一般我们在用Qt开发时,把耗时操作放在线程中执行,避免卡界面,Qt的线程使用有两种方式,一种是继承QThread,一种是moveToThread的方式,以及QtConcurrent方式
首先我们来看第一种:
#ifndef WORKERTHREAD_H
#define WORKERTHREAD_H
#include <QDebug>
#include <QThread>
#include <QDateTime>
#define PRINTTIME QDateTime::currentDateTime().toString("yyyy.MM.dd hh:mm:ss.zzz");
class WorkerThread : public QThread
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit WorkerThread(QObject *parent = nullptr);
int getThreadFun();
void run() override
{
QString result = QString("WorkerThread");
/* ... here is the expensive or blocking operation ... */
QThread::sleep(3);
qDebug() << "WorkerThread::run===============currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
emit resultReady(result);
}
signals:
void resultReady(const QString &result);
};
#endif // WORKERTHREAD_H
#include "workerthread.h"
WorkerThread::WorkerThread(QObject *parent) : QThread(parent)
{
}
int WorkerThread::getThreadFun()
{
qDebug() << "Dialog::getThreadFun============currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
int id = (int)QThread::currentThreadId();
QThread::sleep(2);
return id;
}
使用线程:
void Dialog::initData()
{
m_workerThread = new WorkerThread(this);
connect(m_workerThread, &WorkerThread::resultReady, this, &Dialog::handleResults1);
//connect(m_workerThread, &WorkerThread::finished, m_workerThread, &Dialog::deleteLater);
//m_workerThread->start();
connect(ui->btn1, SIGNAL(clicked()), this, SLOT(slotBtn1()));
}
void Dialog::slotBtn1()
{
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn1================currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
m_workerThread->start();
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn1================currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
m_workerThread->getThreadFun();
}运行结果:
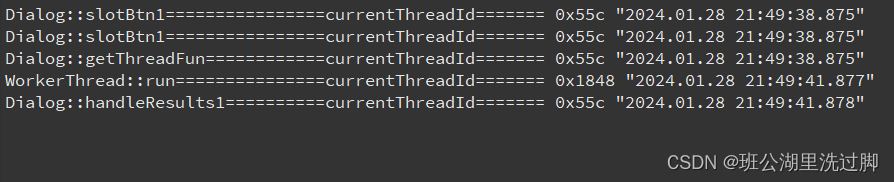
从以上信息可以看到,只有run函数里的执行是属于子线程,getThreadFun函数虽然是WorkerThread类的,但执行起来并不属于子线程,它的线程号与主线程一样,同时,开启线程后还没等结果就执行下面的语句了。run函数执行完,线程就结束了。
那么有没有一种情况,线程一直处理运行中呢?下面看第2种线程的方式:
#ifndef WORKER_H
#define WORKER_H
#include <QObject>
#include <QDebug>
#include <QThread>
#include <QDateTime>
#define PRINTTIME QDateTime::currentDateTime().toString("yyyy.MM.dd hh:mm:ss.zzz");
class Worker : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit Worker(QObject *parent = nullptr);
int getThreadFun();
public slots:
void doWork(const QString ¶meter)
{
QString result = QString("currentThreadId==%1").arg((int)QThread::currentThreadId());
/* ... here is the expensive or blocking operation ... */
QThread::sleep(3);
qDebug() << "Worker::doWork==================currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
emit resultReady(result);
}
signals:
void resultReady(const QString &result);
};
#endif // WORKER_H
#include "worker.h"
Worker::Worker(QObject *parent)
: QObject{parent}
{
}
int Worker::getThreadFun()
{
qDebug() << "Worker::getThreadFun============currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
int id = (int)QThread::currentThreadId();
QThread::sleep(2);
return id;
}
使用线程:
void Dialog::initData()
{
m_worker = new Worker;
m_worker->moveToThread(&workerThread);
connect(&workerThread, &QThread::finished, m_worker, &QObject::deleteLater);
connect(this, &Dialog::operate, m_worker, &Worker::doWork);
connect(m_worker, &Worker::resultReady, this, &Dialog::handleResults2);
workerThread.start();
connect(ui->btn2, SIGNAL(clicked()), this, SLOT(slotBtn2()));
}
void Dialog::slotBtn2()
{
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn2=======1========currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
emit operate("Worker");
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn2=======2========currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
m_worker->getThreadFun();
}
void Dialog::handleResults2()
{
qDebug() << "Dialog::handleResults2==========currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
}
运行结果:

从上面结果也可以看出,由operate信号触发的槽函数是子线程,直接调用getThreadFun函数还是属于子线程,但这个与第一种线程的方案不同在于,线程一起处理运行中,只要触发operate信号都会执行槽函数的子线程,以上两种情况都是线程还没执行完,调用线程的函数就已经结束了。
