文章目录
- adlist
- listNode
- list
- macros[宏定义]
- listCreate
- listInitNode
- listEmpty
- listRelease
- listAddNodeHead
- listLinkNodeHead
- listAddNodeTail
- listLinkNodeTail
- listInsertNode
- listDelNode
- listUlinkNode
- listIndex
- redis3.2.100quicklist
- redis7.2.2quicklist
redis的基本数据类型之一"list"的底层编码从"ziplist"和"LinkedList"[3.2版本之前]升级到"由ziplist组成的LinkedList"[3.2版本及以后]再升级到"由listpack组成的LinkedList"[7.2.2版本]。
本篇文章介绍"LinkedList"
adlist
adlist.h - A generic doubly linked list implementation
adlist 是一个通用的双向链表
listNode
首先看一下链表节点是如何定义的
typedef struct listNode {
struct listNode *prev;//指向前一个节点的指针
struct listNode *next;//指向后一个节点的指针
void *value;
} listNode;
list
链表的定义
typedef struct list {
listNode *head;//头节点
listNode *tail;//尾节点
/*
以下是一些指向"实现特定功能的函数"的指针
*/
void *(*dup)(void *ptr);//dup指向传入参数类型和返回值类型都是"void*"的函数
void (*free)(void *ptr);//dup指向传入参数类型和返回值类型都是"void*"的函数
int (*match)(void *ptr, void *key);//dup指向传入参数类型是两个"void *"和返回值类型都是"int*"的函数
unsigned long len;//记录list中的元素个数
} list;
- 获取list的元素个数的时间复杂度为O(1)因为链表的定义中包含记录节点个数的字段len
macros[宏定义]
来看看都定义了哪些宏方法。
//获取长度,由此可以看出对于OBJ_ENCODING_LINKEDLIST 编码方式的list来说,获取长度的时间复杂度为O(1)
#define listLength(l) ((l)->len)
//获取头节点
#define listFirst(l) ((l)->head)
//获取尾节点
#define listLast(l) ((l)->tail)
//获取当前节点的前一个节点
#define listPrevNode(n) ((n)->prev)
//获取当前节点的下一个节点
#define listNextNode(n) ((n)->next)
//获取节点指向的value值
#define listNodeValue(n) ((n)->value)
listCreate
//创建一个list
list *listCreate(void)
{
struct list *list;
//分配内存失败
if ((list = zmalloc(sizeof(*list))) == NULL)
return NULL;
//分配内存成功
//初始化
list->head = list->tail = NULL;
list->len = 0;
list->dup = NULL;
list->free = NULL;
list->match = NULL;
return list;
}
listInitNode
//初始化链表节点,将前后指针置为空,value值置为对应的value值
void listInitNode(listNode *node, void *value) {
node->prev = NULL;
node->next = NULL;
node->value = value;
}
listEmpty
//清空list,只是将节点从链表中移除而不销毁链表
/* Remove all the elements from the list without destroying the list itself. */
void listEmpty(list *list)
{
unsigned long len;
listNode *current, *next;
current = list->head;
len = list->len;
//逐一释放每个节点
while(len--) {
//先保存下一个节点
next = current->next;
//释放当前节点value指向的内存
if (list->free) list->free(current->value);
//释放当前节点
zfree(current);
current = next;
}
//头尾节点设置为NULL,len设置为0
list->head = list->tail = NULL;
list->len = 0;
}
listRelease
/* Free the whole list.
