当曾经的孩子们慢慢步入社会才知道,那年味渐淡的春节就像是疾驰在人生路上的暂停键。
它允许你在隆隆的鞭炮声中静下心来,瞻前顾后,怅然若失。
也允许你在寂静的街道上屏气凝神,倾听自己胸腔里的那团人声鼎沸。
孩子们会明白的,就像他们步入大学校园时候渐渐明白家乡只有冬夏,再无春秋一样。
人生这场旅途,就是无数个后知后觉的组合。提前看到一些东西不会让我们清醒半分,相反,反而容易让人愈发的沉溺于那来势汹汹的纸醉金迷…
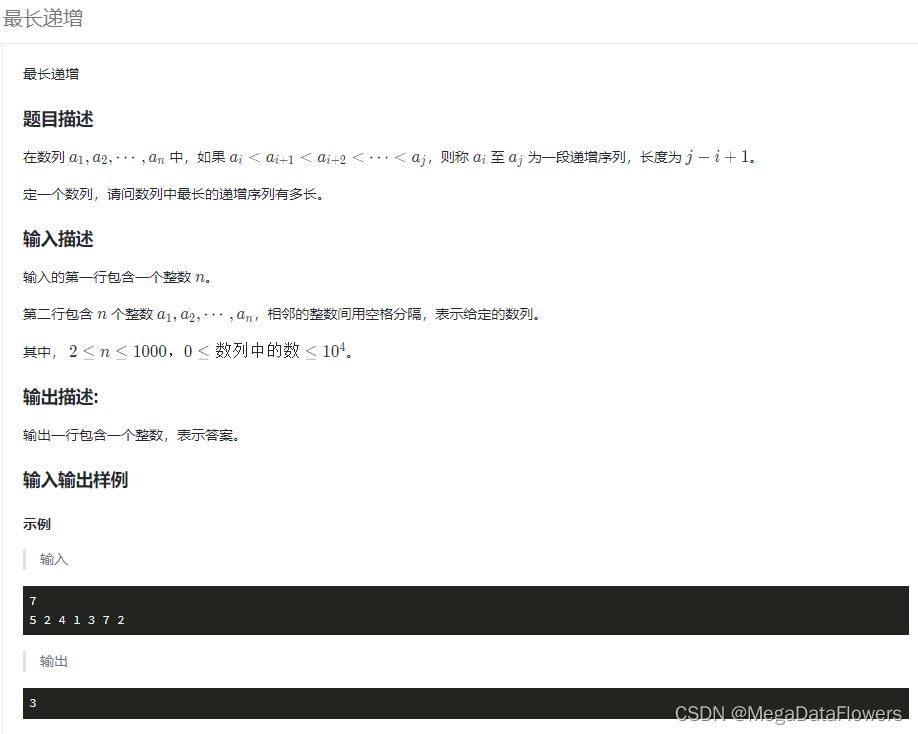
正月初九,对于多数打工人来说是真正意义上新的一年的开始,就像是一条条沉睡的金鱼被人从湖底捞起再次丢进那个金碧辉煌的鱼缸,开始在整个体系内扮演不同的角色。组织架构、行政管理、经理、开发、部署、运维、测试…
今天,我们不妨就着组织架构这个话题,来拆解下结构型设计模式中将聚合思路用到极致的实现方案:组合模式。
一言
组合模式通过创建对象组的的树形结构,让客户以一致的方式处理个别对象以及组合对象。
当组织开始优化

概念和思路是为需求服务的,就比如:
我创办了一家名为“Wayne实业”的集团公司,为了集团战略的更好落实,我对组织结构进行了优化。集团公司下设多个省级分公司,每个省级分公司下设地市级办事处。
现在我要求你在集团公司网页上级联的展示架构信息,有什么思路?
探路式思考
首先明确下,我们不是在具体讨论用Vue或React等成熟前端框架的某个组件更优,而是从实体设计的角度去思考。
相信很多朋友最先想到的就是继承关系,分公司作为集团公司的子类,办事处作为分公司的子类。诚然,需求的描述实在是太契合继承关系的特征了。
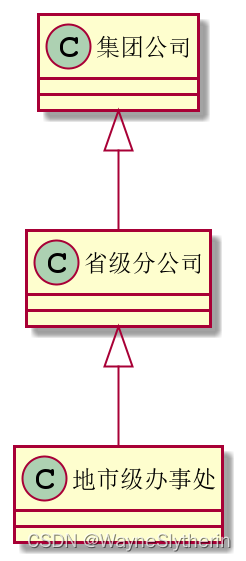
但是我们仔细分析下需求就会发现,这种设计方式实际上存在很大的问题。集团公司有多个分公司,每个分公司下又有大量的办事处。这种设计方式非常不利于对分公司、办事处的管理。可以思考下,一旦需要做遍历或增删操作要投入多大的成本?