但有时候我们需要函数的结果,并且根据结果执行不同的分支要求,那边没有一种方案可以这种做呢,下面看第3种线程方式,使用QtConcurrent获取线程执行的返回结果:
#include "dialog.h"
#include "ui_dialog.h"
#include "workerthread.h"
#include "worker.h"
#include <QDebug>
#include <QSerialPort>
#include <QtConcurrent>
#include <QTime>
#include <QDebug>
#include <QEventLoop>
#include <QtConcurrentMap>
#include <QSerialPortInfo>
using namespace QtConcurrent;
#define PRINTTIME QDateTime::currentDateTime().toString("yyyy.MM.dd hh:mm:ss.zzz");
Dialog::Dialog(QWidget *parent)
: QDialog(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Dialog)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
initData();
}
Dialog::~Dialog()
{
workerThread.quit();
workerThread.wait();
m_workerThread->quit();
m_workerThread->wait();
delete ui;
}
void Dialog::initData()
{
connect(ui->btn3, SIGNAL(clicked()), this, SLOT(slotBtn3()));
}
int threadFun3(int a1, int a2)
{
qDebug() << "threadFun3======================currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
QThread::sleep(2);
qDebug() << "threadFun3======================currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
return a1 + a2;
}
void Dialog::slotBtn3()
{
int a1 = 5092;
int a2 = 542451;
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn3=======1========currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
QFuture<int> future =QtConcurrent::run(threadFun3, a1, a2);
int result = future.result();
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn3=======2========currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn3================result================" << result << PRINTTIME;
}
运行结果:
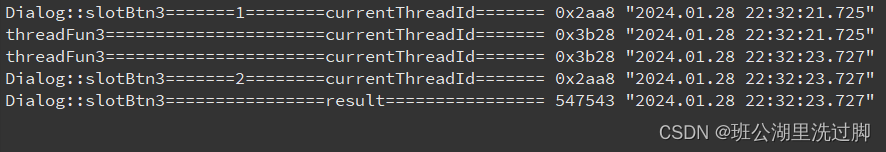
这种方案可以获取线程执行返回的结果了,但是这也存在一个问题,这个返回结果是待slotBtn3函数调用完了才返回,有时我们需要我等待这个结果再执行下面的代码。这时候就需要采用另外一种 方式下了。直接上代码:
void Dialog::initData()
{
connect(ui->btn4, SIGNAL(clicked()), this, SLOT(slotBtn4()));
}
//这里检测串口连接设备,连上设备才算打开串口成功
QString checkDeviceConnectPort()
{
QString openName = "";
QString tempData{""};
QThread::sleep(2);
qDebug() << "checkDeviceConnectPort======================currentThreadId=====" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
QSerialPort *serialPort = new QSerialPort();
foreach (const QSerialPortInfo &info, QSerialPortInfo::availablePorts())
{
serialPort->setPort(info);
if(info.portName().contains("Bluetooth", Qt::CaseInsensitive))
continue;
bool isOpen = serialPort->open(QIODevice::ReadWrite);
qDebug() << "checkDeviceConnectPort(================isOpen==" << isOpen << info.portName() << PRINTTIME;
if(isOpen)
{
//设置参数
serialPort->setBaudRate(115200); //波特率115200
serialPort->setDataBits(QSerialPort::Data8); //数据位8
serialPort->setStopBits(QSerialPort::OneStop); //停止位1
serialPort->setParity(QSerialPort::NoParity); //校验位 无
serialPort->setFlowControl(QSerialPort::NoFlowControl); //设置为无流控制
serialPort->setReadBufferSize(40960); //最大缓存40960
QByteArray sendData("XX\n");//sendData的数据
// 写入发送缓存区
qint64 sendDataLen = serialPort->write(sendData);
qDebug() << "checkDeviceConnectPort================sendDataLen=====" << sendDataLen;
qApp->processEvents();
qDebug() << "SerialPortManage::checkDeviceConnectPort=================processEvents================" << PRINTTIME;
while(serialPort->isOpen() && serialPort->waitForReadyRead(3000)) {
QString array = serialPort->readAll();
qDebug() << "SerialPortManage::checkDeviceConnectPort=====================array============" << array << PRINTTIME;
tempData.append(array);
if(array.isEmpty()) {
qApp->processEvents();
}
if(tempData.contains("end"))
{
qDebug() << "checkDeviceConnectPort=================tempData================" << tempData;
break;
}
}
if(openName.size() > 0)
{
break;
}
}
} //end foreach(
qDebug() << "checkDeviceConnectPort=================openName=================" << openName << PRINTTIME;
serialPort->close();
serialPort->deleteLater();
return openName;
}
void Dialog::slotBtn4()
{
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn4===1========================currentThreadId=====" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
QFuture<QString> future = QtConcurrent::run(checkDeviceConnectPort);
