**需求:**我们需要自动为bean加载资源,代替注册、注入属性、注入bean等功能
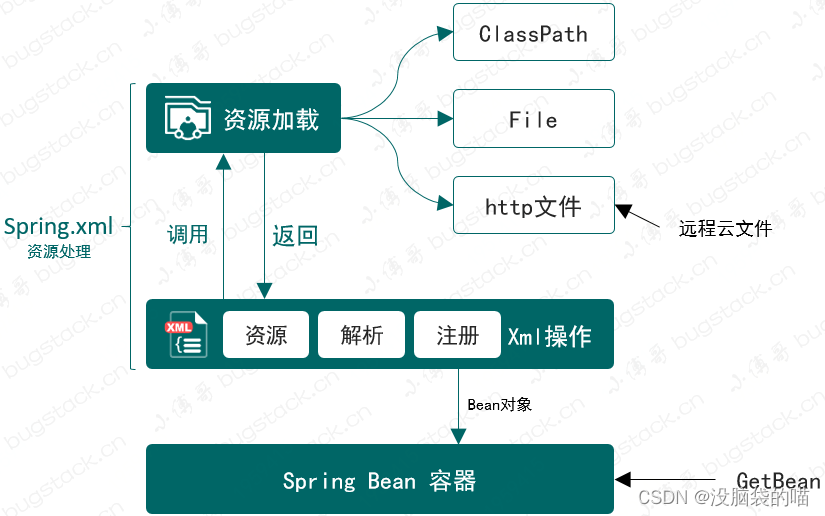
1.资源加载器属于相对独立的部分,它位于 Spring 框架核心包下的IO实现内容,主要用于处理Class、本地和云环境中的文件信息。
2.当资源可以加载后,接下来就是解析和注册 Bean 到 Spring 中的操作,这部分实现需要和DefaultListableBeanFactory 核心类结合起来,因为你所有的解析后的注册动作,都会把 Bean 定义信息放入到这个类中。
3.那么在实现的时候就设计好接口的实现层级关系,包括我们需要定义出 Bean 定义的读取接口BeanDefinitionReader 以及做好对应的实现类,在实现类中完成对 Bean 对象的解析和注册。
Resource
在 Spring 框架下创建 core.io 核心包,在这个包中主要用于处理资源加载流。定义 Resource 接口,提供获取 InputStream 流的方法,接下来再分别实现三种不同的流文件操作:classPath、FileSystem、URL
public interface Resource {
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}
ClassPath
该函数实现是用于通过 ClassLoader 读取ClassPath 下的文件信息,具体的读取过程主要是:classLoader.getResourceAsStream(path)
public class ClassPathResource implements Resource {
private final String path;
private ClassLoader classLoader;
public ClassPathResource(String path) {
this(path, (ClassLoader) null);
}
public ClassPathResource(String path, ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null");
this.path = path;
this.classLoader = (classLoader != null ? classLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
@Override
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
InputStream is = classLoader.getResourceAsStream(path);
if (is == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(
this.path + " cannot be opened because it does not exist");
}
return is;
}
}
FileSystemResource
通过指定文件路径的方式读取文件信息,这部分大家肯定还是非常熟悉的,经常会读取一些txt、excel文件输出到控制台
public class FileSystemResource implements Resource {
private final File file;
private final String path;
public FileSystemResource(File file) {
this.file = file;
this.path = file.getPath();
}
public FileSystemResource(String path) {
this.file = new File(path);
this.path = path;
}
@Override
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return new FileInputStream(this.file);
}
public final String getPath() {
return this.path;
}
}
UrlResource
通过 HTTP 的方式读取云服务的文件,我们也可以把配置文件放到 GitHub 或者 Gitee 上
public class UrlResource implements Resource{
private final URL url;
public UrlResource(URL url) {
Assert.notNull(url,"URL must not be null");
this.url = url;
}
@Override
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
URLConnection con = this.url.openConnection();
try {
return con.getInputStream();
}
catch (IOException ex){
if (con instanceof HttpURLConnection){
((HttpURLConnection) con).disconnect();
}
throw ex;
}
}
}
ResourceLoader
ResourceLoader用于继承不同方式的资源加载
public interface ResourceLoader {
String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = "classpath:";
Resource getResource(String location);
}
实现接口DefaultResourceLoader
public class DefaultResourceLoader implements ResourceLoader {
@Override
public Resource getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()));
}
else {
try {
URL url = new URL(location);
return new UrlResource(url);
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
return new FileSystemResource(location);
}
}
}
}
Bean定义读取接口 BeanDefinitionReader
getRegistry()、getResourceLoader(),都是用于提供给后面三个loadBeanDefinitions方法的工具,用于bean的注册和资源加载
public interface BeanDefinitionReader {
BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry();
ResourceLoader getResourceLoader();
void loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeansException;
void loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeansException;
void loadBeanDefinitions(String location) throws BeansException;
}
bean定义抽象类实现接口
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader
public abstract class AbstractBeanDefinitionReader implements BeanDefinitionReader {
private final BeanDefinitionRegistry registry;
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
protected AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this(registry, new DefaultResourceLoader());
}
public AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.registry = registry;
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
@Override
public BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry() {
return registry;
}
@Override
public ResourceLoader getResourceLoader() {
return resourceLoader;
}
}
抽象类把 BeanDefinitionReader 接口的getRegistry、getResourceLoader两个方法全部实现完了,并提供了构造函数,让外部的调用使用方
这样在接口 BeanDefinitionReader 的具体实现类中,就可以把解析后的 XML 文件中的 Bean 信息,注册到 Spring 容器去了。
解析XML处理Bean注册
XmlBeanDefinitionReader
public class XmlBeanDefinitionReader extends AbstractBeanDefinitionReader {
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
super(registry);
}
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
super(registry, resourceLoader);
}
@Override
public void loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeansException {
