这是一个基于Tasmota的设备、用MQTT协议来通信控制的安卓应用程序。支持ON/OFF命令插座和基本的RGB LED控制。
源码点击此处
只需要关注SmartController-main\app\src的代码

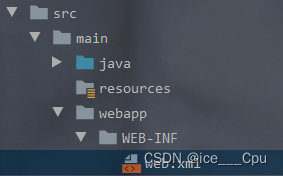
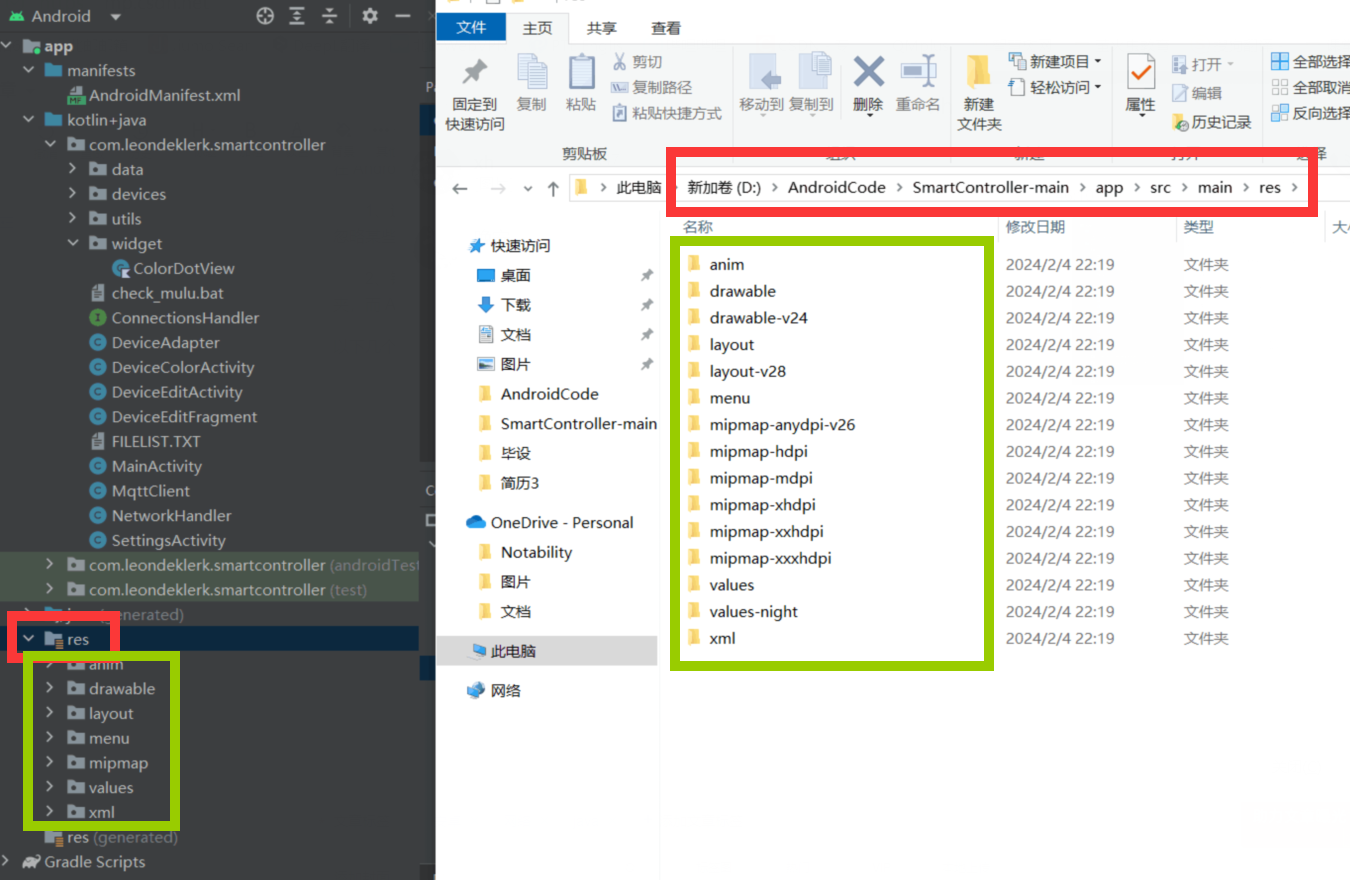
项目解压之后如图
只需要关注“app”文件夹里的东西即可,“gradle”是配置文件,和Android studio的安装环境有关,后续打算出一个讲这部分的
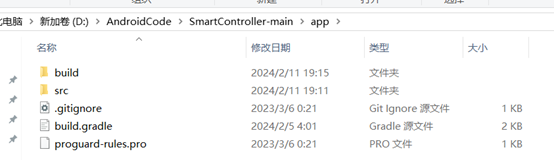
只需要关注“src”文件夹里的东西即可,“build”是 Android 应用构建过程中生成的临时文件和输出,主要涉及编译过程中生成的中间文件以及用于加速编译的临时数据,不需要修改
手动更改这些文件可能会导致构建错误或不稳定的行为。通常,Android Studio和构建工具会负责处理这些生成的文件,你只需专注于修改 D:\AndroidCode\SmartController-main\app\src 目录下的源代码和资源文件,以及适当地修改 build.gradle 等配置文件。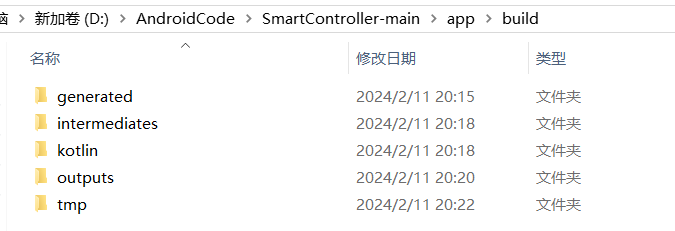

Android studio项目中看到的文件夹
都来自于src文件,src 是 "source"(源代码)的缩写,用于存放应用程序的源代码
为什么在 Android Studio 中打开文件夹和实际文件系统中的文件夹看起来不一致:
1、过滤或忽略文件: Android Studio 可能会根据项目设置或 IDE 配置文件中的规则来过滤或忽略某些文件或文件类型,例如,临时文件、构建输出等。
2、链接文件或文件夹: 在文件系统中,可能存在符号链接或快捷方式指向其他文件或文件夹,而 Android Studio 可能会展示这些链接文件或文件夹的实际内容。
以下几个图示可以知道Android Studio里的项目的实际文件路径
AndroidManifest.xml

com.leondeklerk.smartcontroller

java代码+少数kotlin代码
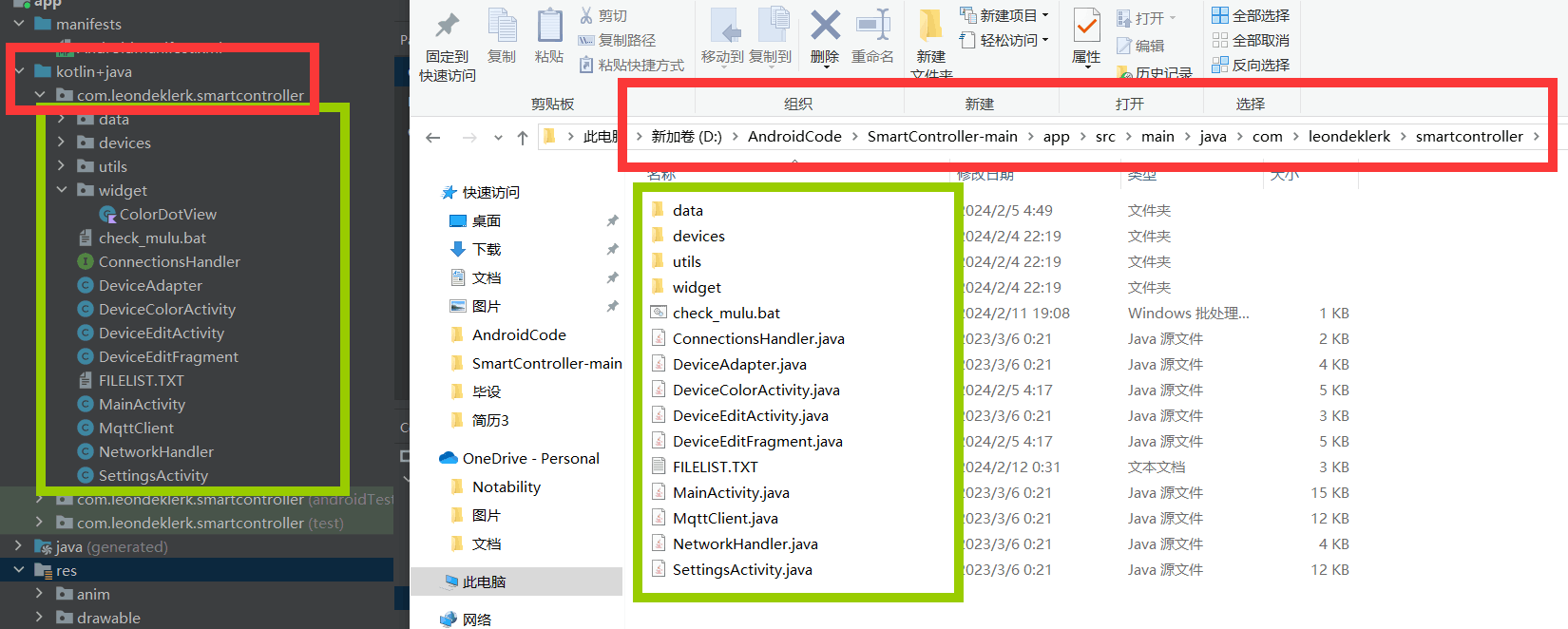
xml代码
接下来就是针对上述4个模块的代码进行详细解释
AndroidManifest.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-- 定义 Android 清单文件 -->
