代码流程
下图就是全部. 剩下文字部分是细节补充,但是内容不变: bash调用python,用python配置好configuration, 一个cpu每个tick运行一次,requestport发出pkt.
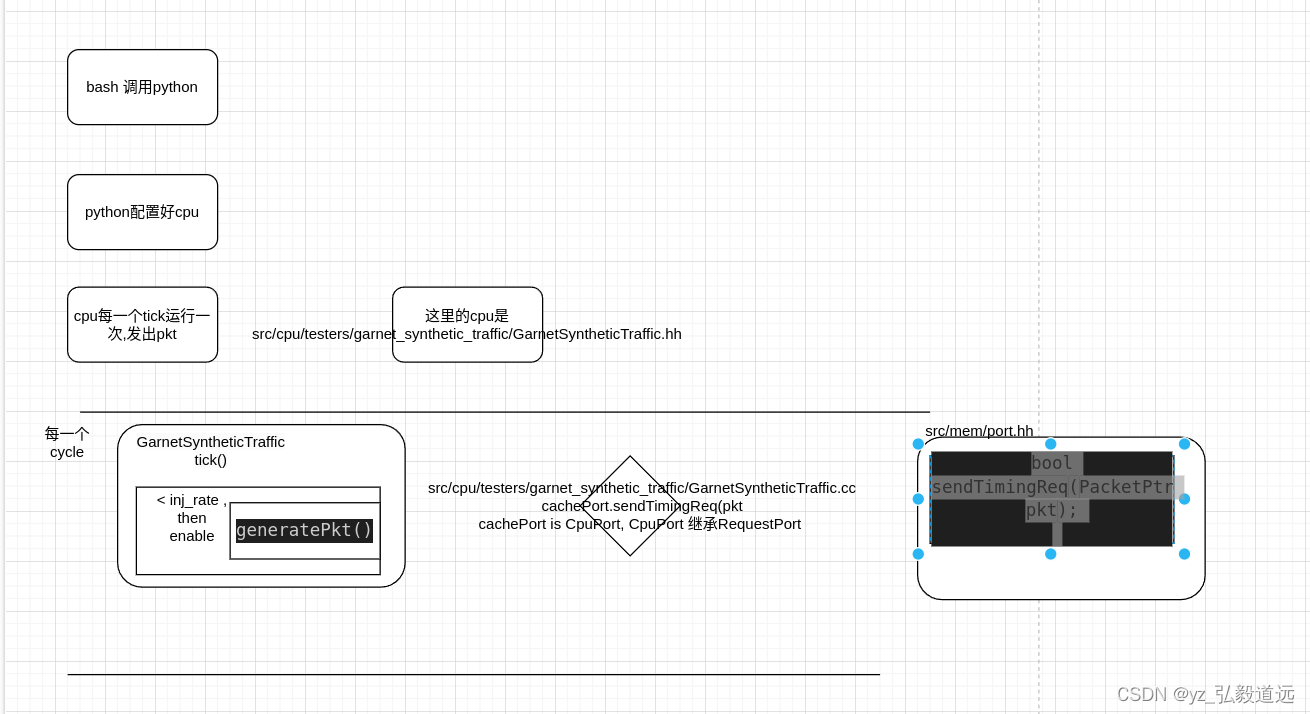
bash 启动 python文件并配置
./build/NULL/gem5.debug configs/example/garnet_synth_traffic.py \
--num-cpus=16 \
--num-dirs=16 \
--network=garnet \
--topology=Mesh_XY \
--mesh-rows=4 \
--sim-cycles=1000000 --inj-vnet=0 \
--synthetic=uniform_random \
--injectionrate=1 \
--single-sender-id=0
代码启动 garnet_synth_traffic.py
代码直接用了 GarnetSyntheticTraffic()函数.
cpus = [
GarnetSyntheticTraffic(
num_packets_max=args.num_packets_max,
single_sender=args.single_sender_id,
single_dest=args.single_dest_id,
sim_cycles=args.sim_cycles,
traffic_type=args.synthetic,
inj_rate=args.injectionrate,
inj_vnet=args.inj_vnet,
precision=args.precision,
num_dest=args.num_dirs,
)
for i in range(args.num_cpus)
]
打印看看cpu类型
for cpu in cpus:
print("yzzzzdebugcpus ", cpu.type, m5.curTick(),cpu.inj_rate,cpu.inj_vnet,cpu.num_dest)
可以看到cpu.type是 GarnetSyntheticTraffic.

