浮动与定位
浮动布局比较灵活,不易控制,而定位可以控制元素的过分灵活性,给元素一个具体的空间和精确的位置。
浮动
我们使用 float 属性指定元素沿其容器的左侧或右侧放置,浮动布局常见取值如下:
• left(左浮动)
• right(右浮动)
使用格式如下所示:
float: left|right;
我们来举个例子吧!
新建一个 index.html 文件,在其中写入以下内容。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
section {
border: 1px solid green;
width: 400px;
float: left;
}
img {
width: 120px;
height: 120px;
}
img:first-child {
float: left;
}
img:nth-child(2) {
float: right;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<section>
<img src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/10532/lotus1.png" />
<img src="https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/10532/lotus2.png" />
<p>
曲曲折折的荷塘上面,弥望的是田田的叶子。叶子出水很高,像亭亭的舞女的裙。层层的叶子中间,零星地点缀着些白花,有袅娜地开着的,有羞涩地打着朵儿的;正如一粒粒的明珠,又如碧天里的星星,又如刚出浴的美人。微风过处,送来缕缕清香,仿佛远处高楼上渺茫的歌声似的。这时候叶子与花也有一丝的颤动,像闪电般,霎时传过荷塘的那边去了。叶子本是肩并肩密密地挨着,这便宛然有了一道凝碧的波痕。叶子底下是脉脉的流水,遮住了,不能见一些颜色;而叶子却更见风致了。
</p>
</section>
</body>
</html>

定位
我们使用 position 属性来对元素的位置进行控制,定位布局可以分为以下四种:
• 静态定位(inherit)
• 相对定位(relative)
• 绝对定位(absolute)
• 固定定位(fixed)
其中,一般的标签元素不加任何定位属性时,默认都属于静态定位,静态定位在页面的最底层属于标准流(普通流),在页面中没有特殊的操作方式和显示效果,在本章节中会重点给同学们讲解其他三种定位方式。
固定定位
fixed 属性值用于固定定位,被固定的元素不会随着滚动条的拖动而改变位置。
使用格式如下:
position: fixed;
我们来举个例子吧!
新建一个 index1.html 文件,在其中写入以下内容。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 100%;
margin-left: 15%;
}
.ad-l {
position: fixed;
top: 100px;
left: 0;
}
.ad-r {
position: fixed;
top: 100px;
right: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<img src="ad-l.png" class="ad-l" />
<img src="ad-r.png" class="ad-r" />
<div class="box">
<img src="box.png" />
</div>
</body>
</html>

相对定位
相对定位是该元素的位置相对于它原始的位置来计算的。position 属性为我们提供了 relative 属性值来设置元素的相对属性。
position: relative;
我们来举个例子吧!
新建一个 index2.html 文件,在其中写入以下内容。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 100%;
}
.ad-l {
position: relative;
left: -40px;
}
.ad-r {
position: relative;
left: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<img src="ad-l.png" class="ad-l" />
<img src="ad-r.png" class="ad-r" />
<div class="box">
<img src="box.png" />
</div>
</body>
</html>
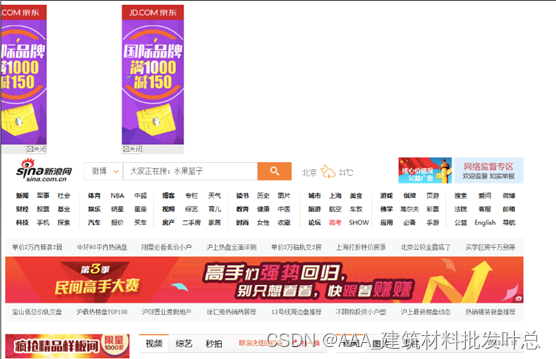
绝对定位
绝对定位,能把元素精确地放在任意位置。position 属性为我们提供了 absolute 属性值来设置元素的相对属性。
语法格式为:
position: absolute;
我们来举个例子吧!
新建一个 index3.html 文件,在其中写入以下内容。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 100%;
margin-left: 180px;
}
.ad-l {
position: absolute;
left: 50px;
top: 150px;
}
.ad-r {
position: absolute;
right: 30px;
top: 150px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<img src="ad-l.png" class="ad-l" />
<img src="ad-r.png" class="ad-r" />
<div class="box">
<img src="box.png" />
</div>
</body>
</html>
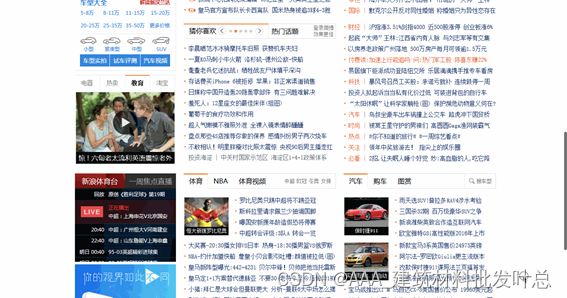
总结
本节实验给大家介绍了布局相关的属性,浮动和定位。
在浮动中,给大家介绍了左浮动(float:left)和右浮动(float:right)的用法。
在定位中,给大家介绍了四种:
• 静态定位(position:inherit)
• 相对定位(position:relative)
• 绝对定位(position:absolute)
• 固定定位(position:fixed)