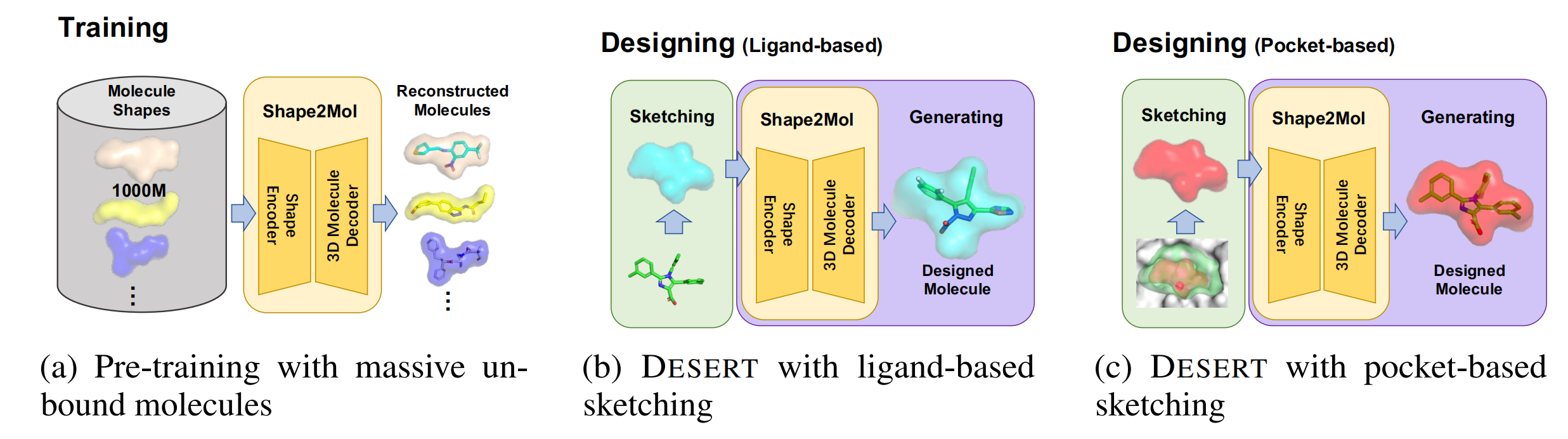
记录一个使用异步命名管道通信的实例。代码参考了 MSDN 的文档:使用完成例程的命名管道服务器 - Win32 apps | Microsoft Learn。
服务端代码
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <tchar.h>
#include <strsafe.h>
#define PIPE_TIMEOUT 5000
#define BUFSIZE 4096
#define MAX_USERNAME_LEN 100
#define MAX_PASSWORD_LEN 100
typedef struct
{
OVERLAPPED oOverlap;
HANDLE hPipeInst;
struct Message {
TCHAR username[MAX_USERNAME_LEN];
TCHAR password[MAX_PASSWORD_LEN];
TCHAR request[BUFSIZE];
} message;
DWORD cbRead;
TCHAR chReply[BUFSIZE];
DWORD cbToWrite;
} PIPEINST, * LPPIPEINST;
VOID DisconnectAndClose(LPPIPEINST);
BOOL CreateAndConnectInstance(LPOVERLAPPED);
BOOL ConnectToNewClient(HANDLE, LPOVERLAPPED);
VOID GetAnswerToRequest(LPPIPEINST);
VOID WINAPI CompletedWriteRoutine(DWORD, DWORD, LPOVERLAPPED);
VOID WINAPI CompletedReadRoutine(DWORD, DWORD, LPOVERLAPPED);
HANDLE hPipe;
int _tmain(VOID)
{
HANDLE hConnectEvent;
OVERLAPPED oConnect;
LPPIPEINST lpPipeInst;
DWORD dwWait, cbRet;
BOOL fSuccess, fPendingIO;
// Create one event object for the connect operation.
hConnectEvent = CreateEvent(
NULL, // default security attribute
TRUE, // manual reset event
TRUE, // initial state = signaled
NULL); // unnamed event object
if (hConnectEvent == NULL)
{
printf("CreateEvent failed with %d.\n", GetLastError());
return 0;
}
oConnect.hEvent = hConnectEvent;
// Call a subroutine to create one instance, and wait for
// the client to connect.
