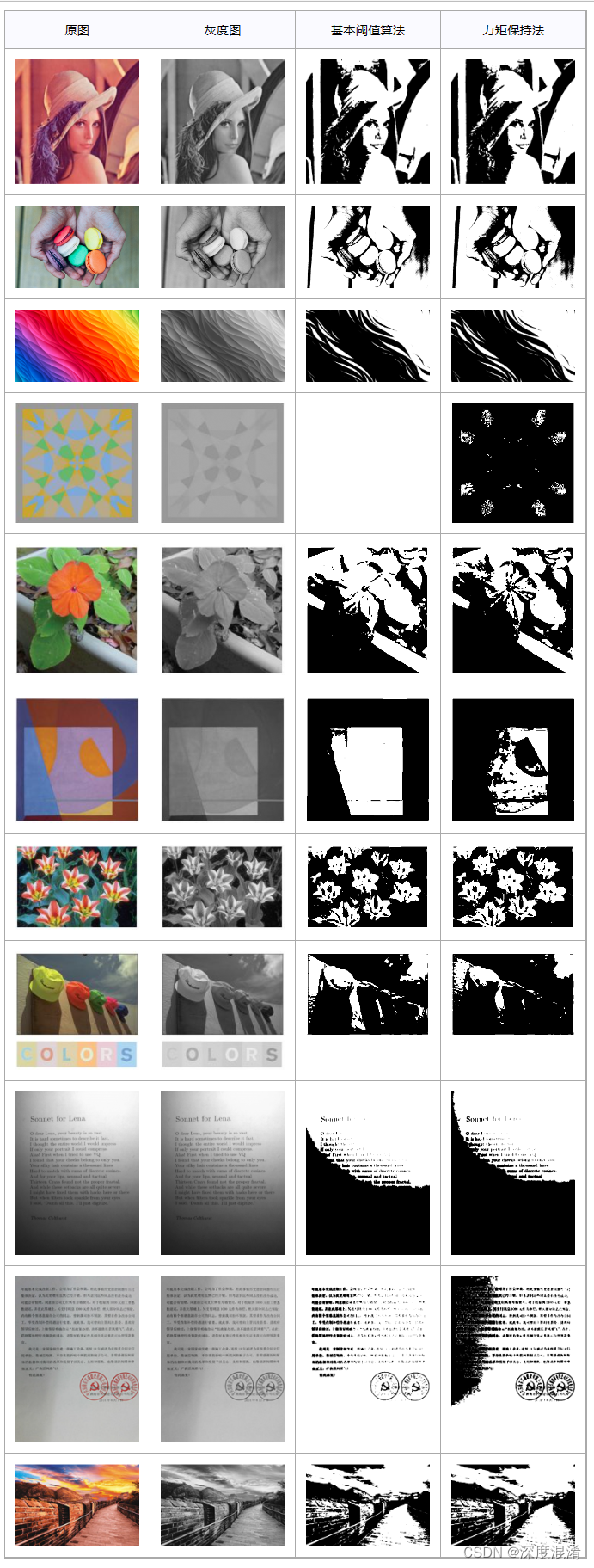
1、力矩保持法
提出了一种基于矩保持原理的自动阈值选择方法。以这样的方式确定地计算阈值,即在输出画面中保留输入画面的时刻。实验结果表明,该方法可以将给定的图像阈值化为有意义的灰度级。该方法描述了全局阈值,但也适用于局部阈值。
A new approach to automatic threshold selection using the moment-preserving principle is proposed. The threshold values are computed deterministically in such a way that the moments of an input picture is preserved in the output picture. Experimental results show that the approach can be employed to threshold a given picture into meaningful gray-level classes. The approach is described for global thresholding, but it is applicable to local thresholding as well.