组合模式的思考
其实,组合模式非常善于解决这样的问题。当我们要处理的对象可以凭借需求进化成一棵树的时候,这一切反而变得简单。
相信很多朋友读到这里会有疑问,树结构在编程中其实并不是一个容易处理的结构,为什么还说它简单?
这是因为在组合模式下,我们对树上的节点或者叶子的操作都是扁平的,根本不用考虑它是节点还是叶子。
就好像一个立体的三维空间突然坍缩成一个平面,我们需要关注的东西突然少了一个维度,简单的幸福由此蔓延开来。
设计
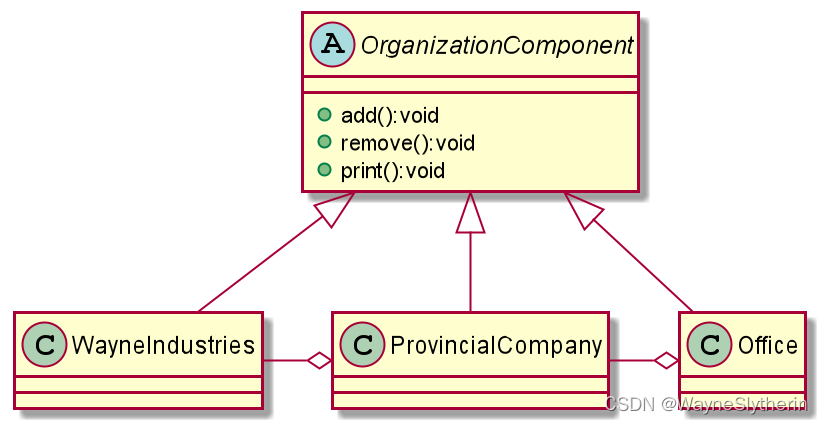
代码实现
核心
public abstract class OrganizationComponent {
private String name ;
private String des;
protected void add(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent){
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
protected void remove(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent){
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
protected abstract void print();
public OrganizationComponent(String name, String des) {
this.name = name;
this.des = des;
}
//setter&getter
}
集团公司
public class WayneIndustries extends OrganizationComponent{
List<OrganizationComponent> organizationComponents = new ArrayList<>();
public WayneIndustries(String name, String des) {
super(name, des);
}
@Override
protected void add(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
organizationComponents.add(organizationComponent);
}
@Override
protected void remove(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
organizationComponents.remove(organizationComponent);
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return super.getName();
}
@Override
public String getDes() {
return super.getDes();
}
@Override
protected void print() {
System.out.println("--------------------"+getName()+"----------------------");
for (OrganizationComponent ogc : organizationComponents)
ogc.print();
}
}
省公司
public class ProvincialCompany extends OrganizationComponent{
List<OrganizationComponent> organizationComponents = new ArrayList<>();
public ProvincialCompany(String name, String des) {
super(name, des);
}
@Override
protected void add(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
organizationComponents.add(organizationComponent);
}
@Override
protected void remove(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
organizationComponents.remove(organizationComponent);
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return super.getName();
}
@Override
public String getDes() {
return super.getDes();
}
@Override
protected void print() {
System.out.println("--------------------"+getName()+"----------------------");
for (OrganizationComponent ogc : organizationComponents)
ogc.print();
}
}
办事处
public class Office extends OrganizationComponent{
public Office(String name, String des) {
super(name, des);
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return super.getName();
}
@Override
public String getDes() {
return super.getDes();
}
@Override
protected void print() {
System.out.println(getName());
}
}
客户端
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OrganizationComponent wayne = new WayneIndustries("Wayne实业", "世界500强");