fPendingIO = CreateAndConnectInstance(&oConnect);
while (1)
{
// Wait for a client to connect, or for a read or write
// operation to be completed, which causes a completion
// routine to be queued for execution.
dwWait = WaitForSingleObjectEx(
hConnectEvent, // event object to wait for
INFINITE, // waits indefinitely
TRUE); // alertable wait enabled
switch (dwWait)
{
// The wait conditions are satisfied by a completed connect
// operation.
case 0:
// If an operation is pending, get the result of the
// connect operation.
if (fPendingIO)
{
fSuccess = GetOverlappedResult(
hPipe, // pipe handle
&oConnect, // OVERLAPPED structure
&cbRet, // bytes transferred
FALSE); // does not wait
if (!fSuccess)
{
printf("ConnectNamedPipe (%d)\n", GetLastError());
return 0;
}
}
// Allocate storage for this instance.
lpPipeInst = (LPPIPEINST)GlobalAlloc(
GPTR, sizeof(PIPEINST));
if (lpPipeInst == NULL)
{
printf("GlobalAlloc failed (%d)\n", GetLastError());
return 0;
}
lpPipeInst->hPipeInst = hPipe;
// Start the read operation for this client.
// Note that this same routine is later used as a
// completion routine after a write operation.
lpPipeInst->cbToWrite = 0;
CompletedWriteRoutine(0, 0, (LPOVERLAPPED)lpPipeInst);
// Create new pipe instance for the next client.
fPendingIO = CreateAndConnectInstance(
&oConnect);
break;
// The wait is satisfied by a completed read or write
// operation. This allows the system to execute the
// completion routine.
case WAIT_IO_COMPLETION:
break;
// An error occurred in the wait function.
default:
{
printf("WaitForSingleObjectEx (%d)\n", GetLastError());
return 0;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
// CompletedWriteRoutine(DWORD, DWORD, LPOVERLAPPED)
// This routine is called as a completion routine after writing to
// the pipe, or when a new client has connected to a pipe instance.
// It starts another read operation.
VOID WINAPI CompletedWriteRoutine(DWORD dwErr, DWORD cbWritten,
LPOVERLAPPED lpOverLap)
{
LPPIPEINST lpPipeInst;
BOOL fRead = FALSE;
// lpOverlap points to storage for this instance.
lpPipeInst = (LPPIPEINST)lpOverLap;
// The write operation has finished, so read the next request (if
// there is no error).
if ((dwErr == 0) && (cbWritten == lpPipeInst->cbToWrite))
fRead = ReadFileEx(
lpPipeInst->hPipeInst,
&lpPipeInst->message,
sizeof(lpPipeInst->message),
(LPOVERLAPPED)lpPipeInst,
(LPOVERLAPPED_COMPLETION_ROUTINE)CompletedReadRoutine);
// Disconnect if an error occurred.
if (!fRead)
DisconnectAndClose(lpPipeInst);
}
// CompletedReadRoutine(DWORD, DWORD, LPOVERLAPPED)
// This routine is called as an I/O completion routine after reading
// a request from the client. It gets data and writes it to the pipe.
VOID WINAPI CompletedReadRoutine(DWORD dwErr, DWORD cbBytesRead,
LPOVERLAPPED lpOverLap)
{
LPPIPEINST lpPipeInst;
BOOL fWrite = FALSE;
// lpOverlap points to storage for this instance.
lpPipeInst = (LPPIPEINST)lpOverLap;
// The read operation has finished, so write a response (if no
// error occurred).
if ((dwErr == 0) && (cbBytesRead != 0))
{
GetAnswerToRequest(lpPipeInst);
if (lpPipeInst->cbToWrite == 0)
{
return;
}
fWrite = WriteFileEx(
lpPipeInst->hPipeInst,
lpPipeInst->chReply,
lpPipeInst->cbToWrite,
(LPOVERLAPPED)lpPipeInst,
(LPOVERLAPPED_COMPLETION_ROUTINE)CompletedWriteRoutine);
}
// Disconnect if an error occurred.
if (!fWrite)
DisconnectAndClose(lpPipeInst);
}
// DisconnectAndClose(LPPIPEINST)
// This routine is called when an error occurs or the client closes
// its handle to the pipe.