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<!-- 请求访问网络状态的权限 -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<!-- 请求访问互联网的权限 -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<!-- 定义应用程序的配置信息 -->
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/MyTheme.DayNight"
android:usesCleartextTraffic="true">
<!-- 定义设置界面的活动 -->
<activity
android:name=".SettingsActivity"
android:label="@string/title_activity_settings" />
<!-- 定义主界面的活动 -->
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<!-- 设置为主活动,应用启动时打开该活动 -->
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<!-- 定义设备编辑界面的活动 -->
<activity
android:name=".DeviceEditActivity"
android:parentActivityName=".MainActivity"
android:windowSoftInputMode="adjustPan" />
<!-- 定义设备颜色选择界面的活动 -->
<activity
android:name=".DeviceColorActivity"
android:parentActivityName=".MainActivity" />
</application>
</manifest>
com.leondeklerk.smartcontroller
"com.leondeklerk.smartcontroller" 是一个应用程序的包名(Package Name),根据通常的Android应用命名规范。应用程序的包名是在开发应用时定义的唯一标识符,通常采用反转的域名形式(例如 com.example.myapp)。

其在实际文件夹中就是一个连续子文件夹

主要项目代码都在“main”里,另外两个只是双端简单的测试代码
“androidTest”是一个基本的Instrumented测试类,用于在Android设备上执行测试
/**
* Instrumented test, which will execute on an Android device.