在许多图像分析应用中,图像阈值处理是必要的步骤。对于阈值技术综述,见[1或21。在最简单的形式中,阈值将给定图像的像素分类为两组的装置(例如背景),其中包括灰度值高于一定值的像素另一个包括灰度值等于或低于门槛这被称为双燃料阈值。一般来说,我们可以选择一个阈值,并使用它们将整个灰度值范围划分为几个子范围。这被称为多级阈值。大多数阈值技术[3-S]在阈值选择中利用图像直方图的形状信息。在理想在这种情况下,具有高对比度对象和背景的图像的直方图将具有双峰形状,两个峰被深谷隔开。可以选择谷作为阈值。在实际应用中,这种直方图双峰性通常是不清楚的,已经提出了几种方法克服这一问题问题[4-81,以便仍然可以应用山谷搜索技术。阈值选择的另一个方向是评估所选的阈值(通过某种度量)[9-131。一种方法是使用熵信息测量阈值类的同质性(9-111或这些类彼此不同[12]。另一种方法是利用课堂判别分析中使用的可分性度量[13]。在本文中,我们提出了另一种基于矩保持原理也已应用于亚像素边缘检测[14]. 具体而言,在阈值化之前,我们计算输入图像。然后以如下方式选择阈值:阈值图像保持不变。这种方法可视为保矩图像变换,其从模糊版本。该方法可以自动且确定地选择多个阈值,而无需迭代或搜索。此外,代表性灰度值也可以针对每个阈值类获得。
Image thresholding is a necessary step in many image analysis applications. For a
survey of thresholding techniques, see [l or 21. In its simplest form, thresholding
means to classify the pixels of a given image into two groups (e.g., objects and
background), one including those pixels with their gray values above a certain
threshold, and the other including those with gray values equal to and below the
threshold. This is called bileuel thresholding. More generally, we can select more than
one threshold, and use them to divide the whole range of gray values into several
subranges. This is called multilevel thresholding. Most thresholding techniques [3-S]
utilize shape information of the image histogram in threshold selection. In the ideal
case, the histogram of an image with high-contrast objects and background will have
a bimodal shape, with two peaks separated by a deep valley. The gray value at the
valley can be chosen as the threshold. In real applications, such histogram bimodality is often unclear, and several methods have been proposed to overcome this
problem [4-81 so that the valley seeking technique can still be applied.
Another direction of threshold selection is to evaluate the goodness of selected
thresholds by a certain measure [9-131. One way is to use entropy information to
measure the homogeneity of the thresholded classes (9-111 or the independency of
the classes from one another [12]. Another way is to make use of the class
separability measures used in discriminant analysis [13].
In this paper, we propose another threshold selection method based on the
moment-preserving principle which has also been applied to subpixel edge detection
[14]. Specifically, before thresholding, we compute the gray-level moments of the
input image. The thresholds are then selected in such a way that the moments of the
thresholded image are kept unchanged. This approach may be regarded as a
moment-preserving image transformation which recovers an ideal image from a
blurred version. The approach can automatically and deterministically select multiple thresholds without iteration or search. In addition, a representative gray value
can also be obtained for each thresholded class.




NOTE Moment-Preserving Thresholding: A New Approach![]() https://people.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~whtsai/Journal%20Paper%20PDFs/Tsai_CVGIP(journal)_1985.pdf
https://people.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~whtsai/Journal%20Paper%20PDFs/Tsai_CVGIP(journal)_1985.pdf
2、力矩保持法的阈值算法及其源代码
二值算法综述请阅读:
C#,图像二值化(01)——二值化算法综述与二十三种算法目录![]() https://blog.csdn.net/beijinghorn/article/details/128425225?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
https://blog.csdn.net/beijinghorn/article/details/128425225?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
支持函数请阅读:
C#,图像二值化(02)——用于图像二值化处理的一些基本图像处理函数之C#源代码![]() https://blog.csdn.net/beijinghorn/article/details/128425984?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
https://blog.csdn.net/beijinghorn/article/details/128425984?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
namespace Legalsoft.Truffer.ImageTools
{
public static partial class BinarizationHelper
{
#region 灰度图像二值化 全局算法 力矩保持法
/// <summary>
/// 力矩保持法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="histogram"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static byte Moment_Preserving_Threshold(int[] histogram)
{
int amount = Histogram_Sum(histogram);
double[] Avec = new double[256];
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
Avec[i] = (double)A(histogram, i) / (double)amount;
}
double X2 = (double)(B(histogram) * C(histogram) - A(histogram) * D(histogram)) / (double)(A(histogram) * C(histogram) - B(histogram) * B(histogram));
double X1 = (double)(B(histogram) * D(histogram) - C(histogram) * C(histogram)) / (double)(A(histogram) * C(histogram) - B(histogram) * B(histogram));
double X0 = 0.5 - (B(histogram) / A(histogram) + X2 / 2) / Math.Sqrt(X2 * X2 - 4 * X1);
int Index = 0;
double Min = double.MaxValue;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
if (Math.Abs(Avec[i] - X0) < Min)
{
Min = Math.Abs(Avec[i] - X0);
Index = i;
}
}
return (byte)Index;
}
public static void Moment_Preserving_Algorithm(byte[,] data)
{
int[] histogram = Gray_Histogram(data);
int threshold = Moment_Preserving_Threshold(histogram);
Threshold_Algorithm(data, threshold);
}
private static double A(int[] histogram, int Index = 255)
{
return Histogram_Sum(histogram, 0, Index);
}
private static double B(int[] histogram, int Index = 255)
{
return Histogram_Sum(histogram, 1, Index);
}
private static double C(int[] histogram, int Index = 255)
{
return Histogram_Sum(histogram, 2, Index);
}
private static double D(int[] histogram, int Index = 255)
{
return Histogram_Sum(histogram, 3, Index);
}
#endregion
}
}
3、力矩保持法的阈值算法计算效果