VOID DisconnectAndClose(LPPIPEINST lpPipeInst)
{
// Disconnect the pipe instance.
if (!DisconnectNamedPipe(lpPipeInst->hPipeInst))
{
printf("DisconnectNamedPipe failed with %d.\n", GetLastError());
}
// Close the handle to the pipe instance.
CloseHandle(lpPipeInst->hPipeInst);
// Release the storage for the pipe instance.
if (lpPipeInst != NULL)
GlobalFree(lpPipeInst);
}
// CreateAndConnectInstance(LPOVERLAPPED)
// This function creates a pipe instance and connects to the client.
// It returns TRUE if the connect operation is pending, and FALSE if
// the connection has been completed.
BOOL CreateAndConnectInstance(LPOVERLAPPED lpoOverlap)
{
LPCTSTR lpszPipename = L"\\\\.\\pipe\\mynamedpipe";
hPipe = CreateNamedPipe(
lpszPipename, // pipe name
PIPE_ACCESS_DUPLEX | // read/write access
FILE_FLAG_OVERLAPPED, // overlapped mode
PIPE_TYPE_MESSAGE | // message-type pipe
PIPE_READMODE_MESSAGE | // message read mode
PIPE_WAIT, // blocking mode
PIPE_UNLIMITED_INSTANCES, // unlimited instances
BUFSIZE * sizeof(TCHAR), // output buffer size
BUFSIZE * sizeof(TCHAR), // input buffer size
PIPE_TIMEOUT, // client time-out
NULL); // default security attributes
if (hPipe == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
{
printf("CreateNamedPipe failed with %d.\n", GetLastError());
return 0;
}
// Call a subroutine to connect to the new client.
return ConnectToNewClient(hPipe, lpoOverlap);
}
BOOL ConnectToNewClient(HANDLE hPipe, LPOVERLAPPED lpo)
{
BOOL fConnected, fPendingIO = FALSE;
// Start an overlapped connection for this pipe instance.
fConnected = ConnectNamedPipe(hPipe, lpo);
