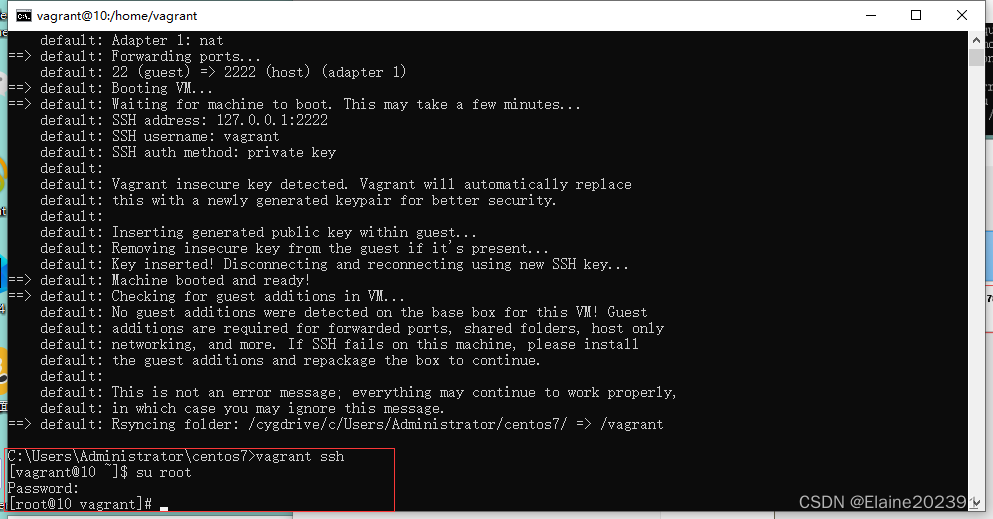
shell
shell就是操作系统提供给用户与操作系统进行交互的命令行界面。它可以理解为一个用户与操作系统之间的接口,用户可以通过输入命令来执行各种操作,如文件管理、进程控制、软件安装等。Shell还可以通过脚本编程实现自动化任务。
常见的Unix系统中使用的默认shell是Bash。除了Bash,还有其他一些常见的shell,如 C Shell、Kron Shell 等,它们对于不同的用户需求和习惯提供了不同的特性和语法。
自定义Shell
打印

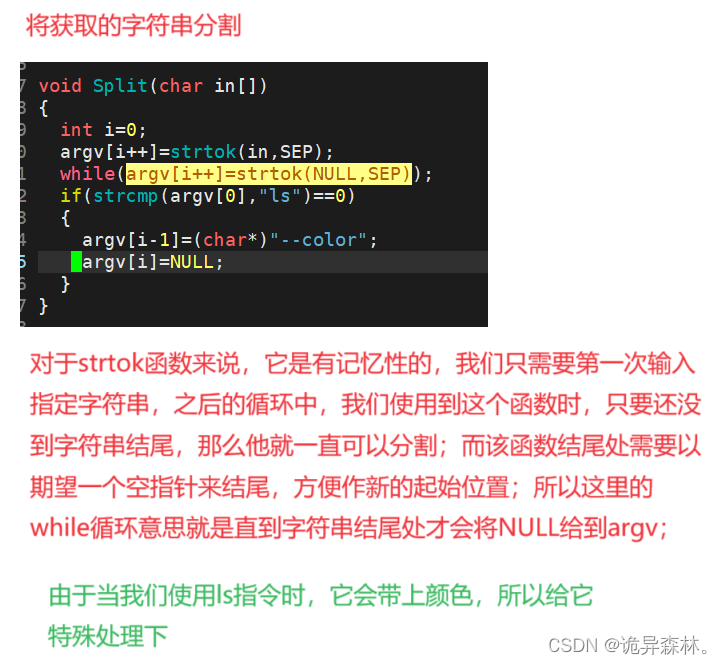
获取的字符串分割
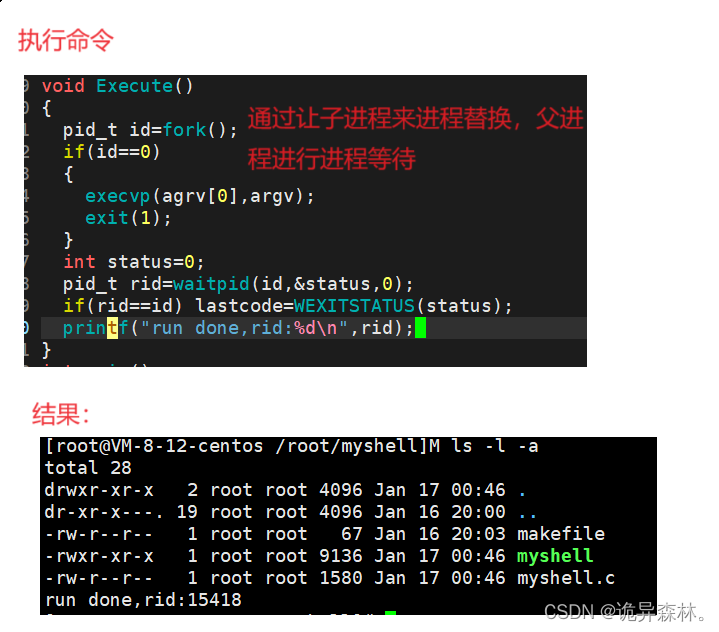
执行命令
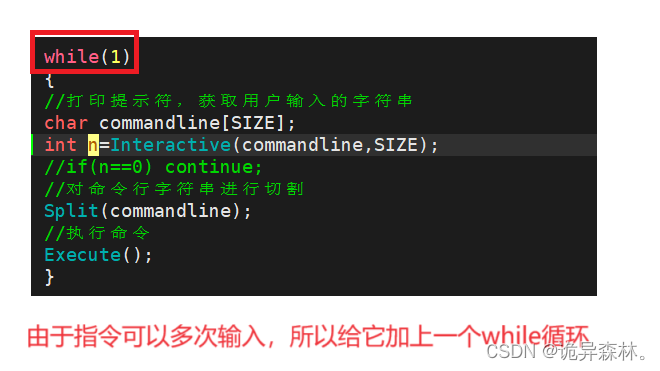
一些问题
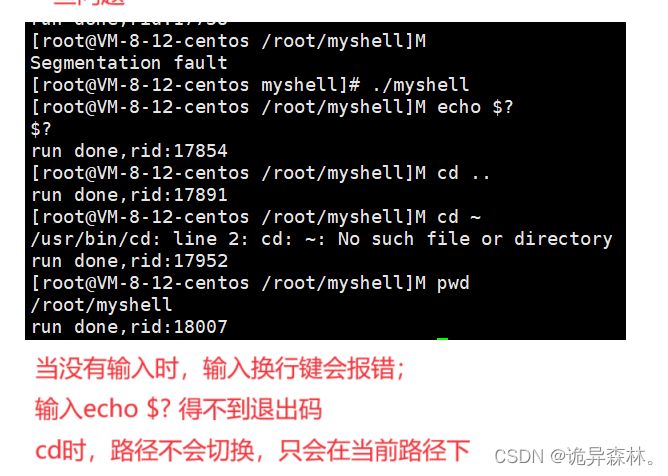

内建命令的处理
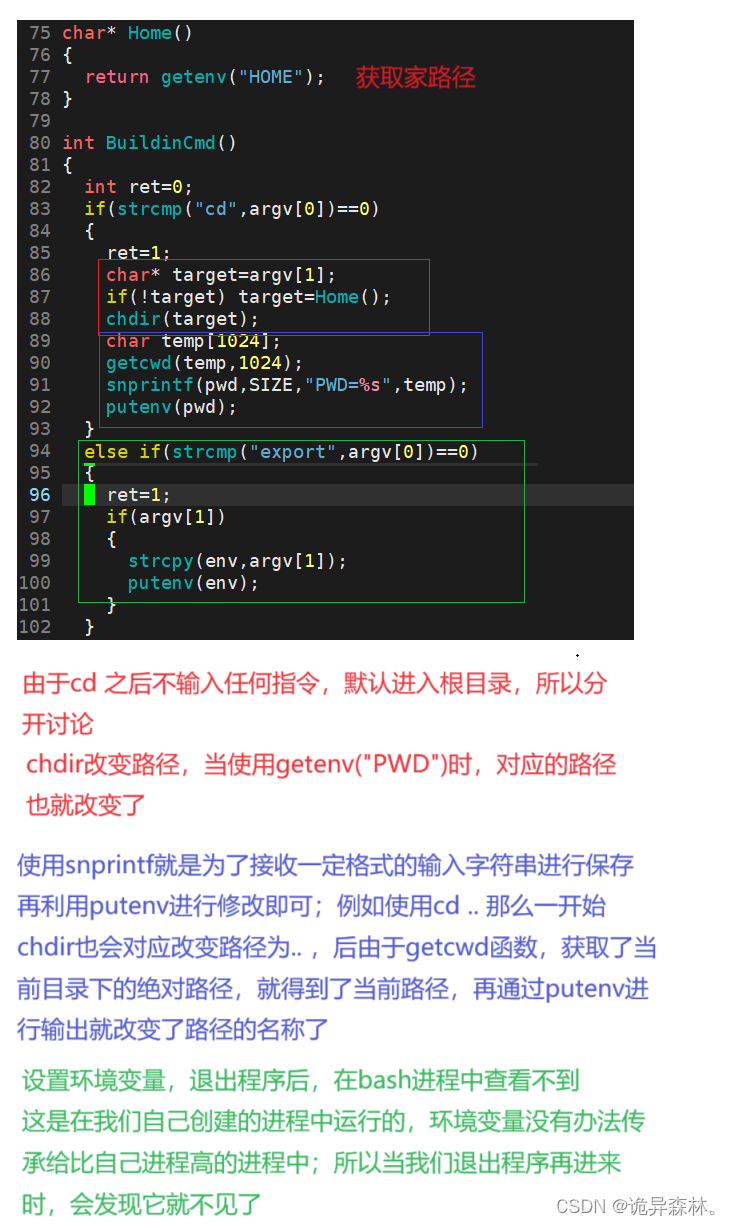


原码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#define SIZE 1024
#define MAX_ARGC 64