while (!future.isFinished()) {
QApplication::processEvents(QEventLoop::AllEvents, 30);
}
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn4============================result==============" << future.result() << PRINTTIME;
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn4===2========================currentThreadId=====" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
}
运行结果:
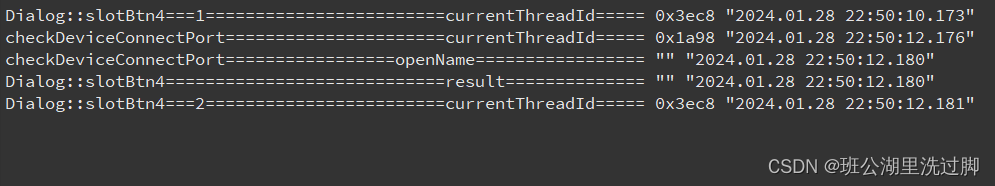
从上面可以看到,待线程函数执行完了,才会执行
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn4============================result==============" << future.result() << PRINTTIME;
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn4===2========================currentThreadId=====" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
的代码,这样就可以根据结果处理后续的逻辑了,同时也不会卡界面。
完整代码中下:
#ifndef DIALOG_H
#define DIALOG_H
#include <QDialog>
#include <QThread>
QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
namespace Ui { class Dialog; }
QT_END_NAMESPACE
class WorkerThread;
class Worker;
class Dialog : public QDialog
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
Dialog(QWidget *parent = nullptr);
~Dialog();
void initData();
public slots:
void slotBtn1();
void slotBtn2();
void slotBtn3();
void slotBtn4();
void handleResults1();
void handleResults2();
signals:
void operate(const QString &result);
private:
Ui::Dialog *ui;
WorkerThread *m_workerThread{nullptr};
QThread workerThread;
Worker *m_worker{nullptr};
};
#endif // DIALOG_H
dialog.cpp文件
#include "dialog.h"
#include "ui_dialog.h"
#include "workerthread.h"
#include "worker.h"
#include <QDebug>
#include <QSerialPort>
#include <QtConcurrent>
#include <QTime>
#include <QDebug>
#include <QEventLoop>
#include <QtConcurrentMap>
#include <QSerialPortInfo>
using namespace QtConcurrent;
#define PRINTTIME QDateTime::currentDateTime().toString("yyyy.MM.dd hh:mm:ss.zzz");
Dialog::Dialog(QWidget *parent)
: QDialog(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Dialog)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
initData();
}
Dialog::~Dialog()
{
workerThread.quit();
workerThread.wait();
m_workerThread->quit();
m_workerThread->wait();
delete ui;
}
void Dialog::initData()
{
m_workerThread = new WorkerThread(this);
connect(m_workerThread, &WorkerThread::resultReady, this, &Dialog::handleResults1);
//connect(m_workerThread, &WorkerThread::finished, m_workerThread, &Dialog::deleteLater);
//m_workerThread->start();
m_worker = new Worker;
m_worker->moveToThread(&workerThread);
connect(&workerThread, &QThread::finished, m_worker, &QObject::deleteLater);
connect(this, &Dialog::operate, m_worker, &Worker::doWork);
connect(m_worker, &Worker::resultReady, this, &Dialog::handleResults2);
workerThread.start();
connect(ui->btn1, SIGNAL(clicked()), this, SLOT(slotBtn1()));
connect(ui->btn2, SIGNAL(clicked()), this, SLOT(slotBtn2()));
connect(ui->btn3, SIGNAL(clicked()), this, SLOT(slotBtn3()));
connect(ui->btn4, SIGNAL(clicked()), this, SLOT(slotBtn4()));
}
void Dialog::slotBtn1()
{
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn1================currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
m_workerThread->start();
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn1================currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
m_workerThread->getThreadFun();
}
void Dialog::slotBtn2()
{
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn2=======1========currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
emit operate("Worker");
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn2=======2========currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
m_worker->getThreadFun();
}
int threadFun3(int a1, int a2)
{
qDebug() << "threadFun3======================currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
QThread::sleep(2);
qDebug() << "threadFun3======================currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
return a1 + a2;
}
void Dialog::slotBtn3()
{
int a1 = 5092;
int a2 = 542451;