// Overlapped ConnectNamedPipe should return zero.
if (fConnected)
{
printf("ConnectNamedPipe failed with %d.\n", GetLastError());
return 0;
}
switch (GetLastError())
{
// The overlapped connection in progress.
case ERROR_IO_PENDING:
fPendingIO = TRUE;
break;
// Client is already connected, so signal an event.
case ERROR_PIPE_CONNECTED:
if (SetEvent(lpo->hEvent))
break;
// If an error occurs during the connect operation...
default:
{
printf("ConnectNamedPipe failed with %d.\n", GetLastError());
return 0;
}
}
return fPendingIO;
}
BOOL AuthenticateClient(LPPIPEINST lpPipeInst) {
// 硬编码的用户名和密码列表
const TCHAR* validUsernames[] = { TEXT("WMsgClientName") };
const TCHAR* validPasswords[] = { TEXT("WMsgClientPassword") };
// 从 lpPipeInst 中获取客户端发送的身份验证信息(例如,用户名和密码)
TCHAR username[MAX_USERNAME_LEN];
TCHAR password[MAX_PASSWORD_LEN];
TCHAR request[BUFSIZE];
// 解析客户端发送的身份验证信息
lstrcpy(username, lpPipeInst->message.username);
lstrcpy(password, lpPipeInst->message.password);
lstrcpy(request, lpPipeInst->message.request);
// 检查用户名和密码是否在有效的用户名和密码列表中
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(validUsernames) / sizeof(validUsernames[0]); i++) {
if (_tcscmp(username, validUsernames[i]) == 0 && _tcscmp(password, validPasswords[i]) == 0) {
// 用户名和密码匹配,身份验证成功
// 将余下的请求部分复制到 lpPipeInst->chRequest 中
lstrcpy(lpPipeInst->message.request, request);
// 设置请求长度
lpPipeInst->cbRead = (lstrlen(lpPipeInst->message.request) + 1) * sizeof(TCHAR);
return TRUE;
}
}
// 如果用户名和密码不匹配任何有效的用户名和密码,身份验证失败
_tprintf(TEXT("Invalid authentication.\n"));
return FALSE;
}
VOID GetAnswerToRequest(LPPIPEINST pipe)