*
* This function can't fail. */
void listRelease(list *list)
{
listEmpty(list);
//释放list本身
zfree(list);
}
listAddNodeHead
list *listAddNodeHead(list *list, void *value)
{
listNode *node;
//为新结点分配内存
if ((node = zmalloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)
return NULL;
node->value = value;
//从头部插入list
listLinkNodeHead(list, node);
return list;
}
listLinkNodeHead
void listLinkNodeHead(list* list, listNode *node) {
if (list->len == 0) {
//第一次插入节点
list->head = list->tail = node;
node->prev = node->next = NULL;
} else {
node->prev = NULL;
node->next = list->head;
list->head->prev = node;
list->head = node;
}
//元素个数加1
list->len++;
}

listAddNodeTail
list *listAddNodeTail(list *list, void *value)
{
listNode *node;
//为新节点分配内存
if ((node = zmalloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)
return NULL;
node->value = value;
listLinkNodeTail(list, node);
return list;
}
listLinkNodeTail
void listLinkNodeTail(list *list, listNode *node) {
if (list->len == 0) {
//第一次插入节点
list->head = list->tail = node;
node->prev = node->next = NULL;
} else {
node->prev = list->tail;
node->next = NULL;
list->tail->next = node;
list->tail = node;
}
//元素个数加1
list->len++;
}
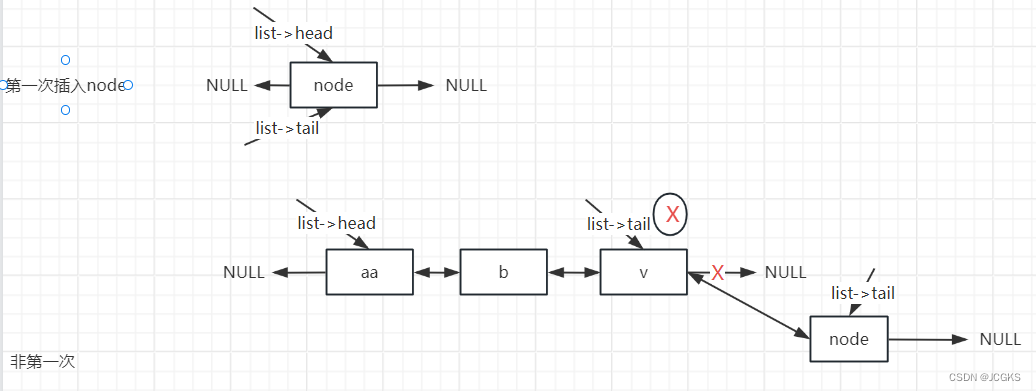
listInsertNode
//如果after为1则在old_node之后插入新节点
//反之在old_node之前插入新节点
list *listInsertNode(list *list, listNode *old_node, void *value, int after) {
listNode *node;
//为node分配内存
if ((node = zmalloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)
return NULL;
node->value = value;
//在old_node之后插入新节点
if (after) {
node->prev = old_node;
node->next = old_node->next;
//如果old_node是尾节点,插入之后要修改tail
if (list->tail == old_node) {
list->tail = node;
}
} else {
//在old_node之前插入新节点
node->next = old_node;
node->prev = old_node->prev;
//如果old_node是头节点,插入之后要修改head
if (list->head == old_node) {
list->head = node;
}
}
if (node->prev != NULL) {
node->prev->next = node;
}
if (node->next != NULL) {
node->next->prev = node;
}
list->len++;
return list;
}
listDelNode
void listDelNode(list *list, listNode *node)
{
listUnlinkNode(list, node);
//移除node并释放内存
if (list->free) list->free(node->value);
zfree(node);
}
listUlinkNode
//从list中移除node
void listUnlinkNode(list *list, listNode *node) {
//node->prev不为空说明node不是第一个元素
if (node->prev)
node->prev->next = node->next;
else
//node是第一个元素,删除之后需要修改head节点
list->head = node->next;
//node不是最后一个元素
if (node->next)
node->next->prev = node->prev;
else
//node是最后一个元素,删除之后需要修改tail节点
list->tail = node->prev;
//从list中移除node
node->next = NULL;
node->prev = NULL;
//元素个数减1
list->len--;
}
listIndex
/*
寻找list中第index个元素,正序遍历index从0开始,0代表head
倒序遍历从-1开始,-1指向tail
*/
listNode *listIndex(list *list, long index) {
listNode *n;
//如果index<0先将其转换为正数
if (index < 0) {
//这里减一是因为,从尾节点找到第一个元素无需移动只需返回尾节点即可;找到第二个元素只需从尾节点向前移动一次即可
index = (-index)-1;
n = list->tail;
while(index-- && n) n = n->prev;
} else {
n = list->head;
while(index-- && n) n = n->next;
}
return n;
}
redis3.2.100quicklist
在redis3.2.100版本中quicklist是由“ziplist”组成的"linkedlist"
quicklist.c - A doubly linked list of ziplists
看一下它的结构
/* quicklistNode is a 32 byte struct describing a ziplist for a quicklist.
* We use bit fields keep the quicklistNode at 32 bytes.
* count: 16 bits, max 65536 (max zl bytes is 65k, so max count actually < 32k).
* encoding: 2 bits, RAW=1, LZF=2.
* container: 2 bits, NONE=1, ZIPLIST=2.