QString str = "AAAAAAAAAAAA";
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn3=======1========currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
QFuture<int> future =QtConcurrent::run(threadFun3, a1, a2);
int result = future.result();
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn3=======2========currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn3================result================" << result << PRINTTIME;
}
//这里检测串口连接设备,连上设备才算打开串口成功
QString checkDeviceConnectPort()
{
QString openName = "";
QString tempData{""};
QThread::sleep(2);
qDebug() << "checkDeviceConnectPort======================currentThreadId=====" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
QSerialPort *serialPort = new QSerialPort();
foreach (const QSerialPortInfo &info, QSerialPortInfo::availablePorts())
{
serialPort->setPort(info);
if(info.portName().contains("Bluetooth", Qt::CaseInsensitive))
continue;
bool isOpen = serialPort->open(QIODevice::ReadWrite);
qDebug() << "checkDeviceConnectPort(================isOpen==" << isOpen << info.portName() << PRINTTIME;
if(isOpen)
{
//设置参数
serialPort->setBaudRate(115200); //波特率115200
serialPort->setDataBits(QSerialPort::Data8); //数据位8
serialPort->setStopBits(QSerialPort::OneStop); //停止位1
serialPort->setParity(QSerialPort::NoParity); //校验位 无
serialPort->setFlowControl(QSerialPort::NoFlowControl); //设置为无流控制
serialPort->setReadBufferSize(40960); //最大缓存40960
QByteArray sendData("XX\n");//sendData的数据
// 写入发送缓存区
qint64 sendDataLen = serialPort->write(sendData);
qDebug() << "checkDeviceConnectPort================sendDataLen=====" << sendDataLen;
qApp->processEvents();
qDebug() << "SerialPortManage::checkDeviceConnectPort=================processEvents================" << PRINTTIME;
while(serialPort->isOpen() && serialPort->waitForReadyRead(3000)) {
QString array = serialPort->readAll();
qDebug() << "SerialPortManage::checkDeviceConnectPort=====================array============" << array << PRINTTIME;
tempData.append(array);
if(array.isEmpty()) {
qApp->processEvents();
}
if(tempData.contains("end"))
{
qDebug() << "checkDeviceConnectPort=================tempData================" << tempData;
break;
}
}
if(openName.size() > 0)
{
break;
}
}
} //end foreach(
qDebug() << "checkDeviceConnectPort=================openName=================" << openName << PRINTTIME;
serialPort->close();
serialPort->deleteLater();
return openName;
}
void Dialog::slotBtn4()
{
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn4===1========================currentThreadId=====" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
QFuture<QString> future = QtConcurrent::run(checkDeviceConnectPort);
while (!future.isFinished()) {
QApplication::processEvents(QEventLoop::AllEvents, 30);
}
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn4============================result==============" << future.result() << PRINTTIME;
qDebug() << "Dialog::slotBtn4===2========================currentThreadId=====" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
}
void Dialog::handleResults1()
{
qDebug() << "Dialog::handleResults1==========currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
}
void Dialog::handleResults2()
{
qDebug() << "Dialog::handleResults2==========currentThreadId=======" << QThread::currentThreadId() << PRINTTIME;
}
QT += core gui serialport concurrent
greaterThan(QT_MAJOR_VERSION, 4): QT += widgets
CONFIG += c++17
# You can make your code fail to compile if it uses deprecated APIs.
# In order to do so, uncomment the following line.
#DEFINES += QT_DISABLE_DEPRECATED_BEFORE=0x060000 # disables all the APIs deprecated before Qt 6.0.0
SOURCES += \
main.cpp \
dialog.cpp \
worker.cpp \
workerthread.cpp
HEADERS += \
dialog.h \
worker.h \
workerthread.h
FORMS += \
dialog.ui
# Default rules for deployment.
qnx: target.path = /tmp/$${TARGET}/bin
else: unix:!android: target.path = /opt/$${TARGET}/bin
!isEmpty(target.path): INSTALLS += target
UI布局:
参考:
QFutureWatcher获取QtConcurrent::run线程函数的返回值_qt怎样异步获取qtconcurrent::run创建的线程的返回结果-CSDN博客