GarnetSyntheticTraffic()函数来自 src/cpu/testers/garnet_synthetic_traffic/GarnetSyntheticTraffic.py
GarnetSyntheticTraffic.py 代码定义了很多 python 里可以 cpu.num_dest 之类调用的子类.
class GarnetSyntheticTraffic(ClockedObject):
type = "GarnetSyntheticTraffic"
cxx_header = (
"cpu/testers/garnet_synthetic_traffic/GarnetSyntheticTraffic.hh"
)
cxx_class = "gem5::GarnetSyntheticTraffic"
block_offset = Param.Int(6, "block offset in bits")
num_dest = Param.Int(1, "Number of Destinations")
memory_size = Param.Int(65536, "memory size")
sim_cycles = Param.Int(1000, "Number of simulation cycles")
num_packets_max = Param.Int(
-1,
"Max number of packets to send. \
Default is to keep sending till simulation ends",
)
single_sender = Param.Int(
-1,
"Send only from this node. \
By default every node sends",
)
single_dest = Param.Int(
-1,
"Send only to this dest. \
Default depends on traffic_type",
)
traffic_type = Param.String("uniform_random", "Traffic type")
inj_rate = Param.Float(0.1, "Packet injection rate")
inj_vnet = Param.Int(
-1,
"Vnet to inject in. \
0 and 1 are 1-flit, 2 is 5-flit. \
Default is to inject in all three vnets",
)
precision = Param.Int(
3,
"Number of digits of precision \
after decimal point",
)
response_limit = Param.Cycles(
5000000,
"Cycles before exiting \
due to lack of progress",
)
test = RequestPort("Port to the memory system to test")
system = Param.System(Parent.any, "System we belong to")
然后cpu变成了system的一部分,system = System(cpu=cpus, mem_ranges=[AddrRange(args.mem_size)])
注意,这里print("\nyzzzzdebugsystem ",system.mem_mode )还是atomic.
system变成了root的一部分 root = Root(full_system=False, system=system)
root.system.mem_mode = “timing” 这里额外设置为timing.
cpp代码 , cpu每一个tick执行一次 tick()
src/cpu/testers/garnet_synthetic_traffic/GarnetSyntheticTraffic.hh
// main simulation loop (one cycle)
void tick();
void
GarnetSyntheticTraffic::tick(){
...
if (senderEnable)
generatePkt();
}
void
GarnetSyntheticTraffic::generatePkt()
{
...
sendPkt(pkt);
}
void
GarnetSyntheticTraffic::sendPkt(PacketPtr pkt)
{
if (!cachePort.sendTimingReq(pkt)) {
retryPkt = pkt; // RubyPort will retry sending
}
std::cout<<"coutyzzzzzdebug "<<cachePort<<" "<<simCycles<<" "<<curTick()<< std::endl;
numPacketsSent++;
}
tick()变成了 cachePort.sendTimingReq(pkt).
cachePort.sendTimingReq(pkt) 到底是什么
RequestPort发送一次pkt
通过 cacheport->CpuPort->RequestPort, tick()函数调用 generatePkt() 函数,再调用sendTimingReq.