#define SEP " "
char *argv[MAX_ARGC];
char pwd[SIZE];
char env[SIZE]; // for test
int lastcode = 0;
const char* HostName()
{
char *hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME");
if(hostname) return hostname;
else return "None";
}
const char* UserName()
{
char *hostname = getenv("USER");
if(hostname) return hostname;
else return "None";
}
const char *CurrentWorkDir()
{
char *hostname = getenv("PWD");
if(hostname) return hostname;
else return "None";
}
char *Home()
{
return getenv("HOME");
}
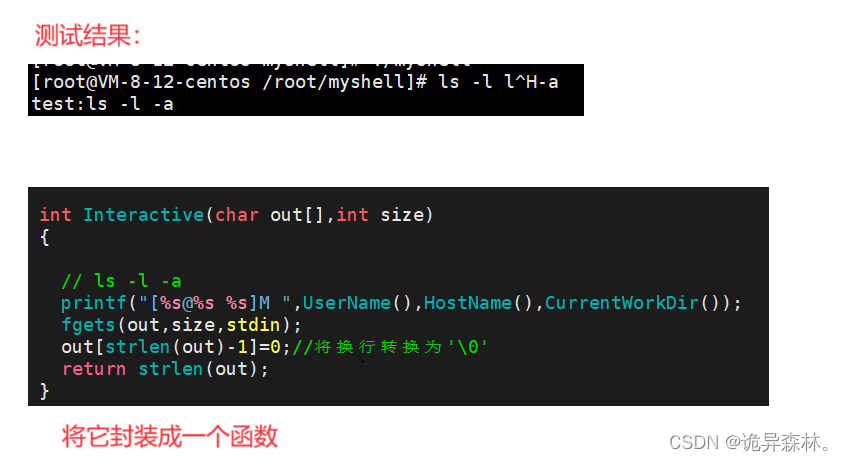
int Interactive(char out[], int size)