* 仪器化测试,将在 Android 设备上执行。
*
* @see <a href="http://d.android.com/tools/testing">Testing documentation</a>
* 参见测试文档链接
*/
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4.class)
// 使用 AndroidJUnit4 运行器来执行测试
public class ExampleInstrumentedTest {
@Test
// 注解标识该方法是一个测试方法
public void useAppContext() {
// Context of the app under test.
// 获取被测试应用的上下文对象
Context appContext = InstrumentationRegistry.getInstrumentation().getTargetContext();
// 断言被测试应用的包名是否符合预期值
assertEquals("com.leondeklerk.smartcontroller", appContext.getPackageName());
}
}
“test”是一个基本的JUnit Jupiter(JUnit 5)本地单元测试类,用于在开发机器(主机)上执行测试
/**
* Example local unit test, which will execute on the development machine (host).
* 示例本地单元测试,将在开发机器(主机)上执行。
*
* @see <a href="http://d.android.com/tools/testing">Testing documentation</a>
* 参见测试文档链接
*/
public class ExampleUnitTest {
@Test
// 注解标识该方法是一个测试方法
public void addition_isCorrect() {
// 使用断言验证加法是否正确
Assertions.assertEquals(4, 2 + 2);
}
}
“main”里的java代码+少数kotlin代码

data 目录:
Command.java - 包含与设备通信的指令相关的类。
DeviceData.java - 包含设备数据的模型类。
Entry.java - 用于表示数据项的类。
devices 目录:
RGBLedController.java - 一个 RGB LED 控制器设备的实现类。
SmartDevice.java - 通用智能设备的实现类。
utils 目录:
DeviceStorageUtils.java - 包含用于设备数据存储的工具方法。
DiffUtilCallback.java - 是用于处理列表数据变更的回调类。
TextInputUtils.java - 包含处理文本输入的实用方法。
widget 目录:
ColorDotView.kt - 是一个用 Kotlin 编写的自定义颜色点视图,可能用于界面显示。(就这里用了kotlin)
其它:
ConnectionsHandler.java - 处理与设备的连接和通信的类。
DeviceAdapter.java - 设备列表的适配器类,用于在界面上显示设备列表。
DeviceColorActivity.java - 设备颜色控制的活动类。
DeviceEditActivity.java - 设备编辑界面的活动类。
DeviceEditFragment.java - 设备编辑界面的片段类。
MainActivity.java - 应用的主活动类。
MqttClient.java - MQTT(Message Queuing Telemetry Transport)客户端类,用于消息传递。
NetworkHandler.java - 处理网络连接的类。
SettingsActivity.java - 应用设置界面的活动类。
data 目录
Command.java
/**
* A class that represents a new MQTT command. Contains a topic and message.
* 表示一个新的MQTT命令的类。包含主题和消息。
*/
public class Command {
private String topic; // 存储消息将要发布的主题
private String message; // 存储将要发布的消息内容
/**
* Class constructor.
* 类的构造方法。
*
* @param topic the topic that the message will be published on.
* 消息将要发布的主题。
* @param message the message that will be published.
* 将要发布的消息。
*/
public Command(String topic, String message) {
this.topic = topic;
this.message = message;
}
// 获取消息将要发布的主题
public String getTopic() {
return topic;
}
// 设置消息将要发布的主题
public void setTopic(String topic) {
this.topic = topic;
}
// 获取将要发布的消息内容
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
// 设置将要发布的消息内容
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
}
DeviceData.java
/**
* 表示与设备相关的所有数据的类。每个设备包含一组数据,这些数据在所有SmartDevices之间共享。此类扩展了BaseObservable以适应与UI的数据绑定。
*/
public class DeviceData extends BaseObservable {
private final int id; // 设备的唯一标识符
private String name; // 设备的名称
private String status; // 设备的状态
private boolean enabled; // 设备是否启用
private final String type; // 设备的类型
private String topic; // 设备将要监听的主题
/**
* Default constructor
* 默认构造方法
*
* @param id the id of this device
* 此设备的唯一标识符
* @param name the name of the device
* 设备的名称
* @param status the status of the device
* 设备的状态
* @param enabled indicates if the device is enabled or not
* 表示设备是否启用
* @param type the type of the device
* 设备的类型
* @param topic the topic this device will listen to
* 此设备将要监听的主题
*/
public DeviceData(int id, String name, String status, boolean enabled, String type, String topic) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.status = status;
this.enabled = enabled;
this.type = type;
this.topic = topic;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
DeviceData that = (DeviceData) o;
return id == that.id
&& enabled == that.enabled
&& Objects.equals(topic, that.topic)
&& Objects.equals(name, that.name)
&& Objects.equals(status, that.status);
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* Set the name of the device
* 设置设备的名称
*
* @param name the new name of the device
* 设备的新名称
* @return this
*/
public DeviceData setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
notifyPropertyChanged(BR._all);
return this;
}
public String getTopic() {
return topic;
}
/**
* Set the topic of this device.