inline bool
RequestPort::sendTimingReq(PacketPtr pkt)
{
try {
addTrace(pkt);
bool succ = TimingRequestProtocol::sendReq(_responsePort, pkt);
//下面是我自己加的
//std::cout<<"coutdebugyzzzzRequestPort::sendTimingReq "<< succ<<" "<<curTick()<<std::endl;
if (!succ)
removeTrace(pkt);
return succ;
} catch (UnboundPortException) {
reportUnbound();
}
}
我加了一行输出,把这行代码解除注释后,运行的命令行如下:
./build/NULL/gem5.debug configs/example/garnet_synth_traffic.py \
--num-cpus=16 \
--num-dirs=16 \
--network=garnet \
--topology=Mesh_XY \
--mesh-rows=4 \
--sim-cycles=1000000 --inj-vnet=0 \
--synthetic=uniform_random \
--injectionrate=1 \
--single-sender-id=0
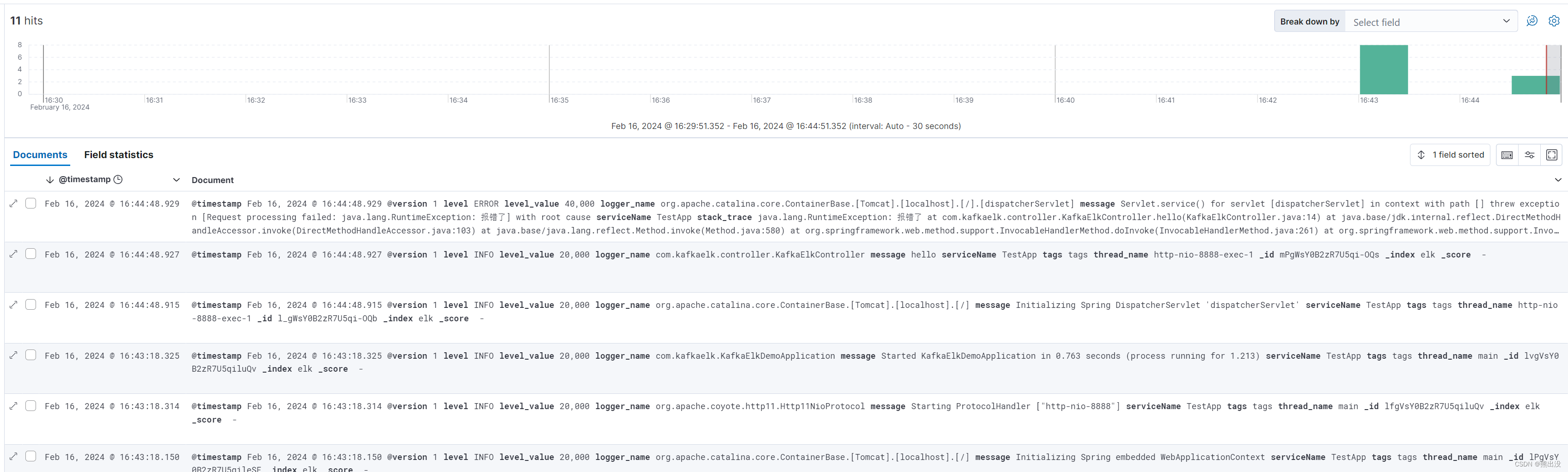
跑出来的结果是:
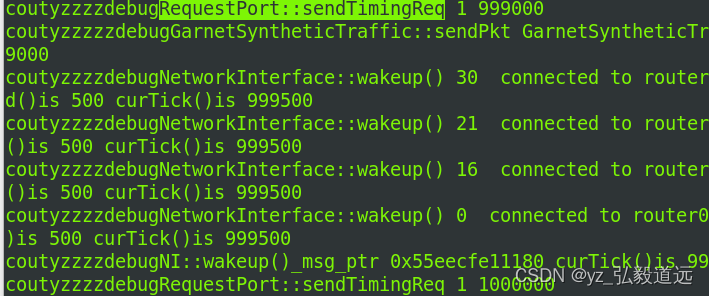
可以看到,每1000 个tick,这个requestport都会发送一个pkt,而且返回的succ是1.
