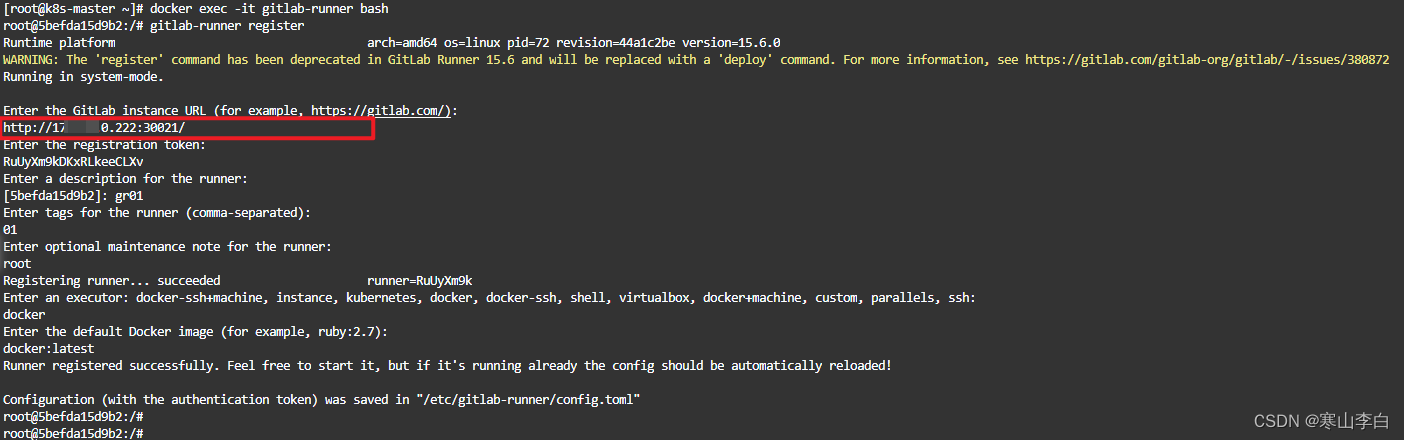
例题:
分析:
题目要求函数get和put要达到O(1)的时间复杂度,可以用 hashMap 来实现,因为要满足逐出最久未使用的元素的一个效果,还需要配合一个双向链表来共同实现。链表中的节点为一组key-value。
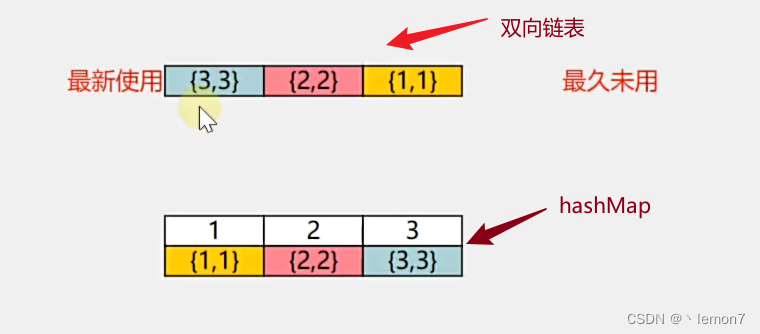
我们可以用双向链表来储存数据(key-value),当调用put方法添加数据时,可以将数据(key-value)添加到双向链表的队头,队头的元素表示最新使用的元素,越靠近队尾,就是最久未用的元素。
当调用get方法时,若存在此元素,则从双向链表中把该组数据(key-value)提到队头来。
代码实现:
package leetcode;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class LRUCacheLeetcode146 {
static class LRUCache {
static class Node{
Node next;
Node prev;
int key;
int value;
public Node(){
}
public Node(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
static class DoublyLinkedList{
Node head;
Node tail;
public DoublyLinkedList() {
head = tail = new Node();
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
//头部添加 head<->1<->2<->tail 假如添加3
public void addFirst(Node newNode){
Node oldFirst = head.next;
oldFirst.prev = newNode;
head.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = head;
newNode.next = oldFirst;
}
//已知节点删除 head<->1<->2<->tail 假如删除2
public void remove(Node node){
Node prev = node.prev;
Node next = node.next;
prev.next = next;
next.prev = prev;
}
//尾部删除
public Node removeLast(){
Node last = tail.prev;
remove(last);
return last;
}
}
private final HashMap<Integer, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
private final DoublyLinkedList list = new DoublyLinkedList();
private final int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
if(!map.containsKey(key)){
return -1;
}
Node node = map.get(key);
//hash表中存在该数据,改组数据应放到队头
//先从中删除原始数据
list.remove(node);
//再将改组数据添加到队头
list.addFirst(node);
return node.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if(map.containsKey(key)){ //更新
Node node = map.get(key);
node.value = value;
list.remove(node);
list.addFirst(node);
}else{ //添加
Node newNode = new Node(key, value);
map.put(key, newNode);
list.addFirst(newNode);
if(map.size() > capacity){
Node removed = list.removeLast();
//删除hash表中的数据
map.remove(removed.key);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LRUCache cache = new LRUCache(2);
cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
System.out.println(cache.get(1)); // 1
cache.put(3, 3);
System.out.println(cache.get(2)); // -1
cache.put(4, 4);
System.out.println(cache.get(1)); // -1
System.out.println(cache.get(3)); // 3
}
}