{
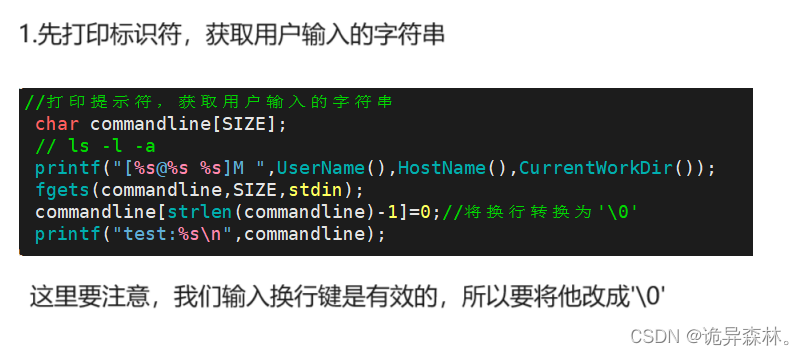
// 输出提示符并获取用户输入的命令字符串"ls -a -l"
printf("[%s@%s %s]$ ", UserName(), HostName(), CurrentWorkDir());
fgets(out, size, stdin);
out[strlen(out)-1] = 0; //'\0'
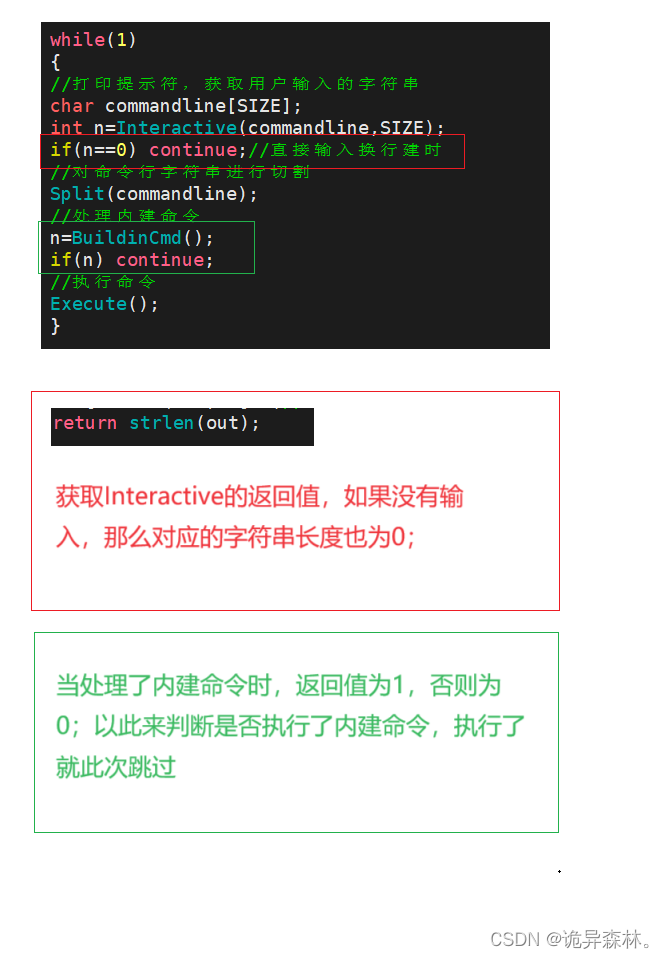
return strlen(out);
}
void Split(char in[])
{
int i = 0;
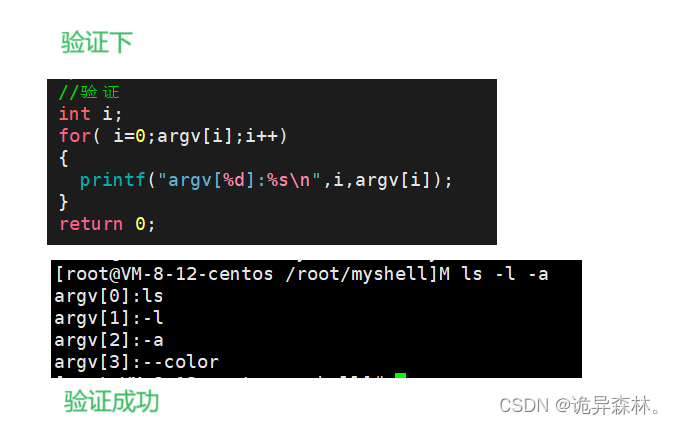
argv[i++] = strtok(in, SEP); // "ls -a -l"
while(argv[i++] = strtok(NULL, SEP));
if(strcmp(argv[0], "ls") ==0)
{
argv[i-1] = (char*)"--color";
argv[i] = NULL;
}
}
void Execute()
{
pid_t id = fork();
if(id == 0)
{
// 让子进程执行命名
execvp(argv[0], argv);