纯虚函数 virtual bool recvTimingReq
下一步, sendReq变成了peer>recvTimingReq(pkt);
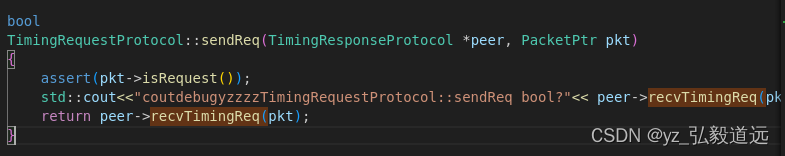
我们发现peer->recvTimingReq是一个复杂的部分,因为他是timing.hh里的纯虚函数,是不固定的,除非我们知道派生类是什么.
纯虚函数:
/**
* Receive a timing request from the peer.
*/
virtual bool recvTimingReq(PacketPtr pkt) = 0;
src/mem/ruby/system/RubyPort.cc 的 RubyPort::MemResponsePort::recvTimingReq(PacketPtr pkt)
找到了! 在下方代码加入打印代码,输出的结果验证了,调用的是 RubyPort::MemResponsePort::recvTimingReq(PacketPtr pkt).


其实用vscode搜 recvTimingReq(会有很多cc文件里有例化,大概二三十个吧,给每一个都加上,编译,运行,就可以知道了.
缺点就是这个方法有点笨.
RubyPort::MemResponsePort::recvTimingReq 其实是 submit rubyrequest
bool
RubyPort::MemResponsePort::recvTimingReq(PacketPtr pkt)
{ std::cout<<"debugyzzzwhichrecvTimingReq?src/mem/ruby/system/rubyport.cc/memresponseport"<<std::endl;
DPRINTF(RubyPort, "Timing request for address %#x on port %d\n",
pkt->getAddr(), id);
if (pkt->cacheResponding())
panic("RubyPort should never see request with the "
"cacheResponding flag set\n");
// ruby doesn't support cache maintenance operations at the
// moment, as a workaround, we respond right away
if (pkt->req->isCacheMaintenance()) {
warn_once("Cache maintenance operations are not supported in Ruby.\n");
pkt->makeResponse();
schedTimingResp(pkt, curTick());
std::cout<<"debugyzzzthisReqIs pkt->req->isCacheMaintenance()"<<std::endl;
return true;
}
// Check for pio requests and directly send them to the dedicated
// pio port.
if (pkt->cmd != MemCmd::MemSyncReq) {
if (!pkt->req->isMemMgmt() && !isPhysMemAddress(pkt)) {
assert(owner.memRequestPort.isConnected());
DPRINTF(RubyPort, "Request address %#x assumed to be a "
"pio address\n", pkt->getAddr());
// Save the port in the sender state object to be used later to
// route the response
pkt->pushSenderState(new SenderState(this));
// send next cycle
RubySystem *rs = owner.m_ruby_system;
owner.memRequestPort.schedTimingReq(pkt,
curTick() + rs->clockPeriod());
std::cout<<"debugyzzzthisReqIs pkt->cmd != MemCmd::MemSyncReq"<<std::endl;
return true;
}
}
// Save the port in the sender state object to be used later to
// route the response
pkt->pushSenderState(new SenderState(this));
// Submit the ruby request
RequestStatus requestStatus = owner.makeRequest(pkt);
// If the request successfully issued then we should return true.
// Otherwise, we need to tell the port to retry at a later point
// and return false.
if (requestStatus == RequestStatus_Issued) {
DPRINTF(RubyPort, "Request %s 0x%x issued\n", pkt->cmdString(),
pkt->getAddr());
std::cout<<"debugyzzzthisReqIs submit the ruby request"<<std::endl;
return true;
}
// pop off sender state as this request failed to issue
SenderState *ss = safe_cast<SenderState *>(pkt->popSenderState());
delete ss;
if (pkt->cmd != MemCmd::MemSyncReq) {
DPRINTF(RubyPort,
"Request %s for address %#x did not issue because %s\n",
pkt->cmdString(), pkt->getAddr(),
RequestStatus_to_string(requestStatus));
}
addToRetryList();
return false;
}

submit rubyrequest 的owener是 rubyport
这里的owener是 RubyPort.