* 设置此设备的主题。
*
* @param topic the new topic.
* 新的主题
* @return this instance.
*/
public DeviceData setTopic(String topic) {
this.topic = topic;
notifyPropertyChanged(BR._all);
return this;
}
public String getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(String status) {
this.status = status;
}
public boolean isEnabled() {
return enabled;
}
public void setEnabled(boolean enabled) {
this.enabled = enabled;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
}
Entry.java
/**
* 表示设备存储数据结构中条目的类。包含一个 id 和设备的引用。id 表示设备在列表中的位置,而设备是实际存储的设备。
*/
public class Entry {
private final int id; // 设备在列表(例如MainActivity RecyclerView)中的位置
private final SmartDevice device; // 实际存储的设备引用
/**
* Default constructor
* 默认构造方法
*
* @param id the id of the device in the list (MainActivity RecyclerView)
* 设备在列表中(例如MainActivity RecyclerView)的位置
* @param device the device itself.
* 设备本身
*/
public Entry(int id, SmartDevice device) {
this.id = id;
this.device = device;
}
// 获取设备在列表中的位置
public int getId() {
return id;
}
// 获取设备引用
public SmartDevice getDevice() {
return device;
}
}
devices 目录
RGBLedController.java
// 表示这是一个LED控制器的SmartDevice的特定实例
public class RGBLedController extends SmartDevice {
/**
* 默认构造方法
*
* @param data the data that represents this device.
* 表示此设备的数据。
*/
public RGBLedController(DeviceData data) {
super(data);
}
/**
* 获取用于检查状态的命令。
*
* @return the color status Command
*/
public Command getColor() {
return new Command(super.getTopic("Color"), "?");
}
/**
* 设置设备的颜色。
*
* @param red the value of red.
* 红色通道的值。
* @param green the value of green.
* 绿色通道的值。
* @param blue the value of blue.
* 蓝色通道的值。
* @return a new command that will be published on the MQTT client.
* 将在MQTT客户端上发布的新命令。
*/
@SuppressLint("DefaultLocale")
public Command setColor(int red, int green, int blue) {
return new Command(super.getTopic("Color2"), String.format("%d,%d,%d", red, green, blue));
}
}
SmartDevice.java
/**
* SmartDevice是所有支持的设备的基类。这包括封装基本数据,如id、名称、IP和可选凭证。该类还提供了一些基本命令,如检查电源状态、打开或关闭电源。其他设备可以从这个类扩展,以提供额外的功能,如LED的颜色控制。
*/
public class SmartDevice {
private final DeviceData data; // 设备的基本数据
/**
* Default constructor to create a new SmartDevice, based on some given device data.
* 根据给定的设备数据创建一个新的SmartDevice的默认构造方法。
*
* @param data the data for this device.
* 此设备的数据。
*/
public SmartDevice(DeviceData data) {
this.data = data;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
return this.getData().equals(((SmartDevice) o).getData());
}
/**
* 根据设备的数据和命令的类型获取要发布的主题。
*
* @param command the command that the device needs to execute.
* 设备需要执行的命令。
* @return the topic formatted with the device data topic.
* 使用设备数据主题格式化的主题。
*/
String getTopic(String command) {
return "cmnd/" + data.getTopic() + "/" + command;
}
/**
* 获取用于检查状态的命令。
*
* @return the power status Command
*/
public Command getPowerStatus() {
return new Command(getTopic("POWER"), "?");
}
/**
* 获取打开或关闭电源的命令。
*
* @param on boolean indicating whether or not to turn the power the device on or off.
* 布尔值,表示是否打开或关闭设备电源。
* @return the command to turn the device on or off.
* 打开或关闭设备的命令。
*/
public Command setPower(boolean on) {
return new Command(getTopic("POWER"), on ? "ON" : "OFF");
}
/**
* 克隆一个设备并返回具有另一个内存地址的精确副本。
*
* @param other the device to clone.
* 要克隆的设备。
* @return a cloned instance of the other device.
* 另一个设备的克隆实例。
*/
public static SmartDevice clone(SmartDevice other) {
DeviceData otherData = other.getData();
return new SmartDevice(
new DeviceData(
otherData.getId(),
otherData.getName(),
otherData.getStatus(),
otherData.isEnabled(),
otherData.getType(),
otherData.getTopic()));
}
public DeviceData getData() {
return data;
}
}
utils 目录
DeviceStorageUtils.java
// 一个用于处理在应用程序的SharedPreferences中存储和检索设备的类
public class DeviceStorageUtils {
private SharedPreferences preferences; // SharedPreferences对象
private Context context; // 上下文对象
/**
* Basic constructor for the DeviceStorageUtils class.
* DeviceStorageUtils类的基本构造方法。
*
* @param preferences the preferences to store and retrieve in/from.
* 用于存储和检索的SharedPreferences对象
* @param context the context of the application.
* 应用程序的上下文对象
*/
public DeviceStorageUtils(SharedPreferences preferences, Context context) {
this.preferences = preferences;
this.context = context;
}
/**
* 从SharedPreferences中的String使用GSON库检索所有SmartDevices的方法。
*
* @return a list of retrieved SmartDevices.
