tips:
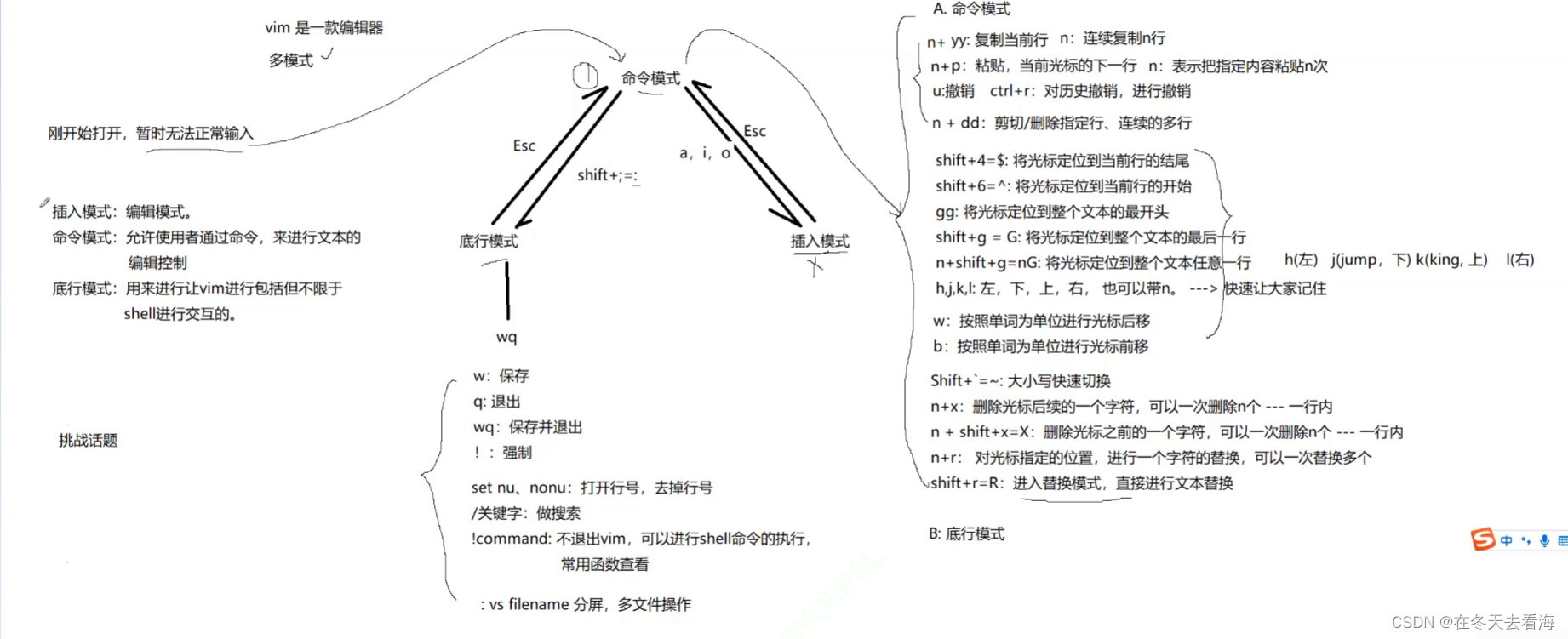
二叉搜索树一定是中序遍历,因为只有中序遍历二叉搜索树它的元素才是有序的。 回溯法则使用后序遍历方式,左右中,主要处理逻辑在中。采用后序是因为中的处理逻辑需要左分支和右分支递归带回来的处理结果,从而通过递归左右中的方式把结果一层层向上带。
530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
刷题 文章讲解 视频讲解 题解(递归双指针法): /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
//中序遍历双指针法
//用来记录上一个遍历的结点
TreeNode pre;
//将结果初始化为最大值,便于存储二叉搜索树中最小值
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
//若二叉树为空,则直接返回最小值0
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
traversal(root);
return result;
}
public void traversal(TreeNode root){
//若遍历到了空结点,直接返回
if(root == null){
return;
}
//左处理
traversal(root.left);
//中处理,双指针法处理
if(pre != null){
result = Math.min(result, root.val - pre.val);
}
pre = root;
//右处理
traversal(root.right);
}
}501.二叉搜索树中的众数
刷题 文章讲解 视频讲解 题解(递归双指针法): /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
//记录当前元素出现次数
int count;
//记录元素出现最大次数
int maxCount;
//记录前一个结点
TreeNode pre;
//记录结果
ArrayList<Integer> resultList;
//主函数
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
resultList = new ArrayList<>();
maxCount = 0;
count = 0;
pre = null;
search(root);
//将ArrayList容器中的结果转移到数组中,从而返回结果数组
int[] result = new int[resultList.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < resultList.size(); i++){
result[i] = resultList.get(i);
}
return result;
}
//递归函数
void search(TreeNode root){
//若遍历到空结点,直接返回
if(root == null){
return;
}
//左处理
search(root.left);
//中处理
if(pre == null){
//当pre还未开始移动时,初始化指向的为null,执行
//此时cur的元素只出现了一次,count修改为1
count = 1;
}else if(pre.val == root.val){
//当pre与cur指向结点值相同时,说明cur的元素出现了一次重复,count自增1
count++;
}else{
//当pre与cur指向结点值不同时,说明当前元素出现次数统计结束,count归1
count = 1;
}
//指针中处理结束,更新结果以及maxCount
//tips:若count < maxCount,则不走以下分支结构,为正常情况,只向后移动双指针即可
if(count > maxCount){
//若当前元素次数大于最大次数
resultList.clear();
resultList.add(root.val);
maxCount = count;
}else if(count == maxCount){
resultList.add(root.val);
}
//为使cur与pre形成双指针
pre = root;
//右处理
search(root.right);
}
}236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
刷题 文章讲解 视频讲解 题解(递归双指针法): /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
//自底向上,后序,递归,回溯
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
//递归出口处理
//若传入二叉树为空或者遍历的结点为空,返回null
if(root == null){
return null;
}
//当遍历到p或者q结点,则直接返回当前结点(p或者q)
if(root == p || root == q){
return root;
}
//左处理
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
//右处理
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