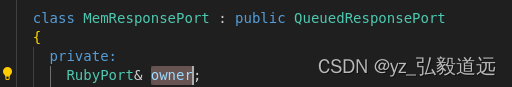
注意下图左边的两个竖线,仔细看,他是在RubyPort的public下面的. 也就是说,rubyPort下定义了class MemResponsePort,还定义了每个RubyPort都有 的makeRequest(). 这里给的虚函数,需要派生类来定义.

直觉告诉我们,sequencer 会有 makeRequest
src/mem/ruby/system/Sequencer.hh
RequestStatus makeRequest(PacketPtr pkt) override;
src/mem/ruby/system/Sequencer.cc
RequestStatus
Sequencer::makeRequest(PacketPtr pkt)
{
std::cout<<"debugyzzzz Sequencer::makeRequest "<<endl;
// HTM abort signals must be allowed to reach the Sequencer
// the same cycle they are issued. They cannot be retried.
if ((m_outstanding_count >= m_max_outstanding_requests) &&
!pkt->req->isHTMAbort()) {
return RequestStatus_BufferFull;
}
RubyRequestType primary_type = RubyRequestType_NULL;
RubyRequestType secondary_type = RubyRequestType_NULL;
if (pkt->isLLSC()) {
// LL/SC instructions need to be handled carefully by the cache
// coherence protocol to ensure they follow the proper semantics. In
// particular, by identifying the operations as atomic, the protocol
// should understand that migratory sharing optimizations should not
// be performed (i.e. a load between the LL and SC should not steal
// away exclusive permission).
//
// The following logic works correctly with the semantics
// of armV8 LDEX/STEX instructions.
if (pkt->isWrite()) {
DPRINTF(RubySequencer, "Issuing SC\n");
primary_type = RubyRequestType_Store_Conditional;
#if defined (PROTOCOL_MESI_Three_Level) || defined (PROTOCOL_MESI_Three_Level_HTM)
secondary_type = RubyRequestType_Store_Conditional;
#else
secondary_type = RubyRequestType_ST;
#endif
} else {
DPRINTF(RubySequencer, "Issuing LL\n");
assert(pkt->isRead());
primary_type = RubyRequestType_Load_Linked;
secondary_type = RubyRequestType_LD;
}
} else if (pkt->req->isLockedRMW()) {
//
// x86 locked instructions are translated to store cache coherence
// requests because these requests should always be treated as read
// exclusive operations and should leverage any migratory sharing
// optimization built into the protocol.
//
if (pkt->isWrite()) {
DPRINTF(RubySequencer, "Issuing Locked RMW Write\n");
primary_type = RubyRequestType_Locked_RMW_Write;
} else {
DPRINTF(RubySequencer, "Issuing Locked RMW Read\n");
assert(pkt->isRead());
primary_type = RubyRequestType_Locked_RMW_Read;
}
secondary_type = RubyRequestType_ST;
} else if (pkt->req->isTlbiCmd()) {
primary_type = secondary_type = tlbiCmdToRubyRequestType(pkt);
DPRINTF(RubySequencer, "Issuing TLBI\n");
} else {
//
// To support SwapReq, we need to check isWrite() first: a SwapReq
// should always be treated like a write, but since a SwapReq implies
// both isWrite() and isRead() are true, check isWrite() first here.
