PTA | 1004 Counting Leaves
1004 Counting Leaves
作者 CHEN, Yue
单位 浙江大学
A family hierarchy is usually presented by a pedigree tree. Your job is to count those family members who have no child.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts with a line containing 0<N<100, the number of nodes in a tree, and M (<N), the number of non-leaf nodes. Then M lines follow, each in the format:
ID K ID[1] ID[2] ... ID[K]
where ID is a two-digit number representing a given non-leaf node, K is the number of its children, followed by a sequence of two-digit ID's of its children. For the sake of simplicity, let us fix the root ID to be 01.
The input ends with N being 0. That case must NOT be processed.
Output Specification:
For each test case, you are supposed to count those family members who have no child for every seniority level starting from the root. The numbers must be printed in a line, separated by a space, and there must be no extra space at the end of each line.
The sample case represents a tree with only 2 nodes, where 01 is the root and 02 is its only child. Hence on the root 01 level, there is 0 leaf node; and on the next level, there is 1 leaf node. Then we should output 0 1 in a line.
Sample Input:
2 1
01 1 02
Sample Output:
0 1万事开头难,先读题!
家族等级通常由家谱树表示。你的工作是统计那些没有孩子的家庭成员。
输入规范:
每个输入文件包含一个测试用例。每种情况都以包含0<N<100(树中的节点数)和M(<N)(非叶节点数)的行开始。接下来是M行,每行的格式如下:
ID K ID[1] ID[2]. ID[K]
其中ID是表示给定非叶节点的两位数,K是其子节点的数量,后面是其子节点的两位数ID的序列。为了简单起见,让我们将根ID固定为01。
输入以N为0结束。这种情况不得处理。
输出规格:
对于每个测试用例,您应该从根开始计算每个资历级别中没有孩子的家庭成员。数字必须打印成一行,用空格分隔,每行末尾不得有多余的空格。
示例案例表示只有2个节点的树,其中01是根节点,02是唯一的子节点。因此,在根01层上,有0个叶节点;在下一层上,有1个叶节点。然后我们应该在一行中输出0 1。
样品输入:
2 1
01 1 02
输出示例:
0 1
根据题意,我们可以提取到:
1, 家庭族谱问题 -> 树,树上问题 - > dfs
2, 输入分成两行,第一行输入的是树中所有的节点数N,所有非叶子节点数M。此后输入每一个节点对应的子节点数量和编号
3, 叶子节点的定义、静态树的实现以及dfs的基础实现
4, 输出要求是每层的无子节点总数,要求两两之间用空格隔开,不允许有多余空格(要求简单将不再单独说明)
题目读完,现在是手搓代码时间!!!
首先,根据题意,本题需要重点关注的数据结构类型是树,重点要求是统计每一层中无子节点的节点数,其实不管是C++还是python,根据题中所涉及的输入类型来构建一棵树终归是一种比较繁琐且难度较大的过程,因此在碰上类似的题目时,除非题中指明需要构建一棵树来解决问题,否则可以采取以下策略构建静态树:
1, 对于C++,使用vector容器,该容器兼容大部分数据结构的特性,初始化对应大小的vector很多时候可以简化问题:
vector<int> child[100];
2, 对于python,可以使用dict+list来解决这一类问题,将父节点视作key,将父节点的所有子节点加入key的value中,作为value列表
child = {}
以上思想不仅在树上好用,在图上其实也有很大的应用场景,熟练掌握可以减少很多的时间花费。
在有了基本的方向之后,就可以着手开始搓代码了,
首先,对于输入的处理:
c++部分代码:
使用int类型的变量n和m分别接收对应的变量N与M,定义parent和child_nums接收第二行输入的节点编号和节点的子节点数,随后循环child_nums次,将其余的输入作为子节点数组和父节点关联。
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
cin >> parent >> child_nums;
for(int j = 0; j < child_nums; j++)
{
int kids;
cin >> kids;
child[parent].push_back(kids);
}
}python部分思路类似,代码如下:
注:*childs部分为变长数组,用于打包后面的子节点部分,这部分是列表的索引部分的内容,忘记的同学赶紧记起来!