* recompress: 1 bit, bool, true if node is temporarry decompressed for usage.
* attempted_compress: 1 bit, boolean, used for verifying during testing.
* extra: 12 bits, free for future use; pads out the remainder of 32 bits */
/*
quicklistnode是“由ziplist组成的linkedlist”的节点,占有32bytes
*/
typedef struct quicklistNode {
struct quicklistNode *prev;
struct quicklistNode *next;
unsigned char *zl;
unsigned int sz; /* ziplist size in bytes ziplist占用的bytes*/
unsigned int count : 16; /* count of items in ziplist ziplist里的entry数量*/
unsigned int encoding : 2; /* RAW==1 or LZF==2 */
unsigned int container : 2; /* NONE==1 or ZIPLIST==2 */
unsigned int recompress : 1; /* was this node previous compressed? */
unsigned int attempted_compress : 1; /* node can't compress; too small */
unsigned int extra : 10; /* more bits to steal for future usage */
} quicklistNode;
/* quicklist is a 32 byte struct (on 64-bit systems) describing a quicklist.
* 'count' is the number of total entries.
* 'len' is the number of quicklist nodes.
* 'compress' is: -1 if compression disabled, otherwise it's the number
* of quicklistNodes to leave uncompressed at ends of quicklist.
* 'fill' is the user-requested (or default) fill factor. */
typedef struct quicklist {
quicklistNode *head;
quicklistNode *tail;
unsigned long count; /* total count of all entries in all ziplists 所有ziplist中的所有entry总和,也就是linkedlist中总的元素个数 */
unsigned int len; /* number of quicklistNodes quicklistnode的个数*/
int fill : 16; /* fill factor for individual nodes */
unsigned int compress : 16; /* depth of end nodes not to compress;0=off */
} quicklist;
redis7.2.2quicklist
在7.2.2版本中quicklist是由“listpack组成的”
quicklist.c - A doubly linked list of listpacks
看一下它的结构
/* quicklistNode is a 32 byte struct describing a listpack for a quicklist.
* We use bit fields keep the quicklistNode at 32 bytes.
* count: 16 bits, max 65536 (max lp bytes is 65k, so max count actually < 32k).
* encoding: 2 bits, RAW=1, LZF=2.
* container: 2 bits, PLAIN=1 (a single item as char array), PACKED=2 (listpack with multiple items).
* recompress: 1 bit, bool, true if node is temporary decompressed for usage.
* attempted_compress: 1 bit, boolean, used for verifying during testing.
* extra: 10 bits, free for future use; pads out the remainder of 32 bits */
typedef struct quicklistNode {
struct quicklistNode *prev;
struct quicklistNode *next;
unsigned char *entry;
size_t sz; /* entry size in bytes listpack占用bytes*/
unsigned int count : 16; /* count of items in listpack listpack中的元素个数*/
unsigned int encoding : 2; /* RAW==1 or LZF==2 */
unsigned int container : 2; /* PLAIN==1 or PACKED==2 */
unsigned int recompress : 1; /* was this node previous compressed? */
unsigned int attempted_compress : 1; /* node can't compress; too small */
unsigned int dont_compress : 1; /* prevent compression of entry that will be used later */
unsigned int extra : 9; /* more bits to steal for future usage */
} quicklistNode;
/* quicklist is a 40 byte struct (on 64-bit systems) describing a quicklist.
* 'count' is the number of total entries.
* 'len' is the number of quicklist nodes.
* 'compress' is: 0 if compression disabled, otherwise it's the number
* of quicklistNodes to leave uncompressed at ends of quicklist.
* 'fill' is the user-requested (or default) fill factor.
* 'bookmarks are an optional feature that is used by realloc this struct,
* so that they don't consume memory when not used. */
typedef struct quicklist {
quicklistNode *head;
quicklistNode *tail;
unsigned long count; /* total count of all entries in all listpacks linkedlist的元素总数*/
unsigned long len; /* number of quicklistNodes quicklistnode的数量 */
signed int fill : QL_FILL_BITS; /* fill factor for individual nodes */
unsigned int compress : QL_COMP_BITS; /* depth of end nodes not to compress;0=off */
unsigned int bookmark_count: QL_BM_BITS;
quicklistBookmark bookmarks[];
} quicklist;
总结
- 不管是ziplist还是listpack构成的quicklist获取元素总数的时间复杂度为都为O(1)。