//
if (pkt->isWrite()) {
//
// Note: M5 packets do not differentiate ST from RMW_Write
//
primary_type = secondary_type = RubyRequestType_ST;
} else if (pkt->isRead()) {
// hardware transactional memory commands
if (pkt->req->isHTMCmd()) {
primary_type = secondary_type = htmCmdToRubyRequestType(pkt);
} else if (pkt->req->isInstFetch()) {
primary_type = secondary_type = RubyRequestType_IFETCH;
} else {
if (pkt->req->isReadModifyWrite()) {
primary_type = RubyRequestType_RMW_Read;
secondary_type = RubyRequestType_ST;
} else {
primary_type = secondary_type = RubyRequestType_LD;
}
}
} else if (pkt->isFlush()) {
primary_type = secondary_type = RubyRequestType_FLUSH;
} else {
panic("Unsupported ruby packet type\n");
}
}
// Check if the line is blocked for a Locked_RMW
if (!pkt->req->isMemMgmt() &&
m_controller->isBlocked(makeLineAddress(pkt->getAddr())) &&
(primary_type != RubyRequestType_Locked_RMW_Write)) {
// Return that this request's cache line address aliases with
// a prior request that locked the cache line. The request cannot
// proceed until the cache line is unlocked by a Locked_RMW_Write
return RequestStatus_Aliased;
}
RequestStatus status = insertRequest(pkt, primary_type, secondary_type);
// It is OK to receive RequestStatus_Aliased, it can be considered Issued
if (status != RequestStatus_Ready && status != RequestStatus_Aliased)
return status;
// non-aliased with any existing request in the request table, just issue
// to the cache
if (status != RequestStatus_Aliased)
issueRequest(pkt, secondary_type);
// TODO: issue hardware prefetches here
return RequestStatus_Issued;
}
打印验证了是sequencer发出的makerequest.

核心代码是 insertRequest 把request放入requsttable 和issueRequest 发出一个msg
RequestStatus status = insertRequest(pkt, primary_type, secondary_type);
// Insert the request in the request table. Return RequestStatus_Aliased
// if the entry was already present.
RequestStatus
Sequencer::insertRequest(PacketPtr pkt, RubyRequestType primary_type,
RubyRequestType secondary_type)
...
//下面是核心代码,把这个request插入到m_RequestTable里.
Addr line_addr = makeLineAddress(pkt->getAddr());
// Check if there is any outstanding request for the same cache line.
auto &seq_req_list = m_RequestTable[line_addr];
// Create a default entry
seq_req_list.emplace_back(pkt, primary_type,
secondary_type, curCycle());
...
src/mem/ruby/system/Sequencer.cc issueRequest
void
Sequencer::issueRequest(PacketPtr pkt, RubyRequestType secondary_type)
{
assert(pkt != NULL);
ContextID proc_id = pkt->req->hasContextId() ?
pkt->req->contextId() : InvalidContextID;
ContextID core_id = coreId();
// If valid, copy the pc to the ruby request
Addr pc = 0;
if (pkt->req->hasPC()) {
pc = pkt->req->getPC();
}
// check if the packet has data as for example prefetch and flush
// requests do not
std::shared_ptr<RubyRequest> msg;
if (pkt->req->isMemMgmt()) {
msg = std::make_shared<RubyRequest>(clockEdge(),
pc, secondary_type,
RubyAccessMode_Supervisor, pkt,
proc_id, core_id);
DPRINTFR(ProtocolTrace, "%15s %3s %10s%20s %6s>%-6s %s\n",
curTick(), m_version, "Seq", "Begin", "", "",
RubyRequestType_to_string(secondary_type));
if (pkt->req->isTlbiCmd()) {
msg->m_isTlbi = true;
switch (secondary_type) {
case RubyRequestType_TLBI_EXT_SYNC_COMP:
msg->m_tlbiTransactionUid = pkt->req->getExtraData();
break;
case RubyRequestType_TLBI:
case RubyRequestType_TLBI_SYNC:
msg->m_tlbiTransactionUid = \
getCurrentUnaddressedTransactionID();
break;
default:
panic("Unexpected TLBI RubyRequestType");
}
DPRINTF(RubySequencer, "Issuing TLBI %016x\n",
msg->m_tlbiTransactionUid);
}
} else {
msg = std::make_shared<RubyRequest>(clockEdge(), pkt->getAddr(),
pkt->getSize(), pc, secondary_type,
RubyAccessMode_Supervisor, pkt,
PrefetchBit_No, proc_id, core_id);
DPRINTFR(ProtocolTrace, "%15s %3s %10s%20s %6s>%-6s %#x %s\n",
curTick(), m_version, "Seq", "Begin", "", "",
printAddress(msg->getPhysicalAddress()),
RubyRequestType_to_string(secondary_type));
}
// hardware transactional memory
// If the request originates in a transaction,
// then mark the Ruby message as such.
