并查集
- 1.并查集原理
- 2.并查集实现
- 3.并查集应用
- 4.并查集的路径压缩
1.并查集原理
在一些应用问题中,需要将n个不同的元素划分成一些不相交的集合。开始时,每个元素自成一个单元素集合,然后按一定的规律将归于同一组元素的集合合并。在此过程中要反复用到查询某一个元素归属于那个集合的运算。适合于描述这类问题的抽象数据类型称为并查集(union-findset)。
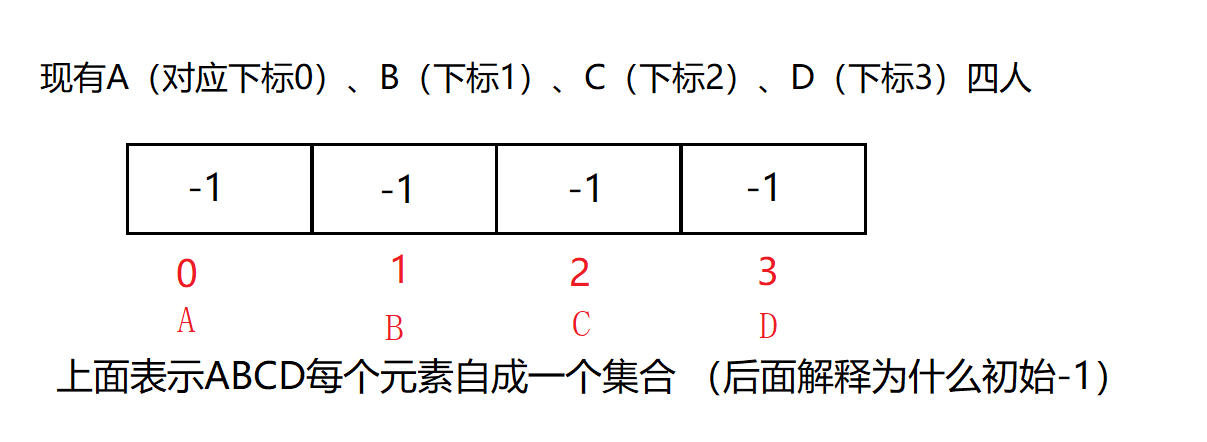
如何合并两个集合:
- 先找到两个集合的根部(负数为根部)。
- 以合并AB为例子,假设让B合并到A,A减去B的值,即变成-2;然后让B的值变成A的下标0。
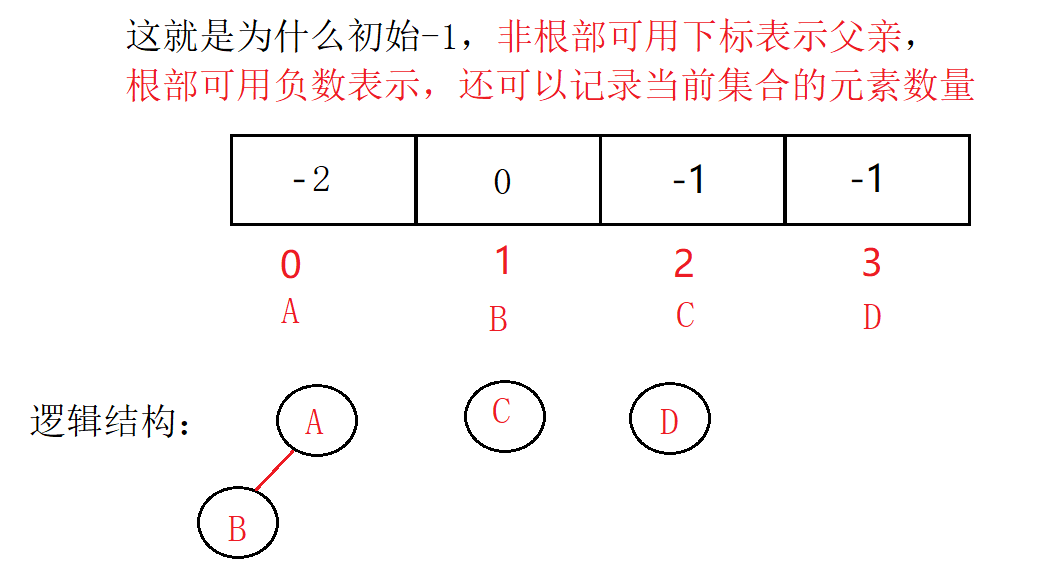
观察合并过程,可以得出以下结论:
- 数组的下标对应集合中元素的编号
- 数组中如果为负数,负号代表根,数字代表该集合中元素个数
- 数组中如果为非负数,代表该元素双亲在数组中的下标
2.并查集实现
并查集一般可以解决以下问题:
- 查找元素属于哪个集合
沿着数组表示树形关系以上一直找到根(即:树中中元素为负数的位置)
int FindRoot(int x) //找根的下标位置
{
int par = x;
while (_ufs[par] >= 0) //如果当前大于0,说明未到根部,更新到父亲下标
{
par = _ufs[par];
}
return par;
}
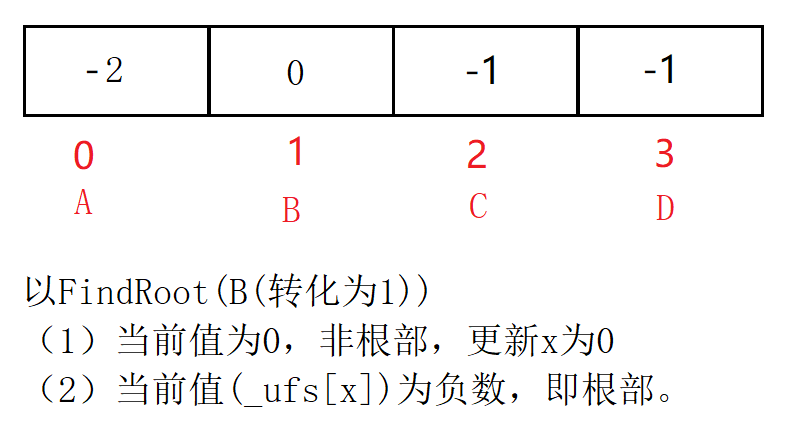
- 查看两个元素是否属于同一个集合
沿着数组表示的树形关系往上一直找到树的根,如果根相同表明在同一个集合,否则不在
bool InSet(int x1, int x2)
{
if (FindRoot(x1) == FindRoot(x2))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
- 将两个集合归并成一个集合
前面讲过,不赘述。
void Union(int x1, int x2) //联合这两棵树,默认x2并到x1
{
int root1 = FindRoot(x1);
int root2 = FindRoot(x2);
if (abs(_ufs[root1]) < abs(_ufs[root2])) //让小的一方并到大的一方就这样
swap(root1, root2);
if (root1 != root2) //本来不是同一个树(集合)
{
_ufs[root1] += _ufs[root2];
_ufs[root2] = root1;
}
}
- 集合的个数
遍历数组,数组中元素为负数的个数即为集合的个数。
int SetSize()const //返回树的个数
{
int size = 0;
for (auto e : _ufs)
if (e < 0) size++;
return size;
}
完整实现:
class UnionFindSet {
public:
UnionFindSet(size_t size) //一开始全都设置为-1