{
_tprintf(TEXT("ClientMsg:[0x%I64X] %s\n"), (UINT64)pipe->hPipeInst, pipe->message.request);
// 验证客户端身份
if (!AuthenticateClient(pipe))
{
pipe->cbToWrite = 0;
DisconnectAndClose(pipe);
return;
}
_tprintf(TEXT("Client authentication completed.\n"));
// 根据客户端发送的不同消息生成不同的回复
if (_tcscmp(pipe->message.request, TEXT("Request1")) == 0)
{
StringCchCopy(pipe->chReply, BUFSIZE, TEXT("Response to Request1"));
}
else if (_tcscmp(pipe->message.request, TEXT("Request2")) == 0)
{
StringCchCopy(pipe->chReply, BUFSIZE, TEXT("Response to Request2"));
}
else
{
StringCchCopy(pipe->chReply, BUFSIZE, TEXT("Default answer from server"));
}
pipe->cbToWrite = (lstrlen(pipe->chReply) + 1) * sizeof(TCHAR);
}
客户端代码
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <tchar.h>
#define BUFSIZE 512
typedef struct
{
TCHAR username[100];
TCHAR password[100];
TCHAR request[BUFSIZE];
} Message;
int _tmain(int argc, TCHAR* argv[])
{
HANDLE hPipe;
Message message;
BOOL fSuccess = FALSE;
DWORD cbRead, cbToWrite, cbWritten, dwMode;
LPCTSTR lpszPipename = L"\\\\.\\pipe\\mynamedpipe";
// 初始化结构体信息
_tcscpy_s(message.username, _T("WMsgClientName"));
_tcscpy_s(message.password, _T("WMsgClientPassword"));
if (argc > 1)
_tcscpy_s(message.request, argv[1]);
else
_tcscpy_s(message.request, _T("Default request from client."));
// 尝试打开命名管道
while (1)
{
hPipe = CreateFile(
lpszPipename, // pipe name
GENERIC_READ | // read and write access
GENERIC_WRITE,
0, // no sharing
NULL, // default security attributes
OPEN_EXISTING, // opens existing pipe
0, // default attributes
NULL); // no template file