if (pkt->isHtmTransactional()) {
msg->m_htmFromTransaction = true;
msg->m_htmTransactionUid = pkt->getHtmTransactionUid();
}
Tick latency = cyclesToTicks(
m_controller->mandatoryQueueLatency(secondary_type));
assert(latency > 0);
assert(m_mandatory_q_ptr != NULL);
m_mandatory_q_ptr->enqueue(msg, clockEdge(), latency);
}
issueRequst的关键是 m_mandatory_q_ptr->enqueue(msg, clockEdge(), latency);.
m_mandatory_q_ptr 是在父类 src/mem/ruby/system/RubyPort.hh 中定义的 MessageBuffer* m_mandatory_q_ptr;
父类 src/mem/ruby/system/RubyPort.cc 中 RubyPort::init()
m_mandatory_q_ptr = m_controller->getMandatoryQueue();
就这样,自己的sequencer的request pkt,变成msg进入了rubyport 自己的 m_mandatory_q_ptr, 并且与m_controller->getMandatoryQueue()画上了等号.
因为我们查看 m_mandatory_q_ptr的操作很少,我们下面看怎么对msg操作的时候,需要看 getMandatoryQueue()
msg 如何从mandatoryq进入NetworkInterface暂定.
这两个代码也许是线索. src/mem/slicc/symbols/StateMachine.py 中
MessageBuffer*
$c_ident::getMandatoryQueue() const
{
return $mq_ident;
}
mq_ident = "NULL"
for port in self.in_ports:
if port.code.find("mandatoryQueue_ptr") >= 0:
mq_ident = "m_mandatoryQueue_ptr"
NI将msg变成flit
核心是 if (flitisizeMessage(msg_ptr, vnet)) ,会把msg变成flit,然后在NoC了里传递.
void
NetworkInterface::wakeup()
{
std::ostringstream oss;
for (auto &oPort: outPorts) {
oss << oPort->routerID() << "[" << oPort->printVnets() << "] ";
}
DPRINTF(RubyNetwork, "Network Interface %d connected to router:%s "
"woke up. Period: %ld\n", m_id, oss.str(), clockPeriod());
std::cout<<"coutdebugyzzzz "<<"NetworkInterface::wakeup() "<<m_id<<" connected to router" <<oss.str() <<" clockPeriod()is "<<clockPeriod()<<" curTick()is "<<curTick()<<std::endl;
assert(curTick() == clockEdge());
MsgPtr msg_ptr;
Tick curTime = clockEdge();
// Checking for messages coming from the protocol
// can pick up a message/cycle for each virtual net
for (int vnet = 0; vnet < inNode_ptr.size(); ++vnet) {
MessageBuffer *b = inNode_ptr[vnet];
if (b == nullptr) {
continue;
}
if (b->isReady(curTime)) { // Is there a message waiting
msg_ptr = b->peekMsgPtr();
std::cout<<"coutdebugyzzzz"<<"NI::wakeup()_msg_ptr "<<msg_ptr.get()<<" curTick()is "<<curTick()<<std::endl;
if (flitisizeMessage(msg_ptr, vnet)) {
b->dequeue(curTime);
}
}
}
小结
这个博客总结了GEM5里,一个PYTHON文件如何生成pkt,这个pkt如何变成msg的. 以及一个msg如何变成flit的. msg如何从sequencer生成,到被Networkinterface操作有待下一篇完善细节…
下面别看,只是草稿
下面别看,只是草稿
下面别看,只是草稿
下面别看,只是草稿
附录
TimingRequestProtocol 和 TimingResponseProtocol的相应
RequestPort::sendTimingReq 方法尝试通过 TimingRequestProtocol 发送数据包,并处理可能出现的异常。TimingRequestProtocol::sendReq 方法则负责确保请求的有效性,并将请求转发给相应的响应协议(TimingResponseProtocol)进行处理。
流程和继承关系:
consumer.hh 定义了 virtual void wakeup() = 0;
src/mem/ruby/network/garnet/Router.hh 定义了 class Router : public BasicRouter, public Consumer继承了 父类 BasicRouter和 Consumer.