try {
try (InputStream inputStream = resource.getInputStream()) {
doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputStream);
}
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new BeansException("IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, e);
}
}
@Override
public void loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeansException {
for (Resource resource : resources) {
loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
}
@Override
public void loadBeanDefinitions(String location) throws BeansException {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
protected void doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputStream inputStream) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Document doc = XmlUtil.readXML(inputStream);
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();
NodeList childNodes = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < childNodes.getLength(); i++) {
// 判断元素
if (!(childNodes.item(i) instanceof Element)) continue;
// 判断对象
if (!"bean".equals(childNodes.item(i).getNodeName())) continue;
// 解析标签
Element bean = (Element) childNodes.item(i);
String id = bean.getAttribute("id");
String name = bean.getAttribute("name");
String className = bean.getAttribute("class");
// 获取 Class,方便获取类中的名称
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
// 优先级 id > name
String beanName = StrUtil.isNotEmpty(id) ? id : name;
if (StrUtil.isEmpty(beanName)) {
beanName = StrUtil.lowerFirst(clazz.getSimpleName());
}
// 定义Bean
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition(clazz);
// 读取属性并填充
for (int j = 0; j < bean.getChildNodes().getLength(); j++) {
if (!(bean.getChildNodes().item(j) instanceof Element)) continue;
if (!"property".equals(bean.getChildNodes().item(j).getNodeName())) continue;
// 解析标签:property
Element property = (Element) bean.getChildNodes().item(j);
String attrName = property.getAttribute("name");
String attrValue = property.getAttribute("value");
String attrRef = property.getAttribute("ref");
// 获取属性值:引入对象、值对象
Object value = StrUtil.isNotEmpty(attrRef) ? new BeanReference(attrRef) : attrValue;
// 创建属性信息
PropertyValue propertyValue = new PropertyValue(attrName, value);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(propertyValue);
}
if (getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
throw new BeansException("Duplicate beanName[" + beanName + "] is not allowed");
}
// 注册 BeanDefinition
getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
}
}
1.loadBeanDefinitions 方法,处理资源加载,这里新增加了一个内部方法:doLoadBeanDefinitions,它主要负责解析 xml
2.在 doLoadBeanDefinitions 方法中,主要是对xml的读取 XmlUtil.readXML(inputStream) 和元素 Element 解析。在解析的过程中通过循环操作,以此获取 Bean 配置以及配置中的 id、name、class、value、ref 信息。
3.最终把配置信息创建成 BeanDefinition 以及 PropertyValue,最终把完整的 Bean 定义内容****注册到 Bean 容器:getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition)
测试
UserDao
package cn.bugstack.springframework.test.bean;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class UserDao {
private static Map<String, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
static {
hashMap.put("10001", "小傅哥");
hashMap.put("10002", "八杯水");
hashMap.put("10003", "阿毛");
}
public String queryUserName(String uId) {
return hashMap.get(uId);
}
}
UserService
public class UserService {
private String uId;
private String company;
private String location;
private UserDao userDao;
public String queryUserInfo() {
return userDao.queryUserName(uId) + "," + company + "," + location;
}
public String getuId() {
return uId;
}
public void setuId(String uId) {
this.uId = uId;
}
public String getCompany() {
return company;
}
public void setCompany(String company) {
this.company = company;
}
public String getLocation() {
return location;
}
public void setLocation(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
public UserDao getUserDao() {
return userDao;
}
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
}
spring.xml
<beans>
<bean id="userDao" class="cn.bugstack.springframework.test.bean.UserDao"/>
<bean id="userService" class="cn.bugstack.springframework.test.bean.UserService">
<property name="uId" value="10001"/>
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
</bean>
</beans>
@Test
public void test_xml() {
// 1.初始化 BeanFactory
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring.xml");
// 2. 获取Bean对象调用方法
UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
String result = userService.queryUserInfo();
System.out.println("测试结果:" + result);
}




![[ESXi 8]安装centos7](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/76c193345769d80e1d7c65c02c5dc43f.png)