// 如果管道句柄有效,则退出循环
if (hPipe != INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
break;
// 如果错误不是 ERROR_PIPE_BUSY,则退出程序
if (GetLastError() != ERROR_PIPE_BUSY)
{
_tprintf(TEXT("Could not open pipe. GLE=%d\n"), GetLastError());
return -1;
}
// 如果所有管道实例都在忙,则等待 20 秒
if (!WaitNamedPipe(lpszPipename, 20000))
{
printf("Could not open pipe: 20 second wait timed out.");
return -1;
}
}
// 设置管道模式为消息读取模式
dwMode = PIPE_READMODE_MESSAGE;
fSuccess = SetNamedPipeHandleState(
hPipe, // 管道句柄
&dwMode, // 新的管道模式
NULL, // 不设置最大字节数
NULL); // 不设置最大时间
if (!fSuccess)
{
_tprintf(TEXT("SetNamedPipeHandleState failed. GLE=%d\n"), GetLastError());
return -1;
}
// 向管道服务器发送消息
cbToWrite = sizeof(message);
_tprintf(TEXT("Sending %d byte message: \"%s\"\n"), cbToWrite, message.request);
fSuccess = WriteFile(
hPipe, // 管道句柄
&message, // 消息
cbToWrite, // 消息长度
&cbWritten, // 写入的字节数
NULL); // 不使用重叠
if (!fSuccess)
{
_tprintf(TEXT("WriteFile to pipe failed. GLE=%d\n"), GetLastError());
return -1;
}
printf("\nMessage sent to server, receiving reply as follows:\n");
// 从管道读取服务器的回复
fSuccess = ReadFile(
hPipe, // 管道句柄
message.request, // 用于接收回复的缓冲区
BUFSIZE * sizeof(TCHAR), // 缓冲区大小
&cbRead, // 读取的字节数
NULL); // 不使用重叠
if (!fSuccess)
{
_tprintf(TEXT("ReadFile from pipe failed. GLE=%d\n"), GetLastError());
return -1;
}
_tprintf(TEXT("Server's reply: \"%s\"\n"), message.request);
printf("\n<End of message, press ENTER to terminate connection and exit>");
_getch();
CloseHandle(hPipe);
return 0;
}
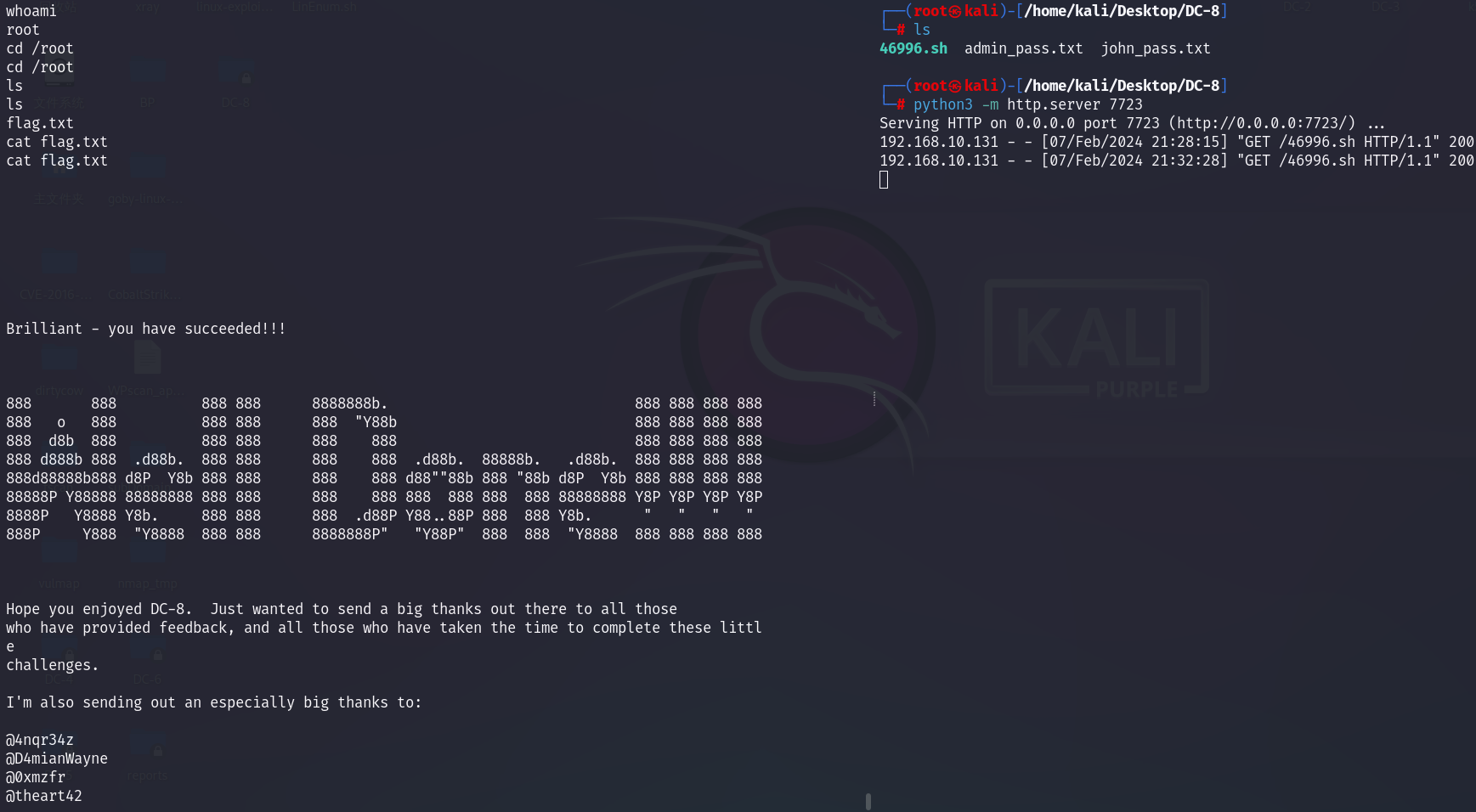
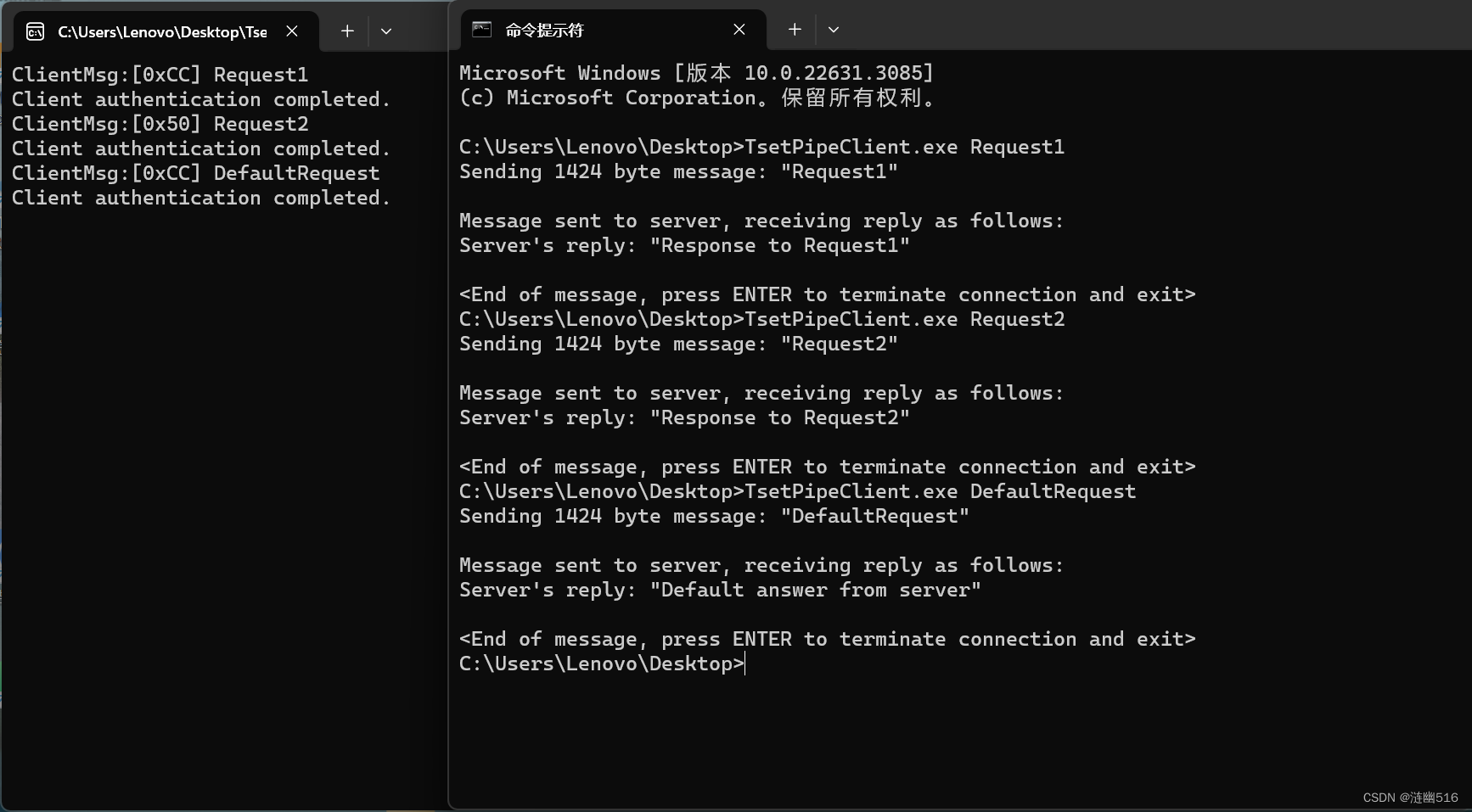
测试结果
发布于:2024.02.08,更新于:2024.02.08.