:_ufs(size, -1)
{}
void Union(int x1, int x2) //联合这两棵树,默认x2并到x1
{
int root1 = FindRoot(x1);
int root2 = FindRoot(x2);
if (abs(_ufs[root1]) < abs(_ufs[root2])) //让小的一方并到大的一方就这样
swap(root1, root2);
if (root1 != root2) //本来不是同一个树(集合)
{
_ufs[root1] += _ufs[root2];
_ufs[root2] = root1;
}
}
int FindRoot(int x) //找根的下标位置
{
int par = x;
while (_ufs[par] >= 0)
{
par = _ufs[par];
}
return par;
}
bool InSet(int x1, int x2)
{
if (FindRoot(x1) == FindRoot(x2))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
int SetSize()const //返回树的个数
{
int size = 0;
for (auto e : _ufs)
if (e < 0) size++;
return size;
}
private:
vector<int> _ufs;
};
3.并查集应用
省份数量
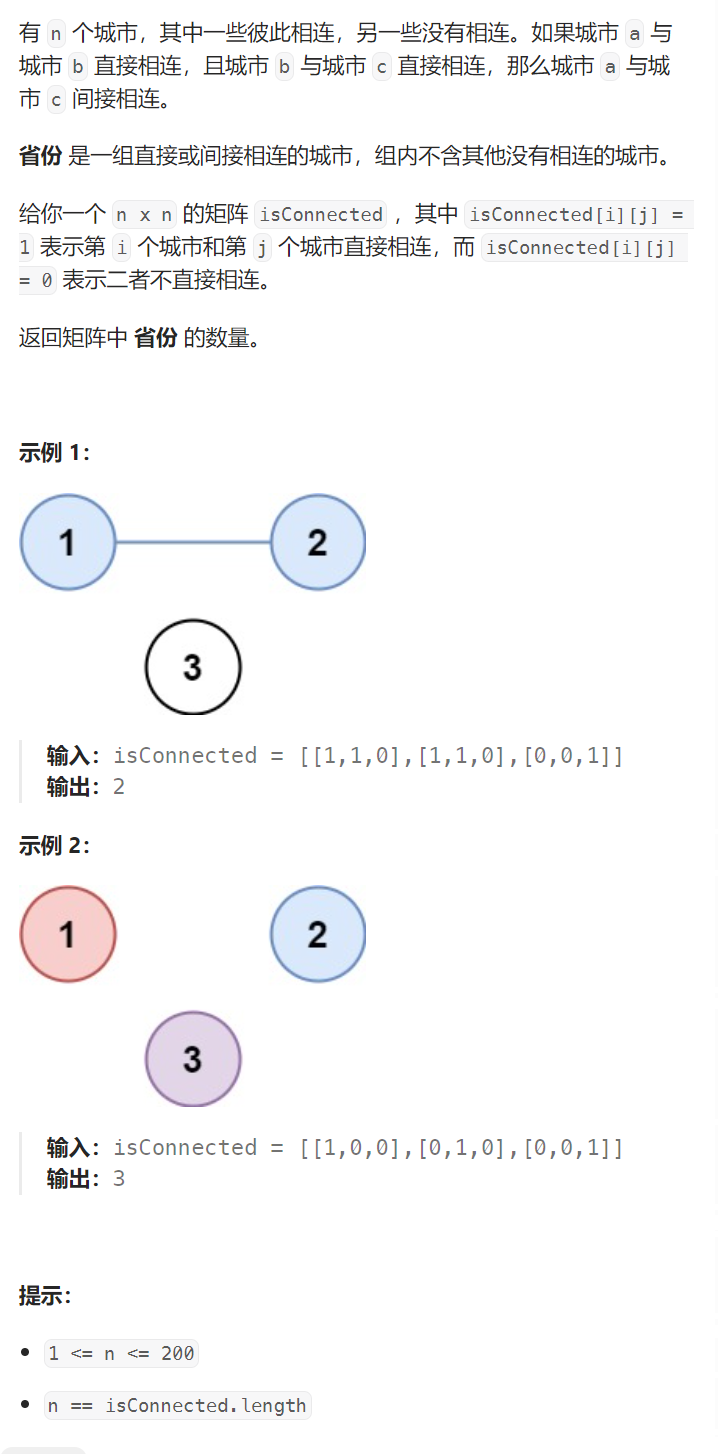
//讲解:并查集,一个城市就是一个集合
//(1)初始每个城市自成一省
//(2)如果isConnected[i][j]为1,说明i城市和j城市在一个省,合并
//(3)合并完成后遍历数组,负数有几个集合(省份)就有几个
//实际并不一定要实现完整的功能,一般需要的功能是找根部函数
class Solution {
public:
int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected) {
vector<int> ufs(isConnected.size(), -1);
auto FindRoot = [&ufs](int x){ //找根函数
while(ufs[x] >= 0) //没到根
{
x = ufs[x];
}
return x;
};
for(int i = 0; i < isConnected.size(); i++)
for(int j = 0; j < isConnected[i].size(); j++)
if(isConnected[i][j] == 1) //有关系
{
int root1 = FindRoot(i), root2 = FindRoot(j);
if(root1 != root2) //不是同个集合
{
ufs[root1] += ufs[root2]; //这一步本题没必要其实
ufs[root2] = root1;
}
}
int ret = 0;