//中处理(主要逻辑,回溯)
if(left == null && right == null){
//若未找到p或q,则返回null
return null;
}else if(left == null && right != null){
//若左分支无p或q,右分支找到p或q,返回右分支
return right;
}else if(left != null && right == null){
//若右分支无p或q,左分支找到p或q,返回左分支
return left;
}else{
//若左右结点返回值均不为空,则说明同时找到p和q
return root;
}
}
}
 https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-absolute-difference-in-bst/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-absolute-difference-in-bst/description/ https://programmercarl.com/0530.%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%90%9C%E7%B4%A2%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%80%E5%B0%8F%E7%BB%9D%E5%AF%B9%E5%B7%AE.html
https://programmercarl.com/0530.%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%90%9C%E7%B4%A2%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%80%E5%B0%8F%E7%BB%9D%E5%AF%B9%E5%B7%AE.html https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1DD4y11779/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1DD4y11779/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062 https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-mode-in-binary-search-tree/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-mode-in-binary-search-tree/description/ https://programmercarl.com/0501.%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%90%9C%E7%B4%A2%E6%A0%91%E4%B8%AD%E7%9A%84%E4%BC%97%E6%95%B0.html
https://programmercarl.com/0501.%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%90%9C%E7%B4%A2%E6%A0%91%E4%B8%AD%E7%9A%84%E4%BC%97%E6%95%B0.html https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1fD4y117gp/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1fD4y117gp/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062 https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/description/ https://programmercarl.com/0236.%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%80%E8%BF%91%E5%85%AC%E5%85%B1%E7%A5%96%E5%85%88.html
https://programmercarl.com/0236.%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%80%E8%BF%91%E5%85%AC%E5%85%B1%E7%A5%96%E5%85%88.html https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1jd4y1B7E2/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1jd4y1B7E2/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062
![[AIGC ~ coze] Kafka 消费者——从源码角度深入理解](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/472b8335579f464b842cd68ef6680eb9.png)