent;
echo $http_cookie;
echo $request_filename;
echo $scheme;
echo $scheme://$host$document_uri?$args;
}
}① 修改配置文件
②测试验证
实验结束:
补充下 正向代理 反向代理
正向代理:代理的是客户端
反向代理:代理的是服务端
反向代理:reverse proxy,指的是代理外网用户的请求到内部的指定的服务器,并将数据返回给用户的一种方式,这是用的比较多的一种方式。
总结
$proxy_add_x_forwarded_for 实现ip 透传,记录每一个地址
#此变量表示将客户端IP追加请求报文中X-Forwarded-For首部字段,多个IP之间用逗号分隔,如果请求中没有X-Forwarded-For,就使用$remote_addrthe “X-Forwarded-For” client request header field with the $remote_addr variable appended to it, separated by a comma. If the “X-Forwarded-For” field is not present in the client request header, the $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for variable is equal to the $remote_addr variable.
客户机 代理1 代理2 nginx服务器
$proxy_add_x_forwarded_for: 在代理1 上存的是 客户机的ip
$proxy_add_x_forwarded_for: 在代理2 上存的是 客户机的ip,代理1的ip 用逗号隔开
$proxy_add_x_forwarded_for: nginx 上存的是 客户机的ip,代理1的ip,代理2的ip
$http_user_agent; 客户端浏览器的详细信息
$server_addr; 服务器的IP地址
$scheme; 请求的协议 例如:http,https,ftp等
$http_cookie; 客户端的缓存信息 缓存:cookie和session
$server_protocol; 你使用的协议的版本
$document_root;指明了主站点目录的位置
#保存了针对当前资源的请求的系统根目录,例如:/apps/nginx/html


5.3.2自定义变量
假如需要自定义变量名称和值,使用指令set $variable value;
语法格式:
Syntax: set $variable value;
Default: —
Context: server, location, if #可以放置的位置代码
location /test {
set $name kgc;
echo $name;
set $my_port $server_port;
echo $my_port;
}5.3.3自定义图标
favicon.ico 文件是浏览器收藏网址时显示的图标,当客户端使用浏览器问页面时,浏览器会自己主动发起请求获取页面的favicon.ico文件,但是当浏览器请求的favicon.ico文件不存在时,服务器会记录404日志,而且浏览器也会显示404报错
【自定义小图标】
wget www.baidu.com/favicon.ico
放到主目录就可以了
不生效可以重新打开浏览器
实验前
实验:定义京东图标
5.4 自定义访问日志
5.4.1日志的格式 可以自由指定
访问日志是记录客户端即用户的具体请求内容信息,而在全局配置模块中的error_log是记录nginx服务器运行时的日志保存路径和记录日志的level,因此两者是不同的,而且Nginx的错误日志一般只有一个,但是访问日志可以在不同server中定义多个,定义一个日志需要使用access_log指定日志的保存路径,使用log_format指定日志的格式,格式中定义要保存的具体日志内容
Syntax: access_log path [format [buffer=size] [gzip[=level]] (flush=time] [if=condition]];access_log off;
Defau1t:
access_log 1ogs/access.1og combined;
Context: http,server, location,if in location,limit_except
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'
'$server_name:$server_port';
log_format test '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'
'$server_name:$server_port';
格式可以定义多个
###注意如果开启 include 注意定义自配置文件与 日志格式的上下关系 , 日志格式一定要在 include 之前 否则会不生效。②自定义 json 格式日志
方便ELK收集日志
log_format access_json '{"@timestamp":"$time_iso8601",'
'"host":"$server_addr",'
'"clientip":"$remote_addr",'
'"size":$body_bytes_sent,'
'"responsetime":$request_time,'
'"upstreamtime":"$upstream_response_time",'
'"upstreamhost":"$upstream_addr",'
'"http_host":"$host",'
'"uri":"$uri",'
'"xff":"$http_x_forwarded_for",'
'"referer":"$http_referer",'
'"tcp_xff":"$proxy_protocol_addr",'
'"http_user_agent":"$http_user_agent",'
'"status":"$status"}';