for(auto e : ufs) if(e < 0) ret++;
return ret;
}
};
等式方程的可满足性

//思路:并查集,先遍历一次,建立起集合联系,如果a!=b,但a与b在一个集合中,就是相悖的,返回false
// 本题只有小写字母,可用0对应a,1对应b,依次类推
class Solution {
public:
bool equationsPossible(const vector<string>& equations) {
vector<int> ufs(26, -1);
auto FindRoot = [&ufs](int x) {
while (ufs[x] >= 0)
{
x = ufs[x];
}
return x;
};
//先遍历一次,建立并查集
for (auto str : equations)
if (str[1] == '=')
{
int root1 = FindRoot(str[0] - 'a'), root2 = FindRoot(str[3] - 'a');
if (root1 != root2)
{
ufs[root1] += ufs[root2]; //这一步没必要
ufs[root2] = root1;
}
}
//再遍历一次,如果在一个集合中就返回false;
for (auto str : equations)
if (str[1] == '!')
{
int root1 = FindRoot(str[0] - 'a'), root2 = FindRoot(str[3] - 'a');
if (root1 == root2)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
4.并查集的路径压缩
并查集一般无需压缩路径,但对数据量大的情况想加快效率就需要压缩路径。
原理:
- 可在查询时压缩,比如6->5->4->3(根部),先找到根部3。
- 把6记录下来,一路向上直到根,即让6、5、4直接做3的孩子,从而完成压缩。
int FindRoot(int x) //找根的下标位置
{
int root = x;
while (_ufs[root] >= 0)
{
root = _ufs[root];
}
//压缩路径
while (_ufs[x] >= 0)
{
int par = _ufs[x]; //先记录父亲下标
_ufs[x] = root;
x = par;
}
return root;
}





![洛谷: P1308 [NOIP2011 普及组] 统计单词数](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/1698be2134e449cdac155a8c6e15107c.png)

![[2024]常用的pip指令](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/b3c1f42d88ef4707be65d792d6994465.png#pic_center)