* 检索到的SmartDevices列表。
*/
public ArrayList<SmartDevice> getDevices() {
String json = preferences.getString("deviceList", null);
if (json != null) {
Gson gson = new Gson();
// Convert back to a Java Object
Type type = new TypeToken<ArrayList<SmartDevice>>() {}.getType();
return gson.fromJson(json, type);
} else {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
}
/**
* A method that converts a list of SmartDevices to a String and stores it in the
* SharedPreferences specified by the class Object.
* 将SmartDevices列表转换为String并将其存储在由类对象指定的SharedPreferences中的方法。
*
* @param devices the list of devices to store.
* 要存储的设备列表。
*/
public void storeDevices(ArrayList<SmartDevice> devices) {
// Set the status to unknown (prevent the status from being stored)
// 将状态设置为未知(防止状态被存储)
for(SmartDevice device : devices) {
device.getData().setStatus(context.getString(R.string.status_unknown));
}
Editor prefsEditor = preferences.edit();
Gson gson = new Gson();
// Convert the object to a String
String json = gson.toJson(devices);
// Store the string
prefsEditor.putString("deviceList", json);
prefsEditor.apply();
}
}
DiffUtilCallback.java
/**
* 一个处理两个ArrayList之间差异计算的类。用于更新RecyclerView及其相应的适配器。
*/
public class DiffUtilCallback extends Callback {
private ArrayList<SmartDevice> oldList; // 旧列表
private ArrayList<SmartDevice> newList; // 新列表
/**
* Default constructor, taking in the two lists that need to be compared.
* 默认构造方法,接收需要进行比较的两个列表。
*
* @param oldList list one.
* 列表一
* @param newList list two.
* 列表二
*/
public DiffUtilCallback(ArrayList<SmartDevice> oldList, ArrayList<SmartDevice> newList) {
this.oldList = oldList;
this.newList = newList;
}
@Override
public int getOldListSize() {
return oldList.size();
}
@Override
public int getNewListSize() {
return newList.size();
}
@Override
public boolean areItemsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) {
return oldList.get(oldItemPosition).equals(newList.get(newItemPosition));
}
@Override
public boolean areContentsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) {
return oldList.get(oldItemPosition).getData().equals(newList.get(newItemPosition).getData());
}
}
TextInputUtils.java
/**
* 一组用于与TextInputLayouts交互的实用方法的集合。功能从设置监听器到检查错误和比较值等。
*/
public class TextInputUtils {
public static final String DEV_TYPE_DEF = "DEFAULT_TYPE";
public static final String DEV_TYPE_RGB = "RGB_CONTROLLER_TYPE";
// An input type that is a field with a max length
public static final String DEFAULT_TYPE = "DEFAULT_TYPE";
/**
* 检查布局列表中是否有任何错误,还检查是否为空的布局。
*
* @param layouts the ArrayList of TextInputLayouts to check.
* @return true if there are errors, false if not.
*/
public static boolean hasErrors(ArrayList<TextInputLayout> layouts) {
// Check if one of the layouts is empty
isEmpty(layouts);
for (TextInputLayout layout : layouts) {
if (layout.getError() != null) {
// If a layout has an error, return true and request the focus on that one.
layout.requestFocus();
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 检查TextInputLayouts的ArrayList是否有任何空字段。如果有一个字段为空,将设置正确的错误。
*
* @param layouts the list of layouts.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("ConstantConditions")
private static void isEmpty(ArrayList<TextInputLayout> layouts) {
for (TextInputLayout layout : layouts) {
// Get the text and resources from the layout
String text = layout.getEditText().getText().toString();
Resources resources = layout.getResources();
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(text)) {
// If empty, set an error
layout.setError(resources.getString(R.string.error_input_required));
}
}
}
/**
* 通过读取一个TextInputLayouts的ArrayList和一些附加信息,创建一个新的SmartDevice。基于这些值,将创建并返回一个新的SmartDevice。
*
* @param layouts the list of fields to read the data from.
* @param nextId the id of this new device.
* @return a new SmartDevice based on the read data.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("ConstantConditions")
public static SmartDevice readDevice(
Context context, String type, ArrayList<TextInputLayout> layouts, int nextId) {
ArrayList<String> inputs = new ArrayList<>();
// Read each input and add it to the list of inputs
for (TextInputLayout layout : layouts) {
EditText editText = layout.getEditText();
inputs.add(editText.getText().toString());
}
// Create a new device
DeviceData data =
new DeviceData(
nextId,
inputs.get(0),
context.getString(R.string.status_unknown),
false,
type,
inputs.get(1));
// Return the type of device
if (type.equals(DEV_TYPE_RGB)) {
return new RGBLedController(data);
}
return new SmartDevice(data);
}
/**
* 从TextInputLayout中检索字符串。
*
* @param layout the layout to retrieve the text from.
* @return the input text.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("ConstantConditions")
public static String getText(TextInputLayout layout) {
return layout.getEditText().getText().toString();
}
/**
* 设置正确的过滤器和错误侦听器以处理用户输入中的错误。
*
* @param layout the layout to set the filter on.