OrganizationComponent company1 = new ProvincialCompany("江苏分公司", "综合贸易");
OrganizationComponent company2 = new ProvincialCompany("广东分公司", "对外贸易");
company1.add(new Office("徐州办事处", "主营冶金"));
company1.add(new Office("连云港办事处", "海港事宜"));
company1.add(new Office("镇江办事处", "旅游业"));
company2.add(new Office("深圳办事处","对外贸易"));
company2.add(new Office("珠海办事处","对澳贸易"));
wayne.add(company1);
wayne.add(company2);
wayne.print();
// company1.print();
// company2.print();
}
}
测试

组合模式在JDK源码中的应用
笔者在学习设计模式的过程中,有一个很直观的感受就是:设计模式给了普通开发者另一个视角来审视问题,也使得我们看待某些问题变得更灵活。比如顶层抽象,它可以依托于接口也可以依托于抽象类,再比如泛化关系,它可以依托于继承和实现,也可以依托于静态内部类。
这种思维方式的提升就像一个兢兢业业在工地上码砖的工人突然间抬头大量起整个房间的布局甚至整栋大厦的结构原理,那种豁然开朗的感觉或许只有亲历者才能感同身受。
在JDK源码中,组合模式也十分常见。比如我们熟知的HashMap:
Map<Integer,String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(0,"江苏");
Map<Integer,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1,"浙江");
map.put(2,"广东");
hashMap.putAll(map);
System.out.println(hashMap);
在HashMap中,既可以用put加入一个键值对,也可以用putAll加入多个键值对。
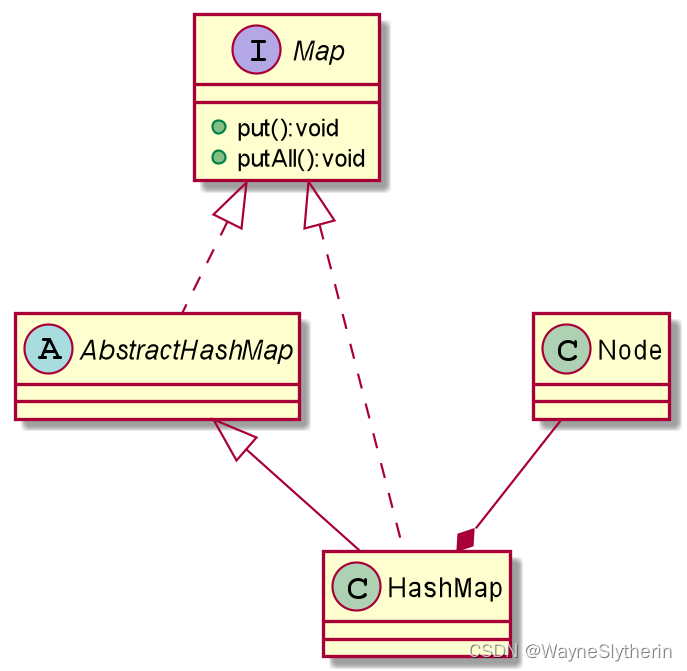
我们通过审视HashMap的结构可以发现它为了扩展性不但继承了抽象AbstractMap的同时也实现了Map接口,这两个抽象实际上都可以看作是组合模式的OrganizationComponent(也就是我之前例子中的集团公司)。而有读过HashMap源码的朋友应该知道,在HashMap中有个及其关键的静态内部类Node。
相关源码片:
/**
* Basic hash bin node, used for most entries. (See below for
* TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.)
*/
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
它是组成链表/红黑树的原子结构(这里与本节无关暂不做展开,感兴趣的朋友可以再查阅下相关资料),hashMap的put方法、putAll方法都以Node为最小执行单位。这样来看,静态内部类Node更像是由HashMap泛化来的另一个实现形式(类似于我之前例子中的省公司、办事处)。这种叶子节点(Node)与子节点(HashMap)同根同源(Map),与组合模式理念“不谋而合”。
相关源码片:
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods.
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
/**
* Copies all of the mappings from the specified map to this map.
* These mappings will replace any mappings that this map had for
* any of the keys currently in the specified map.
*
* @param m mappings to be stored in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
putMapEntries(m, true);
}
/**
* Implements Map.putAll and Map constructor.
*
* @param m the map
* @param evict false when initially constructing this map, else
* true (relayed to method afterNodeInsertion).
*/
final void putMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict) {
int s = m.size();
if (s > 0) {
if (table == null) { // pre-size
float ft = ((float)s / loadFactor) + 1.0F;
int t = ((ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);
if (t > threshold)
threshold = tableSizeFor(t);
}
else if (s > threshold)
resize();
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet()) {
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, evict);
}
}
}
结
组合模式依据树形结构来组合对象,从部分到整体层次分明,是典型的结构型模式。组合模式对用户使用的单个对象表现出极强的一致性,对客户而言无需特别关注个别对象和组合对象。
希望此文能够让大家对组合模式有更进一步的理解。
关注我,共同进步,每周至少一更。——Wayne