src/mem/ruby/network/garnet/GarnetNetwork.cc (注意,不是.hh) 引用了router.hh #include “mem/ruby/network/garnet/Router.hh”.
consumer.hh
表明 wakeup 是一个必须在派生类中实现的接口函数。
= 0 语法: 这个部分将 wakeup 函数声明为纯虚拟(pure virtual)函数。在 C++ 中,纯虚拟函数是一种特殊类型的虚拟函数,它在基类中没有具体的实现,并且要求任何非抽象的派生类必须提供该函数的实现。
flitize msg
分配vc
首先是要找空闲的vc,有一个封装好的函数会返回:
// Looking for a free output vc
int
NetworkInterface::calculateVC(int vnet)
{
for (int i = 0; i < m_vc_per_vnet; i++) {
int delta = m_vc_allocator[vnet];
m_vc_allocator[vnet]++;
if (m_vc_allocator[vnet] == m_vc_per_vnet)
m_vc_allocator[vnet] = 0;
if (outVcState[(vnet*m_vc_per_vnet) + delta].isInState(
IDLE_, curTick())) {
vc_busy_counter[vnet] = 0;
return ((vnet*m_vc_per_vnet) + delta);
}
}
vc_busy_counter[vnet] += 1;
panic_if(vc_busy_counter[vnet] > m_deadlock_threshold,
"%s: Possible network deadlock in vnet: %d at time: %llu \n",
name(), vnet, curTick());
return -1;
}
下面是解读:
函数签名:
int NetworkInterface::calculateVC(int vnet): 这个函数属于 NetworkInterface 类,并返回一个整型值。它接受一个整型参数 vnet,通常代表虚拟网络的标识。
遍历虚拟通道:
for 循环遍历与给定虚拟网络 (vnet) 相关的所有虚拟通道。m_vc_per_vnet 是每个虚拟网络的虚拟通道数。
虚拟通道分配:
循环中的 delta 变量根据 m_vc_allocator[vnet] 的值设置,表示当前虚拟通道的索引偏移。
m_vc_allocator[vnet]++ 更新虚拟通道分配器的值,用于下一次调用此函数时选择不同的虚拟通道。
如果 m_vc_allocator[vnet] 达到 m_vc_per_vnet 的值,它会重置为 0,以循环方式遍历所有虚拟通道。
检查虚拟通道状态:
使用 outVcState[(vnet*m_vc_per_vnet) + delta].isInState(IDLE_, curTick()) 检查当前虚拟通道是否处于空闲(IDLE)状态。如果是空闲状态,函数返回该虚拟通道的索引。
虚拟通道忙碌计数器:
如果所有虚拟通道都不处于空闲状态,vc_busy_counter[vnet] 加一,表示此次调用没有找到空闲的虚拟通道。
如果 vc_busy_counter[vnet] 超过 m_deadlock_threshold 阈值,函数会触发 panic(意味着可能出现网络死锁),并输出错误信息。
返回值:
如果找到空闲的虚拟通道,则返回该通道的索引。
如果没有找到空闲的虚拟通道,则返回 -1,表示当前没有可用的虚拟通道。