* @param type the type of input field, only option now is DEFAULT_TYPE.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("ConstantConditions")
public static void setListener(final TextInputLayout layout, String type) {
if (DEFAULT_TYPE.equals(
type)) { // The default type needs an error handler for surpassing the maximum length.
layout
.getEditText()
.addTextChangedListener(
new TextWatcher() {
@Override
public void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count, int after) {}
@Override
public void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count) {}
@Override
public void afterTextChanged(Editable s) {
// If the length is too great, write an error
if (s.length() > layout.getCounterMaxLength()) {
Resources resources = layout.getResources();
layout.setError(resources.getString(R.string.error_input_length));
} else {
layout.setError(null);
}
}
});
} else {
Log.d("TextInputLayout type", type);
}
}
}
widget 目录
ColorDotView.kt
/*
* 版权所有 2019 年 Android 开源项目
*
* 根据 Apache 许可证 2.0 版本(以下简称“许可证”)获得许可;
* 您不得使用此文件,除非符合许可证的规定。
* 您可以在以下网址获得许可证副本:
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* 除非适用法律要求或书面同意,否则按“原样”分发软件,
* 无任何形式的明示或暗示的保证或条件。
* 有关许可证下的特定语言,请参阅许可证。
*/
/**
* 该项目代码简单绘制了带有描边的填充圆圈。
*/
class ColorDotView @JvmOverloads constructor(
context: Context,
attrs: AttributeSet? = null,
defStyleAttr: Int = 0
) : View(context, attrs, defStyleAttr) {
var fillColor: Int = Color.LTGRAY
set(value) {
paintFill.color = value
field = value
this.invalidate()
}
private val paintFill = Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG).apply {
style = Paint.Style.FILL
color = Color.RED
}
private var cx: Float = 0F
private var cy: Float = 0F
private var radius: Float = 0F
init {
// 从 XML 属性获取填充颜色
val a = context.theme.obtainStyledAttributes(
attrs,
R.styleable.ColorDotView,
defStyleAttr,
0
)
fillColor = a.getColor(R.styleable.ColorDotView_colorFillColor, fillColor)
a.recycle()
}
override fun onSizeChanged(w: Int, h: Int, oldw: Int, oldh: Int) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh)
// 计算圆的位置和半径
cx = w / 2F
cy = h / 2F
// 稍微减小我们圆的半径,以防止描边被裁剪。
radius = (w / 2F) - 1F
}
override fun onDraw(canvas: Canvas) {
// 在 Canvas 上绘制圆圈
canvas.drawCircle(cx, cy, radius, paintFill)
}
}
其它
ConnectionsHandler.java
//一个接口,用于处理所有需要得到适当处理的不同类型的连接。包含用于MQTT回调和NetworkHandler类的回调的方法。
public interface ConnectionsHandler {
/**
* 当"stat/+/RESULT"主题上的新MqttMessage到达时的回调。从这里开始,可以解析并相应地处理消息。
*
* @param topic 收到消息的主题。
* @param message 收到的实际消息。
*/
void onMqttMessage(String topic, MqttMessage message);
void onMqttSubscribe();//当MqttClient成功订阅主题时的回调。用于通知活动客户端现在已完全设置并准备好。
/**
* 当客户端连接到服务器时使用的回调。尚未建立订阅。用于处理连接后需要设置的订阅和其他参数。
* @param connected 指示客户端是否连接的标志。
*/
void onMqttConnected(boolean connected);
void onNetworkChange();//设备网络更改时的回调。用于在例如WiFi重新连接时适当处理状态更新。
}DeviceAdapter.java
/**
* 用于填充RecyclerView的SmartDevice实例的适配器,用于显示SmartDevice实例的卡片
*/
public class DeviceAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<CardViewHolder> {
private final ArrayList<SmartDevice> devices;
private final Activity context;
/**
* RecyclerView中每个卡片的视图。
*/
static class CardViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
ComponentCardsBinding binding;
/**
* 默认构造函数
* @param binding 表示视图的绑定。
*/
CardViewHolder(ComponentCardsBinding binding) {
super(binding.getRoot());
this.binding = binding;
}
/**
* 将smartDevice绑定到布局。
*
* @param device 要绑定的设备。
*/
public void bind(SmartDevice device) {
binding.setDevice(device);
binding.executePendingBindings();
}
}
/**
* 适配器的默认构造函数,接受上下文和设备列表。
*
* @param devices 用于创建此适配器的设备。
* @param context 用于使用的应用程序上下文。
*/
DeviceAdapter(ArrayList<SmartDevice> devices, Activity context) {
this.devices = devices;
this.context = context;
}
// 创建新视图(由布局管理器调用)
@NotNull
@Override
public CardViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
// 为此项创建一个新的MaterialCardView
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext());
ComponentCardsBinding binding = ComponentCardsBinding.inflate(inflater, parent, false);
return new CardViewHolder(binding);
}
// 替换视图的内容(由布局管理器调用)
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(@NotNull CardViewHolder holder, final int pos) {
final int position = holder.getAdapterPosition();
final SmartDevice device = devices.get(position);
holder.bind(device);
ComponentCardsBinding binding = holder.binding;
// 编辑Activity的按钮
binding.deviceEdit.setOnClickListener(
v -> {
Intent intent = new Intent(context, DeviceEditActivity.class);
intent.putExtra(DeviceEditActivity.EXTRA_SELECTED_DEV, position);
intent.putExtra(DeviceEditActivity.EXTRA_NUM_DEV, getItemCount());
context.startActivityForResult(intent, 0);
});
// 颜色Activity的按钮
