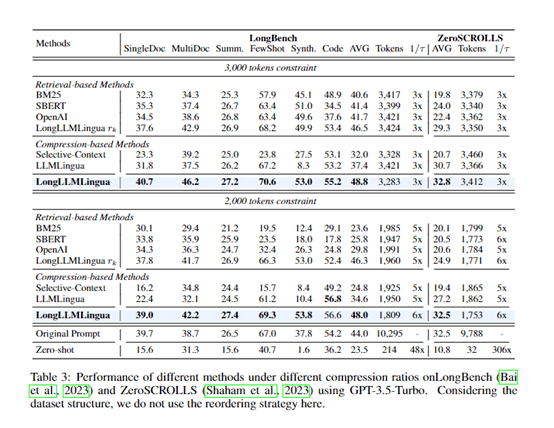
一、默认值与额外参数

1.1、默认值
1.1.1、urls.py
from django.urls import path
from . import views
urlpatterns = [
# http://127.0.0.1:8000/polls/blog/ 等同于
# http://127.0.0.1:8000/polls/blog/1/
path('blog/', views.page),
# http://127.0.0.1:8000/polls/blog/1/
# http://127.0.0.1:8000/polls/blog/10/
# http://127.0.0.1:8000/polls/blog/99/
path('blog/<int:num>/', views.page),
]
1.1.2、views.py
def page(request, num=1):
# 编写对应的业务逻辑
1.2、额外的参数
1.2.1、urls.py
from django.urls import path
from . import views
urlpatterns = [
# 会传递给 views.
path('blog/<int:year>/', views.year_archive, {'foo': 'bar'}),
]
1.2.2、views.py
def year_archive(request, year=2005, foo='bar')
# 编写对应的业务逻辑
二、错误处理

- handler400- 状态码400
- handler403- 状态码403
- handler404- 状态码404
- handler500- 状态码500
-
在 settings中修改配置:
DEBUG = False ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['*'] -
在主应用的urls中配置:
# polls是子应用 handler404 = "polls.views.page_not_found" -
在polls应用的views中添加函数page_not_found:
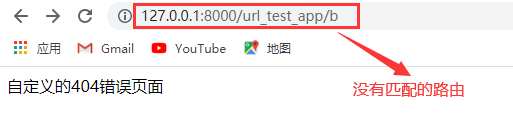
def page_not_found(request, exception): return HttpResponse('自定义的404错误页面') -
浏览器测试访问,找不到匹配的路由
三、引用其他URL调度器

3.1、include(str)
from django.urls import include, path
urlpatterns = [
path('community/', include('aggregator.urls')),
path('contact/', include('contact.urls')),
]
3.2、include(list/tuple)
from django.urls import include, path
from apps.main import views as main_views
from credit import views as credit_views
extra_patterns = [
path('reports/', credit_views.report),
path('reports/<int:id>/', credit_views.report),
path('charge/', credit_views.charge),
]
urlpatterns = [
path('', main_views.homepage),
path('help/', include('apps.help.urls')),
path('credit/', include(extra_patterns)),
]
3.3、技巧
优化繁琐的URL地址编写
from django.urls import path
from . import views
urlpatterns = [
path('<page_slug>-<page_id>/history/', views.history),
path('<page_slug>-<page_id>/edit/', views.edit),
path('<page_slug>-<page_id>/discuss/', views.discuss),
path('<page_slug>-<page_id>/permissions/', views.permissions),
]
优化
from django.urls import include, path
from . import views
urlpatterns = [
path('<page_slug>-<page_id>/', include([
path('history/', views.history),
path('edit/', views.edit),
path('discuss/', views.discuss),
path('permissions/', views.permissions),
])),
]
四、URL反向解析

url调度器除了从用户发起请求,到匹配对应的view,还能在python程序中调用进行匹配,通过 path或re_path 中 的name属性进行解析
-
在模板中,使用url模板标签
-
在Python代码中(主要是views),使用 reverse() 函数
4.1、示例
urls中配置
from django.urls import path
from . import views
urlpatterns = [
#...
path('articles/<int:year>/', views.year_archive, name='news-year-archive'),
#...
]
4.2、在模板中测试
- views.py跳转到页面
def do_html(request):
return render(request,'redirect_test.html')
def year_archive(request,year):
return HttpResponse(f'重定向成功{year}')
- 模板中代码
# 模板中: <a href="{% url 'news-year-archive' 2030 %}">2030 Archive</a>4.3、在python代码测试
from django.urls import reverse from django.http import HttpResponseRedirect def redirect_to_year(request): return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('news-year-archive', args=(2030,)))五、命名空间

命名空间主要用于配合url反向解析使用,多个不同的urls文件中可能配置同名的 name,那么为了进行区分,给不同的urls进行不同的命名
注意
同一个项目下命名空间不能重复,切记!
5.1、命名空间基本使用
通过在 url调度器的模块中,定义 app_name = 'polls' 来命名
from django.urls import path from . import views # 定义,一般命名空间和子应用名相同,便于记忆 app_name = 'polls' urlpatterns = [ path('', views.index_view, name='index'), path('<int:pk>/', views.detail_view, name='detail'), ... ] # 调用,一旦有了命名空间,调用时就必须使用 polls: 前缀 reverse('polls:index')5.2、命名空间嵌套
# 在 urls 中配置如下: from django.urls import path from . import views # 定义命名空间,一般命名空间名和子应用名相同,便于记忆 app_name = 'polls' extra_patterns = ( [ path('app_name/', views.app_name, name='app_name'), ], # 此处就是嵌套的命名空间 'extra' ) urlpatterns = [ path('', views.index_view, name='index'), path('<int:pk>/', views.detail_view, name='detail'), path('extra/', include(extra_patterns)), ... ] # 在模板中使用: <a href="{% url 'polls:extra:app_name' %}">点击链接</a>