exit(1);
}
int status = 0;
pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, 0);
if(rid == id) lastcode = WEXITSTATUS(status);
//printf("run done, rid: %d\n", rid);
}
int BuildinCmd()
{
int ret = 0;
// 1. 检测是否是内建命令, 是 1, 否 0
if(strcmp("cd", argv[0]) == 0)
{
// 2. 执行
ret = 1;
char *target = argv[1]; //cd XXX or cd
if(!target) target = Home();
chdir(target);
char temp[1024];
getcwd(temp, 1024);
snprintf(pwd, SIZE, "PWD=%s", temp);
putenv(pwd);
}
else if(strcmp("export", argv[0]) == 0)
{
ret = 1;
if(argv[1])
{
strcpy(env, argv[1]);
putenv(env);
}
}
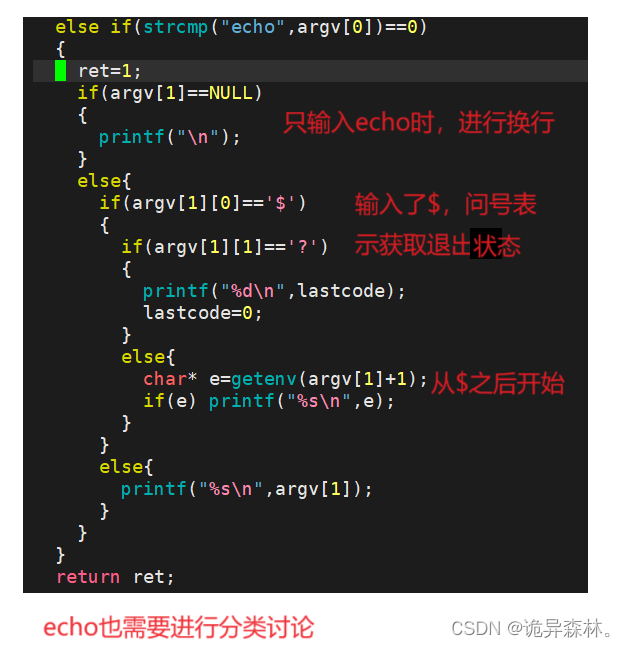
else if(strcmp("echo", argv[0]) == 0)
{
ret = 1;
if(argv[1] == NULL) {
printf("\n");
}
else{
if(argv[1][0] == '$')
{
if(argv[1][1] == '?')
{
printf("%d\n", lastcode);
lastcode = 0;
}
else{
char *e = getenv(argv[1]+1);
if(e) printf("%s\n", e);
}
}
else{
printf("%s\n", argv[1]);
}
}
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
while(1)
{
char commandline[SIZE];
// 1. 打印命令行提示符,获取用户输入的命令字符串
int n = Interactive(commandline, SIZE);
if(n == 0) continue;
// 2. 对命令行字符串进行切割
Split(commandline);
// 3. 处理内建命令
n = BuildinCmd();
if(n) continue;
// 4. 执行这个命令
Execute();
}
return 0;
}