binding.deviceColor.setOnClickListener(
v -> {
Intent intent = new Intent(context, DeviceColorActivity.class);
intent.putExtra(DeviceColorActivity.EXTRA_SELECTED_DEV, position);
context.startActivity(intent);
});
// 电源的开关
binding.devicePower.setOnCheckedChangeListener(
(buttonView, isChecked) -> {
// 检查是否由用户按下(而不是其他什么)
if (buttonView.isPressed()) {
MqttClient client = ((MainActivity) context).getMqttClient();
client.publish(device.setPower(isChecked));
}
});
}
// 返回数据集的大小(由布局管理器调用)
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return devices.size();
}
}
DeviceColorActivity.java
/**
* 这个DeviceColorActivity用于处理显示和更新RGBLedController的颜色,它包括与MQTT客户端的交互和网络更改的响应。该活动使用相应的布局和UI元素来显示颜色信息,并在用户交互时执行相应的操作。
*/
public class DeviceColorActivity extends FragmentActivity
implements View.OnClickListener, ConnectionsHandler {
public static final String EXTRA_SELECTED_DEV = "com.leondeklerk.smartcontroller.SELECTED_DEV";
private ActivityDeviceColorBinding binding;
private RGBLedController device;
private MqttClient client;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
NetworkHandler handler = NetworkHandler.getHandler();
handler.setCurrentHandler(this);
binding = ActivityDeviceColorBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater());
View view = binding.getRoot();
setContentView(view);
binding.toolbar.setNavigationOnClickListener(
new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
onBackPressed();
}
});
Intent intent = getIntent();
int deviceNum = intent.getIntExtra(EXTRA_SELECTED_DEV, 0);
// 设置MqttCient并注册正确的接收器。
client = MqttClient.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
client.registerHandler("DeviceColorActivity", this);
client.setHandler("DeviceColorActivity");
SharedPreferences preferences =
this.getSharedPreferences(getString(R.string.dev_prefs), Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
DeviceStorageUtils deviceStorageUtils = new DeviceStorageUtils(preferences, this);
ArrayList<SmartDevice> devices = deviceStorageUtils.getDevices();
device = new RGBLedController(devices.get(deviceNum).getData());
client.publish(device.getColor());
binding.colorInfo.setText(device.getData().getName());
binding.colorCancel.setOnClickListener(this);
binding.colorSet.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int id = v.getId();
if (id == R.id.color_cancel) {
this.onBackPressed();
} else if (id == R.id.color_set) {
int red = (int) binding.sliderRed.getValue();
int green = (int) binding.sliderGreen.getValue();
int blue = (int) binding.sliderBlue.getValue();
client.publish(device.setColor(red, green, blue));
} else {
Log.d("DeviceColorActivity@onClick", "Non-existent button clicked (color)");
}
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
client.setHandler("MainActivity");
}
@Override
public void onMqttMessage(String topic, MqttMessage message) {
parseResponse(message);
}
@Override
public void onMqttSubscribe() {}
@Override
public void onMqttConnected(boolean connected) {}
@Override
public void onNetworkChange() {
client = MqttClient.reconnect(this);
}
/**
* 解析接收到的MQTT消息的响应并相应地更新布局。
*
* @param message 要解析的消息。
*/
private void parseResponse(MqttMessage message) {
String colorString = "";
try {
JSONObject obj = new JSONObject(message.toString());
colorString = obj.getString("Color");
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
String[] colors = colorString.split(",");
binding.sliderRed.setValue(Float.parseFloat(colors[0]));
binding.sliderGreen.setValue(Float.parseFloat(colors[1]));
binding.sliderBlue.setValue(Float.parseFloat(colors[2]));
}
}
DeviceEditActivity.java
/** 这个DeviceEditActivity用于编辑设备数据,它包含一个ViewPager2,通过它可以左右滑动切换不同的DeviceEditFragment。DeviceEditFragmentAdapter是ViewPager2的适配器,负责管理所有的DeviceEditFragment。在onCreate方法中,根据传递的Intent设置ViewPager2和适配器,并指定当前显示的页面。 */
public class DeviceEditActivity extends FragmentActivity {
public static final String EXTRA_SELECTED_DEV = "com.leondeklerk.smartcontroller.SELECTED_DEV";
public static final String EXTRA_NUM_DEV = "com.leondeklerk.smartcontroller.NUM_DEV";
private static int numOfDevices;
static ActivityDeviceEditBinding binding;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
binding = ActivityDeviceEditBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater());
View view = binding.getRoot();
setContentView(view);
binding.toolbar.setNavigationOnClickListener(
new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
onBackPressed();
}
});
Intent intent = getIntent();
numOfDevices = intent.getIntExtra(EXTRA_NUM_DEV, 0);
ViewPager2 viewPager = binding.pager;
FragmentStateAdapter pagerAdapter = new DeviceEditFragmentAdapter(this);
viewPager.setAdapter(pagerAdapter);