n, m = [int(i) for i in input().split()]
child = {}
for i in range(m):
child_id, child_num, *childs = input().split()
child[child_id] = childs此后,定义相关的变量:
对于C++,初始化的必要变量如下::
int n, m, max_depth=1;
int parent, child_nums;
vector<int> child[100];
int nums_of_level[101] = {0};
对于python,初始化以下变量:
nums_of_level = [0] * (n+1) : 每一层的叶子节点数
is_visited = {} : 已遍历节点,已遍历为True,未遍历不加入
max_depth = 0 : 最大深度
此后,设计本题核心部分:dfs
对于C++部分,我们可以当前节点,和当前所在层数传进去,首先判断当前层数和最大层数大小关系,根据判断结果更新最大层数;
此后判断当前节点id是否存在子节点,由于传入的时候,我们呢使用的是vector,使用key:value的结构,此时只要 child[node].size() 其结果大于零,则可以判断,当前节点存在子节点,接下来将对其所有子节点进行dfs,其中传入dfs函数得到参数中,除了node需要改变之外,当前深度depth也需要+1;
若该节点 child[node].size() 结果为零,则表明该节点并没有子节点,即此节点为该层的一个叶子节点,更新nums_of_level[depth],
c++部分代码如下:
void dfs(int node, int depth){
max_depth = max(depth, max_depth);
if(child[node].size() == 0)
{
nums_of_level[depth] += 1;
return;
}
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < child[node].size(); i++)
{
dfs(child[node][i], depth + 1);
}
对于python部分,传入参数同样为当前的节点node和当前深度depth,
进入dfs之后,首先将该节点node的遍历状态改为True,然后比较当前深度和最大深度,根据结果更新最大深度参数,
由于使用dict结构对输入进行存储,python将面临一个比较大的问题,那就是节点id可能并不是连续的,此时就有可能出现 child[node] 报错node不存在的尴尬时刻,换个角度思考,其实这个编号的节点的节点不在的话,直接更新对应的level所对应的数量。
若 child[node] 非空,则循环遍历其中的节点,将其进入dfs中,同样传入参数中depth+1,
python部分代码如下:
def dfs(node, depth):
global max_depth
is_visited[node] = True
max_depth = max(max_depth, depth)
if node not in child:
nums_of_level[depth] += 1
return
for c in child[node]:
if c not in is_visited:
dfs(c, depth+1)完整的代码如下:
C++部分:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, m, max_depth=1;
int parent, child_nums;
vector<int> child[100];
int nums_of_level[101] = {0};
void dfs(int node, int depth){
max_depth = max(depth, max_depth);
if(child[node].size() == 0)
{
nums_of_level[depth] += 1;
return;
}
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < child[node].size(); i++)
{
dfs(child[node][i], depth + 1);
}
}
int main(){
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
cin >> parent >> child_nums;
for(int j = 0; j < child_nums; j++)
{
int kids;
cin >> kids;
child[parent].push_back(kids);
}
}
dfs(1, 1);
printf("%d", nums_of_level[1]);
for(int i = 2; i <= max_depth; i++)
{
printf(" %d", nums_of_level[i]);
}
return 0;
}python部分代码:
n, m = [int(i) for i in input().split()]
child = {}
for i in range(m):
child_id, child_num, *childs = input().split()
child[child_id] = childs
nums_of_level = [0] * (n+1)
is_visited = {}
max_depth = 0
def dfs(node, depth):
global max_depth
is_visited[node] = True
max_depth = max(max_depth, depth)
if node not in child:
nums_of_level[depth] += 1
return
for c in child[node]:
if c not in is_visited:
dfs(c, depth+1)
dfs("01", 0)
print(" ".join(str(i) for i in nums_of_level[0:max_depth + 1]))最后附上AK截图:
C++: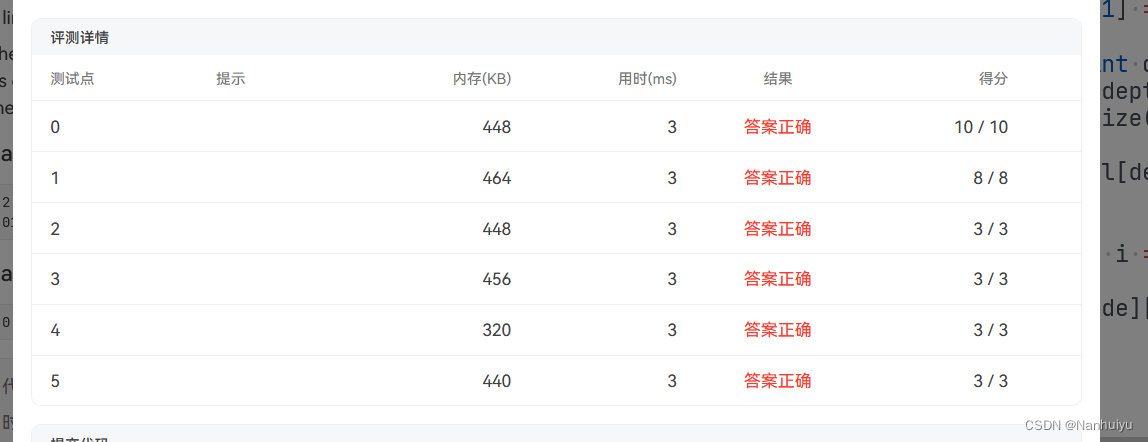
python:
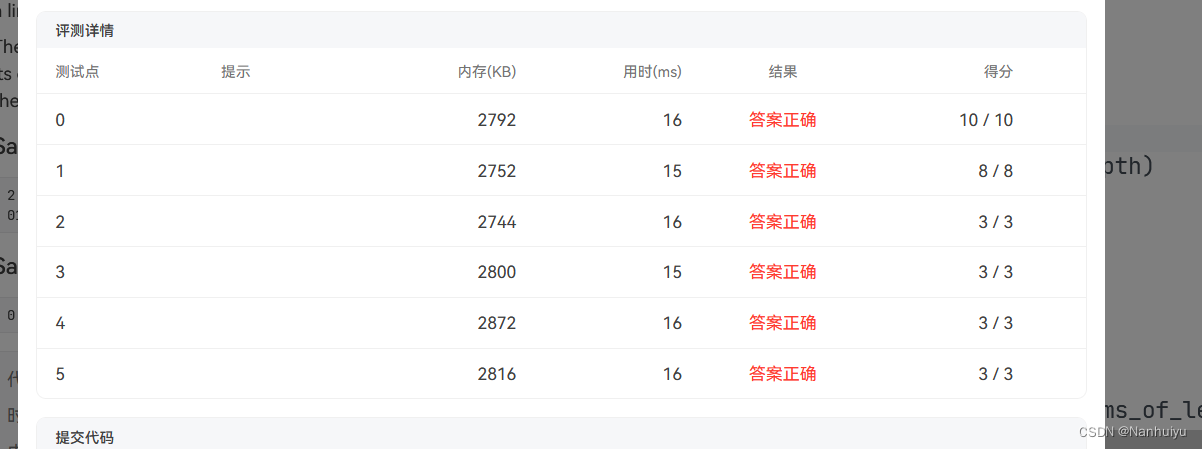
写在后面:
本题难度适中,只是简单的考察dfs的应用和静态树的构建以及叶子节点的概念,在处理时应该要小心谨慎!题主在用C++解题时就是因为在测试代码阶段一个多余输入未删除,白白浪费大好时光。。。。请各位一定要引以为鉴!莫要因为题目大意就掉以轻心!
最后,如果对本题有更好的见解,或者是题主的叙述让你感到困惑、存在不合理的地方,请在评论区交流,欢迎斧正!