viewPager.setCurrentItem(intent.getIntExtra(EXTRA_SELECTED_DEV, 0));
}
/** 包含所有DeviceEditFragments的适配器。 */
private static class DeviceEditFragmentAdapter extends FragmentStateAdapter {
/**
* 默认构造函数。
*
* @param fragmentActivity 与此片段相关的Activity。
*/
DeviceEditFragmentAdapter(FragmentActivity fragmentActivity) {
super(fragmentActivity);
}
@NotNull
@Override
public Fragment createFragment(int position) {
Fragment fragment = new DeviceEditFragment();
Bundle args = new Bundle();
args.putInt(DeviceEditFragment.ARG_FRAG_NUM, position);
fragment.setArguments(args);
return fragment;
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return numOfDevices;
}
}
}
DeviceEditFragment.java
/**
* 代表设备编辑屏幕中的实际设备编辑界面的Fragment。包含设备的所有数据以及更改此数据的选项。
*/
public class DeviceEditFragment extends Fragment implements View.OnClickListener {
static final String ARG_FRAG_NUM = "com.leondeklerk.smartcontroller.FRAG_NUM";
private Activity context;
private int devNum;
private ArrayList<SmartDevice> devices;
private DeviceStorageUtils deviceStorageUtils;
private FragmentDeviceEditBinding binding;
private SmartDevice device;
private SmartDevice initial;
private ArrayList<TextInputLayout> fragList;
@Override
public View onCreateView(
@NotNull LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
binding = FragmentDeviceEditBinding.inflate(inflater, container, false);
context = getActivity();
return binding.getRoot();
}
@Override
public void onViewCreated(@NotNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
Bundle args = getArguments();
if (args != null) {
devNum = args.getInt(ARG_FRAG_NUM);
} else {
context.finish();
}
SharedPreferences preferences =
context.getSharedPreferences(getString(R.string.dev_prefs), Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
deviceStorageUtils = new DeviceStorageUtils(preferences, context);
devices = deviceStorageUtils.getDevices();
device = devices.get(devNum);
// 设置对当前设备的引用
initial = SmartDevice.clone(device);
// 绑定数据类
binding.setDevice(device);
binding.executePendingBindings();
// 设置按钮监听器
binding.editDelete.setOnClickListener(this);
binding.editUpdate.setOnClickListener(this);
setUpUtilsFrag();
}
@Override
public void onResume() {
super.onResume();
// 更改Activity的标题
DeviceEditActivity.binding.toolbar.setTitle(device.getData().getName());
}
@Override
public void onDestroyView() {
super.onDestroyView();
binding = null;
}
@SuppressLint("NonConstantResourceId")
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int id = v.getId();
if (id == R.id.edit_delete) {
// 删除设备并存储
devices.remove(devNum);
deviceStorageUtils.storeDevices(devices);
setResult(true);
// 返回
context.onBackPressed();
} else if (id == R.id.edit_update) {
if (!TextInputUtils.hasErrors(fragList)) {
// 更新设备并返回
updateDevice();
context.onBackPressed();
} else {
setResult(false);
}
} else {
Log.d("DeviceEditFragment@onClick", String.valueOf(id));
}
}
/** 设置Fragment中的输入字段,添加它们的错误监听器。 */
private void setUpUtilsFrag() {
fragList = new ArrayList<>();
// 将所有输入布局添加到列表中
fragList.add(binding.editName);
fragList.add(binding.editTopic);
// 设置错误监听器
TextInputUtils.setListener(binding.editName, TextInputUtils.DEFAULT_TYPE);
TextInputUtils.setListener(binding.editTopic, TextInputUtils.DEFAULT_TYPE);
}
/**
* 设置父Activity的结果Intent,将在MainActivity重新进入时进行检查。
*
* @param removed 如果设备已删除,则为true;否则为false
*/
private void setResult(boolean removed) {
// 创建一个新的Intent
Intent resultIntent = new Intent();
if (removed) {
// 如果设备已删除,则标记此项
resultIntent.putExtra(MainActivity.EXTRA_DEV_REMOVED, devNum);
} else {
if (!initial.equals(device)) {
// 如果设备已编辑,则标记此项
resultIntent.putExtra(MainActivity.EXTRA_DEV_CHANGED, devNum);
}
}
context.setResult(Activity.RESULT_OK, resultIntent);
}
/** 更新并存储当前设备。 */
private void updateDevice() {
// 更新设备数据
device
.getData()
.setName(TextInputUtils.getText(binding.editName))
.setTopic(TextInputUtils.getText(binding.editTopic));
setResult(false);
// 存储新的设备数据
deviceStorageUtils.storeDevices(devices);
}
}
MainActivity.java
MqttClient.java
NetworkHandler.java
SettingsActivity.java
“main/res”里的xml代码

关于res:在 Android 开发中,res 文件夹是 "resources"(资源)的缩写,它是 Android 应用项目中存放各种资源文件的目录之一。这个目录主要包含了应用在运行时使用的非代码资源,例如图像、布局文件、字符串、颜色等。res 文件夹通常在应用的 app 模块下,是 Android 项目的标准结构之一。
anim: 包含动画资源文件,用于定义应用中的动画效果。
drawable: 存放应用图标、图片等可绘制资源。(就是一些矢量图)
layout: 包含应用中的布局文件,用于定义用户界面的结构和外观。
menu:在这个项目中定义应用右上角的弹出菜单。
mipmap: 存放应用图标的不同分辨率版本,用于适配不同屏幕密度的设备。
values: 包含了资源文件,如字符串、颜色、尺寸等,这些资源可以在应用的代码和布局文件中引用。
xml: 用于存放一些 XML 格式的资源文件,如菜单文件、布局文件引用等。(在这个项目中存放了用于配置MQTT的相关参数)
另外如果后续有需要的话还有raw,raw存放原始资源文件,例如音频或视频文件,这些文件在运行时不会被编译成资源 ID。

![第四节课[XTuner微调]作业](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/9f02fba73f7e48898df1c735ada18360.png)